Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Money Market
Money Market
Uploaded by
Uniq ManjuCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Indian Financial SystemDocument16 pagesIndian Financial Systemshankarinadar100% (1)
- Introduction-to-Financial-Systems-and-Banking-Regulations Stage-1 SYLLABUSDocument31 pagesIntroduction-to-Financial-Systems-and-Banking-Regulations Stage-1 SYLLABUSAHSANNo ratings yet
- Emfs Project: ROLL NO.-50Document25 pagesEmfs Project: ROLL NO.-50Ishaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Financial Market PDFDocument64 pagesFinancial Market PDFsnehachandan91No ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial MarketsDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Financial MarketsPradnya HingeNo ratings yet
- SL& C Study 3Document28 pagesSL& C Study 3abhibth151No ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument13 pagesMoney MarketrohitkoliNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument13 pagesMoney MarketDeepak R GoradNo ratings yet
- FINANCIALMARKETSINNIGERIADocument16 pagesFINANCIALMARKETSINNIGERIAJennifer LaurettaNo ratings yet
- Final Project-Money MarketDocument60 pagesFinal Project-Money MarketSneha Dubey50% (4)
- Financial Institutions and Markets (MBA 406B) Module - I: Financial MarketsDocument62 pagesFinancial Institutions and Markets (MBA 406B) Module - I: Financial MarketsMothish Chowdary GenieNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesResearch MethodologyBalakrishna ChakaliNo ratings yet
- Money Market Detailed NotesDocument14 pagesMoney Market Detailed Notesmohammad723mehdiNo ratings yet
- Arsh Advani - 1 Abhishek Dhariwal - 8 Pooja Jain - 17 Priyanka Majmundar - 32 Himanshu SanghviDocument14 pagesArsh Advani - 1 Abhishek Dhariwal - 8 Pooja Jain - 17 Priyanka Majmundar - 32 Himanshu SanghviArshAdvaniNo ratings yet
- Money Market in IndiaDocument67 pagesMoney Market in IndiaBeth RoweNo ratings yet
- Money Market:-: The Money Market Is A Key Component of The Financial System - It Is A Market For Short - TermDocument6 pagesMoney Market:-: The Money Market Is A Key Component of The Financial System - It Is A Market For Short - TermVenkatesh GajulaNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Vs Money MarketDocument4 pagesCapital Market Vs Money Market6tpnwtfmzyNo ratings yet
- Financial System Refers To A Network of Financial InstitutionsDocument3 pagesFinancial System Refers To A Network of Financial InstitutionspoolheronayanNo ratings yet
- Financial Management 1 (Bbpw3103) : May Semester 2021Document17 pagesFinancial Management 1 (Bbpw3103) : May Semester 2021Freshlynero JonalNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Fms NCDocument17 pagesUNIT 2 Fms NCHemalathaNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Lec NoticeDocument30 pagesCapital Market Lec NoticeZabibu SadickNo ratings yet
- The Money Market: - Nabaraj Adhikari, PHDDocument91 pagesThe Money Market: - Nabaraj Adhikari, PHDNiraj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System For BBADocument11 pagesIndian Financial System For BBARajat Pawan0% (2)
- Vikas B Com Pass Course Eafm Sem Ii Paper Ii Public Fin & Fsi EnglishDocument32 pagesVikas B Com Pass Course Eafm Sem Ii Paper Ii Public Fin & Fsi EnglishPriyankNo ratings yet
- Sathyabama University Faculty of Business AdministrationDocument16 pagesSathyabama University Faculty of Business AdministrationGracyNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - MMSDocument16 pagesStudy Notes - MMSAlok GoyalNo ratings yet
- Money Market Vs Capital MarketDocument53 pagesMoney Market Vs Capital MarketrajNo ratings yet
- Indian Money MarketDocument73 pagesIndian Money MarketPriya ShahNo ratings yet
- Capital N Money MarketDocument22 pagesCapital N Money MarketColin Castor FdesNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 (Definition) Yeye: Money MarketsDocument6 pagesSlide 1 (Definition) Yeye: Money MarketsCyeonjNo ratings yet
- Capital Market: Financial Market Debt Equity SecuritiesDocument33 pagesCapital Market: Financial Market Debt Equity SecuritiesRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Money Market NewDocument40 pagesMoney Market NewMaitreyeeNo ratings yet
- Chit Ran ShuDocument5 pagesChit Ran ShuHaritika ChhatwalNo ratings yet
- Money VS Capital MarketDocument4 pagesMoney VS Capital MarketUsmanNo ratings yet
- "Governmentsecurities": Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For Master of Management Studies (MMS)Document35 pages"Governmentsecurities": Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For Master of Management Studies (MMS)Kaustubh BhandariNo ratings yet
- State Management of Financial Market Development: A Case Study in VietnamDocument11 pagesState Management of Financial Market Development: A Case Study in VietnamNguyen Ha TrangNo ratings yet
- Money Market Concept, Meaning: 1. Maturity PeriodDocument17 pagesMoney Market Concept, Meaning: 1. Maturity Periodb_nagarjuna5814No ratings yet
- Unit 1: ObjectivesDocument21 pagesUnit 1: ObjectivesbibijackyNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument70 pagesMoney Marketvandana_daki3941No ratings yet
- Money Market NoteDocument20 pagesMoney Market NoteSiddhant BajhalNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Economic Development and Indian Financial SystemDocument20 pages1.1 Economic Development and Indian Financial SystemBhoomi NataniNo ratings yet
- Term Paper ON: "The Role of Money Market in Bangladesh"Document30 pagesTerm Paper ON: "The Role of Money Market in Bangladesh"Pushpa BaruaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Importance of Banking SystemDocument19 pagesUnit I: Importance of Banking SystemdollyNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument19 pagesFinancial MarketAshishNo ratings yet
- Various Instruments in Capital MarketDocument31 pagesVarious Instruments in Capital MarketAzim SamnaniNo ratings yet
- Money Market InstrumentsDocument15 pagesMoney Market InstrumentsDharmendra Singh100% (1)
- A Developed Money MarketDocument1 pageA Developed Money MarketAmi Parekh MehtaNo ratings yet
- FM-Module 3 Act1&2Document3 pagesFM-Module 3 Act1&2Erica XaoNo ratings yet
- Financial Market - Unit 1 (1) (Autosaved)Document71 pagesFinancial Market - Unit 1 (1) (Autosaved)learnerme129No ratings yet
- Islamic Money Market: An Instrument For Managing Liquidity Risk in Islamic BanksDocument21 pagesIslamic Money Market: An Instrument For Managing Liquidity Risk in Islamic BanksFarah EgalNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument44 pagesMoney MarketReshma MaliNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument44 pagesUntitled Documentjamwalvarun58No ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument19 pagesIndian Financial SystemAlex VamanapuramNo ratings yet
- Capital Market and Intermediaries NotesDocument62 pagesCapital Market and Intermediaries NoteslavanyaNo ratings yet
- International Trade Finance: A NOVICE'S GUIDE TO GLOBAL COMMERCEFrom EverandInternational Trade Finance: A NOVICE'S GUIDE TO GLOBAL COMMERCENo ratings yet
- Computer Science - One Mark - Test 2Document16 pagesComputer Science - One Mark - Test 2Uniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Courier ServicesDocument59 pagesCourier ServicesUniq Manju100% (1)
- SMS Based Student InformationDocument8 pagesSMS Based Student InformationUniq Manju67% (3)
- A Report On Indian Automobile IndustryDocument33 pagesA Report On Indian Automobile IndustryUniq Manju100% (1)
- Computer Science One Mark Test 4: Choose The Best AnswerDocument11 pagesComputer Science One Mark Test 4: Choose The Best AnswerUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Monthly Test NovDocument9 pagesComputer Science Monthly Test NovUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- A Study of Export of Diamond ProductsDocument71 pagesA Study of Export of Diamond ProductsUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Abstract For Airline Reservation SystemDocument2 pagesAbstract For Airline Reservation SystemUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- A Study of Export of Diamond ProductsDocument39 pagesA Study of Export of Diamond ProductsUniq Manju100% (1)
- Front PagesDocument2 pagesFront PagesUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Credit RatingDocument50 pagesCredit RatingUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Competitive AnalysisDocument133 pagesCompetitive AnalysisUniq Manju0% (1)
- Competitive Analysis and MarketingDocument9 pagesCompetitive Analysis and MarketingUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- A Study On Export of Ayurvedic Products From IndiaDocument60 pagesA Study On Export of Ayurvedic Products From IndiaUniq Manju100% (3)
- Report of The Advisory Group On Securities Market RegulationDocument21 pagesReport of The Advisory Group On Securities Market RegulationUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- The Internal Auditor: Definition, Duties and Responsibilities, Relationships, Ethics, and IndependenceDocument17 pagesThe Internal Auditor: Definition, Duties and Responsibilities, Relationships, Ethics, and IndependenceUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Farhat ProjectDocument49 pagesFarhat ProjectAbdur Rafe Al-AwlakiNo ratings yet
- Topic1 Introductionto Financial Market and SecuritiesDocument19 pagesTopic1 Introductionto Financial Market and SecuritiesMirza VejzagicNo ratings yet
- PadgettDocument15 pagesPadgettDonna RespondekNo ratings yet
- NSDLDocument260 pagesNSDLumesh151170No ratings yet
- Financial Economics Chapter OneDocument46 pagesFinancial Economics Chapter OnebikilahussenNo ratings yet
- Financial Market, Instrument and InstitutionDocument43 pagesFinancial Market, Instrument and InstitutionMarkus Bernabe DaviraNo ratings yet
- Gide To Indiv Work-2Document13 pagesGide To Indiv Work-2Daiva ValienėNo ratings yet
- Top 50 CAIIB Practice Questions For BFM: Download Free PDF NowDocument10 pagesTop 50 CAIIB Practice Questions For BFM: Download Free PDF NowAkthar fathimaNo ratings yet
- LaksonDocument21 pagesLaksonMariyam AkhundNo ratings yet
- FIN546 - Exam QuestionDocument8 pagesFIN546 - Exam QuestionLuqmanulhakim JohariNo ratings yet
- Gencap Hela Imara Money Market Fund - FaqsDocument3 pagesGencap Hela Imara Money Market Fund - FaqsErick M'bwanaNo ratings yet
- ABSLI Fortune Wealth Plan V01 - Brochure - Web VersionDocument22 pagesABSLI Fortune Wealth Plan V01 - Brochure - Web VersionsharmaoriginalNo ratings yet
- Mba II Financial Management (14mba22) SolutionDocument10 pagesMba II Financial Management (14mba22) SolutionSangeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Asset Classes and Financial InstrumentsDocument33 pagesAsset Classes and Financial Instrumentskaylakshmi8314No ratings yet
- Nism Securities Operations and Risk ManagementDocument117 pagesNism Securities Operations and Risk ManagementKailashnath GantiNo ratings yet
- SAPM (Indian Financial System)Document6 pagesSAPM (Indian Financial System)Sharon SequeiraNo ratings yet
- FINMARDocument28 pagesFINMARrou ziaNo ratings yet
- Indian Finance Service and Standards MCQS 1 PDFDocument16 pagesIndian Finance Service and Standards MCQS 1 PDFAbhijit MishraNo ratings yet
- International Finance 2019 Section No.3Document22 pagesInternational Finance 2019 Section No.3yahiasambozyaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Mutual FundsDocument15 pagesModule 5 Mutual FundsShanna MaeNo ratings yet
- Financial Market OperationsDocument28 pagesFinancial Market OperationsdeepeshmahajanNo ratings yet
- StudentDocument33 pagesStudentW11No ratings yet
- Indian FSDocument27 pagesIndian FSnitishbhardwaj123No ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument15 pagesWorking Capital ManagementOW YuNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument16 pagesIndian Financial SystemSarada NagNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction of FinanceDocument53 pagesUnit 1 Introduction of FinanceMalde KhuntiNo ratings yet
- Himanshu PalDocument71 pagesHimanshu PalChandan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1shraddha amatyaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ifrs Chapter 7Document11 pagesTugas Ifrs Chapter 7Nabilla salsaNo ratings yet
Money Market
Money Market
Uploaded by
Uniq ManjuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Money Market
Money Market
Uploaded by
Uniq ManjuCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION TO MONEY MARKET
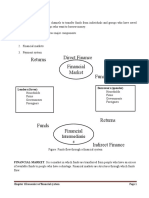
INTRODUCTION A market where short-term funds are borrowed and lent is called money market is a market for short-term financial assets, which are near substitutes for money. The instruments dealt within the money market are liquid and can be turned over quickly at low transaction cost and without loss. The money market comprises individuals, institutions, and the government. These agencies create demand for money and also ensure supply of money for a short-term period. The demand for money emanates from merchants, traders, brokers, manufacturers, speculators and even government institutions, the suppliers include commercial banks, insurance companies, nonbanking financial concerns and the of the economy. DEFINITION #. According to the McGraw Hill Dictionary o Modern Econo!ic"# $oney market is the term designed to include the financial institutions which handle the purchase, sale, and transfers of short-term credit instruments. The money market includes the entire machinery for the canali%ing of borrowing, and government short-term obligations& it differs from the long-term or capital market which devotes its attention to dealings in bonds, corporate stocks and mortgage credit. '. According to Geo rey# money market is the collective name given to the various firms and institutions that deal in the various grades of the near-money. (. According to the Re"er$e %an& o India# a money market is the centre for dealings, mainly of short-term character in money assets& it meets the short-term requirements of borrowers and provides liquidity or cash to the lenders. )t is the place where short-term surplus investible funds at the disposal of financial and other institutions and individuals are bid by borrowers" agents comprising institutions and individuals and also the government itself. # entral !ank of the country. Thus, the money market represents the country"s pool of short-term investible funds to meet the short-term requirements
HI'TORY OF INDIAN MONEY MARKET Till #*(+, when the ,!) was set up, the )ndian money market remained highly disintegrated, unorgani%ed, narrow, shallow and therefore, very backward. The planned economic development that commenced in the year #*+# marked an important beginning in the annals of the )ndian money market. The nationali%ation of banks in -roup .#*/01, the setting up of 2iscount and 3inance 4ouse of )ndia 5td .#*//1, the 6aghul working of )ndia .#**71 and the commencement of liberali%ation and globali%ation process in #**# gave a further fillip for the integrated and efficient development of )ndian money market. IM(ORTANCE ) FUNCTION OF MONEY MARKET GENERA* CHARACTERI'TIC The general characteristics of a money market are outlined below8 #. 'hort+ter! ,nd" are borrowed and lent. '. No i-ed .lace for conduct of operations, the transactions being conducted even over the phone and therefore there is an essential need for the presence of well developed communications system. (. 2ealings may be conducted with or without the help of /ro&er"0 7. The short-term financial assets that are dealt in are clo"e ",/"tit,te" or !oney# financial assets being converted into money with ease, speed, without loss and with minimum transactions cost. +. 3unds are traded for a ma9imum .eriod o one year0 0. :resence of a large number of ",/!ar&et" such as inter-bank call money, bills rediscounting, treasury bills, etc.
'
O%1ECTI2E' A well-developed money market serves the following ob;ectives8 #. :roviding an e3,ili/ri,! !echani"! for ironing out short-term surplus and deficits. '. :roviding a ocal .oint or central /an& inter$ention for influencing liquidity in the economy. (. :roviding acce"" to ,"er" o "hort+ter! !oney to meet their requirements at a reasonable price. IM(ORTANCE The functioning of an efficient money market in a country is helpful to its various segments as detailed below8 'OURCE OF CA(ITA* $oney market is an important source of financing for trade and industry. The short-term finances are made available through bills, commercial papers, etc. The happenings in the money market influence the availability of finances both for the national and international trade. !esides trade and industry, money market offers to the government an important non-inflationary avenue of raising short-term funds through bills that are subscribed by commercial banks and the public.
IDEA* IN2E'TMENT $oney market offers an ideal source of investment for the commercial banks. The market helps them invest their short-term surplus funds so as to meet statutory reserve requirements. 3or instance, the requirements of .=2T51. EFFECTI2E MONETARY MANAGEMENT An efficient money market being sensitive in nature allows for the effective implementation of monetary policy of the central bank and thus paves way for the efficient ( ash ,eserve ,atio . ,,1 and <tatutory 5iquidity ,atio .<5,1 vary every fortnight depending on banks" =et 2emand and Time 5iability
monetary management of the country. )n fact, the money market events serve as an important guide to the government in formulation, revising and implementing its monetary policy. This is rightly so, given the fact that the conditions prevailing in money market serve as an indicator of monetary state of an economy. The monetary authority uses the money market for diffusing the effects of its actions throughout the banking system and the economy, so as to promote economic growth with stability. ECONOMIC DE2E*O(MENT $oney market being an integral part of a country"s economy, contributes substantially to the economic development of a country. A developed money market is indispensable for the rapid development of the economy. )n fact, the stage of development of the economy will be reflected in the stage of development of a money market. This is borne out by the fact that illdeveloped nature of a money market is responsible for the primitive nature of economic development of a country. The absence of a well-developed money market would constrain the economies from making available, on a continuous basis the supply of adequate funds. EFFICIENT %ANKING 'Y'TEM The e9istence of a developed money market greatly facilitates the smooth and efficient functioning of the banking and financial system. <uch an advantage contributes to the promotion of trade and industry in the economy. 3urther the mediating role played by the commercial bankers ensures delivery of credit at the most opportune time. <imilarly, money market enables the commercial banks to meet much of their une9pected needs for funds quickly and cheaply. )t is possible for the commercial banks to utili%e their funds profitably and with liquidity. FACI*ITATING TRADE $oney market is of immense help to the business community in the following ways8 :roviding an ideal payment mechanism making it possible for e9peditious transfer of large sums of money. $eeting the working capital requirements for carrying out the production and marketing activities.
$aking efficient investment of surplus funds into near-money assets which can be quickly converted into money as and when needed.
HE*(FU* TO GO2ERNMENT The government uses the money market as an arena in which short-term funds are raised by floating treasury bills. )t helps the government manage its monetary position smoothly through the central bank of the county. GENERA* FUNCTION' $oney market performs diverse functions within the banking system of an economy, as discussed below8 IN2E'TMENT FUNCTION The money market provides an ideal source for investment of the funds for a short period of time for commercial banks, non banking financial concerns, business corporations and other investors. )t enables businessmen, with temporary surplus funds, to invest them for a short period. FINANCING FUNCTION $oney market provides an ideal source for short-term financing for businessmen, industrialists, traders, etc to meet their day-to-day requirements of working capital. 3unds are available for borrowing by the government and its agencies also. FACI*ITATING FUNCTION $oney market provides an ideal play ground for the central monetary authority of the country to carry out various regulatory operations relating to the banking and financial system of the country. The sensitive nature of the money market helps the central bank to make it an ideal arena for the e9ecution of various credit control measures.
DEFECT' ) MEA'URE' FOR DE2E*O(MENT DEFECT' #. UNORGANI4ED MONEY MARKET The presence of indigenous bankers, village money lenders, etc. in villages and semi-urban areas make the )ndian money market highly unorgani%ed. They follow their own rules and practices of finance and banking and are not sub;ect to the regulation and control of the ,eserve !ank of )ndia. There are not in place adequate and proper rules and regulations in order to allow for the orderly growth of the money market in )ndia. '. A%'ENCE OF INTEGRATION This is the serious lacuna afflicting the )ndian money market. <everal sectors are very loosely connected with each other. >ften, there used to be hostility among the different sections of the money market. There is hardly any cohesive working relationship between the organi%ed banking system and the unorgani%ed indigenous bankers. (. INADE5UATE NATIONA* MARKET The market has been a late entry of national level players such as the 234), <T ), etc in the )ndian financial system. This to great e9tent retarded the early growth of the money market. The so-called advancements in computeri%ation and telecommunications are also very limited and confined mostly to urban and semi-urban areas. oordination between various money markets and their constituents is lacking. )t is imperative that a well- coordinated and operationally uniform money market has to emerge in the country. 7. INTERE'T RATE DI'(ARITY A ma;or defect of the )ndian money market has been that the interest rate varies from place to place, from time to time and from segment to segment. ?ide disparity in money rates e9ists. This condition makes it difficult for any worthwhile regulatory mechanisms to be put in place. +. DEFICIENT %I** MARKET 5ack of popularity of bill culture among the traders both at national and international arena, has given rise to a sick and a deficient bill market. This has greatly affected the development of the money market. The transactions relating 0
to bill discounting and purchasing are limited. !esides, they also constitute only a small part of total money market operations in the country. )t is a sad commentary that the different sub markets in the bill market have not shown much development too. 3or instance, the market for government and semigoverment securities is narrow. This has greatly affected the efficient use of the monetary control measures of the ,!) so as to curb the inflationary pressure or to keep the slump away from the economy. 0. $oreover, the investment in government securities is largely confined to )nstitutional investors comprising mainly the ,eserve !ank of )ndia, )nsurance ommercial !anks, 5ife orporation of )ndia, and in certain cases, provident 3und schemes and other
trust funds. This prevents the ,!) from using these instruments effectively for influencing the level of liquidity in the money market, through open market operations. <imilarly, transactions in the interbank call money market, despite constituting the fulcrum of the )ndian money market, are not appreciably large enough to form a sensitive segment. 2espite a series of serious measures initiated by the ,!) over a period of time, the plight of )ndian bill market largely remains secluded, constrained, and under developed much to the chagrin of the monetary managers. @. *IMITED FUND' There has been noticed a perceptible shortage in the supply of loan able funds. The far e9ceeding demand has created a wide chasm in the )ndian money market. This situation can be attributed to such factors as lower savings rate on account of poverty, inadequate banking facilities, poor banking habits among the people, inadequate facilities for investment of small saving and the e9istence of a parallel economy with vast amount of black money defying all regulations. /. 'EA'ONA* 2ARIATION' An essential characteristic of the )ndian money market is the e9istence of seasonality of the demand for money and short-term funds. This seasonal variation follows the pattern of the seasonal variations in agricultural activities. Accordingly during the busy season from >ctober to April, the demand for money is more, as more funds are needed for financing the post harvest movement for the @
marketing of agricultural products, for the financing of seasonal industries such as sugar, etc and also for financing the higher tempo economic activities in general, after the dull rainy season. This is one of the problems faced by the )ndian money market. The frequent seasonal variations in demand and the supply of funds, rates of interest, etc could be attributed to the seasonal nature of the )ndian agriculture. <imilarly, the cyclical fluctuations in the industrial sector also debilitate the working of the )ndian money market. *. UN'TA%*E CONDITION' The variations in the rates of interest, demand and supply of funds, etc create unstable conditions in the money market. This affects the ability of the central bank of the country to monitor the functioning of the various segments. #A. *ACK OF 6E**+ORGANI4ED %ANKING 'Y'TEM 2eveloped money market presupposes the e9istence of a well-organi%ed commercial banking system. !ut, unfortunately, the development in the realm of commercial banking sector has been uneven, although it has been e9panding rapidly. $oreover, the banking facilities are inadequate, highly urban-centric and organi%ed inefficiently. !anks are still lacking computeri%ation, technological up gradation and well-developed branch network. ##. INADE5UATE FOREIGN FUND' An important perquisite for the successful conduct of operations in all the segments of the money market is the movement of foreign funds on a higher scale. Although there has been an enhanced inflow of funds from abroad with the commencement of the process of liberali%ation under various routes such as the 32), it is not in keeping with the actual requirements of the market. This has also affected the development of the )ndian money $arket. #'. INADE5UATE IN'TRUMENT' A significant deficiency of the )ndian money market has been the non availability of adequate number of quality credit instruments especially for a short period. <upply of short-term instruments such as commercials bills, treasury bills, etc is highly inadequate. This to a very large e9tent retards the development in the )ndian money market. /
#(. CON'TRICTED 'ECONDARY MARKET The true development of a financial market depends on the e9tent of secondary market facilities is available in the country. As far as the )ndian money market concern, the secondary market for the money market instrument is mainly restricted to rediscounting of commercial bills and treasury bills. Absence of sufficient number of credit instrument also adds to the woes. 3urther, there has been reluctance on the part of the some of the big borrowers to avail finances against discount of commercial bills. #7. *IMITED (ARTICI(ANT' The highly regulated kind of regimen prevailing in the )ndian capital market deters the free entry and e9it of large numbers of players. 3or instance, institutions such as 234), <T ), banks, specified all-)ndia financial institutions and a few big companies chiefly dominate the market. There is also a lopsided growth in the number of participants spared across the different domains of money markets causing considerable disharmony. MEA'URE' FOR DE2E*O(MENT Beeping in mind the need for a developed money market for a fast growing economy like )ndia, and based on series of recommendations put forth by the committees such were initiated by ,!) towards developing the )ndian money market8 #. INFRA'TRUCTURE ,!) undertook several measures for setting institutions, to help hasten the -rowth and development in the )ndian money market. Accordingly, the discount and 3inance 4ouse of )ndia 5td. .243)1 was established to broaden and deepen the money market operations. )t acts as a market maker. <imilarly, the <ecurities and C9changes !oard of )ndia .<C!)1 was set up to function as an ape9 regulatory body relating to all aspects of security market activities. money market. * redit ,ating agencies such as ,5<)5, ) ,A, etc. were promoted for making possible easy raising of funds from the hakraborty ommittee on $onetary <ystem and 6aghul ?orking $oney $arket the following measures
'. DE2E*O(ING %I** CU*TURE The ,!), to develop the bill culture by promoting and encouraging credit transactions, made all-out efforts by introducing rediscounting of bills, besides giving stamp duty e9emptions for rediscounting of derivatives usance promissory notes arising out of genuine trade bill transaction. (. INNO2ATI2E 'U%MARKET' 6ery recently, several innovative markets such as certificate of deposit, call money market, collateral loan market, commercial paper market, $$$3s, etc came to be introduced to strength to the money market. 7. CREDIT CONTRO* MEA'URE' redit control measures such as ,, and <5, are efficiently manipulated to tone up and buoy the money market operations especially in the commercial banking sector. +. RE(O O(ERATION' the reintroduction of repos .ready forward1 in =ovember #**0, was aim at mopping up e9cess liquidity thus reducing volatility in call money market and the foreign money markets. !eginning >ctober '#, #**@, repo facility was further e9tended to corporate debt and :<D !onds. Dnder these arrangements, ,!) made reverse repo facility available to primary dealers in government security market, at the bank rate, on a discretionary basis and sub;ect to certain regulations from time to time. 0. MMMF' The introduction of $oney $arket $utual 3unds .$$$3s1 for investment in money market instrument marked an important development in the realm of )ndian $oney $arket. $$$3 are required to invest in callEnotice money, certificates of deposits . 2s1, commercial papers . :s1, commercial bill arising out of genuine tradeEcommercial transactions, treasury bills and dated government securities having an une9pired maturity up to # year. :ioneer $oney $arket Account was launched on 3ebruary '7, #**@ as )ndia"s first $$$3. The DT) F $oney $arket $utual 3und launched on April '(, #**@ followed this.
#A
You might also like
- Indian Financial SystemDocument16 pagesIndian Financial Systemshankarinadar100% (1)
- Introduction-to-Financial-Systems-and-Banking-Regulations Stage-1 SYLLABUSDocument31 pagesIntroduction-to-Financial-Systems-and-Banking-Regulations Stage-1 SYLLABUSAHSANNo ratings yet
- Emfs Project: ROLL NO.-50Document25 pagesEmfs Project: ROLL NO.-50Ishaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Financial Market PDFDocument64 pagesFinancial Market PDFsnehachandan91No ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial MarketsDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Financial MarketsPradnya HingeNo ratings yet
- SL& C Study 3Document28 pagesSL& C Study 3abhibth151No ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument13 pagesMoney MarketrohitkoliNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument13 pagesMoney MarketDeepak R GoradNo ratings yet
- FINANCIALMARKETSINNIGERIADocument16 pagesFINANCIALMARKETSINNIGERIAJennifer LaurettaNo ratings yet
- Final Project-Money MarketDocument60 pagesFinal Project-Money MarketSneha Dubey50% (4)
- Financial Institutions and Markets (MBA 406B) Module - I: Financial MarketsDocument62 pagesFinancial Institutions and Markets (MBA 406B) Module - I: Financial MarketsMothish Chowdary GenieNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesResearch MethodologyBalakrishna ChakaliNo ratings yet
- Money Market Detailed NotesDocument14 pagesMoney Market Detailed Notesmohammad723mehdiNo ratings yet
- Arsh Advani - 1 Abhishek Dhariwal - 8 Pooja Jain - 17 Priyanka Majmundar - 32 Himanshu SanghviDocument14 pagesArsh Advani - 1 Abhishek Dhariwal - 8 Pooja Jain - 17 Priyanka Majmundar - 32 Himanshu SanghviArshAdvaniNo ratings yet
- Money Market in IndiaDocument67 pagesMoney Market in IndiaBeth RoweNo ratings yet
- Money Market:-: The Money Market Is A Key Component of The Financial System - It Is A Market For Short - TermDocument6 pagesMoney Market:-: The Money Market Is A Key Component of The Financial System - It Is A Market For Short - TermVenkatesh GajulaNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Vs Money MarketDocument4 pagesCapital Market Vs Money Market6tpnwtfmzyNo ratings yet
- Financial System Refers To A Network of Financial InstitutionsDocument3 pagesFinancial System Refers To A Network of Financial InstitutionspoolheronayanNo ratings yet
- Financial Management 1 (Bbpw3103) : May Semester 2021Document17 pagesFinancial Management 1 (Bbpw3103) : May Semester 2021Freshlynero JonalNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Fms NCDocument17 pagesUNIT 2 Fms NCHemalathaNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Lec NoticeDocument30 pagesCapital Market Lec NoticeZabibu SadickNo ratings yet
- The Money Market: - Nabaraj Adhikari, PHDDocument91 pagesThe Money Market: - Nabaraj Adhikari, PHDNiraj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System For BBADocument11 pagesIndian Financial System For BBARajat Pawan0% (2)
- Vikas B Com Pass Course Eafm Sem Ii Paper Ii Public Fin & Fsi EnglishDocument32 pagesVikas B Com Pass Course Eafm Sem Ii Paper Ii Public Fin & Fsi EnglishPriyankNo ratings yet
- Sathyabama University Faculty of Business AdministrationDocument16 pagesSathyabama University Faculty of Business AdministrationGracyNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - MMSDocument16 pagesStudy Notes - MMSAlok GoyalNo ratings yet
- Money Market Vs Capital MarketDocument53 pagesMoney Market Vs Capital MarketrajNo ratings yet
- Indian Money MarketDocument73 pagesIndian Money MarketPriya ShahNo ratings yet
- Capital N Money MarketDocument22 pagesCapital N Money MarketColin Castor FdesNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 (Definition) Yeye: Money MarketsDocument6 pagesSlide 1 (Definition) Yeye: Money MarketsCyeonjNo ratings yet
- Capital Market: Financial Market Debt Equity SecuritiesDocument33 pagesCapital Market: Financial Market Debt Equity SecuritiesRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Money Market NewDocument40 pagesMoney Market NewMaitreyeeNo ratings yet
- Chit Ran ShuDocument5 pagesChit Ran ShuHaritika ChhatwalNo ratings yet
- Money VS Capital MarketDocument4 pagesMoney VS Capital MarketUsmanNo ratings yet
- "Governmentsecurities": Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For Master of Management Studies (MMS)Document35 pages"Governmentsecurities": Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For Master of Management Studies (MMS)Kaustubh BhandariNo ratings yet
- State Management of Financial Market Development: A Case Study in VietnamDocument11 pagesState Management of Financial Market Development: A Case Study in VietnamNguyen Ha TrangNo ratings yet
- Money Market Concept, Meaning: 1. Maturity PeriodDocument17 pagesMoney Market Concept, Meaning: 1. Maturity Periodb_nagarjuna5814No ratings yet
- Unit 1: ObjectivesDocument21 pagesUnit 1: ObjectivesbibijackyNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument70 pagesMoney Marketvandana_daki3941No ratings yet
- Money Market NoteDocument20 pagesMoney Market NoteSiddhant BajhalNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Economic Development and Indian Financial SystemDocument20 pages1.1 Economic Development and Indian Financial SystemBhoomi NataniNo ratings yet
- Term Paper ON: "The Role of Money Market in Bangladesh"Document30 pagesTerm Paper ON: "The Role of Money Market in Bangladesh"Pushpa BaruaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Importance of Banking SystemDocument19 pagesUnit I: Importance of Banking SystemdollyNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument19 pagesFinancial MarketAshishNo ratings yet
- Various Instruments in Capital MarketDocument31 pagesVarious Instruments in Capital MarketAzim SamnaniNo ratings yet
- Money Market InstrumentsDocument15 pagesMoney Market InstrumentsDharmendra Singh100% (1)
- A Developed Money MarketDocument1 pageA Developed Money MarketAmi Parekh MehtaNo ratings yet
- FM-Module 3 Act1&2Document3 pagesFM-Module 3 Act1&2Erica XaoNo ratings yet
- Financial Market - Unit 1 (1) (Autosaved)Document71 pagesFinancial Market - Unit 1 (1) (Autosaved)learnerme129No ratings yet
- Islamic Money Market: An Instrument For Managing Liquidity Risk in Islamic BanksDocument21 pagesIslamic Money Market: An Instrument For Managing Liquidity Risk in Islamic BanksFarah EgalNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument44 pagesMoney MarketReshma MaliNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument44 pagesUntitled Documentjamwalvarun58No ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument19 pagesIndian Financial SystemAlex VamanapuramNo ratings yet
- Capital Market and Intermediaries NotesDocument62 pagesCapital Market and Intermediaries NoteslavanyaNo ratings yet
- International Trade Finance: A NOVICE'S GUIDE TO GLOBAL COMMERCEFrom EverandInternational Trade Finance: A NOVICE'S GUIDE TO GLOBAL COMMERCENo ratings yet
- Computer Science - One Mark - Test 2Document16 pagesComputer Science - One Mark - Test 2Uniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Courier ServicesDocument59 pagesCourier ServicesUniq Manju100% (1)
- SMS Based Student InformationDocument8 pagesSMS Based Student InformationUniq Manju67% (3)
- A Report On Indian Automobile IndustryDocument33 pagesA Report On Indian Automobile IndustryUniq Manju100% (1)
- Computer Science One Mark Test 4: Choose The Best AnswerDocument11 pagesComputer Science One Mark Test 4: Choose The Best AnswerUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Monthly Test NovDocument9 pagesComputer Science Monthly Test NovUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- A Study of Export of Diamond ProductsDocument71 pagesA Study of Export of Diamond ProductsUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Abstract For Airline Reservation SystemDocument2 pagesAbstract For Airline Reservation SystemUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- A Study of Export of Diamond ProductsDocument39 pagesA Study of Export of Diamond ProductsUniq Manju100% (1)
- Front PagesDocument2 pagesFront PagesUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Credit RatingDocument50 pagesCredit RatingUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Competitive AnalysisDocument133 pagesCompetitive AnalysisUniq Manju0% (1)
- Competitive Analysis and MarketingDocument9 pagesCompetitive Analysis and MarketingUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- A Study On Export of Ayurvedic Products From IndiaDocument60 pagesA Study On Export of Ayurvedic Products From IndiaUniq Manju100% (3)
- Report of The Advisory Group On Securities Market RegulationDocument21 pagesReport of The Advisory Group On Securities Market RegulationUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- The Internal Auditor: Definition, Duties and Responsibilities, Relationships, Ethics, and IndependenceDocument17 pagesThe Internal Auditor: Definition, Duties and Responsibilities, Relationships, Ethics, and IndependenceUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Farhat ProjectDocument49 pagesFarhat ProjectAbdur Rafe Al-AwlakiNo ratings yet
- Topic1 Introductionto Financial Market and SecuritiesDocument19 pagesTopic1 Introductionto Financial Market and SecuritiesMirza VejzagicNo ratings yet
- PadgettDocument15 pagesPadgettDonna RespondekNo ratings yet
- NSDLDocument260 pagesNSDLumesh151170No ratings yet
- Financial Economics Chapter OneDocument46 pagesFinancial Economics Chapter OnebikilahussenNo ratings yet
- Financial Market, Instrument and InstitutionDocument43 pagesFinancial Market, Instrument and InstitutionMarkus Bernabe DaviraNo ratings yet
- Gide To Indiv Work-2Document13 pagesGide To Indiv Work-2Daiva ValienėNo ratings yet
- Top 50 CAIIB Practice Questions For BFM: Download Free PDF NowDocument10 pagesTop 50 CAIIB Practice Questions For BFM: Download Free PDF NowAkthar fathimaNo ratings yet
- LaksonDocument21 pagesLaksonMariyam AkhundNo ratings yet
- FIN546 - Exam QuestionDocument8 pagesFIN546 - Exam QuestionLuqmanulhakim JohariNo ratings yet
- Gencap Hela Imara Money Market Fund - FaqsDocument3 pagesGencap Hela Imara Money Market Fund - FaqsErick M'bwanaNo ratings yet
- ABSLI Fortune Wealth Plan V01 - Brochure - Web VersionDocument22 pagesABSLI Fortune Wealth Plan V01 - Brochure - Web VersionsharmaoriginalNo ratings yet
- Mba II Financial Management (14mba22) SolutionDocument10 pagesMba II Financial Management (14mba22) SolutionSangeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Asset Classes and Financial InstrumentsDocument33 pagesAsset Classes and Financial Instrumentskaylakshmi8314No ratings yet
- Nism Securities Operations and Risk ManagementDocument117 pagesNism Securities Operations and Risk ManagementKailashnath GantiNo ratings yet
- SAPM (Indian Financial System)Document6 pagesSAPM (Indian Financial System)Sharon SequeiraNo ratings yet
- FINMARDocument28 pagesFINMARrou ziaNo ratings yet
- Indian Finance Service and Standards MCQS 1 PDFDocument16 pagesIndian Finance Service and Standards MCQS 1 PDFAbhijit MishraNo ratings yet
- International Finance 2019 Section No.3Document22 pagesInternational Finance 2019 Section No.3yahiasambozyaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Mutual FundsDocument15 pagesModule 5 Mutual FundsShanna MaeNo ratings yet
- Financial Market OperationsDocument28 pagesFinancial Market OperationsdeepeshmahajanNo ratings yet
- StudentDocument33 pagesStudentW11No ratings yet
- Indian FSDocument27 pagesIndian FSnitishbhardwaj123No ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument15 pagesWorking Capital ManagementOW YuNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument16 pagesIndian Financial SystemSarada NagNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction of FinanceDocument53 pagesUnit 1 Introduction of FinanceMalde KhuntiNo ratings yet
- Himanshu PalDocument71 pagesHimanshu PalChandan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1shraddha amatyaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ifrs Chapter 7Document11 pagesTugas Ifrs Chapter 7Nabilla salsaNo ratings yet