Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peds SG
Peds SG
Uploaded by
mzjackie9Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SAQs AnatomyDocument238 pagesSAQs AnatomyDrHassan Ahmed Shaikh80% (5)
- Slides For Pediatric Osce ExamDocument389 pagesSlides For Pediatric Osce Examadan yare100% (1)
- Choanal Atresia2Document40 pagesChoanal Atresia2pramod555No ratings yet
- Tuberculous Spondylitis (TB Spine/pott's Disease)Document28 pagesTuberculous Spondylitis (TB Spine/pott's Disease)Divo Septian Zarwin100% (1)
- Potts FractureDocument18 pagesPotts FractureOves PatniNo ratings yet
- Extra SAQsDocument24 pagesExtra SAQsIshan DevNo ratings yet
- RQ of Nbde Part 2 Dec 2017Document7 pagesRQ of Nbde Part 2 Dec 2017ParneetNo ratings yet
- Interesting Cases PediatricsDocument253 pagesInteresting Cases PediatricsomkamaleshNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument25 pagesCerebral PalsyDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Paeds Osce Batch Compiled and Solved-1Document33 pagesPaeds Osce Batch Compiled and Solved-1bismahNo ratings yet
- PediaDocument43 pagesPediaRahaf Bin ManieNo ratings yet
- Neuro SGDocument29 pagesNeuro SGgew123No ratings yet
- 18 Tonsil, Adenoid Notes Cumming Abd Key Topics (New Moe)Document7 pages18 Tonsil, Adenoid Notes Cumming Abd Key Topics (New Moe)osamaeNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Maria Victoria M. Villarica MD OLFU College of Medicine Department of PediatricsDocument81 pagesThe Digestive System: Maria Victoria M. Villarica MD OLFU College of Medicine Department of PediatricsSven OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- ORE Part 1 August 2017Document20 pagesORE Part 1 August 2017sajna1980No ratings yet
- Birthinjuries Dr.M.maniDocument65 pagesBirthinjuries Dr.M.manimaniNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in Ingestion: Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate 1. Cleft Lip/cleft PalateDocument15 pagesDisturbances in Ingestion: Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate 1. Cleft Lip/cleft PalatehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Diseases With Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument52 pagesClinical Diseases With Chromosomal AbnormalitiesAzifah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve PalsyDocument3 pagesFacial Nerve PalsyGayle VillarizaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric - Hearing - Loss Lau 3-17-10Document45 pagesPediatric - Hearing - Loss Lau 3-17-10Arief FakhrizalNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy (L)Document30 pagesCerebral Palsy (L)Touseef Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Choanal Atresia2Document40 pagesChoanal Atresia2Mavina ReeNaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Aganglionic Megacolon (Hirschsprung Disease) : Kristin N. Fiorino and Chris A. LiacourasDocument6 pagesCongenital Aganglionic Megacolon (Hirschsprung Disease) : Kristin N. Fiorino and Chris A. LiacourasSyakilla AuliaNo ratings yet
- File BookDocument13 pagesFile BookusamaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBz6SCL6SA VJUDh46tP6NUDhw3P47 NPjiCaRlywgh9trN 5PhQeKcHqMl2xUsHtUBcc7n4mL1On5SlTP2X94BYDVb HoGkGegg5erftVOvtVci7Q4s0omLCXYn6dldjBQhk2bZ6Jpfl6cDocument24 pagesACFrOgBz6SCL6SA VJUDh46tP6NUDhw3P47 NPjiCaRlywgh9trN 5PhQeKcHqMl2xUsHtUBcc7n4mL1On5SlTP2X94BYDVb HoGkGegg5erftVOvtVci7Q4s0omLCXYn6dldjBQhk2bZ6Jpfl6cMalavika A GNo ratings yet
- Septic ArthritisDocument21 pagesSeptic ArthritisDawex IsraelNo ratings yet
- MRCPCH Guide New QuestionsDocument11 pagesMRCPCH Guide New QuestionsRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- Toacs 6Document159 pagesToacs 6Mobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (2)
- SHCN 1Document14 pagesSHCN 1Suma TettaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemDocument116 pagesCongenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemVii syilsaNo ratings yet
- Deletion Syndromes: By: Rania ZahoDocument55 pagesDeletion Syndromes: By: Rania ZahoRania ZahoNo ratings yet
- 0 Yazan Mini-OSCE PedsDocument60 pages0 Yazan Mini-OSCE Pedsmoyasserayoub78No ratings yet
- Pedia SummaryDocument10 pagesPedia SummaryBea GozaNo ratings yet
- Birth InjuriesDocument2 pagesBirth InjuriesMohd FadhliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Spot Diagnosis: Abdulrahman BashireDocument20 pagesPediatric Spot Diagnosis: Abdulrahman Bashireعبدالرحمن بشير100% (1)
- Common Health Problems InfancyDocument147 pagesCommon Health Problems Infancymark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- CNS 2Document9 pagesCNS 2husainozelNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument9 pagesCerebral PalsyAngy100% (2)
- Cerebral Palsy: Reported By: Felvee M. Basibas, PTRP MDDocument67 pagesCerebral Palsy: Reported By: Felvee M. Basibas, PTRP MDBobby ReynerNo ratings yet
- Episode 436 Eye findingsDocument16 pagesEpisode 436 Eye findingsmohora1030No ratings yet
- Pediatric OrthopaedicDocument66 pagesPediatric OrthopaedicDhito RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Syng Nathi ADocument29 pagesSyng Nathi AMuhammad Azhar ImranNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders, Skeletal Dysplasias, and Malformations: Appley's Reading Achmad Fachroni, DRDocument38 pagesGenetic Disorders, Skeletal Dysplasias, and Malformations: Appley's Reading Achmad Fachroni, DRAchmad FachroniNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Study GuideDocument22 pagesPediatrics Study GuideElizabeth McKee100% (1)
- Pediatric Eye DiseasesDocument5 pagesPediatric Eye DiseasesfrnksusNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Kelainan Kongenital Dan TumorDocument54 pagesInfeksi Kelainan Kongenital Dan Tumorniska darliantiNo ratings yet
- CEREBRAL+PALSY-+final NewDocument56 pagesCEREBRAL+PALSY-+final NewMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Neurologic Disorders: Ma. Tosca Cybil A. Torres, RN, MANDocument97 pagesPediatric Neurologic Disorders: Ma. Tosca Cybil A. Torres, RN, MANMa Tosca Cybil TorresNo ratings yet
- OrthodonticsDocument5 pagesOrthodonticsAlbisladys Castellanos PujolsNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic DisordersDocument15 pagesOrthopedic Disordershasanatiya41No ratings yet
- T Collins SyndromeDocument21 pagesT Collins SyndromeMoe KebabNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Clerkship NotesDocument4 pagesPediatric Clerkship Notesxx_caligurl_93xxNo ratings yet
- El - MagnificoDocument137 pagesEl - MagnificoAbhi Thakkar100% (1)
- Mandibulofacial Dysostosis, Also Known As Treacher CollinsDocument19 pagesMandibulofacial Dysostosis, Also Known As Treacher CollinsMoe KebabNo ratings yet
- 醫科Document85 pages醫科Jason LinNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument17 pagesCerebral Palsymohammed almaaziNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Orthopaedics: Dr. Andreas Siagian SpotDocument66 pagesPediatric Orthopaedics: Dr. Andreas Siagian SpotFirdausi RiskiviawinandaNo ratings yet
- Mongolian SpotsDocument9 pagesMongolian SpotsiekafzNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube DefectDocument8 pagesNeural Tube DefectReema Akberali nooraniNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics RemarksDocument62 pagesPediatrics RemarksGÖKSU SAYGILINo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- Semiology Lecture 4. Facies, Neck, ThyroidDocument59 pagesSemiology Lecture 4. Facies, Neck, ThyroidmlinaballerinaNo ratings yet
- Newborn DDXDocument1 pageNewborn DDXmzjackie9No ratings yet
- Platelet Aggregation, If A Patient With Atherosclerotic Coronary Arteries Who Was Taking AspirinDocument1 pagePlatelet Aggregation, If A Patient With Atherosclerotic Coronary Arteries Who Was Taking Aspirinmzjackie9No ratings yet
- Obesity SurgeriesDocument2 pagesObesity Surgeriesmzjackie9No ratings yet
- Comparing Food Labels: Food Label A Food Label BDocument1 pageComparing Food Labels: Food Label A Food Label Bmzjackie9No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemCHRISTIANNE DENISE EBREONo ratings yet
- Dr. Bhatia Medical Coaching Institute Hyderabad: Post Class Test - AnatomyDocument9 pagesDr. Bhatia Medical Coaching Institute Hyderabad: Post Class Test - AnatomyPNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document29 pagesWeek 1chito refrea0% (1)
- 12.musculoskeletal System 4 Blocks Eduwaves360Document729 pages12.musculoskeletal System 4 Blocks Eduwaves360ÇağlaNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy in Sport: Seth O'Neill, Simon Barry, Paul WatsonDocument8 pagesPhysical Therapy in Sport: Seth O'Neill, Simon Barry, Paul WatsonmorbreirNo ratings yet
- Bone and Joint Infection: Dr. Zainab AbdulwahabDocument89 pagesBone and Joint Infection: Dr. Zainab Abdulwahabzen.maree6No ratings yet
- The Biomechanics of Stretching: Duane KnudsonDocument10 pagesThe Biomechanics of Stretching: Duane KnudsonSanjanaNo ratings yet
- Mobilization With MovementDocument8 pagesMobilization With Movementapi-661333402No ratings yet
- Ergonomics: A Work Place Realities in Pakistan: Topics To Be DiscussedDocument13 pagesErgonomics: A Work Place Realities in Pakistan: Topics To Be DiscussedRameez KhalidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Review - Parts of The Body 1-2-3Document25 pagesLesson 5 - Review - Parts of The Body 1-2-3Alejandro GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Bones Joints Anatomy Week 3Document5 pagesBones Joints Anatomy Week 3hassan razaNo ratings yet
- Motor Fitness TestDocument23 pagesMotor Fitness Testdharmendra jhaNo ratings yet
- Chondromalacia Patella - Causes & Treatment - Knee Pain ExplainedDocument5 pagesChondromalacia Patella - Causes & Treatment - Knee Pain ExplainedJames MukhwanaNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument24 pagesLower LimbLola KhatimNo ratings yet
- Tractions in OrthopaedicsDocument88 pagesTractions in OrthopaedicsParth Chaudhary50% (2)
- Dry Needling Article SRF JournalDocument3 pagesDry Needling Article SRF JournalObreNo ratings yet
- Elbow Dislocation Orthoinfo AaosDocument4 pagesElbow Dislocation Orthoinfo AaosAnonymous L9D1I7DZNo ratings yet
- Notability Notes PDFDocument2 pagesNotability Notes PDFMuhammad Khaled TaubehNo ratings yet
- Types of Synovial JointsDocument7 pagesTypes of Synovial Jointsaulia nurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Common Sports Injuries: August 2016Document8 pagesCommon Sports Injuries: August 2016Binte SajjadNo ratings yet
- The Sternomastoid "Tumor" of Infancy.Document12 pagesThe Sternomastoid "Tumor" of Infancy.Dr. Ammar KhalilNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System HDocument23 pagesThe Skeletal System HRajorshi MishraNo ratings yet
- 8 Ankle SprainDocument11 pages8 Ankle Sprainapi-241264935No ratings yet
- 6401-Article Text-23230-1-4-20220803Document12 pages6401-Article Text-23230-1-4-20220803Subhan Zul ArdiNo ratings yet
- Case Report Session - Fracture - : Nabila Maularizka (130112190690)Document45 pagesCase Report Session - Fracture - : Nabila Maularizka (130112190690)Novi AdriNo ratings yet
- Vulovic - Brskovo Final PDFDocument27 pagesVulovic - Brskovo Final PDFDraganaNo ratings yet
Peds SG
Peds SG
Uploaded by
mzjackie9Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peds SG
Peds SG
Uploaded by
mzjackie9Copyright:
Available Formats
COMBANK PEDIATRIC Anaphylactic reaction o Management: IM epinephrine 1:1000. Obtain airway stabilization first and IV access.
s. IV epinephrine = 1:10000 dose instead. Birth Injuries: o Clavicular fx crepitus felt over clavicle o Erbs Palsy neuro findings (C5/C6 injury decrease biceps reflex, moro reflex, adduction and internal rotation of arm). o Klumpkes palsy claw hand. Weakness of wrist and finger flexors. Infantile botulism bacterial toxin blocks presynaptic vesicles, preventing the relase of NT. Initially, presents with constipation and poor feeding hypotonia, weakness, diminished eye movement, papillary paralysis, and ptosis. o Ddx: Neonatal myasthenia gravis transient form of the disease found in those whose mother has the disease. Facial diplegia more than ocular involvement. Tx: supportive care with anticholinesterase inhibitors. o Hypermagnesium (due to mom getting magnesium sulfate) blocking of Ca+2 release inhibits Ach release from presynaptic vesicles. Tx: diuresis with IV fluids to dilute the Mg concentration o Congenital myasthenia gravis: ocular mm involvement seen Arm fractures o Supracondylar fx: transverse type fx just proximal to the level of the medial/lateral epicondyles of humerus (supracondylar). Displacement of the anterior humeral line as normally the anterior humeral line should intersect the middle third of the capitellum. Usually occurs due to fall on outstretch hand o Radial head subluxation: adult pulling upwards at wrist of child hyperextension and entrapment of radial annular ligament holds arm in flexion/pronation o Humeral surgical neck fx located below the great/lesser tubercles, located on the proximal portion of the humerus. o Humeral diaphysis fx spiral fx (longitudinal fx of humeral shaft); transverse fx (perpendicular to long axis of bone); comminuted fx (with 3 or more involved bone fragments) o Elbow dislocation gross deformity seen and complete immobility of elbow joint Potty training begin between 18-24 yo (AAP guidelines) Benzodiazepine toxicity decreased mentation, delirium, HA, weakness, slurred speech. Tx = flumazenil Rett Syndrome o 4 stages: stage 1 (developmental arrest) around 6-18 mo with decreased eye contact and lack of interest; stage 2 (regression) around 1-4 yo with loss of oral communication and purposeful hand movements; stage 3 (pseudostationary) around 2-10 yo with some improvement in hand and
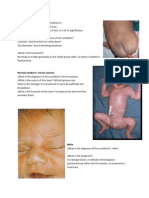
language skills; stage 4 (late motor deterioration) around >10yo with more motor issues (parksonism sx, hypertonia, etc) Febrile Seizures o Simple febrile seizures: children ages 6 mo 6 yo. Lasting <15 min. If patient >18 month old then can be d/c home on supportive care. If <1 yo, should do LP. Lytic bone lesions in child: o Infectious (brodie abscess from osteomyelitis) o Endocrine (hyperparathyroidism osteitis fibrosa cystica, o neoplastic (Ewing Sarcome, Langerhans histiocytosis, metastasis), o idiopathic (benign bone cyst) o Langerhans: cause solitary, lytic, long bone lesions; painful with overlying tender swelling and can cause pathologic fx. Typically resolves spontaneously. o Osteogenesis Imperfecta: defect in collagen. Blue sclerae. o Osteomyelitis: fever. No hypercalcemia. o Primary Hyperparathyroidism: hypercalcemia. Parathyroid adenoma is MC cause. Usually over 50 yo so unlikely in children. Hirschsprungs Disease: congenital aganglionosis of the distal bowel o both myeneteric (Auerbach) and submucosal (Meissner) plexus absent reduced bowel peristalsis and fxn. Area missing ganglion cells is just distal to the megacolon section which has expanded due to feces that cant be pushed passed the affected segment. o Usually fail to pass meconium within 48 hrs of life + vomiting + FTT (failure to thrive) o If less severe lesion, present later in life with chronic constipation o Barium enema for imaging. Plain film will show distended bowel w/ paucity of air in rectum o Anorectal manometry detects failure of internal sphincter to relax after distention of rectal lumen. o Rectal bx just distal to the expanded segment confirms dx - no plexus + hypertrophied nerve trunks enhanced with Acetylcholinesterase staining o
You might also like
- SAQs AnatomyDocument238 pagesSAQs AnatomyDrHassan Ahmed Shaikh80% (5)
- Slides For Pediatric Osce ExamDocument389 pagesSlides For Pediatric Osce Examadan yare100% (1)
- Choanal Atresia2Document40 pagesChoanal Atresia2pramod555No ratings yet
- Tuberculous Spondylitis (TB Spine/pott's Disease)Document28 pagesTuberculous Spondylitis (TB Spine/pott's Disease)Divo Septian Zarwin100% (1)
- Potts FractureDocument18 pagesPotts FractureOves PatniNo ratings yet
- Extra SAQsDocument24 pagesExtra SAQsIshan DevNo ratings yet
- RQ of Nbde Part 2 Dec 2017Document7 pagesRQ of Nbde Part 2 Dec 2017ParneetNo ratings yet
- Interesting Cases PediatricsDocument253 pagesInteresting Cases PediatricsomkamaleshNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument25 pagesCerebral PalsyDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Paeds Osce Batch Compiled and Solved-1Document33 pagesPaeds Osce Batch Compiled and Solved-1bismahNo ratings yet
- PediaDocument43 pagesPediaRahaf Bin ManieNo ratings yet
- Neuro SGDocument29 pagesNeuro SGgew123No ratings yet
- 18 Tonsil, Adenoid Notes Cumming Abd Key Topics (New Moe)Document7 pages18 Tonsil, Adenoid Notes Cumming Abd Key Topics (New Moe)osamaeNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Maria Victoria M. Villarica MD OLFU College of Medicine Department of PediatricsDocument81 pagesThe Digestive System: Maria Victoria M. Villarica MD OLFU College of Medicine Department of PediatricsSven OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- ORE Part 1 August 2017Document20 pagesORE Part 1 August 2017sajna1980No ratings yet
- Birthinjuries Dr.M.maniDocument65 pagesBirthinjuries Dr.M.manimaniNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in Ingestion: Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate 1. Cleft Lip/cleft PalateDocument15 pagesDisturbances in Ingestion: Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate 1. Cleft Lip/cleft PalatehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Diseases With Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument52 pagesClinical Diseases With Chromosomal AbnormalitiesAzifah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve PalsyDocument3 pagesFacial Nerve PalsyGayle VillarizaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric - Hearing - Loss Lau 3-17-10Document45 pagesPediatric - Hearing - Loss Lau 3-17-10Arief FakhrizalNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy (L)Document30 pagesCerebral Palsy (L)Touseef Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Choanal Atresia2Document40 pagesChoanal Atresia2Mavina ReeNaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Aganglionic Megacolon (Hirschsprung Disease) : Kristin N. Fiorino and Chris A. LiacourasDocument6 pagesCongenital Aganglionic Megacolon (Hirschsprung Disease) : Kristin N. Fiorino and Chris A. LiacourasSyakilla AuliaNo ratings yet
- File BookDocument13 pagesFile BookusamaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBz6SCL6SA VJUDh46tP6NUDhw3P47 NPjiCaRlywgh9trN 5PhQeKcHqMl2xUsHtUBcc7n4mL1On5SlTP2X94BYDVb HoGkGegg5erftVOvtVci7Q4s0omLCXYn6dldjBQhk2bZ6Jpfl6cDocument24 pagesACFrOgBz6SCL6SA VJUDh46tP6NUDhw3P47 NPjiCaRlywgh9trN 5PhQeKcHqMl2xUsHtUBcc7n4mL1On5SlTP2X94BYDVb HoGkGegg5erftVOvtVci7Q4s0omLCXYn6dldjBQhk2bZ6Jpfl6cMalavika A GNo ratings yet
- Septic ArthritisDocument21 pagesSeptic ArthritisDawex IsraelNo ratings yet
- MRCPCH Guide New QuestionsDocument11 pagesMRCPCH Guide New QuestionsRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- Toacs 6Document159 pagesToacs 6Mobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (2)
- SHCN 1Document14 pagesSHCN 1Suma TettaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemDocument116 pagesCongenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemVii syilsaNo ratings yet
- Deletion Syndromes: By: Rania ZahoDocument55 pagesDeletion Syndromes: By: Rania ZahoRania ZahoNo ratings yet
- 0 Yazan Mini-OSCE PedsDocument60 pages0 Yazan Mini-OSCE Pedsmoyasserayoub78No ratings yet
- Pedia SummaryDocument10 pagesPedia SummaryBea GozaNo ratings yet
- Birth InjuriesDocument2 pagesBirth InjuriesMohd FadhliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Spot Diagnosis: Abdulrahman BashireDocument20 pagesPediatric Spot Diagnosis: Abdulrahman Bashireعبدالرحمن بشير100% (1)
- Common Health Problems InfancyDocument147 pagesCommon Health Problems Infancymark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- CNS 2Document9 pagesCNS 2husainozelNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument9 pagesCerebral PalsyAngy100% (2)
- Cerebral Palsy: Reported By: Felvee M. Basibas, PTRP MDDocument67 pagesCerebral Palsy: Reported By: Felvee M. Basibas, PTRP MDBobby ReynerNo ratings yet
- Episode 436 Eye findingsDocument16 pagesEpisode 436 Eye findingsmohora1030No ratings yet
- Pediatric OrthopaedicDocument66 pagesPediatric OrthopaedicDhito RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Syng Nathi ADocument29 pagesSyng Nathi AMuhammad Azhar ImranNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders, Skeletal Dysplasias, and Malformations: Appley's Reading Achmad Fachroni, DRDocument38 pagesGenetic Disorders, Skeletal Dysplasias, and Malformations: Appley's Reading Achmad Fachroni, DRAchmad FachroniNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Study GuideDocument22 pagesPediatrics Study GuideElizabeth McKee100% (1)
- Pediatric Eye DiseasesDocument5 pagesPediatric Eye DiseasesfrnksusNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Kelainan Kongenital Dan TumorDocument54 pagesInfeksi Kelainan Kongenital Dan Tumorniska darliantiNo ratings yet
- CEREBRAL+PALSY-+final NewDocument56 pagesCEREBRAL+PALSY-+final NewMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Neurologic Disorders: Ma. Tosca Cybil A. Torres, RN, MANDocument97 pagesPediatric Neurologic Disorders: Ma. Tosca Cybil A. Torres, RN, MANMa Tosca Cybil TorresNo ratings yet
- OrthodonticsDocument5 pagesOrthodonticsAlbisladys Castellanos PujolsNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic DisordersDocument15 pagesOrthopedic Disordershasanatiya41No ratings yet
- T Collins SyndromeDocument21 pagesT Collins SyndromeMoe KebabNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Clerkship NotesDocument4 pagesPediatric Clerkship Notesxx_caligurl_93xxNo ratings yet
- El - MagnificoDocument137 pagesEl - MagnificoAbhi Thakkar100% (1)
- Mandibulofacial Dysostosis, Also Known As Treacher CollinsDocument19 pagesMandibulofacial Dysostosis, Also Known As Treacher CollinsMoe KebabNo ratings yet
- 醫科Document85 pages醫科Jason LinNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument17 pagesCerebral Palsymohammed almaaziNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Orthopaedics: Dr. Andreas Siagian SpotDocument66 pagesPediatric Orthopaedics: Dr. Andreas Siagian SpotFirdausi RiskiviawinandaNo ratings yet
- Mongolian SpotsDocument9 pagesMongolian SpotsiekafzNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube DefectDocument8 pagesNeural Tube DefectReema Akberali nooraniNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics RemarksDocument62 pagesPediatrics RemarksGÖKSU SAYGILINo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- Semiology Lecture 4. Facies, Neck, ThyroidDocument59 pagesSemiology Lecture 4. Facies, Neck, ThyroidmlinaballerinaNo ratings yet
- Newborn DDXDocument1 pageNewborn DDXmzjackie9No ratings yet
- Platelet Aggregation, If A Patient With Atherosclerotic Coronary Arteries Who Was Taking AspirinDocument1 pagePlatelet Aggregation, If A Patient With Atherosclerotic Coronary Arteries Who Was Taking Aspirinmzjackie9No ratings yet
- Obesity SurgeriesDocument2 pagesObesity Surgeriesmzjackie9No ratings yet
- Comparing Food Labels: Food Label A Food Label BDocument1 pageComparing Food Labels: Food Label A Food Label Bmzjackie9No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemCHRISTIANNE DENISE EBREONo ratings yet
- Dr. Bhatia Medical Coaching Institute Hyderabad: Post Class Test - AnatomyDocument9 pagesDr. Bhatia Medical Coaching Institute Hyderabad: Post Class Test - AnatomyPNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document29 pagesWeek 1chito refrea0% (1)
- 12.musculoskeletal System 4 Blocks Eduwaves360Document729 pages12.musculoskeletal System 4 Blocks Eduwaves360ÇağlaNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy in Sport: Seth O'Neill, Simon Barry, Paul WatsonDocument8 pagesPhysical Therapy in Sport: Seth O'Neill, Simon Barry, Paul WatsonmorbreirNo ratings yet
- Bone and Joint Infection: Dr. Zainab AbdulwahabDocument89 pagesBone and Joint Infection: Dr. Zainab Abdulwahabzen.maree6No ratings yet
- The Biomechanics of Stretching: Duane KnudsonDocument10 pagesThe Biomechanics of Stretching: Duane KnudsonSanjanaNo ratings yet
- Mobilization With MovementDocument8 pagesMobilization With Movementapi-661333402No ratings yet
- Ergonomics: A Work Place Realities in Pakistan: Topics To Be DiscussedDocument13 pagesErgonomics: A Work Place Realities in Pakistan: Topics To Be DiscussedRameez KhalidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Review - Parts of The Body 1-2-3Document25 pagesLesson 5 - Review - Parts of The Body 1-2-3Alejandro GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Bones Joints Anatomy Week 3Document5 pagesBones Joints Anatomy Week 3hassan razaNo ratings yet
- Motor Fitness TestDocument23 pagesMotor Fitness Testdharmendra jhaNo ratings yet
- Chondromalacia Patella - Causes & Treatment - Knee Pain ExplainedDocument5 pagesChondromalacia Patella - Causes & Treatment - Knee Pain ExplainedJames MukhwanaNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument24 pagesLower LimbLola KhatimNo ratings yet
- Tractions in OrthopaedicsDocument88 pagesTractions in OrthopaedicsParth Chaudhary50% (2)
- Dry Needling Article SRF JournalDocument3 pagesDry Needling Article SRF JournalObreNo ratings yet
- Elbow Dislocation Orthoinfo AaosDocument4 pagesElbow Dislocation Orthoinfo AaosAnonymous L9D1I7DZNo ratings yet
- Notability Notes PDFDocument2 pagesNotability Notes PDFMuhammad Khaled TaubehNo ratings yet
- Types of Synovial JointsDocument7 pagesTypes of Synovial Jointsaulia nurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Common Sports Injuries: August 2016Document8 pagesCommon Sports Injuries: August 2016Binte SajjadNo ratings yet
- The Sternomastoid "Tumor" of Infancy.Document12 pagesThe Sternomastoid "Tumor" of Infancy.Dr. Ammar KhalilNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System HDocument23 pagesThe Skeletal System HRajorshi MishraNo ratings yet
- 8 Ankle SprainDocument11 pages8 Ankle Sprainapi-241264935No ratings yet
- 6401-Article Text-23230-1-4-20220803Document12 pages6401-Article Text-23230-1-4-20220803Subhan Zul ArdiNo ratings yet
- Case Report Session - Fracture - : Nabila Maularizka (130112190690)Document45 pagesCase Report Session - Fracture - : Nabila Maularizka (130112190690)Novi AdriNo ratings yet
- Vulovic - Brskovo Final PDFDocument27 pagesVulovic - Brskovo Final PDFDraganaNo ratings yet