Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk For Injury
Risk For Injury
Uploaded by
Joanne Kaye TaylorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk For Injury
Risk For Injury
Uploaded by
Joanne Kaye TaylorCopyright:
Available Formats
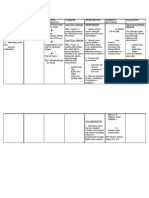
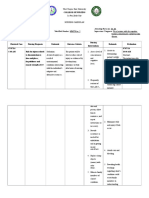
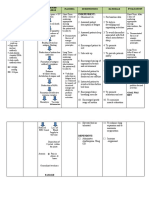
Assessment Subjective data: Report of seizure.
. Objective data: Altered level of consciousness (+) Seizure activity (+) Right sided weakness GCS 11
Risk for self-directed injury related to seizures secondary to brain injury. . Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Risk for falls related to impaired physical mobility secondary to altered level of consciousness. Short term goal: After 30 minutes of effective nursing intervention, the client and watcher will develop and follow risk control strategies as manifested by verbalization of understanding. Long term goal: After 8 hours of effective nursing intervention, the client will have no incidence of injury-causing events such as falls. Independent: 1. Observed individuals general health status, noticing factors that might affect safety such as chronic or debilitating conditions. 2. Assessed muscle strength, gross and fine motor coordination. 3. Reviewed history of prior falls associated with immobility, weakness, or prolonged bed rest. 4. Recognized clients cognitive status including extent of brain injury and neurological disorders. 5. Considered environmental hazards in the care setting.
Evaluation Short term: Goal met.
To evaluate source or degree of risk.
To evaluate the degree of risk. To predict current risk for falls. Long term: Goal met.
To evaluate the clients ability to perceive own limitations or recognize danger. To provide opportunities for intervention and instruction.
6. Maintained side rails raised.
To protect the patient from rolling and falling out of bed. To ensure the clients safety.
7. Advised the clients relative to maintain a safe environment.
8. Advised the clients relative to never leave the client unattended. Dependent: 9. Administered medications as ordered. Collaborative: 12. Assisted in treatments and provided information regarding clients conditions that may result in increased risk of falls. 13. Referred to rehabilitation team, physical or occupational therapist as appropriate.
To ensure clients safety. To treat the underlying condition. To assist caregiver to reduce or correct individual risk factors. To improve clients balance, strength, or mobility and to improve or relearn ambulation.
You might also like
- NCP-Risk For InjuryDocument1 pageNCP-Risk For InjuryLave Majorenos80% (10)
- Risk For Injury NCP SeizuresDocument2 pagesRisk For Injury NCP Seizurestimie_reyes88% (8)
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument6 pagesNCP Impaired Physical MobilityRene John Francisco100% (1)
- NCP Modified Radical MastectomyDocument5 pagesNCP Modified Radical MastectomyIvan Jules P. PALMARESNo ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For InjuryDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InjuryIngrid Sasha Fong75% (12)
- NCP Risk of AspirationDocument2 pagesNCP Risk of AspirationNura Zein100% (1)
- NCP - Self-Care DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP - Self-Care DeficitEricka B. Banaszczuk100% (15)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- NCP #1 Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesNCP #1 Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionsteffiNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InjuryDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InjuryAbigail Joy Tabones75% (4)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionAngelo ︻╦̵̵͇̿̿̿̿╤── Bulacan50% (6)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNo ratings yet
- POC Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pagePOC Ineffective Breathing Patterncuicuita100% (1)
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Self Care DeficitIgorot Hector100% (2)
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainIsrael Soria EsperoNo ratings yet
- CVA NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesCVA NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceJoanne Kaye Taylor100% (1)
- Cholera PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCholera PathophysiologyJoanne Kaye TaylorNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing FNCPDocument4 pagesCommunity Health Nursing FNCPJoanne Kaye Taylor82% (11)
- Risk For Injury NCPDocument3 pagesRisk For Injury NCPZen DurezaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityVhin Lim100% (2)
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Document2 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implimentation Rationale ResponseDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implimentation Rationale Responsekhate fonteNo ratings yet
- XIII. NCP Risk For FallsDocument1 pageXIII. NCP Risk For FallsMartin T Manuel100% (2)
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- Self Care DeficitDocument2 pagesSelf Care DeficitRen Aezzle Garcia Aceveda100% (1)
- Ncp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDDocument4 pagesNcp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Gcic NCP Seizure PICUOSMUNDocument2 pagesGcic NCP Seizure PICUOSMUNhanyaklein100% (3)
- Or NCP (Risk For Injury)Document1 pageOr NCP (Risk For Injury)Nikki M. ArapolNo ratings yet
- NCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument9 pagesNCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Related To Insufficient Knowledge To Avoid Exposure To Pathogens As Evidence by Dirty Nails.Document2 pagesRisk For Infection Related To Insufficient Knowledge To Avoid Exposure To Pathogens As Evidence by Dirty Nails.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Document8 pagesRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitNo ratings yet
- NCP FolliculitisDocument3 pagesNCP Folliculitismichpadua50% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveMaverick Lim100% (1)
- NCP For Seizures........Document3 pagesNCP For Seizures........LP Benoza67% (3)
- NCP DobDocument2 pagesNCP DobTata Wendz100% (1)
- NXCP Disturbed Sensory Perception3Document2 pagesNXCP Disturbed Sensory Perception3marielle_dellaNo ratings yet
- Self-Care DeficitDocument2 pagesSelf-Care DeficitNDJNo ratings yet
- 3 Altered Renal Tissue Perfusion Chronic Renal Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pages3 Altered Renal Tissue Perfusion Chronic Renal Renal Failure Nursing Care Planssapiah raman100% (1)
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Self Care Deficit BahtingDocument1 pageSelf Care Deficit BahtingNaj SoliveresNo ratings yet
- NCP Near DrowningDocument1 pageNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- NCP CVA Impaired Physical Mobility 1Document2 pagesNCP CVA Impaired Physical Mobility 1Frency Anne Causo Pascual100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Seizuretimie_reyes100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2Document4 pagesNCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2ejoanbNo ratings yet
- Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesRisk For InfectionChristy Berry100% (1)
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaNo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument4 pagesRisk For InjuryJanina Patricia BuddleNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesLevofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- NCP OptDocument3 pagesNCP Optdeathstar_diorama100% (2)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- MS Neuro (Lab) Sas 1Document4 pagesMS Neuro (Lab) Sas 1Jake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument9 pagesNCP Impaired Physical MobilityChristian Apelo SerquillosNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument8 pagesCrisis ManagementneuronurseNo ratings yet
- De-Escalation in Health Care. Quick Safety. The Joint Commission, Division of Healthcare Improvement Issue 47 - January 2019Document4 pagesDe-Escalation in Health Care. Quick Safety. The Joint Commission, Division of Healthcare Improvement Issue 47 - January 2019Urgencias HorwitzNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Prevention PlanDocument8 pagesEpilepsy Prevention Planzainab.bspsy1735No ratings yet
- Neuroncp PDFDocument2 pagesNeuroncp PDFCedrick John Gabbac DalagNo ratings yet
- 14 Stroke (CVA) Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing CarDocument10 pages14 Stroke (CVA) Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Caralaaf2340No ratings yet
- NCP For SamDocument1 pageNCP For SamRussell AltamiaNo ratings yet
- S E L F - P E R C E P T I O N - S E L F - C O N C E P T P A T T E R A. 1Document4 pagesS E L F - P E R C E P T I O N - S E L F - C O N C E P T P A T T E R A. 1Diana TardecillaNo ratings yet
- CMS Standards Regarding The Use of Restraints and SeclusionDocument4 pagesCMS Standards Regarding The Use of Restraints and Seclusionapi-299934163No ratings yet
- Stand by Me! Reducing The Risk of Injurious Falls in Older AdultsDocument7 pagesStand by Me! Reducing The Risk of Injurious Falls in Older AdultsAnonymous ZUaUz1wwNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Immunomodulating DrugsDocument2 pagesMiscellaneous Immunomodulating DrugsJoanne Kaye TaylorNo ratings yet
- CholeraDocument4 pagesCholeraJoanne Kaye TaylorNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument2 pagesOxytocinJoanne Kaye TaylorNo ratings yet