Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Error Raising in PO BADI
Error Raising in PO BADI
Uploaded by
SDFSDF123998EWYOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Error Raising in PO BADI
Error Raising in PO BADI
Uploaded by
SDFSDF123998EWYCopyright:
Available Formats
Metafields
Metafields are used in the Enjoy transactions of Purchasing to characterize business content and detach it from concrete data holding. Using metafields in the system, you can thus reference a business variable on a uniform basis. Example The business variable 'purchase order unit' is represented in the user interface by the technical field MEPO1211-MEINS and in data holding by the field EKPO-MEINS. Technically, metafields are integer constants, whose definitions you can find in the type group MMMFD. Note A name range starting from 90000000 is available for customer applications (mmmfd_cust_01).
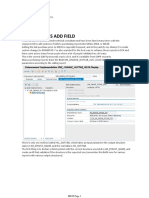
Metafield and field selection
The field selection is determined on the basis of the metafields. For this purpose, the customer's own subscreen must know the list of the fields represented and their assignment to the metafields. This relationship is created in the BAdI ME_GUI_PO_CUST. There on the one hand a DDIC structure is specified in the method SUBSCRIBE, from the components of which the field catalog is created. In addition, the link to the relevant metafield in each case is established in the method MAP_DYNPRO_FIELDS. In method FIELDSELECTION_ITEM of the BAdI ME_PROCESS_PO_CUST, which is a prerequisite for BAdI ME_GUI_PO_CUST, these metafields are then used to influence the selection of the customer's own fields.
Metafield and error handling
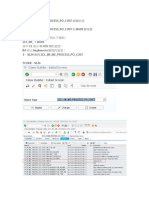
Metafields also have an important function in error handling. They establish the connection between a message and the business content. Example You can control the positioning of the cursor during the processing of messages. If you wish to do this when implementing your own checks, use the following macros:
mmpur_metafield This macro links the metafield with the message generated with the subsequent macro mmpur_message_forced (see below). A list of the known metafields can be found in the type group MMMFD. This also contains some definitions for customer enhancements (MMMFD_CUST_01 to MMMFD_CUST_10). mmpur_message_forced You use this macro to generate the actual message. The message is linked to the known business object (e.g. document header, document item) and the previously specified metafield. The macro requires exactly sevem parameters: message category (I,W,E), message class, message number and the four message parameters. (See also the ABAP message statement).
Further notes
The above-mentioned macros are defined in the program MM_MESSAGES_MAC. Please include this program in your own application. Never issue messages in BAdI ME_GUI_PO_CUST! This is the task of the business logic and must therefore be done via the BAdI ME_PROCESS_PO_CUST. Never use the ABAP statement MESSAGE in the BAdI ME_PROCESS_PO_CUST. Please use the macro mmpur_message_forced only. This macro only writes a message in the message collector. If you wish to mark the business object as invalid in order to prevent posting, you must additionally use the INVALIDATE ( ) method of the relevant interface. In this connection, see also the code example in the PROCESS_ITEM method of the BAdI ME_PROCESS_PO_CUST.
You might also like
- VL 10 BDocument8 pagesVL 10 BrexjonathanNo ratings yet
- BAPI Filling The Configuration StructuresDocument3 pagesBAPI Filling The Configuration StructuresBora GürNo ratings yet
- Output Management in Sap S4 HanaDocument6 pagesOutput Management in Sap S4 HanaRo Gomez MonNo ratings yet
- Displaying Dynamic Columns in ALV With Layout VariantDocument2 pagesDisplaying Dynamic Columns in ALV With Layout VariantVaibhav SambareNo ratings yet
- Enhance The CRM WebClient UI With Custom Fields PDFDocument10 pagesEnhance The CRM WebClient UI With Custom Fields PDFBhattahcarjee RupakNo ratings yet
- Implementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesFrom EverandImplementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesNo ratings yet
- SE37: FI - PAYM - FILENAME - CREATE - File Name ModificationDocument5 pagesSE37: FI - PAYM - FILENAME - CREATE - File Name ModificationRajib Lochan MohapatraNo ratings yet
- How Install Offline / Local SAP Web IDEDocument4 pagesHow Install Offline / Local SAP Web IDEsureshNo ratings yet
- (TEST CASE) PIR Maintenance Via BAPI - ERP Manufacturing (PP)Document7 pages(TEST CASE) PIR Maintenance Via BAPI - ERP Manufacturing (PP)S BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- AS01 EnhancementDocument6 pagesAS01 EnhancementgopigundetiNo ratings yet
- Data Structure MCQDocument31 pagesData Structure MCQVallari Shah88% (8)
- CTS0343 PACCAR-Approved Materials Test Labs 2014-03-10Document3 pagesCTS0343 PACCAR-Approved Materials Test Labs 2014-03-10mpedraza-1No ratings yet
- Detailed Explanation About BADI and The Ways To Find The BADI With An Example (ME23n Transaction)Document14 pagesDetailed Explanation About BADI and The Ways To Find The BADI With An Example (ME23n Transaction)shrirangkattiNo ratings yet
- Creating A Custom MetanetDocument10 pagesCreating A Custom Metanetparthasc100% (1)
- Me28 or Me55 Add Field: Sunday, March 6, 2022 4:17 PMDocument2 pagesMe28 or Me55 Add Field: Sunday, March 6, 2022 4:17 PMfatma100% (1)
- How To Maintain and Use Entries Within TVARVCDocument4 pagesHow To Maintain and Use Entries Within TVARVCSOUMEN DASNo ratings yet
- How To Check and Implement OSS NotesDocument12 pagesHow To Check and Implement OSS NotesAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Smartforms XML FormatDocument35 pagesSmartforms XML FormatNurdin AchmadNo ratings yet
- Create Purchase Order With BAPIDocument14 pagesCreate Purchase Order With BAPIAhmed SalahNo ratings yet
- Navigation Between Different ViewsDocument13 pagesNavigation Between Different ViewsVaibhav SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Zvendor Link Check ReportDocument3 pagesZvendor Link Check ReportnstomarNo ratings yet
- ABAP WebDynpro - Exporting Internal Table Contents To An Excel FileDocument16 pagesABAP WebDynpro - Exporting Internal Table Contents To An Excel FileErcanNo ratings yet
- Step 1: Go To SE11 and Give Your Table Name and Open It. Here My Table Is ZEMPID - TABLEDocument10 pagesStep 1: Go To SE11 and Give Your Table Name and Open It. Here My Table Is ZEMPID - TABLEleela venkata phani sainadhNo ratings yet
- Create An Advanced Search View Using Wizard in Sap CRMDocument7 pagesCreate An Advanced Search View Using Wizard in Sap CRMswamy_yalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- What Is The Field Name For PO Header Text in ME23nDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Field Name For PO Header Text in ME23nrobnunesNo ratings yet
- SAP CRM MethodsDocument7 pagesSAP CRM Methodskenguva_tirupati100% (1)
- Adding Extra Tab Through BadiDocument11 pagesAdding Extra Tab Through BadiShafeequr Raheman AwatiNo ratings yet
- Web UI Enhancement of Transmitting Data From Main Component To The Component of Search Help in SAP CRM 7 0Document9 pagesWeb UI Enhancement of Transmitting Data From Main Component To The Component of Search Help in SAP CRM 7 0nossucramNo ratings yet
- Unveiling The Power of SAP ABAP Implicit EnhancementsDocument12 pagesUnveiling The Power of SAP ABAP Implicit EnhancementsAleax RaoNo ratings yet
- 4 Settings in BDT - Business Data ToolsetDocument5 pages4 Settings in BDT - Business Data ToolsetRaj PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Changing The Sap Logo in CRM UiDocument2 pagesChanging The Sap Logo in CRM Uiirexen2012No ratings yet
- S4HANA Utilities For CM Extensibility 2022Document94 pagesS4HANA Utilities For CM Extensibility 2022Mohammed EttahriouiNo ratings yet
- Customer Parameter Id CreationDocument3 pagesCustomer Parameter Id CreationRommel SorengNo ratings yet
- Adding Custom Fields To The FI Report FBL5N Using BTEsDocument7 pagesAdding Custom Fields To The FI Report FBL5N Using BTEsRahul ShindeNo ratings yet
- PO Check EnhancementDocument9 pagesPO Check Enhancement詹俊儒No ratings yet
- BAPI For PM ObjectsDocument2 pagesBAPI For PM ObjectsSreenivasa R ChNo ratings yet
- SAP CRM Web UI F4 Help Without Search CriteriaDocument4 pagesSAP CRM Web UI F4 Help Without Search Criteriaswamy_yalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- IPc ConfigurationDocument11 pagesIPc Configurationsapsd_n5No ratings yet
- Example ABAP Code For Creating Business PartnerDocument3 pagesExample ABAP Code For Creating Business PartnerSaurabh GargNo ratings yet
- Adobe Forms 1 How To Create A Adobe Form and Print The FormDocument24 pagesAdobe Forms 1 How To Create A Adobe Form and Print The FormBIJAYALAXMI PANIGRAHINo ratings yet
- Call Transaction 2. Session Method 3. Direct Input MethodDocument9 pagesCall Transaction 2. Session Method 3. Direct Input MethodChris BaileyNo ratings yet
- BADI ExampleDocument12 pagesBADI ExampleEmilSNo ratings yet
- Steps Create Badi Implementation PDFDocument3 pagesSteps Create Badi Implementation PDFAneesh ShamsudeenNo ratings yet
- Inside VOFMDocument36 pagesInside VOFMthuanderNo ratings yet
- Ale Idocs Basic ConceptsDocument7 pagesAle Idocs Basic ConceptsSwati JainNo ratings yet
- Adding New Field To Pricing Catalog in SapDocument5 pagesAdding New Field To Pricing Catalog in SapkarthikbjNo ratings yet
- Conversion of ABAP Data To XMLDocument15 pagesConversion of ABAP Data To XMLbasiler89No ratings yet
- ALE Between Two SAP SystemsDocument24 pagesALE Between Two SAP Systemsraghava nimmala100% (1)
- Badi For Cs01Document23 pagesBadi For Cs01Amit SharmaNo ratings yet
- New Field in Fbl1n Fbl2n Fbl3nDocument4 pagesNew Field in Fbl1n Fbl2n Fbl3nselva kumarNo ratings yet
- Business Transaction EventsDocument5 pagesBusiness Transaction EventsDebebookNo ratings yet
- mm01 BapiDocument24 pagesmm01 BapisapmaryNo ratings yet
- Steps For Inbound IdocDocument6 pagesSteps For Inbound Idocsurajit6349No ratings yet
- Custom Fiori Applications in SAP HANA: Design, Develop, and Deploy Fiori Applications for the EnterpriseFrom EverandCustom Fiori Applications in SAP HANA: Design, Develop, and Deploy Fiori Applications for the EnterpriseNo ratings yet
- User Exit Enhancement: and Explained in DetailDocument5 pagesUser Exit Enhancement: and Explained in Detailyugandhar19No ratings yet
- User Exit For Pricing ConditionDocument2 pagesUser Exit For Pricing ConditionSudarshan SundararajanNo ratings yet
- Userexit Userxits Allow Us To Add Our Own Functionality To SAP Standard ProgramDocument4 pagesUserexit Userxits Allow Us To Add Our Own Functionality To SAP Standard ProgramSreelu123No ratings yet
- Add Fields To Field Catalog - Example - SapDocument5 pagesAdd Fields To Field Catalog - Example - SapRavinutala Srikanth100% (3)
- Sap SD User ExitsDocument4 pagesSap SD User ExitsNarayana100% (3)
- Flashing Text in ExcelDocument8 pagesFlashing Text in ExcelRahul ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Algorithmic Trading CourseDocument3 pagesAlgorithmic Trading CourseRODRIGO TROCONISNo ratings yet
- SAP HR ABAP Infotype 2 Enhancement For Displaying Age Based On The AGEDocument11 pagesSAP HR ABAP Infotype 2 Enhancement For Displaying Age Based On The AGEChitturi PraveenNo ratings yet
- DBA DictionaryDocument156 pagesDBA DictionaryVikas GaurNo ratings yet
- Binding Source For DataGridView From Linq To SQL QueryDocument4 pagesBinding Source For DataGridView From Linq To SQL QueryPhuong LeNo ratings yet
- OAB TechnicalDocument2 pagesOAB Technicalvanitha_kundaramNo ratings yet
- PCDocument55 pagesPCEndika Larrea GonzalezNo ratings yet
- IDAProject Information For Website March 2013Document33 pagesIDAProject Information For Website March 2013jmouleatcityNo ratings yet
- Tablespace MGMTDocument5 pagesTablespace MGMTshaikali1980No ratings yet
- Wedge 623Document2 pagesWedge 623Teo DorNo ratings yet
- Creating A Calculated Field With Access 2007Document2 pagesCreating A Calculated Field With Access 2007Debaprasad ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Exam - Sample SolutionDocument6 pagesMid-Term Exam - Sample SolutionDerwin LayneNo ratings yet
- FLS BOISE MD070 Order Acknowledgement 1.1Document27 pagesFLS BOISE MD070 Order Acknowledgement 1.1Satish Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Demo BSPDocument4 pagesDemo BSPgo2kaattNo ratings yet
- Lab #6: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 2 (120 PTS)Document4 pagesLab #6: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 2 (120 PTS)Muhammad Imran AminNo ratings yet
- UG 24301381 - W - PRODUCT - D.PROD - CAT1 - WID Populated With 0s For Non Inventory ItemsDocument8 pagesUG 24301381 - W - PRODUCT - D.PROD - CAT1 - WID Populated With 0s For Non Inventory ItemsMohamed ZakiNo ratings yet
- Table ValueDocument7 pagesTable Valueankur1040No ratings yet
- Sap PM End User Manual Calibration ProcessDocument41 pagesSap PM End User Manual Calibration ProcessMike Tan100% (2)
- Report Abap AlvDocument10 pagesReport Abap AlvDavid RoqueNo ratings yet
- Jenny Chan 01062007 HandoutDocument48 pagesJenny Chan 01062007 Handoutchristy1rc09ec007No ratings yet
- How To Create Pivat TableDocument4 pagesHow To Create Pivat Tablesurender1978No ratings yet
- What We're Providing YouDocument3 pagesWhat We're Providing Yourakshit123No ratings yet
- Digital IODocument4 pagesDigital IOGolframNo ratings yet
- Quiz DB HelperDocument4 pagesQuiz DB Helperjohnny daveNo ratings yet
- Visual Basic Concept1Document2 pagesVisual Basic Concept1shalinda99No ratings yet
- Batch ReserveDocument166 pagesBatch ReserveSree Laxmi AdibhatlaNo ratings yet
- Testing and DebuggingDocument36 pagesTesting and DebuggingMuhammad YasirNo ratings yet
- MESH2D - Automatic 2D Mesh GenerationDocument5 pagesMESH2D - Automatic 2D Mesh GenerationIgor GjorgjievNo ratings yet