Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beilinson Residues and Adeles 1980
Beilinson Residues and Adeles 1980
Uploaded by
bhaumiksauravCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beilinson Residues and Adeles 1980
Beilinson Residues and Adeles 1980
Uploaded by
bhaumiksauravCopyright:
Available Formats
RESIDUES A. A.
AND
ADELES UDC 513.60
Beilinson
In this b r i e f a r t i c l e T a t e ' s c o n s t r u c t i o n in [1] f o r the r e s i d u e s of d i f f e r e n t i a l s on c u r v e s is g e n e r a l i z e d to the m u l t i d i m e n s i o n a l c a s e . The l o c a l r e s i d u e of P a r s h i n [2, 3] and E l z e i n [4] a r i s e s f r o m the c l a s s of c o h o m o l o g i e s of s o m e i n f i n i t e - d i m e n s i o n a l L i e a l g e b r a . M o r e o v e r , it is s h o w n that the g l o b a l m o r p h i s m of the G r o t h e n d i e c k t r a c e s p l i t s up into the s u m of r e s i d u e s . H e n c e w e h a v e the p - p a r t of the r e c i p r o c i t y l a w s in [3]. 1. C o n s i d e r the s e t T,. = ( C . , Ai., Bi.), c o n s i s t i n g of the c o m p l e x C , of v e c t o r s p a c e s o v e r the f i e l d k, and i t s s u b c o m p l e x e s A i B 1 , 1 < i < N. L e t S(n) be the s e t of p a i r s (P, Q ) , p , Q ~ {l . . . . ~} s u c h that[ P N Q [ = n, [ P U Q I - - ~ r . F o r a - - - - ( P , q ) ~ S (n),~ P N Q - - { ~ . . . . . in}, i ~ < . . . < i n , s e t a (h 0 ) ~ ( P , Q \ { i j } ) , a ( / , l ) = ( P \ f f f , q )
S (n--t);
*' 0 (], T , j ~ i~e N Ai*~_Q ~ B)"
r):
r . a - - , r,~0.r)(r-~ 0J) a r e n a t u r a l e m b e d d i n g s . L e t
r.~ ----o~S(n) + r.~; " 0~ ffi
~ (--W t~.$<n+l
(0 (1, 0) -- a (], i)): r.,+t ~ r . , ; ] ~0: r.o ~ c , be the s u m o f e m b e d d i n g s . I t is e a s i l y s e e n t h a t O,,o0n+x= 0, Oo0o= 0. S u p p o s e t h a t w e a r e g i v e n a n a s s o c i a t i v e k - a l g e b r a E and i t s t w o - s i d e d i d e a l s X i , y i , 1 _< i _< N s u c h t h a t X i + y i = E f o r a l l i. W e a s s o c i a t e w i t h T = 0g, X i, y i ) the s e t T . = ( C . , Ai., Bi.), w h e r e C . i s a c o m p l e x of c h a i n s E c o n s i d e r e d a s a L i e a l g e b r a o v e r k: C r = A r E , the d i f f e r e n t i a l d r : Cr+~ --" C , i s g i v e n by the f o r mula d, (e~A . . . A e~+~)ffi ~ ( - I f +~+x(~ej - e~) A e, A. :. A ~ A . . . A ~ A . . . A e~+x; and Al = X i A C,_~, B, _- y l A c,_~ a r e s u b c o m p l e x e s of C , . s L E M M A . a) The s e q u e n c e 0 ~ T , N ~ . . . --- T , 0 ~ C , ~ 0 is e x a c t . Thus w e h a v e r r ~ IIo,- (I~N+I(C,),
L e t O be a c o m m u t a t i v e s u b a l g e b r a of E . If 10. . . . . l~ ~ ~ , t h e n w e d e n o t e by r r if0. . . . . IN) ~ ~ (r,~) the v a l u e of r T o n the c y c l e lo A A 1~. b) T h e r e e x i s t s a (unique) m o r p h i s m Rest: fi~l~ --,Hx (r,N) s u c h t h a t Res(lodh A A diN) = rr (to . . . . . . IN)"
2. L e t V be a N o e t h e r i a n s c h e m e , P(V) the s e t of p o i n t s o f V w i t h n a t u r a l o r d e r i n g [for ~ ~ P (v) nt > n~ m e a n s t h a t ~ ~ ~ ], and l e t S(V) be the s i m p l i c i a l s e t c o n n e c t e d w i t h P(V) [the n - s i m p l e x A ~ s (V)n i s the s e t (~0 > . . . > ~?n),*l~ ~ P(V~. If K ~ S ( D ~ , ~ I ~ P ( V ) , then
~K,, =
{(~ > . . .
> 'l~) ~ S ( D , , - ~ I (q > ~h > > ~h) ~ K~}.
By i n d u c t i o n on n, w e d e f i n e a f u n c t o r A(Kn, ) on the c a t e g o r y of q u a s i c o r e g e n t O v - b u n d l e s , a s the unique f u n c t o r c o m m u t i n g w i t h the i n d u c t i v e l i m i t s , and c o i n c i d i n g w i t h II lira M ~ On/m ~ f o r n = 0 on c o r e g e n t b u n d l e s M, and w i t h ~I~P(V)TII lira A (,flKn, M @ O~/m~) f o r n -> 1 (m~? is a m a x i m a l i d e a l o f the l o c a l r i n g O~?). T h e n A ( K n , ) is a n e x a c t f u n c t o r . If Kn ~ K~, K~_,C0~(K~), w e have the obvious m o r p h i s m s .4 (Kn, -) ~ A (K~, .),
A (K~_,, .) ~ a i(~n, .). S e t A n ( v , ) = A(S(V)n, ), and f o r a ~ s (v), s !.)(a) = ,4 ({a}, .). C l e a r l y , ~i t u r n A * ( V , . ) into a s i m p l i c i a l c o m p l e x , and S ( . )(A) into a s y s t e m of c o e f f i c i e n t s o n S(V), and m o r e o v e r t h e r e e x i s t n a t u r a l e m b e d d i n g s A * ( V , . ) - - C*(S(V), S ( . )), H(V, ) --.-H{A*(V, )). W e note t h a t S(V), S ( . ), A*(V, ) d e p e n d f u n c t o r i a l l y on V. I n p a r t i c u l a r , w e have d e f i n e d a c o m p l e x of p r e b u n d l e s A * ( . ) on V: A * (M)(U) = A*(U, M IU), and a m o r p h i s m i: M - - H(A*(IVI)). LEMIVIA. A l l the Ai(M) a r e i n e r t b u n d l e s , __A*( M ) = M ~ A * (Or) , i is a n i s o m o r p h i s m , OV f o r j ~ 0. C O R O L L A R Y . H ' ( V , M) = H ' ( A * ( V , M)). and HJ(_A*(M)) = 0
M o s c o w S t a t e U n i v e r s i t y . T r a n s l a t e d f r o m F u n k t s i o n a l ' n y i A n a l i z i E g o P r i l o z h e n i y a , Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 4 4 - 4 5 , J a n u a r y - M a r c h , 1980. O r i g i n a l a r t i c l e s u b m i t t e d M a y 8, 1979.
34
0 0 1 6 - 2 6 6 3 / 8 0 / 1 4 0 1 - 0 0 3 4 $07.50
1980 P l e n u m P u b l i s h i n g C o r p o r a t i o n
R e m a r k . The c o m p l e x of a d e l e s A* is a " f o r m a l " a n a l o g of the G o d e m a n c a n o n i c a l s i m p l i c i a l r e s o l v e n t . The n a t u r a l f a c t o r s of A* a r e the K u z e n c o m p l e x and the c o m p l e x C* f r o m [2]. H e n c e f o r w a r d , V will be a n N - d i m e n s i o n a l p r o p e r s c h e m e o v e r the p e r f e c t field k. F o r b r e v i t y , let MA = S(M)(A), ~ i = ~ / k " Fix A ~ s (~9~-. T h e n O A is a n A r t i n k - a l g e b r a , on e a c h field K of r e s i d u e s o f w h i c h t h e r e is a n a t u r a l N - d i m e n s i o n a l l o c a l s t r u c t u r e o v e r k (see [3]). This m e a n s that f o r N - 1, K is the field of f r a c t i o n s of a c o m p l e t e d i s c r e t e l y n o r m e d r i n g R 1, w h o s e field of r e s i d u e s K 1 has a n ( N - 1 ) - d i m e n s i o n a l local s t r u c t u r e , and f o r N = 0 K is finite o v e r k (for R 1 we need to take the whole c l o s u r e of the i m a g e Oo0(A) in K, and the l o c a l s t r u c t u r e on K 1 is defined inductively). Any N - d i m e n s i o n a l l o c a l field is i s o m o r p h i c to k ' ( ( t N ) ) . . . ((tl)), w h e r e k' is finite o v e r k {with the obvious l o c a l s t r u c t u r e ) . In [2, 3] ReSK: ~ K N ---k w a s defined by the f o r m u l a aes x (aY[:~* dr, A . . . A dtN)= trk'/k(a) for l 1 = . . . = l N = - 1 , 0 in the opposite c a s e (a ~ k'), and m o r e o v e r R e s K does not depend on the i s o m o r p h i s m K = k' ((tN)) ((tl)). Set nesk = z. ~ nes~: ~ - . k, w h e r e l is the length of 0170, and the s u m is t a k e n o v e r all fields of r e s i d u e s
OA. F u r t h e r m o r e , we denote by R e s k the c o m p o s i t i o n ~ - ~ A N (V, fire)-. H~v (V, ~ N ) ~ k, w h e r e T r is the m o r p h i s m of the G r o t h e n d i e c k t r a c e . 3. We now show how to c o n n e c t the t r i p l e (E, X i, yi) f r o m Sec. 1 with the N - s i m p l e x . L e t ~ = (~],~> ~ > . . . > ~,) ~ s (v)~, A' = 0o (A) = (~, > : .. > r,,). F o r e a c h finite O~?0-module M, let (M) = {L C M [ L is a finite O ~ l - m o d u l e , L - 0~?0 = M~. If Li ~ (I)(M), L t ~ La, then L I a , ~ M a and (Lt/L~) a, : LI,/L~a,. F o r p a i r s M1, M 2 of finite O~0-modules , we define inductively i n n ~H~(M,, M2)= 1! ~ H o m k ( M l a , M~a)] VLI~(D(Mt), L2~P(M2) ~tLI~EP(M1), L 2 ~ ( M 2 ) : LI"~ LL L~ D L,,[ (L~') C L,a,, / ( L~a,) C L~a': and f o r n _> 1 the induced m o r p h i s m f. ( n~/ Li) ~. -~ ( L~/ L~)~. belongs to tl a,( L,/ L~, L~/L,)} , and X ~':- " n -> i > 1, X ~ ( r e s p e c t i v e l y , y i ) c o n s i s t s of those ! ~ H a , f o r w h i c h all the f in the definition of HA belong to i-1 X ~ I ( L 1 / L 1 , L 2 / L 2) [ r e s p e c t i v e l y , YA' (" ' ")]" C l e a r l y , //~_D Horn% (M~a, M,~). L e t 5 ~ S (~)~-. C o n s i d e r the a s " v v . ~
s o c i a t i v e k - a l g e b r a Ea = ~/~ (~o, ~0) ~ Ead~ (~a, ~a) and its t w o - s i d e d ideals x~ ---- x~(~0, ~ ) , YA = E A f r a l l i ~ N , ZA_~$a. We apply the c o n s t r u c t i o n of See. 1 t o T = depends only on the l o c a l s t r u c t u r e on the fields of r e s i d u e s ~ ). T H E O R E M . a) All the e l e m e n t s tr: H, (r.N) --~ k. b) aes~ = Res~ = troRes~ra. C O R O L L A R Y (formula for r e s i d u e s in P a r s h i n ' s form). F o r 5 ' ~ s (v)N_i, (~ ~ ~ 7 ~
A~A'
y~. T h e n X ~ +
(EA, X , Y ) (incidentally, T
Q x~ ~ Y~ a r e finitely potent [1], and the t r a c e defines a m o r p h i s m
ms~
0.
I a m deeply g r a t e f u l to A. N. P a r s h i n , w h o s e c o n s e r v a t i o n s with me f o r m e d the b a s i c s o u r c e f o r this a r t i c l e , and to I.. N. B e r n s h t e i n and Yu. I. Manin for their a t t e n t i o n to the a r t i c l e and the a u t h o r . LITERATURE
1.
CITED
2. 3. 4.
J. A. A. F.
Tate, M a t e m a t i k a , 1__33,No. 1, 5-14 (1969). N. P a r s h i n , Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Mat., 40, 736-773 (1976). N. P a r s h i n , Dokl. Akad. N a u k S S S R , 243, No. 4, 355-358 (1978). E l z e i n , C o m p o s i t i o Math., 29, 9-33 (1974).
35
You might also like
- Technical Manual: KVH DSP-1760 Multi-Axis GyroscopeDocument111 pagesTechnical Manual: KVH DSP-1760 Multi-Axis GyroscopeNT0% (1)
- Tantra BibliographyDocument11 pagesTantra BibliographybhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- ISB 4 Cylinder and ISBe 4 and 6 Cylinder Series Engine Familiarization 4021288 PDFDocument31 pagesISB 4 Cylinder and ISBe 4 and 6 Cylinder Series Engine Familiarization 4021288 PDFslipsittinNo ratings yet
- Art:10 1007/BF01077528-1 PDFDocument2 pagesArt:10 1007/BF01077528-1 PDFhelmantico1970No ratings yet
- Conformal Invariance of Massless Dirac-Like Wave EquationsDocument7 pagesConformal Invariance of Massless Dirac-Like Wave EquationsArgha MondalNo ratings yet
- BF01015003Document7 pagesBF01015003jymmyneutronnNo ratings yet
- Campesino Romeo1982Document5 pagesCampesino Romeo1982Rudolf KiraljNo ratings yet
- SHUMLYANSKII - Stability Criterion of The Longitudinal-Torsional Vibrations of A Hoisting Cable With An End Load in Rigid GuidesDocument5 pagesSHUMLYANSKII - Stability Criterion of The Longitudinal-Torsional Vibrations of A Hoisting Cable With An End Load in Rigid GuidesAnonymous PsEz5kGVaeNo ratings yet
- Art:10 1007/BF01040228Document6 pagesArt:10 1007/BF01040228Sukhmander SinghNo ratings yet
- Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics, Vol. 72, No. 3, 1999Document16 pagesJournal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics, Vol. 72, No. 3, 1999thotalnNo ratings yet
- Approximate Relativistic Equations of Motion For An Extended Charged Particle in An Inhomogeneous External Electromagnetic FieldDocument20 pagesApproximate Relativistic Equations of Motion For An Extended Charged Particle in An Inhomogeneous External Electromagnetic FieldHK AbbasiNo ratings yet
- OpenGate vs. Thermo FisherDocument40 pagesOpenGate vs. Thermo FisherDan PrimackNo ratings yet
- Complex Variable and Analytic Function Harmonic FunctionsDocument8 pagesComplex Variable and Analytic Function Harmonic Functionsfebin sajiNo ratings yet
- About Lorentz Transformations and TachyonsDocument4 pagesAbout Lorentz Transformations and Tachyonsherms12345No ratings yet
- Polygon TorsionDocument1 pagePolygon TorsionArash AghagolNo ratings yet
- Ladyzhenskaya1975 Article ADynamicalSystemGeneratedByTheDocument22 pagesLadyzhenskaya1975 Article ADynamicalSystemGeneratedByTheAbdullah IlyasNo ratings yet
- P o W D e R Technology. 11 (1975) 87 - 88: / P. Gardner and K. VergheseDocument2 pagesP o W D e R Technology. 11 (1975) 87 - 88: / P. Gardner and K. VergheseDirceu NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Application of The Finite Element Method To Molecular Quantum PDFDocument5 pagesApplication of The Finite Element Method To Molecular Quantum PDFhhakim32No ratings yet
- About A Dirac Like Equation For The PhotDocument5 pagesAbout A Dirac Like Equation For The PhotcerconeNo ratings yet
- A Model (, Hidden-Variable, Theory For Hydrogen.: (X, T) FDX' .D - (.Document7 pagesA Model (, Hidden-Variable, Theory For Hydrogen.: (X, T) FDX' .D - (.Kokipro KokiproNo ratings yet
- 12 Initial SegmentsDocument13 pages12 Initial SegmentsgodwskyNo ratings yet
- Large Number of More Recent Papers.: NeverDocument11 pagesLarge Number of More Recent Papers.: NeverEpic WinNo ratings yet
- p374 KroghDocument12 pagesp374 KroghY.No ratings yet
- Transactions of Society of Actuaries 1 9 8 2 VOL. 3 4: '/2f10) + F (L) + F (2) + - . - +Document30 pagesTransactions of Society of Actuaries 1 9 8 2 VOL. 3 4: '/2f10) + F (L) + F (2) + - . - +JPPhNo ratings yet
- 1 ChemistryDocument43 pages1 ChemistrySulveNo ratings yet
- MATH2105 - (5) Chain-Rule 1Document15 pagesMATH2105 - (5) Chain-Rule 1Aslı ErenNo ratings yet
- BF02712305Document10 pagesBF02712305Ivie RibeiroNo ratings yet
- f/ono Q: BBQ RDocument5 pagesf/ono Q: BBQ RManas Ranjan MohapatraNo ratings yet
- BlundonDocument12 pagesBlundonphnhongmotNo ratings yet
- Wess 1960Document22 pagesWess 1960Guillermo RNo ratings yet
- RaviartThomas PDFDocument24 pagesRaviartThomas PDFJesse ClarkNo ratings yet
- Scan 6 Oct 2021Document4 pagesScan 6 Oct 2021VedalakshmiNo ratings yet
- A Proof of Kolmogorov's TheoremDocument23 pagesA Proof of Kolmogorov's TheoremIgnazioNo ratings yet
- 0 ' 1 T - 0 - , ) - K, Sin 4 (V + 0) - K - Sin 2 (:? - I) .Document4 pages0 ' 1 T - 0 - , ) - K, Sin 4 (V + 0) - K - Sin 2 (:? - I) .ehagar60No ratings yet
- Pallavi Kumari EX-3 Big Data LabDocument6 pagesPallavi Kumari EX-3 Big Data LabjulietNo ratings yet
- Privarnikov Radovskii Moving Load On Viscoelastic Multi Layer Base 1981 EngDocument7 pagesPrivarnikov Radovskii Moving Load On Viscoelastic Multi Layer Base 1981 EngBORISRADNo ratings yet
- SignalsDocument23 pagesSignalsSuseela reddy PulagamNo ratings yet
- BF 02196496Document3 pagesBF 02196496b10022024No ratings yet
- Bect 200 Edu-G-4-1058-20 Lencer ChelangatDocument3 pagesBect 200 Edu-G-4-1058-20 Lencer Chelangatlencer chelangatNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics North-Holland Publishing Co., AmsterdamDocument41 pagesNuclear Physics North-Holland Publishing Co., AmsterdamDiego Antonio Rodriguez CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 16, 2021Document13 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 16, 2021PavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Management of Sporting EventsDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Management of Sporting EventsVandana VasandaniNo ratings yet
- 1977.... Williams, The Formation and Performance of ChromateDocument13 pages1977.... Williams, The Formation and Performance of ChromateMaría De Fátima LRNo ratings yet
- Integer Functions and Life ContingenciesDocument31 pagesInteger Functions and Life ContingenciesvenetigreNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn, Brooklyn, New York USADocument2 pagesDepartment of Physics Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn, Brooklyn, New York USAYoni Ramirez RoblesNo ratings yet
- Madison Bowie - 2.2 Mind Your Money Video NotesDocument2 pagesMadison Bowie - 2.2 Mind Your Money Video NotesmadiirbowieNo ratings yet
- Nagaland University: Online Examination 2021Document12 pagesNagaland University: Online Examination 2021Eku Nahoi HoilepeNo ratings yet
- 024 034 PDFDocument11 pages024 034 PDFDragan KankarasNo ratings yet
- Asymptotic Layer Solunon of A Boundary Problem: SucnonDocument10 pagesAsymptotic Layer Solunon of A Boundary Problem: SucnonlakiizNo ratings yet
- Indexing Powder Photographs of Tetragonal, Hexagonal and Orthorhombic CrystalsDocument8 pagesIndexing Powder Photographs of Tetragonal, Hexagonal and Orthorhombic CrystalsDanavathBaluNo ratings yet
- Third Imperium Issue 1Document18 pagesThird Imperium Issue 1atpollard100% (3)
- Beginners' Corner Edited by Dmitri Thoro San Jose State CollegeDocument3 pagesBeginners' Corner Edited by Dmitri Thoro San Jose State CollegeKishalaya KunduNo ratings yet
- 10 Subsystems of PADocument11 pages10 Subsystems of PAgodwskyNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Model of The Impact of A Solid On IceDocument6 pagesHydrodynamic Model of The Impact of A Solid On IceYaoke WenNo ratings yet
- 13 The Standard SystemDocument23 pages13 The Standard SystemgodwskyNo ratings yet
- PR Ujian Minicex1Document2 pagesPR Ujian Minicex1GBY channelNo ratings yet
- Mainframes (4 Modules) CompressedDocument155 pagesMainframes (4 Modules) Compressedrahul tejNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Structured Text (ST) ProgrammingDocument17 pagesChapter - Structured Text (ST) ProgrammingrdsrajNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 31 Mar 2023Document18 pagesAdobe Scan 31 Mar 2023shivyanshsinghdec18No ratings yet
- George Arfken - Solutions - 03Document6 pagesGeorge Arfken - Solutions - 03Almaram Aljweher100% (1)
- Foth M: O/O RR, Th'Ms N ".Document15 pagesFoth M: O/O RR, Th'Ms N ".joxekojNo ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-21), Volume 1: Measures and Integrals. (AM-21)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-21), Volume 1: Measures and Integrals. (AM-21)No ratings yet
- Contributions to the Theory of Nonlinear Oscillations (AM-20), Volume IFrom EverandContributions to the Theory of Nonlinear Oscillations (AM-20), Volume INo ratings yet
- Ghost Story CollectionDocument8 pagesGhost Story CollectionbhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Tantra BibliographyDocument11 pagesTantra BibliographybhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Burdwan Syllabus - MA HISTDocument70 pagesBurdwan Syllabus - MA HISTbhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Proposition 0.1. Let V Be An Irreducible, Finite Type Scheme Over Spec R. AlsoDocument1 pageProposition 0.1. Let V Be An Irreducible, Finite Type Scheme Over Spec R. AlsobhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Tanpura TuningDocument1 pageTanpura TuningbhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Grothendieck at 80, IHES at 50: Allyn JacksonDocument2 pagesGrothendieck at 80, IHES at 50: Allyn JacksonbhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- GandhinagarDocument4 pagesGandhinagarbhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Deepak Bisaria 11th HouseDocument4 pagesDeepak Bisaria 11th HousebhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Horoscopes Authenticated by KN RaoDocument1 pageHoroscopes Authenticated by KN RaobhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Automorphisms of C, CP1 and The Upper Half PlaneDocument10 pagesAutomorphisms of C, CP1 and The Upper Half PlanebhaumiksauravNo ratings yet
- Estimating Natural-Fracture Permeability From Mud-Loss DataDocument5 pagesEstimating Natural-Fracture Permeability From Mud-Loss DatanaufalNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: ChemistryDocument22 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry장위No ratings yet
- Shading Devices - HSA and VSADocument5 pagesShading Devices - HSA and VSANikita Sahuji100% (1)
- Course Syllabus in Nat. Sci. 1L - Chemistry For EngineersDocument14 pagesCourse Syllabus in Nat. Sci. 1L - Chemistry For EngineersVincent BaguioNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4: Antenna Array and SynthesisDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 4: Antenna Array and SynthesisTibebu Xibe TeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Single Degree of Freedom Systems - Forced Vibratory SystemsDocument43 pagesChapter 3: Single Degree of Freedom Systems - Forced Vibratory Systemsjawad khalidNo ratings yet
- Earthing MaterialsDocument2 pagesEarthing MaterialsMohammed MustafaNo ratings yet
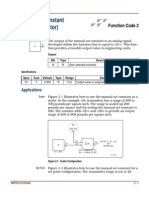
- Manual Set Constant (Signal Generator) : Function Code 2Document2 pagesManual Set Constant (Signal Generator) : Function Code 2Bapiraju Marri100% (1)
- Core - 11 Statistics-and-Probability Q3 2 Mean-and-Variance v1-1Document14 pagesCore - 11 Statistics-and-Probability Q3 2 Mean-and-Variance v1-1jajaNo ratings yet
- Furukawa 1500-EDII - D20II - Engine Starting Circuit X PDFDocument28 pagesFurukawa 1500-EDII - D20II - Engine Starting Circuit X PDFthomaz100% (3)
- University of CalcuttaDocument94 pagesUniversity of CalcuttaAmlan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Arduino Pid ResearchDocument19 pagesArduino Pid ResearchMuhammad MoollaNo ratings yet
- MudCube Data Sheet - PPT26184 4Document1 pageMudCube Data Sheet - PPT26184 4rezaNo ratings yet
- Another AMSI-Bypass PaperDocument19 pagesAnother AMSI-Bypass PaperHangup9313No ratings yet
- Registers & RecordsDocument11 pagesRegisters & RecordsShesha ShayanNo ratings yet
- ACS758 DatasheetDocument22 pagesACS758 Datasheetmachadofelipe88No ratings yet
- Knust School of Engineering: Abp Consult LTDDocument1 pageKnust School of Engineering: Abp Consult LTDKwaku frimpongNo ratings yet
- Jindal PaperDocument2 pagesJindal PaperSibasish SarkhelNo ratings yet
- The Holt-Winters Forecasting ProcedureDocument17 pagesThe Holt-Winters Forecasting ProcedureHimeko UshioNo ratings yet
- Document : Valve Terminal/valve Sensor Terminal With Field Bus Connection VIFB1-/IIFB1-02-1/..-nDocument133 pagesDocument : Valve Terminal/valve Sensor Terminal With Field Bus Connection VIFB1-/IIFB1-02-1/..-nwilliam tolentinoNo ratings yet
- ATT Lab ProgramsDocument8 pagesATT Lab Programsnirikshith pNo ratings yet
- C. Cash DiscountsDocument17 pagesC. Cash DiscountsClarisse-joan Bumanglag GarmaNo ratings yet
- Aw PSD FMW Wls Java Thread Dumps v7Document62 pagesAw PSD FMW Wls Java Thread Dumps v7Muhammad Ahmad HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument46 pagesChapter 2 PDFejamrespectNo ratings yet
- Dkrci - Py.fn0.b2.02 Fia InsertsDocument1 pageDkrci - Py.fn0.b2.02 Fia Insertsyoye1968No ratings yet
- Mai DLM 77100-06 ENDocument330 pagesMai DLM 77100-06 ENSalvador Valero BermejoNo ratings yet
- CRM Business PartnerDocument25 pagesCRM Business PartnerShiva_1912No ratings yet
- Lab 1 PDFDocument15 pagesLab 1 PDFRamesh KonakallaNo ratings yet