Professional Documents
Culture Documents
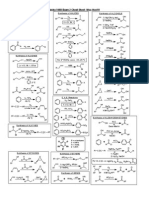
Chem 215 Myers: The Heck Reaction
Chem 215 Myers: The Heck Reaction
Uploaded by
dubstepoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem 215 Myers: The Heck Reaction
Chem 215 Myers: The Heck Reaction
Uploaded by
dubstepoCopyright:
Available Formats
Myers
Reviews: Belestskaya, I. P.; Cheprakov, A. V. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 30093066.
The Heck Reaction
Chem 215
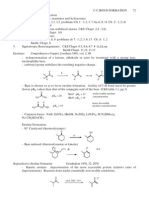
Pd(II) is reduced to the catalytically active Pd(0) in situ, typically through the oxidation of a phosphine ligand.
Brase, S.; de Meijere, A. In Metal-catalyzed Cross-coupling Reactions, Diederich, F., and Stang, P. J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: New York, 1998, pp. 99166. Cabri, W.; Candiani, I. Acc. Chem. Res. 1995, 28, 27. de Meijere, A.; Meyer, F. E. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1994, 33, 23792411. Intramolecular: Link, J. T.; Overman, L. E. In Metal-catalyzed Cross-coupling Reactions, Diederich, F., and Eds.; Wiley-VCH: New York, 1998, pp. 231269. Gibson, S. E.; Middleton, R. J. Contemp. Org. Synth. 1996, 3, 447471. Asymmetric: Shibasaki, M.; Boden, C. D. J.; Kojima, A. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 73717393. Solid phase: Franzn, R. Can. J. Chem. 2000, 78, 957962. General transformation: Pd(II) or Pd(0) catalyst RX R' base X = halide, triflate R R' HX
Pd(OAc)2 + H2O + nPR3 + 2R'3N
Pd(PR3)n-1 + O=PR3 + 2R'3NHOAc
Ozawa, F.; Kubo, A.; Hayashi, T. Chemistry Lett. 1992, 21772180.
Ag+ / Tl+ salts irreversibly abstract a halide ion from the Pd complex formed by oxidative addition. Reductive elimination from the cationic complex is probably irreversible.
An example of a proposed mechanism involving cationic Pd:
PhBr
Pd catalyst CH3O2C Ag+ CH3O2C
Ph
R = alkenyl, aryl, allyl, alkynyl, benzyl Mechanism:
R' = alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, CO2R, OR, SiR3 AgHCO3 reductive elimination AgCO3 HPd(II)L2+ CH3O2C Ph
Pd(II) 2 L; 2 e Pd(0)L2 PhBr oxidative addition
Proposed mechanism involving neutral Pd: PhBr Pd catalyst CH3O2C Pd(II) KHCO3 + KBr reductive elimination K2CO3 HPd(II)L2Br Pd(0)L2 2 L; 2 e PhBr oxidative addition CH3O2C Ph
PhPd(II)L2Br Ag + AgBr PhPd(II)L2 Pd(II)L2+ Ph H H
+
syn elimination
Pd(II)L2+ H H CH3O2C Ph H H CH3O2C
halide abstraction
PhPd(II)L2Br CH3O2C internal rotation
syn elimination
CH3O2C Ph H CH3O2C Pd(II)L2Br H Ph H H CH3O2C Pd(II)L2Br Ph H H
CH3O2C
syn addition
syn addition
Abelman, M. M.; Oh, T.; Overman, L. E. J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 41334135. Andrew Haidle
internal rotation
Reactions with vinyl or aryl triflates often parallel those of the corresponding halides in the presence of silver salts. TMS I I N SO2Ph
Pd(OAc)2 (3 mol %) PPh3 (6 mol %) DMF, 23 C N SO2Ph
Ag2CO3, eq 1 1 2
Time, h 24 48 5
Yield, % 50 35 80
TMS I Pd(OAc)2 (3 mol %) Et3N DMSO, 100 C, 15 h 12%
CH3 57% GC yields TMS 30% Sakamoto, T.; Kondo, Y.; Uchiyama, M.; Yamanaka, H. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1993, 19411942. By-product: N SO2Ph
TMS I Pd(OAc)2 (3 mol %) AgNO3, Et3N DMSO, 50 C, 3 h 64%
TMS Pd(OAc)2 (3 mol%) Et3N DMSO, 50 C, 3 h Ohff, M.; Ohff, A.; van der Boom, M. E.; Milstein, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 1168711688. 61% Shaw, B. L.; Perera, S. D.; Staley, E. A. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1998, 13611362. OTf With some ligands, experimental evidence points to a Pd(II)/Pd(IV) catalytic cycle, although the debate is ongoing.
Karabelas, K.; Hallberg, A. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 49094914. Reversible -hydride elimination can lead to alkene isomerization. HPd * Pd * Pd H * Conditions: Catalysts: Pd(OAc)2 Pd2(dba)3 stable Pd(0) source; useful if substrate O N CH3 I Conditions Pd(OAc)2 (1 mol %) PPh3 (3 mol %) Et3N (2 equiv) acetonitrile, 3h, reflux as above, plus AgNO3 (1 equiv) and 23 C 26 : 1 Dielectric constant 2.4 7.6 10.5 38.3 Solvent toluene THF 1,1-dichloroethane DMF 1 : 1 Solvents: Typically aprotic; a range of polarities. CH3 N O CH3 N most common is sensitive to oxidation O dba =
Use of silver salts can minimize alkene isomerization.
Ligands: Phosphines (PR3), used to prevent deposition of Pd(0) mirror.
Abelman, M. M.; Oh, T.; Overman, L. E. J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 41334135. Andrew Haidle
Bases: Both soluble and insoluble bases are used. Soluble examples Insoluble examples
Regiochemistry of addition: Neutral Pd complexes: regiochemistry is governed by sterics; position of Ar attachment: 10 CH3 Ph OH 100 90 40 O Y 100 Y = CO2R CN CONH2 60 N 80 OH OAc mixture 20 100 OH
CH3 CH3 N CH3 CH3 CH3
Et3N
K2CO3
Ag2CO3
1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidine (PMP)
Jeffery conditions: The combination of tetraalkylammonium salts (phase-transfer catalysts) and insoluble bases accelerates the rate to the extent that lower reaction temperatures are possible.
CO2CH3
Pd(OAc)2 (5 mol %) NaHCO3, 3 A ms DMF, 50 C, 2 h Equiv. of nBu4NCl 0 1
CO2CH3
GC Yield(%) 2
Cationic Pd complexes: regiochemistry is affected by electronics. The cationic Pd complex 99 increases the polarization of the alkene favoring transfer of the vinyl or aryl group to the site of least electron density. Jeffery, T. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 1011310130.
One proposed explanation for this rate enhancement is based on the fact that palladium complexes can be stabilized by the coordination of halide ions; thus, the catalyst is less likely to decompose under the Heck reaction conditions. 60 Amatore, C.; Azzabi, M.; Jutand, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991 , 113, 83758384.
40 Ph
95 CH3 OH 5 100 O 90 OH 10
100 OH
95 OAc 5
Conditions for the Heck coupling of aryl chlorides have been developed. 100 Pd2(dba)3 (1.5 mol %) Cl CH3O CO2CH3 P(t-Bu)3 (6 mol %) Cs2CO3 (1.1 equiv) dioxane, 120 C, 24 h 82% CH3O CO2CH3
Y = CO2R CN CONH2
Cabri, W.; Candiani, I. Acc. Chem. Res. 1995, 28, 27. Cabri, W.; Candiani, I.; Bedeschi, A.; Penco, S.; Santi, R. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 14811486.
Littke, A. F.; Fu, G. C. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 1011. Andrew Haidle
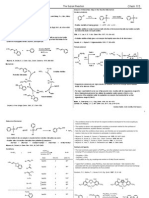
A major issue in intramolecular Heck reactions is the mode of ring closure, i.e., exo versus endo. endo PdLn H endo
Conformational effects are more important when forming smaller rings. The eclipsed orientation is preferred for the reaction, even if this means the rest of the molecule must adopt a less than ideal conformation. O O
LnPd LnPd R eclipsed R twisted
exo
exo O For large rings, conformational effects can be minimal. If a neutral Pd complex is used, sterics enforce endo selectivity. The Heck reaction is useful for macrocylization. O PdCl2(CH3CN)2 (100 mol %) Et3N CH3CN, 25 C 55% CH3 H O H O Ziegler, F. E.; Chakraborty, U. R.; Weisenfeld, R. B. Tetrahedron 1981, 37, 40354040. O eclipsed (boat) O O O PdLn NHCO2CH3 O O O O
stereochemistry defines the incipient quaternary center NHCO2CH3
Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol %) PPh3 (40 mol %) Ag2CO3, THF, 66 C 73% PdLn CH3O2CN H O O twisted (chair) O
I O CH3 H O
Five-, six-, and seven-membered ring closures (the most efficient Heck ring closures) give predominantly exo products. O
O NHCO2CH3 O H O CH3O2CN H O O > 20 : 1 O
O O
DBSN H
Pd(OCOCF3)2 (PPh3)2 (10 mol %) PMP, toluene, 120 C
OCH3 OBn DBSN
CH3O OBn
I 60%
H O OH ()-Morphine O CH3N OH H H CH3O
O OH O N H CH 3
DBS = dibenzosuberyl
()-6a-epipretazettine Overman, L. E. Pure & Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 14231430. Andrew Haidle
Hong, C. Y.; Kado, N.; Overman, L. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 1102811029.
Variation of reaction conditions can greatly influence exo versus endo selectivity in small rings.
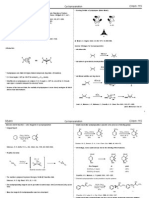
Tandem Reaction: Additional reaction pathways become available when the initial PdC species does not (or can not)
TBSO CH3O CH3O I N
OTBS Pd(OAc)2 (6 mol %) nBu4NCl NHR O OTBS Pd(OAc)2 (2 mol %) PPh3 (6 mol %) N O NHR Et3N, CH3CN 80 C, 2 h 32% TBSO CH3O CH3O KOAc, DMF 80 C, 22h 58% CH3O CH3O
TBSO TBSO NHR N O
decompose via -hydride elimination. R3 PdX R1 Heck sp cascade
2
R3 PdX R2 R3 R1PdX PdX R1 R2 -hydride elimination Oxidation, Nu
R2
R1 R3
R2 Heck sp cascade R3 R1 R2 Alkylation Nu
TBSO CH3O CH3O I
TBSO NHR N O R1
M R2
R3M CO CH3OH CO 2CH3
R3X
Transmetalation
R1 The authors' rationale for these results is that under the Jeffery conditions, the coordination Carbonylation sphere of palladium is relatively smaller, and thus the metal can be accommodated at the more substituted alkene site during migratory insertion.
R2 R1 R2
R1
R2 Nucleophilic attack
Heck reaction Tandem Heck reactions:
Rigby, J. H.; Hughes, R. C.; Heeg, M. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 78347835. R CH3 OTBS Pd(PPh3)4 (100 mol %) CH3 K2CO3, CH3CN O OBn 4 A ms, 90 C 49% O O CH3 Steric and electronic effects begin to compete with conformational effects when forming mediumsized rings. O N H Masters, J. J.; Link, J. T.; Snyder, L. B.; Young, W. B.; Danishefsky, S. J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 17231726. Taxol O CH3 O OH CH3 O O OCH OH 3 CH3 CH3 OH O O H O O O CH3 R = O O HO2C HO H O O Scopadulcic acid A Kucera, D. J.; O'Connor, S. J.; Overman, L. E. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 53045306. Fox, M. E.; Li, C; Marino, J. P.; Overman, L. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 54675480. OH H R CH3 CH3 H O OBn I H TfO CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 O O O H OTBS TBSO CH3 O Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol %) PPh3 (20 mol %) Ag2CO3, THF, 65 C LnPd R CH3 H OTBS LnPd R
CH3
H OTBS TBAF, THF, 23C 82%
CH3 O
CH3
Andrew Haidle
Tandem Heck reaction, intermolecular CH3 CH3 TDSO OTBS Br
Tandem Heck/allylpalladium reactions
CH3 H CH3
Pd2(dba)3 (5 mol %) PPh3 (48 mol %) Et3N, toluene 120 C, 1.5 h 76% overall CH3 CH3 H H O PdLn CH3N H ()-Morphine OH H CH3O CH3O CH3 CH3 OH OH I CH3O2C N H Pd(TFA)2(PPh3)2 (20 mol %) PMP, toluene, 120 C 56% CH3O O N
OCH3 OH PdLn
OCH3 O N O
TDSO TBSO
Hong, C. Y.; Overman, L. E. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 34533456.
Tandem Suzuki/Heck reactions CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 TBSO CH3 H TDSO TDSO CH3 CH3 OTBS 1:9 CH3 CH3 [1,7]-H-shift H TfO CH3 CH3 CH3 O O 9-BBN H CO2CH3 TfO B H CO2CH3 PdCl2(dppf) (10 mol %) AsPh3 (10 mol %) CsHCO3, DMSO, 85 C CH3 O CH3 O I OTDS
CH3 CH3 TBAF CH3 O THF 79% TDSO CH3 H CO2CH3 65% O TfO CH3
CH3 O
H CO2CH3
HO
OH
Alphacalcidiol
OTDS Kojima, A.; Honzawa, S.; Boden, C. D. J.; Shibasaki, M. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 34553458.
Trost, B. M.; Dumas, J.; Villa, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 98369845.
Andrew Haidle
The ease of reaction (Heck versus Suzuki) is highly dependent upon the reaction conditions:
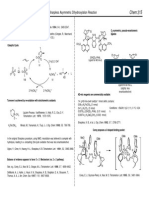
Enantioselective Heck Reactions: Typical yields = 5080% Typical ee's = 8095%
Pd(OAc)2 (1 mol %) PPh3 (5 mol %) B O O 87 CH3 CH3 Bu3N, CH3CN, 120 C H3CO B O O CH3 CH3 O : 13
Formation of tertiary stereocenters: Pd2(dba)3CHCl3 (2.5 mol %) CH3O CH3 I Si(CH3)3 (R)BINAP (7.0 mol %) Ag3PO4 (1.1 equiv) DMF, 48 h, 80 C 91%, 92% ee Tietze, L. F.; Raschke, T. Synlett 1995, 597598. Pd[(R)BINAP]2 (3 mol %) CO2Et (CH3)2N N CO2CH3 benzene, 60 C, 20 h 95%, > 99% ee N(CH3)2 N H3CO2C H CO2Et
CH3O CH3
CH3 CH3 I O OCH3 Pd(OAc)2 (5 mol %) Phenanthroline (5 mol %) t-BuOK, CH3CN, 45 C
OCH3
H3C CH3 0 : 100
7-Desmethyl-2-methoxycalamenene
Hunt, A. R.; Stewart, S. K.; Whiting, A. Tetrahedron Lett., 1993, 34, 35993602.
OTf
Tandem Heck/6-electrocyclization reactions:
Note that the alkene within the intially formed pyrrolidine has migrated under the reaction conditions. Ozawa, F.; Kobatake, Y.; Hayashi, T. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 25052508.
Pd(OAc)2 (3 mol %) PPh3 (6 mol %) Br EtO2C EtO2C OH Ag2CO3 (2 eq) CH3CN, 80 C, 3 h EtO2C EtO2C
BrPdLn H HO
CO2CH3
Pd(OAc)2 (5 mol %) (R)BINAP (10 mol %) K2CO3 (2 equiv) KOAc (1 equiv) ClCH2CH2Cl, 60 C, 41 h 70%, 86% ee
CO2CH3 O H O H
OH
TfO
O O
(+)-Vernolepin
PdLnBr H H HO EtO2C CO2Et 85% EtO2C EtO2C HO EtO2C EtO2C HO H
Ohari, K.; Kondo, K.; Sodeoka, M.; Shibasaki, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 1173711748.
TfO O
Pd2(dba)3 (3 mol %) L (6 mol %) (i-Pr)2NEt benzene, 30 C, 72 h 92%, > 99% ee O
H O L= Ph2P N
Henniges, H.; Meyer, F. E.; Schick, U.; Funke, F.; Parsons, P. J.; de Meijere, A. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 1154511578. Loiseleur, O.; Hayashi, M.; Schmees, N.; Pfaltz, A. Synthesis 1997, 13381345. Andrew Haidle
Formation of quaternary stereocenters: CH3 CH3O OTf OTDS Pd(OAc)2 (7 mol %) (R)BINAP (17 mol %) K2CO3 (3 equiv) THF, 60 C, 72 h 90%, 90% ee CH3 N CH3O CH3 OTDS
Kinetic Resolution: CH3 O O H Pd(OAc)2 (20 mol %) (R)TolBINAP (40 mol %) K2CO3 (2.5 equiv) toluene, 100 C TDSO CH3 O O H 1.7% CH3 O O H 18.3%, 96% ee
MOMO TfO CH3
MOMO CH3
OTDS racemic MOMO CH3
HO Takemoto, T.; Sodeoka, M.; Sasai, H.; Shibasaki, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 84778488. CH3 ()-Eptazocine O O O O O (S), 71%, 66% ee CH3 N neutral CH3O O AcO CH3
CH3 O
TDSO
The choice of base influences whether the Pd complex is neutral or cationic; this in turn can influence the stereochemical outcome. O O O N CH3 I Pd2(dba)3 (5 mol %) (R)BINAP (11 mol %) PMP (5 equiv) DMA, 110 C, 8 h
H O
(+)-Wortmannin The enantiomer of the major product not observed. Instead, a complex mixture of products was formed.
Honzawa, S.; Mizutani, T.; Shibasaki, M. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 311314. O O O N CH3 I Pd2(dba)3 (5 mol %) (R)BINAP (11 mol %) Ag3PO4 (2 equiv) NMP, 80 C, 26 h O O (R), 86%, 70% ee Ashimori, A.; Bachand, B.; Overman, L. E.; Poon, D. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 64776487. CH3 CH3O I O OTIPS Pd2(dba)3CHCl3 (10 mol %) (S)BINAP (23 mol %) N CH3 CH3 PMP, DMA, 100 C 3 M HCl 23 C CH3O CHO O N CH3 (S), 84%, 95% ee Initial products are 2,3 dihydrofurans: O CH3 N cationic O OTf Pd(OAc)2 (3 mol %) (R)TolBINAP (6 mol %) (iPr)2NEt (3 equiv) benzene, 30 C O (R), 71%, 93% ee O (S), 7%, 67% ee
Only the (R) isomer can isomerize due to the asymmetric environment of the ligand. O
CH3 Matsuura, T.; Overman, L. E.; Poon, D. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 65006503.
H N O
CH3 N N H CH3 CH3
Ozawa, F.; Kubo, F.; Matsumoto, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Nishioka, E.; Yanagi, K.; Moriguchi, K. Organometallics 1993, 12, 41884196. Andrew Haidle
()-Physostigmine
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet For Midterm2015 Ucsc Chem110bDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Cheat Sheet For Midterm2015 Ucsc Chem110bStarrx714100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet For Midterm2015Document1 pageOrganic Chemistry Cheat Sheet For Midterm2015Norma Leticia Ramos100% (6)
- Cambio de Nomenclatura de Los EquiposDocument44 pagesCambio de Nomenclatura de Los Equiposjulio peña lima100% (1)
- Summary of Important Organic ReactionsDocument41 pagesSummary of Important Organic ReactionsKathyNo ratings yet
- Governor and Load Limit ModeDocument5 pagesGovernor and Load Limit ModeSamir100% (1)
- PSMC SecureDocument390 pagesPSMC Securedanish_1985100% (3)
- MouseDocument15 pagesMouseBadri NarayananNo ratings yet
- Zinc Alloys EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesZinc Alloys EncyclopediavkmsNo ratings yet
- Suzuky ReactionDocument13 pagesSuzuky ReactionAlbornoz JuanNo ratings yet
- AKD BuchwaldhartwigDocument39 pagesAKD BuchwaldhartwigMurali Venkat NagNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reactions of Organic ChemistryDocument28 pagesOxidation Reactions of Organic ChemistryviejayNo ratings yet
- Chem 215 Myers: The Suzuki ReactionDocument10 pagesChem 215 Myers: The Suzuki ReactionRajathi YadavNo ratings yet
- Carbenoids 2Document15 pagesCarbenoids 2costea0028No ratings yet
- Chem 215 Myers: Birch ReductionDocument7 pagesChem 215 Myers: Birch ReductionPrasanna AndojuNo ratings yet
- Chem 115 Myers: Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation ReactionDocument5 pagesChem 115 Myers: Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation ReactionashisdasNo ratings yet
- 7 Magnesium HalogenDocument5 pages7 Magnesium HalogenMai ChiNo ratings yet
- Chem 115 Myers: Birch ReductionDocument7 pagesChem 115 Myers: Birch ReductionNimz02No ratings yet
- 2007 Aus. Chem OlympiadDocument31 pages2007 Aus. Chem OlympiadRunpeng LiuNo ratings yet
- Epoxidation & Opening PDFDocument84 pagesEpoxidation & Opening PDFRajkumar ChinnuNo ratings yet
- Conjugated DienesDocument80 pagesConjugated DienesKishor MazumderNo ratings yet
- Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation: Comprehensive Organic Synthesis 1991, Vol. 2, 99Document31 pagesCarbon-Carbon Bond Formation: Comprehensive Organic Synthesis 1991, Vol. 2, 99mmiliyasNo ratings yet
- Shenvi Sep 04Document10 pagesShenvi Sep 04patilamardip007No ratings yet
- KT CH ActivationDocument36 pagesKT CH ActivationJayendra Pandit AhireNo ratings yet
- Mcclory-Lit-03 16 09Document58 pagesMcclory-Lit-03 16 09Vasudevan SubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- CO 301 Heterocyclic ChemistryDocument31 pagesCO 301 Heterocyclic ChemistryMohini BajajNo ratings yet
- PD Catalyzed Functionalization of C-H BondsDocument49 pagesPD Catalyzed Functionalization of C-H BondsLafonda LamontéNo ratings yet
- Conjugated DienesDocument80 pagesConjugated Dienestrie_79No ratings yet
- Oxidation (Myers)Document10 pagesOxidation (Myers)YouTibeNo ratings yet
- Flow Charts in Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesFlow Charts in Organic ChemistryJessie McCartney85% (27)
- 16 Sharpless Asymmetric EDocument4 pages16 Sharpless Asymmetric ENicolò MarnoniNo ratings yet
- Fukuyama Group - Group Meeting Problems 09/05/2012: P-Tsoh (Cat.)Document2 pagesFukuyama Group - Group Meeting Problems 09/05/2012: P-Tsoh (Cat.)Anonymous rhUNqC1s0No ratings yet
- Memorization List: Ions-Names and ChargeDocument4 pagesMemorization List: Ions-Names and ChargepringlekNo ratings yet
- Chimie OrganicaDocument16 pagesChimie OrganicaDana CapbunNo ratings yet
- Regioselective Hydromethoxycarbonylation of Terminal Alkynes Catalyzed by Palladium (II) Tetraphos ComplexesDocument6 pagesRegioselective Hydromethoxycarbonylation of Terminal Alkynes Catalyzed by Palladium (II) Tetraphos ComplexesGreciel Egurrola SanchezNo ratings yet
- Properties of SiliconDocument16 pagesProperties of SiliconGabriela ResendeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 4 Edition: Reactions of Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfur-Containing CompoundsDocument50 pagesOrganic Chemistry 4 Edition: Reactions of Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfur-Containing CompoundsDella AinurrohmaNo ratings yet
- Artigo Controle Cinetico e TermodinamicoDocument6 pagesArtigo Controle Cinetico e TermodinamicoPatricia Amaral CeldeiraNo ratings yet
- Chen Feb 07Document9 pagesChen Feb 07Debdeep RayNo ratings yet
- 16 Cycloaddition Rxns 1Document13 pages16 Cycloaddition Rxns 1Aulia RhamdaniNo ratings yet
- Ja6b03383 Si 001Document10 pagesJa6b03383 Si 001Mérito MéritoNo ratings yet
- Chem 215 Myers: Sharpless Asymmetric Dihydroxylation ReactionDocument4 pagesChem 215 Myers: Sharpless Asymmetric Dihydroxylation ReactionPrabhakar S AchantaNo ratings yet
- 28 CyclopropanationDocument11 pages28 CyclopropanationRajesh TammanaNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Catalysis PDFDocument99 pagesHomogeneous Catalysis PDFevsgoud_goudNo ratings yet
- T WilsonDocument34 pagesT WilsonBình Lớp PhóNo ratings yet
- F Ac 18 1 2012 0510Document36 pagesF Ac 18 1 2012 0510Handugan Quinlog NoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter04 OxidationdDocument46 pagesChapter04 OxidationdWilliam H. BasingerNo ratings yet
- Wilkinson CatalystDocument19 pagesWilkinson Catalystjagabandhu_patraNo ratings yet
- FGIDocument6 pagesFGIJulia MaramatNo ratings yet
- Mitsos Aug 04Document9 pagesMitsos Aug 04fersg12No ratings yet
- 4 5 PDFDocument11 pages4 5 PDFRomNo ratings yet
- Borrowing HydrogenDocument7 pagesBorrowing HydrogenVinayak KhairnarNo ratings yet
- A Stereoselective Synthesis of (-) - TetrodotoxinDocument16 pagesA Stereoselective Synthesis of (-) - TetrodotoxinbroccolikimNo ratings yet
- Stereoselectivity of The Secondary Isotope Effect in The Aquation of (Co (NH) CL)Document4 pagesStereoselectivity of The Secondary Isotope Effect in The Aquation of (Co (NH) CL)Fabian MelinaoNo ratings yet
- Ferreira Lit 7-17-03Document14 pagesFerreira Lit 7-17-03bocahupiNo ratings yet
- Witting Reaction by Suman BalyaniDocument22 pagesWitting Reaction by Suman BalyaniSuman Balyani50% (2)
- Alkenes Class PresentationDocument68 pagesAlkenes Class PresentationAdityaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds 1Document25 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds 1dubstepoNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument25 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsdubstepoNo ratings yet
- M01 Unit4 ChartsDocument21 pagesM01 Unit4 ChartsdubstepoNo ratings yet
- Bar WidthsDocument7 pagesBar WidthsdubstepoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3dubstepoNo ratings yet
- Figure 2-1: Pork Market Equilibrium: Q, Million KG of Pork Per YearDocument7 pagesFigure 2-1: Pork Market Equilibrium: Q, Million KG of Pork Per YeardubstepoNo ratings yet
- Summary-First Chapter - Indian Economic Outlook BookDocument3 pagesSummary-First Chapter - Indian Economic Outlook BookdubstepoNo ratings yet
- Sudoku and Other Number PuzzlesDocument36 pagesSudoku and Other Number PuzzlesdubstepoNo ratings yet
- Prodigy Finance Brochure (Oct 2017) - 18Document26 pagesProdigy Finance Brochure (Oct 2017) - 18dubstepoNo ratings yet
- Vss3nofHpZI PDFDocument13 pagesVss3nofHpZI PDFdubstepoNo ratings yet
- Regno Name SUB Phy Che Mat Bio CsDocument66 pagesRegno Name SUB Phy Che Mat Bio Csdubstepo100% (1)
- Breakfast: Bread Milk Rice PuddingDocument14 pagesBreakfast: Bread Milk Rice PuddingdubstepoNo ratings yet
- Excel Keyboard Shortcuts: Moving Around An Excel SheetDocument1 pageExcel Keyboard Shortcuts: Moving Around An Excel SheetdubstepoNo ratings yet
- Profitability FrameworkDocument2 pagesProfitability FrameworkdubstepoNo ratings yet
- 216 S11-Expt 5Document2 pages216 S11-Expt 5dubstepoNo ratings yet
- 35 Exp 12Document4 pages35 Exp 12dubstepoNo ratings yet
- Viscosity of Resin Solutions: Standard Test Method ForDocument2 pagesViscosity of Resin Solutions: Standard Test Method Foralienz1988newNo ratings yet
- Well-Site Formation Evaluation by Analysis of Hydrocarbon Ratios G.H. FerrieDocument12 pagesWell-Site Formation Evaluation by Analysis of Hydrocarbon Ratios G.H. Ferriec_b_umashankarNo ratings yet
- Huawei Anti-DDoS Solution BrochureDocument2 pagesHuawei Anti-DDoS Solution BrochurejjfloressNo ratings yet
- G10 ABDULAZIZ, DINSEFA, TOFIK, 2021 ProposalDocument10 pagesG10 ABDULAZIZ, DINSEFA, TOFIK, 2021 ProposalHabtamu Ye Asnaku LijNo ratings yet
- Chilled AHU FCU PDFDocument4 pagesChilled AHU FCU PDFKhaled ELSaftawyNo ratings yet
- Solved Examples Heat TransferDocument9 pagesSolved Examples Heat TransferAshutosh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Hmine115 Workshop Practice Welding ProcessDocument72 pagesHmine115 Workshop Practice Welding ProcessGareth MashingaidzeNo ratings yet
- LX3V-2RS485-BD 1Document8 pagesLX3V-2RS485-BD 1Marko GavrilovicNo ratings yet
- A1dh 1Document2 pagesA1dh 1Mohammed Sajid100% (1)
- 2012chennai SubmarineDesignDocument27 pages2012chennai SubmarineDesignPericlesleiteNo ratings yet
- Spooky2 Healing Frequency Anleitung Englisch Version 2.0Document26 pagesSpooky2 Healing Frequency Anleitung Englisch Version 2.0StellaEstel100% (4)
- ME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Document6 pagesME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Kumar RajeshNo ratings yet
- Appendix C Fault Level Calculation Rev 0Document2 pagesAppendix C Fault Level Calculation Rev 0Vikram Singh100% (1)
- TheDynamicConePenetrationTest ModifyDocument17 pagesTheDynamicConePenetrationTest ModifyInfo MilestoneNo ratings yet
- General Us Lite PDFDocument179 pagesGeneral Us Lite PDF2791957No ratings yet
- 2794 990 RevADocument36 pages2794 990 RevAgovindarulNo ratings yet
- 17 Urban Cruiser (Cont. Next Page) : Taillight and IlluminationDocument4 pages17 Urban Cruiser (Cont. Next Page) : Taillight and IlluminationHEMIL ROBERTO RODRIGUEZ HERRERANo ratings yet
- Concrete Tech AssignmentDocument7 pagesConcrete Tech AssignmentShehan FernandoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Aerospace Engineering Soler 2014 PDFDocument404 pagesFundamentals Aerospace Engineering Soler 2014 PDFAnousack KittilathNo ratings yet
- 670901086669-Influence of Supplementary Cementitious Materials On Engineering Properties of High Strength ConcreteDocument11 pages670901086669-Influence of Supplementary Cementitious Materials On Engineering Properties of High Strength ConcreteNM2104TE06 PRATHURI SUMANTHNo ratings yet
- Dobladoras BraunDocument4 pagesDobladoras BraunDiana Marcela Londoño MárquezNo ratings yet
- Numerical Derivatives Scilab 2Document59 pagesNumerical Derivatives Scilab 2Alejandro MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Methyl RedDocument4 pagesMethyl RedBenelux ModeNo ratings yet
- Philips Active Subwoofer - SW-200Document18 pagesPhilips Active Subwoofer - SW-200lasser22832165No ratings yet