Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bioavailability/Bioequivalence: I. Routes of Drug Administration and Dosage Forms
Bioavailability/Bioequivalence: I. Routes of Drug Administration and Dosage Forms
Uploaded by
ang3lwingsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bioavailability/Bioequivalence: I. Routes of Drug Administration and Dosage Forms
Bioavailability/Bioequivalence: I. Routes of Drug Administration and Dosage Forms
Uploaded by
ang3lwingsCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmaceutics I Lesson Ten
Dr. Jun Shao
Lesson Ten I. Routes of Drug Administration and Dosage Forms A. Reasons for various routes and dosage forms Local: direct application of drug to desired site of action. Systemic: result from the entrance of the drug into the circulatory system and transport to the cellular site of its action. Long-term or short-term treatment Time allowed to exert effects Physical description! si"e! crystalline structure! melting point! solu#ility$%chemical structure!form!reactivity$ &iologic properties: relate to its a#ility to get to a site of action and elicit a #iologic su#stance 'rug Sta#ility in different routes Bioavailability/Bioequivalence &ioavaila#ility: The rate and extent of a drug #eing a#sor#ed and availa#le to the site of action. &ioe(uivalence: The comparison of #ioavaila#ilities of the same drug from different products. Pharmaceutical )(uivalent: drug products that contain identical amounts of the identical active drug ingredient! that is! the same salt or ester of the same therapeutic moiety! in identical dosage forms #ut not necessarily containing the same inactive Pharmaceutical Alternative: drug products the contain the identical therapeutic moiety%precursor #ut not the same amount! dosage form! or same salt%ester &ioe(uivalent 'rug Products: pharmaceutical e(uivalents or alternatives whose rate and extent of a#sorption do not show a significant difference when administered at the same dose A. *ral Route a. &ioavaila#le +raction f$ : may #e calculated #y comparison of the A,- after oral administration with that o#tained after intravenous administration + . A,-$oral% A,-$intravenous . A#sorption +raction x /- +$ +: +irst-pass meta#olism fraction #. Advantages%'isadvantages: safest! #ut slow drug response! chance of irregular a#sorption! destruction #y 01 en"ymes c. Possi#le dosage forms: ta#lets! capsules! suspensions! &. Rectal Route a. Advantages%'isadvantages: can a#sor# many solu#le drugs. Preferred for drugs destroyed%inactivated #y stomach environment. Also preferred when patient vomiting%unconscious. 2345 of drug a#sor#ed rectally #ypasses the liver. 6ay #e inconvenient%offensive. A#sorption irregular%difficult to predict #. +easi#le dosage forms: solutions! suppositories! ointments &. Parenteral Route a. Advantages%'isadvantages: rapid a#sorption emergencies$! #lood levels more predicta#le! unconscious patients. 'ifficult to remove drug after administration #. +easi#le dosage forms: done outside of intestine! in7ected through the follow of a fine needle into the #ody at various sites. c. 8 primary sites: -su#cutaneous: a( solutions%suspensions! small volumes. )x. 1nsulin. -intramuscular: greater volumes! long lasting. -intravenous: directly into vein. -an #e single! small volume or large volume drip. Allows desired #lood level to #e achieved in optimal manner. d. )ither a sterile suspension or solution or in a suita#le vegeta#le oil. 'rugs administered in a(ueous solution are a#sor#ed more rapidly than solid #%c no disintegration%dissolution$ Slow a#sorption . prolonged drug action depot! repository$. -. )picutaneous Route a. Advantages%'isadvantages #. +easi#le dosage forms: applied topically to the s9in.
1
Pharmaceutics I Lesson Ten
Dr. Jun Shao
You might also like
- BHRAMANKAR - BiopharmaceuticsDocument410 pagesBHRAMANKAR - Biopharmaceuticsbhargav42787% (298)
- 1 - Elmar 10K English ALL GENERIC PDFDocument74 pages1 - Elmar 10K English ALL GENERIC PDFElectro kill100% (1)
- BiopharmaceuticsDocument21 pagesBiopharmaceuticsSilvy100% (1)
- Introduction To Biopharmaceutics (And Pharmacokinetics)Document14 pagesIntroduction To Biopharmaceutics (And Pharmacokinetics)Kim MoranoNo ratings yet
- Torts OutlineDocument57 pagesTorts Outlineang3lwings100% (1)
- Boric Acid (Orthoboric Acid) : GOST 18704-78 DescriptionDocument2 pagesBoric Acid (Orthoboric Acid) : GOST 18704-78 Descriptiontakkar1392No ratings yet
- PHR 504: Bipoharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics-IDocument14 pagesPHR 504: Bipoharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics-IMD REFATNo ratings yet
- Bio Lec.1Document7 pagesBio Lec.1taha.21ph119No ratings yet
- Effect of Physico-Chemical Properties of Drug On AbsorptionDocument37 pagesEffect of Physico-Chemical Properties of Drug On AbsorptionnoamaliaNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability: Dr. Hiba Algaali AltayebDocument17 pagesBioavailability: Dr. Hiba Algaali AltayebAbdalla KazzamNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability and BioequivalenceDocument81 pagesBioavailability and BioequivalenceNiharika ModiNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability and BioequivalenceDocument82 pagesBioavailability and Bioequivalenceكسلان اكتب اسمي100% (1)
- In Vivo in Vitro CorrelationDocument4 pagesIn Vivo in Vitro CorrelationAmira HelayelNo ratings yet
- Adme 1: Absorption and DistributionDocument48 pagesAdme 1: Absorption and DistributionAlex LesNo ratings yet
- Ba MeasurementsDocument86 pagesBa MeasurementsNavya cleetusNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Drug Delivery 3Document21 pagesPulmonary Drug Delivery 3Pharmswipe KenyaNo ratings yet
- Purpose of BABE: Chu Yuan ShanDocument9 pagesPurpose of BABE: Chu Yuan ShanJessie ChuNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NotesDocument22 pagesPharmacology NotesflixiexpressNo ratings yet
- Drug Absorption-DistributionDocument60 pagesDrug Absorption-DistributionRuqayya AdamuNo ratings yet
- Central Theme of ChapterDocument10 pagesCentral Theme of ChapterPrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Farmakokinetika-Bu Farida PDFDocument39 pagesBahan Ajar Farmakokinetika-Bu Farida PDFrianiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: Drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and EliminationDocument25 pagesPharmacokinetics: Drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and EliminationYoshiNo ratings yet
- Ba-Be PDFDocument30 pagesBa-Be PDFUswatun Hasanah7201No ratings yet
- Pharmacology BasicsDocument69 pagesPharmacology BasicsAassh DcmbrNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument24 pagesNotesriann leigh TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Rectal SuppositoriesDocument6 pagesRectal SuppositoriesLinh PhamNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability and BioequivalenceDocument23 pagesBioavailability and BioequivalenceSaeed RashidNo ratings yet
- Bio AvailabilityDocument22 pagesBio AvailabilityAreej RehanNo ratings yet
- MedicationDocument26 pagesMedicationAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics Lecture 8 UquDocument24 pagesBiopharmaceutics Lecture 8 Uquرنا الشريفNo ratings yet
- BioavailabilityDocument15 pagesBioavailabilitywriter noreenNo ratings yet
- Advanced Drug Delivery and TargetingDocument17 pagesAdvanced Drug Delivery and Targetinghafiz patahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiopharmaceuticsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Biopharmaceuticsgelary sousaNo ratings yet
- Basics of PharmacologyDocument24 pagesBasics of PharmacologyMahfuja khatun UrmeNo ratings yet
- بيDocument48 pagesبيMojied AmeerNo ratings yet
- Ivivc: in Vitro-In Vivo CorrelationDocument46 pagesIvivc: in Vitro-In Vivo CorrelationMubammad Mursaleen100% (1)
- Muhammad Zubair B P D 0 2 1 8 1 1 7 5 Biopharm Sir MoosarazaDocument12 pagesMuhammad Zubair B P D 0 2 1 8 1 1 7 5 Biopharm Sir MoosarazaMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Advanced Drug Delivery and TargetingDocument32 pagesAdvanced Drug Delivery and Targetinghafiz patahNo ratings yet
- Loksewa Exam Questions 2081Document25 pagesLoksewa Exam Questions 20812000lovekingNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability: Drug Product PerformanceDocument38 pagesBioavailability: Drug Product PerformancesaadNo ratings yet
- Adams4e Tif Ch04Document26 pagesAdams4e Tif Ch04fbernis1480_11022046No ratings yet
- Pharmacokine, CS: Learning Objec, VesDocument24 pagesPharmacokine, CS: Learning Objec, Vesjwinco1804No ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument8 pagesPharmacokineticsPinay YaunNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability and BioequivalenceDocument56 pagesBioavailability and Bioequivalenceنور الهدى100% (1)
- Bioavailability Studies. Chap 3-2Document40 pagesBioavailability Studies. Chap 3-2dilka dariyaNo ratings yet
- Bio AvailabilityDocument87 pagesBio Availabilitysubash karkiNo ratings yet
- Bio A ViabilityDocument8 pagesBio A ViabilityBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- BioavailabilityDocument35 pagesBioavailabilityDr. Bharat JainNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability o Fdisperse Dosage FormDocument94 pagesBioavailability o Fdisperse Dosage Formpharmashri5399No ratings yet
- نم هدمتعم و هعجارم اهنل اهب قوثوم لخادلاب تامولعملا Certified fromDocument20 pagesنم هدمتعم و هعجارم اهنل اهب قوثوم لخادلاب تامولعملا Certified fromMedhat EyadaNo ratings yet
- BIOPHARMACEUTICS Part1aDocument225 pagesBIOPHARMACEUTICS Part1aAmirabbas SaffariNo ratings yet
- Copy ofDocument94 pagesCopy ofPreetibah PatelNo ratings yet
- Bioavailabilitas Bioekivalen 1Document28 pagesBioavailabilitas Bioekivalen 1DeliaGvin SimatupangNo ratings yet
- Bioavailabilitas Bioekivalen 1Document28 pagesBioavailabilitas Bioekivalen 1DeliaGvin SimatupangNo ratings yet
- MCQs 01-01 Introduction To Basic Principal of PharmacologyDocument146 pagesMCQs 01-01 Introduction To Basic Principal of PharmacologyNomi Waqas GulNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability of DrugsDocument17 pagesBioavailability of DrugsDua waheedNo ratings yet
- Genericdrugs 0Document43 pagesGenericdrugs 0Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Bioavailabilitas & BioekivalenDocument27 pagesBioavailabilitas & Bioekivalendonghaesayangela100% (1)
- KJBVGGVVVDocument10 pagesKJBVGGVVVSuvojit BasakNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Book on Experimental PharmaceuticsFrom EverandA Comprehensive Book on Experimental PharmaceuticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Flow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsFrom EverandFlow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsNo ratings yet
- Prescription Painkillers: History, Pharmacology, and TreatmentFrom EverandPrescription Painkillers: History, Pharmacology, and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Professor Lukeman Torts OutlineDocument18 pagesProfessor Lukeman Torts Outlineang3lwingsNo ratings yet
- Joinder HypoDocument2 pagesJoinder Hypoang3lwingsNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Rule ProofsDocument18 pagesCivil Procedure Rule Proofsang3lwings100% (2)
- Sample Flow Chart Civ ProDocument26 pagesSample Flow Chart Civ Proang3lwings50% (2)
- Compounding StepsDocument1 pageCompounding Stepsang3lwingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Terms/Definitions/Concepts Terms and DefinitionsDocument1 pageChapter 7 Terms/Definitions/Concepts Terms and Definitionsang3lwingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Thinking Critically With Psychological ScienceDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Thinking Critically With Psychological Scienceang3lwingsNo ratings yet
- WATEErDocument13 pagesWATEErArav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Trihalomethanes: and Related Pentane-Extractable Organic HalidesDocument33 pagesAnalysis of Trihalomethanes: and Related Pentane-Extractable Organic HalidesaviantaraNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Sesi 2 Webinar Bromat AMDKDocument46 pagesPresentasi Sesi 2 Webinar Bromat AMDKAOC BPOM Jambi 2022No ratings yet
- 05 - 07 Elelyso (Taliglucerase Alpha) Final PresentationDocument105 pages05 - 07 Elelyso (Taliglucerase Alpha) Final PresentationDiti ShahNo ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatDocument23 pagesTemperature and HeatAlessia BostiogNo ratings yet
- LIQUID/LIQUID MIXTURES: Examples: Alcoholic Beverages: They Are A Mixture ofDocument1 pageLIQUID/LIQUID MIXTURES: Examples: Alcoholic Beverages: They Are A Mixture ofnicolas100% (1)
- Edm 244Document9 pagesEdm 244Jhohan Steven Muñoz PinedaNo ratings yet
- Toxicology - Lesson Plan - KnightonDocument7 pagesToxicology - Lesson Plan - Knightonapi-257588494100% (1)
- Water Lettuce Leaves As Main Component in The Production of Biodegradable Plastic BagsDocument9 pagesWater Lettuce Leaves As Main Component in The Production of Biodegradable Plastic BagsExcel Ace ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- 7 Transfer of Electrons at A DistanceDocument5 pages7 Transfer of Electrons at A DistanceAMIR ABD KADIR KadirNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy Process PDFDocument28 pagesPowder Metallurgy Process PDFAravindhan AnbalaganNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: AllenDocument9 pagesThermodynamics: AllenronakNo ratings yet
- Thermal Pollution ProjectDocument15 pagesThermal Pollution ProjectSneha Parab25% (4)
- Molecules: Practical Asymmetric Synthesis of Sitagliptin Phosphate MonohydrateDocument12 pagesMolecules: Practical Asymmetric Synthesis of Sitagliptin Phosphate MonohydrateNgô Tuấn KiệtNo ratings yet
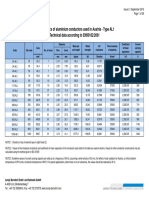
- Characteristics of Aluminium Conductors Used in Austria - Type AL1 Technical Data According To EN50182/2001Document26 pagesCharacteristics of Aluminium Conductors Used in Austria - Type AL1 Technical Data According To EN50182/2001Harshal KohaleNo ratings yet
- BBCCT-101 - English July2021-Dec2022Document3 pagesBBCCT-101 - English July2021-Dec2022Cricket ClutchNo ratings yet
- Dupont Oasis 120TWT561 Datasheet 1Document2 pagesDupont Oasis 120TWT561 Datasheet 1kamlesh vaishnavNo ratings yet
- 3-Dimensional Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Both Thermal and Mechanical Response of Friction Stir Welded 6061-T6 Aluminum PlatesDocument6 pages3-Dimensional Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Both Thermal and Mechanical Response of Friction Stir Welded 6061-T6 Aluminum PlatesspiritveluNo ratings yet
- Thermo Dynamics Question BankDocument3 pagesThermo Dynamics Question Banknisar_ulNo ratings yet
- Amber Value, Price, and Jewelry Information - International Gem SocietyDocument7 pagesAmber Value, Price, and Jewelry Information - International Gem Societyasset68No ratings yet
- Raghavendra R. Hegde, M. G. Kamath, Atul DahiyaDocument7 pagesRaghavendra R. Hegde, M. G. Kamath, Atul DahiyaarunkumardoraiNo ratings yet
- Roux Technology PaperDocument9 pagesRoux Technology Papersebastian_javier_bNo ratings yet
- 2 ADocument8 pages2 AMayur PatelNo ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah VitaminDocument14 pagesMateri Kuliah VitaminFeniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FermentationDocument6 pagesChapter 7 FermentationBRENDAN CHIEW CHANG RONG MoeNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Determination of Ranitidine in Human Plasma by SPE and ESI-LC-MS/MS For Use in Bioequivalence StudiesDocument8 pagesResearch Article: Determination of Ranitidine in Human Plasma by SPE and ESI-LC-MS/MS For Use in Bioequivalence StudiesSrujana BudheNo ratings yet
- Materials and Design: I. Hajiannia, M. Shamanian, M. KasiriDocument8 pagesMaterials and Design: I. Hajiannia, M. Shamanian, M. KasiriBurhanuddin As-SirajNo ratings yet
- SX Solvent Extraction Process Principles TheoryDocument28 pagesSX Solvent Extraction Process Principles TheoryHamed PiriNo ratings yet