Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mash pH/Proton Deficit Calculator. See November MBAA Presentation Slides For Explanation
Mash pH/Proton Deficit Calculator. See November MBAA Presentation Slides For Explanation
Uploaded by
rtcpOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mash pH/Proton Deficit Calculator. See November MBAA Presentation Slides For Explanation
Mash pH/Proton Deficit Calculator. See November MBAA Presentation Slides For Explanation
Uploaded by
rtcpCopyright:
Available Formats
Mash pH/Proton Deficit Calculator.
See November MBAA prese
26.42007926
100
57.14285714
100
100
0
4.40924884
17.63699536
0
0
0
66.13873261
DI pH@47C
5.483
4.553
4.621
4.621
4.621
4.621
4.621
Alk End Point
gal
Water
L
Water Alk, mval
Water pH
Target pH @ 20 C
RA
Water, Ca++ mval
Water Mg++, mval
Lbs
Malt1
kg
Lbs
Malt2
kg
Lbs
Malt3
kg
Lbs
Malt4
kg
Lbs
Malt 5
kg
Lbs
Malt 6
kg
Lbs
Malt 7
kg
Strong Acid(-)/Base(+) Added, mEq
Phosphoric acid added , mmol
Bicarbonate Addded, mmol
Carbonate Added, mmol
pH Est at 47 C
4
100
2
8.3
5.440
1.14
2
2
0
2
8
0
0
0
30
0
0
0
0
5.305
DI pH (@ 20 C)
Malt 1 Weyermann Regular Pils
Malt 2 (600L Chocolate) model
Malt 3 (80L Caramel) model
Malt 4 model
Malt 5 model
Malt 6 model
Malt 7 Weyermann Floor Pils
22.0462442 lbs
4.793574637 qts/lb
total malt
kg
L/kg
5.623
4.699
4.766
4.077
4.480
4.766
5.855
40
10
r1
0.00416869
83.1763771
0.11477741
57.1428571
0.0%
5.0%
20.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
75.0%
r1
2074.22764
1st coef
-40.69
-76.43
-89.684
-90
-61
-37
-31.299
Generic Acid Charge calculato
Charge Calculator for Arbitrary Acid:
Enter negative number for strong acid pK's
Enter a large positive number for pK of non existant proton.
Example: Lactic acid: pK1 = 3.86; pK2 = pK3 = pK4 = 40
pH
pK1
pK2
pK3
pK4
The following data are taken from Kai Troesters paper " The effect of brewing water and grist composition on the pH of
amount of base required to move 1 kg to pH 5.7 i.e. he measured the proton surfeits of each of the tabulated malts WRT
gives the average slope between DI pH and 5.7 which is an approximation to the slope at DI pH and, therefore, an appro
models above with the 2nd and 3rd coefficients set to 0. Based on color data you can use 1st_Coef = -32.9
0.02*EBC_Color (r = 0.73) for the DI pH for colored, but not roast malts. As Troester's data does assumes linearity some
of pH drift over time nor did he use laboratory grade titrants. Nonetheless this data may be useful for obtaining approxi
DI pH
Munich II Weyermann
Munich I Weyermann
Munich Light Franco Belges
Vienna Weyermann
Cara Munich III Weyermann
Caramunich II Weyermann
Cara Minich I Weyermann
Cara Aroma Weyermann
Crystal 10 L Briess
Crystal 20L Briess
Crystal 40 L Briess
Crystal 60 L Briess
Crystal 90 L Briess
Crystal 120 L Briess
Crystal 150 L Briess
Roast Barley Briess
Black Patent Briess
Carafa III Weyerman
Carafa I Weyermann
Carafa I (sp) Weyermann
Biscuit
Sauermalz
Sauermalz Weyermann
5.54
5.44
5.62
5.65
4.92
4.71
5.1
4.48
5.38
5.22
5.02
4.66
4.77
4.75
4.48
4.68
4.62
4.81
4.71
4.73
5.08
3.43
3.44
Acid to 5.7
5.6
8.4
3
1.6
31.2
49
22.4
74.4
9.6
14.2
25.6
50.4
45
46
59.8
39.6
44.8
35.4
42
46.4
20.2
315.2
358.2
161.2903226
19
4.001367009
7.019907606
mber MBAA presentation slides for explanation
Q(pHt)
Water Alk
r2
f1
f2
f3
=
0.10199015
4.16869E-07 0.99584861 0.004151388 1.7306E-09 -0.00415139 Carbo
0.008317638 0.011782975 0.980065197 0.00815183 -0.99636885
1.912897046
1.14777E-05 0.897039005 0.102959813 1.1817E-06 -0.10296218
0.893406676
r2
r3
f1
f2
0.016821178 9.99669E-08 0.000473907 0.98299102
2nd coef
14.821
-0.404
31.837
0
0
0
3.869
f3
0.016535067
3d coef
-10.008
-3.837
-10.056
0
0
0
-1.986
-591.396852
eneric Acid Charge calculator
r's
7
6.38 4.168693835
10.38 0.000416869
30
1E-23
30
1E-23
f's
Q
0.19340745 mEq/mmol
0.806256446 -0.8069287
0.000336104
3.36104E-27
3.36104E-50
rist composition on the pH of the mash" www.braukaiser.com, Table 4. He measured DI mash pH and the
ch of the tabulated malts WRT pH 5.7. Dividing these numbers by the difference between DI pH and 5.7
DI pH and, therefore, an approximation to the first coefficient. These numbers can be used in the malt
1st_Coef = -32.9 - 0.05816*EBC_color for the slope (r = -0.86) and, from the paper, pHDI = 5.82 does assumes linearity some error has to be expected. Also his titration method did not include the effects
e useful for obtaining approximate estimates of mash pH.
1st Coef (aprox) color, EBC
-35
22
-32.30769231
15
-37.5
17.35
-32
7.5
-40
150
-49.49494949
120
-37.33333333
90
-60.98360656
400
-30
25.3
-29.58333333
51.8
-37.64705882
104.8
-48.46153846
157.8
-48.38709677
237.3
-48.42105263
316.8
-49.01639344
396.3
-38.82352941
793.8
-41.48148148
1323.8
-39.7752809
1400
-42.42424242
900
-47.83505155
900
-32.58064516
-138.8546256
5
-158.4955752
5
-40.90744219
Carbo Charge/L Acid Req/L
PROTON DEFICITS
Proton source or sink
-1.905951034
-0.196956043
1.810985141
181.10 The Water
-0.571428571
-0.285714286
-57.14 Calcium reaction with phosphate
-28.57 Magnesium reaction with phosphate
HLac mL
f4
0.00
1.65296E-09
mEq/kg-pH
Acid Req/kg
-47.11360512
7.996574491
-82.15347294 -58.42648505
-60.4675745 -49.07567946
-90 -122.6498894
-61 -58.55124145
-37 -24.94563744
-35.53820775
13.80247219
Wt'd Sum
pH/mEq
-1714.193774 -0.000583365
Wtd Avg
-42.85484436 -0.023334585
INSTRUCTIONS:
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
-116.85
-392.61
0.00
0.00
0.00
414.07
Strong Acid/Base
Phosphoric acid
Bicarbonate Added
Carbonate Added
Malt 1
Malt 2
Malt 3
Malt 4
Malt 5
Malt 6
Malt 7
0.00 Total: all sources and sinks
INSTRUCTIONS:
1.Enter water parameters in liters, mVal (mVal = ppm_as_CACO3/50) in Col C. English values and ppm as CaCO3 are calcula
A. Alk End Point is the value to which you or the lab titrated when measuring water alkalinity. If unknown, use 4.5.
2. Enter mVal calcium ((mg/L)/50) and magnesium ((mg/L)/12.15) ions in Col C. ppm as CaCO3 calculated in Col. A.
3. Enter amounts of each malt type in kg in Col C. Pounds are calculated in Col. A.
4. Enter total mEq of strong acid (HCl, H2SO4, HLac) as a negative number and of strong base )NaOH, KOH,
Ca(OH2) as a
number.
5. Enter total mmol phosphoric acid added as a positive number
6. Enter total mmol of bicarbonate added as a positive number (e.g. you added NaHCO3)
7. Enter total mmol of cabonate added as a positive number (e.g. you added Na2CO3)
8. Enter DI water mash pH (Col. C) and three malt coefficients (Col D, E, F) for each malt. If you do not have malt data you
pH and 1st coeff data taken from Troester's paper (Rows 53 - 76)
9. Enter a trial pH in C5. Read Total Proton Deficit in M33.
10. Tell Solver (Tools) to zero cell M33 by adjusting cell C5 or do this manually using a bisection scheme (see MBAA slides)
guessing. Value in C5 wjem M33 = 0 is predicted pH.
11. To set to a desired pH enter it in C5 and adjust malt quantities, amounts of added acids or base, alkalinity of water unt
177.7777778 176.133862 1.81098514
-2.90251E-07 per kg
and ppm as CaCO3 are calculated in Col
. If unknown, use 4.5.
3 calculated in Col. A.
e )NaOH, KOH,
Ca(OH2) as a positive
u do not have malt data you can use DI
on scheme (see MBAA slides) or just
r base, alkalinity of water until M33 = 0.
20200
You might also like
- Hydrolysis of Salt and PH of Buffer Solutions.Document16 pagesHydrolysis of Salt and PH of Buffer Solutions.amiraaikharah100% (1)
- Determination of Ka of Weak Acids Lab ReportDocument3 pagesDetermination of Ka of Weak Acids Lab ReportNick Schweitzer78% (9)
- Lesson Plan Biomolecules-Nucleic AcidsDocument10 pagesLesson Plan Biomolecules-Nucleic AcidsLeo Jude LopezNo ratings yet
- EZ Water - Calculator 3.0.2Document4 pagesEZ Water - Calculator 3.0.2MariusCapraNo ratings yet
- Kaiser Water CalculatorDocument32 pagesKaiser Water CalculatorSahil PalNo ratings yet
- PLA PresentationDocument43 pagesPLA PresentationPooja DadlaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project ON NUTRIENTS IN BISCUITDocument28 pagesChemistry Project ON NUTRIENTS IN BISCUITSrishti Goel86% (22)
- A02 355Document68 pagesA02 355jaimeNo ratings yet
- ch18 PDFDocument111 pagesch18 PDFPatrick Malcolm SantosNo ratings yet
- Neutralization Reactions Worksheet: Hi + Naoh H O + NaiDocument2 pagesNeutralization Reactions Worksheet: Hi + Naoh H O + NaiahaanNo ratings yet
- TestsDocument2 pagesTestsabekhti2008No ratings yet
- Ka Lab RubenDocument3 pagesKa Lab Rubenrubenq270% (10)
- Carboxylic Acids Reactions: Presented By: Mizgin Q.AbdullahDocument10 pagesCarboxylic Acids Reactions: Presented By: Mizgin Q.AbdullahSafwan BakrmanyNo ratings yet
- Preparation of PH Buffer SolutionsDocument5 pagesPreparation of PH Buffer SolutionsAndrew Sumaya AldeNo ratings yet
- Kps Equilibrium ConstantsDocument12 pagesKps Equilibrium ConstantsDanny Cabrera100% (1)
- Ernst's Cichlid Buffer CalculatorDocument357 pagesErnst's Cichlid Buffer CalculatorErnst SmitNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Indicators (PH Range and Preparation)Document3 pagesAcid Base Indicators (PH Range and Preparation)Juan Camilo OrozcoNo ratings yet
- 8A Salts - AnswerDocument14 pages8A Salts - AnswerFrankieNgNo ratings yet
- Identifying of Unknown Monoprotic AcidDocument21 pagesIdentifying of Unknown Monoprotic AcidjuaxxoNo ratings yet
- EuSalt AS007-2005 Potassium - Sodium Tetraphenylborate Volumetric MethodDocument5 pagesEuSalt AS007-2005 Potassium - Sodium Tetraphenylborate Volumetric MethodNguyễn Khắc HảiNo ratings yet
- A Single-Solution Method For The Determination of Soluble Phosphate in Sea WaterDocument6 pagesA Single-Solution Method For The Determination of Soluble Phosphate in Sea WaterA'yunil HisbiyahNo ratings yet
- Buffer TablesDocument5 pagesBuffer TablesMahesh AithalNo ratings yet
- BioQuant2 (Schreibgeschützt)Document10 pagesBioQuant2 (Schreibgeschützt)Laorencia PraptiwiNo ratings yet
- PAN Kjeldahl BroschureDocument4 pagesPAN Kjeldahl BroschureSadia KhanNo ratings yet
- 360exp10-02 EsterificationDocument14 pages360exp10-02 EsterificationlewisrahimiNo ratings yet
- Buffer SolutionDocument8 pagesBuffer SolutionAbubakar UmarNo ratings yet
- Precipitation CaCo3Document6 pagesPrecipitation CaCo3marsulexNo ratings yet
- Acesulfame K CAS 55589-62-3Document2 pagesAcesulfame K CAS 55589-62-3Eliana SusiloNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel From Waste or Unrefined Oils Using Calcium Oxide-Based CatalystsDocument32 pagesBiodiesel From Waste or Unrefined Oils Using Calcium Oxide-Based Catalystsdoulat2000No ratings yet
- Table of Solubility Product ConstantDocument2 pagesTable of Solubility Product ConstantIqbal Wardani100% (1)
- CH421 D1 SlidesDocument20 pagesCH421 D1 SlideslikeleliletabaNo ratings yet
- Test For Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives - Online ClassDocument3 pagesTest For Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives - Online Classjoseph cyron solidumNo ratings yet
- ES252 Lab Manual (Spring 2022)Document40 pagesES252 Lab Manual (Spring 2022)Sumit kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of Potassium Acid Phthalate KHPDocument17 pagesQuantitative Determination of Potassium Acid Phthalate KHPMichelle Cruz AbrilNo ratings yet
- Preparation of PH Buffer SolutionsDocument5 pagesPreparation of PH Buffer SolutionscscsscNo ratings yet
- Kaiser Water CalculatorDocument34 pagesKaiser Water CalculatorPot StillerNo ratings yet
- Salp FaoDocument2 pagesSalp FaoRuthNo ratings yet
- Exp.7 Alkalinity TestDocument12 pagesExp.7 Alkalinity Testhero100% (1)
- CSTR PICDocument2 pagesCSTR PICThornNo ratings yet
- Lampiran A Data Percobaan: L.A.1 Hasil Pembuatan Larutan Kmno 0,75 NDocument1 pageLampiran A Data Percobaan: L.A.1 Hasil Pembuatan Larutan Kmno 0,75 NElfrida Margaretha SitumeangNo ratings yet
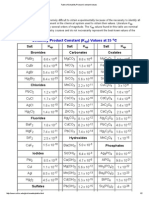
- 03 - Ingredient Analysis Table 2010 EditionDocument2 pages03 - Ingredient Analysis Table 2010 EditionHussein TorabiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of A Synthesis Process For The Production of Calcium Nitrate Liquid FertilizerDocument6 pagesEvaluation of A Synthesis Process For The Production of Calcium Nitrate Liquid FertilizerLeandro QuevedoNo ratings yet
- PH Meter It's Applications: Practical Advance Pharmaceutical AnalysisDocument19 pagesPH Meter It's Applications: Practical Advance Pharmaceutical AnalysisarjunkumbharchemNo ratings yet
- Sulfat Electroplacare PDFDocument2 pagesSulfat Electroplacare PDFCorina StanculescuNo ratings yet
- Pbs 1 DatDocument2 pagesPbs 1 DatJaya LekhwaniNo ratings yet
- Donohoe Lab Reagent ListDocument9 pagesDonohoe Lab Reagent Listmcclain_matthewNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Title: Properties of Period 3 Oxides Aim:: Utar FHSC1134 Inorganic Chemistry Trimester 2/3Document28 pagesExperiment 1 Title: Properties of Period 3 Oxides Aim:: Utar FHSC1134 Inorganic Chemistry Trimester 2/3ersuenboonNo ratings yet
- Appendix 2 PDFDocument19 pagesAppendix 2 PDFشعمروم المكمعرNo ratings yet
- Pbs 1 DatDocument2 pagesPbs 1 DatAlineNo ratings yet
- Iodine Clock ReactionDocument6 pagesIodine Clock Reactionilias19730% (1)
- Catalogue EnglishDocument59 pagesCatalogue Englishbigweb100% (2)
- chm474 (Exp6)Document16 pageschm474 (Exp6)farah100% (1)
- Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesCarboxylic AcidmushindiboazNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy II: Physicochemical Principles of Drugs in Relation To Dosage Form DesignDocument27 pagesPhysical Pharmacy II: Physicochemical Principles of Drugs in Relation To Dosage Form DesignYulia PrimasariNo ratings yet
- Protein Buffers: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesProtein Buffers: Page 1 of 2shimo1992No ratings yet
- The Characteristics of Calcium Arsenate Compounds Relevant To The Disposal of Arsenic From Industrial ProcessesDocument11 pagesThe Characteristics of Calcium Arsenate Compounds Relevant To The Disposal of Arsenic From Industrial ProcessesMaysam MohamNo ratings yet
- Titration of Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument4 pagesTitration of Amino Acids and PeptidesANGELO CUYSONNo ratings yet
- Kris Arvid BerglundDocument40 pagesKris Arvid BerglundckleinnikeNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ka of Weak AcidsDocument4 pagesDetermination of Ka of Weak AcidsJohanson Bombaes100% (6)
- Brewing Water Chemistry Calculator - Brewer's FriendDocument4 pagesBrewing Water Chemistry Calculator - Brewer's FriendCurro Espadafor Fernandez AmigoNo ratings yet
- Titrametric Analysis Lab ReportDocument11 pagesTitrametric Analysis Lab Reportapi-546161612No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Application of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchFrom EverandApplication of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchRajmund MichalskiNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- Uppp2 Sem 3 2017Document8 pagesUppp2 Sem 3 2017jeff avecenixNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chemical Equations WorksheetDocument2 pagesChemistry - Chemical Equations WorksheetKareesh ShamilsanNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds: Class 10 Science (Chemistry)Document33 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds: Class 10 Science (Chemistry)Sarfraz AnsariNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument16 pagesAcid BaseSazzad Tanim100% (1)
- CET Chemical Nomenclature Set BDocument8 pagesCET Chemical Nomenclature Set BCris BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Cannizzaro ReactionDocument16 pagesCannizzaro ReactionEm NaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: CarbanionDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry: CarbanionDiana DedoNo ratings yet
- Acid ValueDocument6 pagesAcid ValueAshok MauryaNo ratings yet
- Reach SVHC List Excel TableDocument7 pagesReach SVHC List Excel TableirwanchemNo ratings yet
- Dequest 2040, 2050 and 2060 Product SeriesDocument9 pagesDequest 2040, 2050 and 2060 Product SeriesLê CôngNo ratings yet
- Laporan Resmi ProteinDocument74 pagesLaporan Resmi ProteinAhlan RiwahyuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Acids, Bases, and Salts PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 11 - Acids, Bases, and Salts PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- P Block 17-18Document23 pagesP Block 17-18Aditya BansalNo ratings yet
- ANO4A-oxidation States-Nomenclatuur-2018 PDFDocument30 pagesANO4A-oxidation States-Nomenclatuur-2018 PDFJelte de WitNo ratings yet
- Demonstration On Endothermic or Exothermic Reaction (Latest) PDFDocument5 pagesDemonstration On Endothermic or Exothermic Reaction (Latest) PDFLester PioquintoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: 2011 Trial ExaminationDocument16 pagesChemistry: 2011 Trial ExaminationENo ratings yet
- PFAS ListDocument6 pagesPFAS ListĐoànKimThoaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Lecture PDFDocument156 pagesChapter 12 Lecture PDFjoseph changNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry Study Material 2022 2023 English Medium PDF DownloadDocument15 pages12th Chemistry Study Material 2022 2023 English Medium PDF Downloaddhinesh athiyurNo ratings yet
- Nitroglycerine, C3H5N3O9, Is An Explosive Which, On Detonation, Decomposes RapidlyDocument14 pagesNitroglycerine, C3H5N3O9, Is An Explosive Which, On Detonation, Decomposes Rapidlyapi-25909541No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReviewerDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReviewerRanie Magpoc67% (3)
- Aliphatic Cyclic Carbonates and Spiroorthocarbonates As MonomersDocument84 pagesAliphatic Cyclic Carbonates and Spiroorthocarbonates As MonomersMá Xì TrumNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch09 Biomolecules PDFDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch09 Biomolecules PDFprashanth100% (1)
- Relative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocument2 pagesRelative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud100% (4)
- Chem Lec. Module 5Document8 pagesChem Lec. Module 5Aivan NovillaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry-Mole ConceptDocument8 pagesIGCSE Chemistry-Mole ConceptmarkusNo ratings yet