Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of English Tenses
Table of English Tenses
Uploaded by
Gonzalo AstorgaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of English Tenses
Table of English Tenses
Uploaded by
Gonzalo AstorgaCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of English Tenses
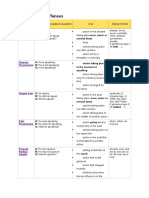
TENSE AFFIRMATIVE, NEGATIVE, QUESTION A: He speaks. N: He does not speak. Q: Does he speak? USE
action in the present taking place once,
SIGNAL WORDS always, every , never, normally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually - if sentences type 1 (If I talk, )
Simple Present
never or several times facts actions taking place one after another action set by a timetable or schedule
action taking place in the moment of
Present Progressive
A: He is speaking. N: He is not speaking. Q: Is he speaking?
speaking action taking place only for a limited period of time action arranged for the future
action in the past taking place once, never
at the moment, just, just now, Listen!, Look!, now, right now
Simple Past
A: He spoke. N: He did not speak. Q: Did he speak?
or several times actions taking place one after another action taking place in the middle of another action
action going on at a certain time in the past actions taking place at the same time action in the past that is interrupted by
yesterday, 2 minutes ago, in 1990, the other day, last Friday - if sentence type 2 (If I talked, )
Past Progressive
A: He was speaking. N: He was not speaking. Q: Was he speaking?
when, while, as long as
another action
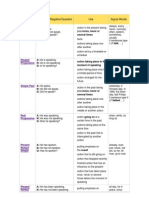
Present Perfect Simple
A: He has spoken. N: He has not spoken. Q: Has he spoken?
putting emphasis on the result action that is still going on action that stopped recently finished action that has an influence on the present action that has taken place once, never or several times before the moment of speaking
already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till now, up to now
putting emphasis on the course or duration
Present Perfect Progressive
A: He has been speaking. N: He has not been speaking. Q: Has he been speaking?
(not the result) action that recently stopped or is still going on finished action that influenced the present
action taking place before a certain time in
all day, for 4 years, since 1993, how long?, the whole week
Past Perfect Simple
A: He had spoken. N: He had not spoken. Q: Had he spoken?
the past sometimes interchangeable with past perfect progressive putting emphasis only on the fact (not the duration)
action taking place before a certain time in
already, just, never, not yet, once, until that day - if sentence type 3 (If I had talked, )
Past Perfect Progressive
A: He had been speaking. N: He had not been speaking. Q: Had he been speaking?
the past sometimes interchangeable with past perfect simple putting emphasis on the duration or course of an action
for, since, the whole day, all day
action in the future that cannot be
Future I Simple
A: He will speak. N: He will not speak. Q: Will he speak?
influenced
spontaneous decision assumption with regard to the future
in a year, next , tomorrow - if sentence type 1 (If you ask her, she will help you.) assumption: I think, probably, perhaps in one year, next week, tomorrow
Future I Simple (going to)
A: He is going to speak. N: He is not going to speak. Q: Is he going to speak? A: He will be speaking. N: He will not be speaking. Q: Will he be speaking?
decision made for the future conclusion with regard to the future action that is going on at a certain time in
the future
action that is sure to happen in the near
Future I Progressive
future
in one year, next week, tomorrow
Future II Simple
A: He will have spoken. N: He will not have spoken. Q: Will he have spoken? A: He will have been speaking. N: He will not have been speaking. Q: Will he have been speaking? A: He would speak. N: He would not speak. Q: Would he speak? A: He would be speaking. N: He would not be speaking. Q: Would he be speaking? A: He would have spoken. N: He would not have spoken. Q: Would he have spoken? A: He would have been speaking. N: He would not have been speaking. Q: Would he have been speaking?
action that will be finished at a certain time
in the future
action taking place before a certain time in
by Monday, in a week
Future II Progressive
the future
putting emphasis on the course of an action action that might take place action that might take place putting emphasis on the course / duration
for , the last couple of hours, all day long - if sentences type 2 (If I were you, I would go home.)
Conditional I Simple
Conditional I Progressive
of the action
action that might have taken place in the
Conditional II Simple
past
action that might have taken place in the
if sentences type 3 (If I had seen that, I would have helped.)
Conditional II Progressive
past puts emphasis on the course / duration of the action
You might also like
- Think - 4 Teacher's Book PDFDocument128 pagesThink - 4 Teacher's Book PDFPri Canchi68% (25)
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesAgung ArdyantoNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument3 pagesTenseKiki MulqiahNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Document3 pagesSimple Present: I Talk, )Krupesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument4 pagesTable of English TensesKashif WakeelNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDenis SăndicăNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesMariana Crăciun100% (1)
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAndrea Paredes GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAbdulaziz2012No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentSorin Mihai VassNo ratings yet
- Table TensesDocument4 pagesTable TensesmariminniNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentXorianopoulou SofiaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentPavlina HaralampievaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsTaris TallasaNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesEnglish Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAndreaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesCristina-Raluca RuşeţNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVeronica BurdujaNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument3 pagesTenseMădălina RădulescuNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentHazel-mae LabradaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAdaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJavier J SalazarNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument2 pagesEnglish TensesGustavo SteffenNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentLyana LorenzaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentRuxanda RusuNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentFitrie RnaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsAdriana MuresanNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMariana PasatNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Presentdddiana21No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleRobertaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsanon1000No ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument6 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRatmi 'Bundanya Rena'No ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesZandaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument4 pagesTable of English Tensesdieba105No ratings yet
- Verb Tense Overview With ExamplesDocument5 pagesVerb Tense Overview With ExamplesSaulo ZunigaNo ratings yet
- Summary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument1 pageSummary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsCTMundialNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsthirtysecondsmarsNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordshpeter195798No ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument5 pagesTable of English TensesMaria CristianNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsyingying1102No ratings yet
- Simple Present: TalkedDocument4 pagesSimple Present: TalkedDangVanTamNo ratings yet
- Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsMyriam GGoNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesShoba DevarajanNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument5 pagesTensesGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chart of English TensesDocument2 pagesChart of English TensesNorafiqah Rifhan RamlanNo ratings yet
- Timpuri LeDocument3 pagesTimpuri LemadybyaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument18 pagesTensesNora Mestiri100% (1)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Presentgulzar72No ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: I Talk, )romina5_13No ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDebyPuspitaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument5 pagesTable of English TenseskaterynavelNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument6 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentTigercubx9No ratings yet
- English Tenses SummaryDocument2 pagesEnglish Tenses SummaryRedi BylekNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument1 pageTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVlasta LoncaricNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/ Use Signal Words: Ifi TalkDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/ Use Signal Words: Ifi Talkshel087No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentLecherooMendozaNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of Speech TableDocument6 pages8 Parts of Speech TableAnonymous UadvwxNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Use Example: Present Simple ... Present Continuous ..Document4 pagesVerb Tense Use Example: Present Simple ... Present Continuous ..charanpalsinghNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/ USE Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/ USE Signal WordsradivojerNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice ExerciseDocument6 pagesPassive Voice ExerciseIlyana HaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Complete The Questions With The Verbs in BracketsDocument7 pages3 Complete The Questions With The Verbs in BracketsElizbeth Castro PerezNo ratings yet
- English Language Tenses: Venetia Kimioni, Esl TeacherDocument14 pagesEnglish Language Tenses: Venetia Kimioni, Esl TeacherMon RojasNo ratings yet
- English 2grammar TensesDocument153 pagesEnglish 2grammar TensesNadeem ArainNo ratings yet
- 12 Contoh TensesDocument14 pages12 Contoh TensesLuhungNo ratings yet
- 9° Reinforcement ActivitiesDocument3 pages9° Reinforcement ActivitiesedasabaqNo ratings yet
- Unit 3, American Headway 3: Simple Past (過去簡單式)Document2 pagesUnit 3, American Headway 3: Simple Past (過去簡單式)陳亭瑋No ratings yet
- Conditionals - All TypesDocument4 pagesConditionals - All TypesBernardo ZacaronNo ratings yet
- G9slm2q1final For StudentDocument20 pagesG9slm2q1final For StudentVILLA 2 ANACITA LOCIONNo ratings yet
- Quiz Ingles 2 CorteDocument7 pagesQuiz Ingles 2 CorteAndrêaGeraldineGomezNo ratings yet
- Narrative Tenses PracticeDocument3 pagesNarrative Tenses PracticeAlina SemeniukNo ratings yet
- Revision:: Past Tense ContrastDocument3 pagesRevision:: Past Tense ContrastRobNo ratings yet
- Focus4 2E Grammar Quiz Unit2.2 GroupA 1kolDocument2 pagesFocus4 2E Grammar Quiz Unit2.2 GroupA 1kol86t4dc6sdzNo ratings yet
- Mixed Tenses ExerciseDocument7 pagesMixed Tenses ExerciseMANDYHONo ratings yet
- Past Progressive TenseDocument7 pagesPast Progressive TenseOK ImmunyNo ratings yet
- Письмо 9 кл 2 семDocument2 pagesПисьмо 9 кл 2 семКаргин ДанилNo ratings yet
- Narrative Tenses - Docx - Google DokumentiDocument2 pagesNarrative Tenses - Docx - Google DokumentiMatea GašparićNo ratings yet
- S2 Grammar 10 - Direct Speech and Indirect Speech PDFDocument26 pagesS2 Grammar 10 - Direct Speech and Indirect Speech PDFguanqi tanNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous and Past SimpleDocument12 pagesPast Continuous and Past SimpleainhoamsNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument143 pagesEnglishtameratNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Road 2Document108 pagesBeyond The Road 2Leo Viloria100% (1)
- Passive Voice: Siti Nur Qomariah, S.Kep., Ns.,M.Kep Psik Fik Univ. GresikDocument14 pagesPassive Voice: Siti Nur Qomariah, S.Kep., Ns.,M.Kep Psik Fik Univ. GresikFika SuhartinaNo ratings yet
- Present and Past Participles As Noun Modifiers: Ing, ED, D, T, - N - ENDocument9 pagesPresent and Past Participles As Noun Modifiers: Ing, ED, D, T, - N - ENRafael Chipana ChaconNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Tenses Basic Tenses Sub-Tenses 1 2 3 4 Present Past Future How Should We Understand The Application of Tenses?Document9 pagesGrammar: Tenses Basic Tenses Sub-Tenses 1 2 3 4 Present Past Future How Should We Understand The Application of Tenses?Naila ChNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesReported Speech Lesson PlanyoubfattoulNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice GrammarDocument12 pagesPassive Voice GrammarKornel SikiNo ratings yet
- New PP StructureDocument31 pagesNew PP Structuregalih febriandryNo ratings yet
- Tabel 16 Tenses Bahasa Inggris: 1. Simple Present TenseDocument8 pagesTabel 16 Tenses Bahasa Inggris: 1. Simple Present TenseRiska FebriyaniNo ratings yet
- Subject: English (Grammar) Topic: Tenses For Secondary SchoolDocument27 pagesSubject: English (Grammar) Topic: Tenses For Secondary SchoolGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet