Professional Documents
Culture Documents
American Institute of Steel Construction
American Institute of Steel Construction
Uploaded by
sojeckOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
American Institute of Steel Construction
American Institute of Steel Construction
Uploaded by
sojeckCopyright:
Available Formats
The non-profit organization that regulates the industrial standards for the structural steel design and American
Institute of Steel Construction construction industries. If welding involves steel construction, designers use AISC codes. The non-profit organization that regulates the industrial standards for the oil and natural gas industry. If welding involves oil pipelines or related materials, designers use API codes. The non-profit organization that regulates the industrial standards for welding and promotes the welding industry in the United States. The arrow which extends from either end of the reference line and points to a diagram of the intended welded joint. The part of the welding symbol that is below the reference line. Instructions that appear on the arrow side of the welding symbol correspond with the arrow side of the base metal to be welded. A set of American Welding Society codes that govern welding structures such as buildings and bridges. If welding involves structural construction, designers use AWS structural codes. A device used for weld testing that bends weld test specimens to test their quality. A document containing all the instructions necessary for making a project. A blueprint with instructions for welding contains one or more welding symbols. A type of joint between two metal parts that lie in the same plane. A butt joint is the most common joint type. The process by which a welder earns permission to weld with specific variables. A type of intermittent weld that requires a sequence of welds on each side of the joint that line up evenly with each other. A collection of laws or standards that outline practices for a particular application. Welding codes ensure safe welding practices and high-quality welded products. Curving inward like the inside of a bowl. Many fillet
American Petroleum Institute
American Welding Society
arrow element
arrow side
AWS Structural Codes
bending jig
blueprint
butt joint
certification
chain-intermittent weld
code concavity
welds have concave faces. consumable insert A type of filler material added to the welded joint. Consumable inserts often add strength to the welded joint. A supplementary symbol that tells the welder the shape of the finished weld bead. An agreement, usually in writing, between two or more parties. A welding contract outlines all of the specific requirements and codes for a particular welding application. Curving outward like the exterior part of a circle. Many fillet welds have convex faces. A type of joint between two metal parts located at right angles to one another. Corner joints require large amounts of weld metal. The interior part of a weld. The cross-section is often subject to weld testing and inspection to ensure weld quality. A metal's ability to be drawn, stretched, or formed without breaking. A type of joint in which the surface of the two metal parts to be joined are parallel to one another, and the weld is made at their common edges. A variable used in the welding process that, if changed, will affect the mechanical properties of the finished weld. A supplementary symbol that instructs the welder to perform a weld on a job site, not in the welding shop. A type of weld that is triangular in shape and joins two surfaces at right angles to each other in a lap joint, Tjoint, or corner joint. Fillet welds are the most common types of welds. A weld test performed on fillet welds that places a fillet weld test specimen onto a load and bends it flat onto itself so that it can be inspected for defects. A visual weld test performed on the weld and heataffected zone of fillet welds. A symbol that appears within the welding symbol that
contour symbol
contract
convexity
corner joint
cross-section
ductility
edge joint
essential variable
field weld symbol
fillet weld
fillet weld performance test
fillet weld procedure test finish symbol
tells the welder how to complete the finished welded joint. Finish symbols indicate the need for processes like grinding, power brushing, or machining. grinding groove groove angle A means of finishing a weld by using an abrasive. An opening between two parts that can contain a weld. The angle of the groove between the two workpieces that are welded together. A weld placed in an opening between two parts. There are eight groove weld symbols that represent different groove weld shapes. A weld test used for thinner base metals that places a weld test specimen into a jig and bends it 180. The weld test specimen must not break and must not have defects beyond those specified by the code. A weld test used for thicker base metals that places a weld test specimen into a jig and bends it 180. The weld test specimen must not break and must not have defects beyond those specified by the code. The portion of the base metal that has not been melted, but its mechanical properties have been altered by the heat of welding. Welding that does not require one continuous weld along the length of the entire joint. Intermittent welds are shorter welds, spaced evenly along the joint. A type of groove weld with an opening in the shape of the letter "J." The edge of one metal part is concave, and the other is square. The meeting point of two materials that are joined together. Welding creates a permanent joint. A type of joint between two overlapping metal parts in parallel planes. A machine that places a large amount of pressure and weight onto a device. Weld test specimens are placed on a load and bent so they can be inspected for defects. The properties that describe a material's ability to compress, stretch, bend, scratch, dent, or break. A supplementary symbol that tells the welder that complete joint penetration is necessary on one side of
groove weld
guided-face and root-bend test
guided-side bend test
heat-affected zone
intermittent welding
J-groove weld
joint lap joint
load
mechanical properties melt-through symbol
the joint. multiple reference lines The use of two or more reference lines. Multiple reference lines are used when a joint requires a sequence of operations. A variable used in the welding process that, if changed, will not affect the mechanical properties of the finished weld. The part of the welding symbol that is above the reference line, opposite the arrow side. Instructions that appear on the other side of the welding symbol correspond with the other side of the base metal to be welded. An inspection in which an inspector takes measurements of a part. A physical inspection of a weld involves measuring the weld length and size. The distance from the center of one intermittent weld bead to the center of the next intermittent weld bead. A type of weld made by joining one metal part with a circular hole to another metal part positioned directly beneath it. The application of heat to the weld immediately after welding. Post heating helps reduce stress in the weld metal. A means of finishing a weld with a motorized brush. The application of heat to a base metal immediately before welding. Preheating helps reduce hardness in the weld metal. The horizontal line in the center of the welding symbol from which all elements of the welding symbol are referenced. The reference line is one of the most important elements of the welding symbol. The angle of the groove at the weld root of the two workpieces. The weld root is the point at which the base metals are closest together. A type of continuous weld made between or upon overlapping metal parts. A detailed description of particulars. Specification is often used interchangeably with the term code when referring to welding codes.
nonessential variable
other side
physical inspection
pitch
plug weld
post heating power brushing preheating
reference line
root angle
seam weld
specification
spot weld
A type of weld made between or upon overlapping metal parts. Multiple spot welds are generally required to join parts. A groove weld placed in an opening between two parts in the shape of a square. A type of intermittent weld that requires a sequence of welds on each side of the joint that do not line up evenly with each other. An established rule or set of expectations. Standard is often used interchangeably with the term code when referring to welding codes. A symbol that appears within the welding symbol that gives further information about the weld. Supplementary symbols are not always included in the welding symbol. Something that is used to signify something else. A weld symbol tells the welder which type of weld to deposit into a joint. The part of the welding symbol that appears opposite the arrow element on the reference line. The tail contains special directions about the weld. The ability of a metal to resist forces that attempt to pull it apart or stretch it. A machine used to test a metal's tensile strength. To calculate a weld's tensile strength, the tensile testing machine stretches a weld test specimen until it breaks. A weld test that places a weld into a tensile testing machine to determine the metal's ductility. A weld performed on a sample piece of metal with exactly the same variables outlined in the welding procedure specification for the purpose of testing and inspection. A portion of the test coupon that undergoes weld testing and inspection. A type of joint produced when two metal parts are perpendicular to each other, forming the shape of the letter "T." An unwanted but acceptable deviation from a given dimension. Tolerances indicate the allowable
square groove weld
staggered-intermittent weld
standard
supplementary symbol
symbol
tail
tensile strength
tensile testing machine
tension-reduced section test
test coupon
test specimen
T-joint
tolerance
difference between a physical feature and its intended design. U-groove weld A type of groove weld with an opening in the shape of the letter "U." The edges of a U-groove weld are concave. A type of groove weld with an opening in the shape of the letter "V." V-groove welds require more joint preparation but less weld metal. An inspection that requires an inspector to look closely at a welded part. A mix of metals that joins at least two separate parts. Welds can be produced by applying heat, or pressure, or both heat and pressure, and they may or may not use an additional filler metal. A strip of metal located on the side opposite of the weld that provides a surface for depositing the first layer of metal to prevent molten metal from escaping through the joint. Weld backing is used for complete penetration welds. A supplementary symbol that indicates the need for weld backing during welding. A specific measurement of a weld. Weld dimensions include length, pitch, and size. The exposed surface of a weld on the side from which welding occurs. The distance from the root to the toe of the fillet weld. The size of the fillet weld is determined by the length of its legs. The dimensions of a weld that include leg length, convexity, and concavity. A metal strip that acts as weld backing, but is inserted in the root of a joint of a groove weld. Weld spacing maintains a joint's root opening during welding. A supplementary symbol that indicates the need for a weld spacer during welding. A symbol that appears within the welding symbol that tells the welder the type of weld to deposit into a joint. A supplementary symbol that instructs the welder to
V-groove weld
visual inspection
weld
weld backing
weld backing symbol weld dimension weld face
weld leg
weld size
weld spacer
weld spacer symbol weld symbol weld-all-around symbol
weld on all sides of the joint. welding code A standard used to govern welding processes and ensure safe welding practices and high-quality welded products. A test administered to a welder to determine the welder's capacity to perform a specific welding application. Welding performance qualification tests are specific to a WPS. A written document that records the results of a weld that has undergone weld testing and inspection. A written document that contains all necessary and specific information regarding the application of a welding project. Welding procedure specifications must be approved and tested before welding can begin. A systematic grouping of symbols that together, denote welding instructions clearly and concisely. A term sometimes used to refer to the person who welds.
welding performance qualification test
welding procedure qualification record
welding procedure specification
welding symbol weldor
You might also like
- Envicool Cabinet Air Conditioner Service ManualDocument22 pagesEnvicool Cabinet Air Conditioner Service ManualCONSORCIO TECA 2019100% (2)
- Arch College THESISDocument43 pagesArch College THESISParth Narula79% (33)
- 0160e-Welding Procedures Data Sheet PDFDocument1 page0160e-Welding Procedures Data Sheet PDFShane SNo ratings yet
- DBMSC Steel BrochureDocument5 pagesDBMSC Steel BrochureDaniel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lionweld Kennedy GratingDocument40 pagesLionweld Kennedy Gratingscribd-123No ratings yet
- EN 13480-3 Straight Pipes PDFDocument1 pageEN 13480-3 Straight Pipes PDFmasatusNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification 1420288037Document51 pagesTechnical Specification 1420288037gaurao nasare100% (1)
- Bolt AnchorageDocument6 pagesBolt AnchoragesdewssNo ratings yet
- Ssec - Tip - 56 Cambered Steel Beams PDFDocument4 pagesSsec - Tip - 56 Cambered Steel Beams PDFAdrian Guerra EspinosaNo ratings yet
- SATR-L-2001 Rev 2 - Flange Joint Tightening Inspection ReportDocument12 pagesSATR-L-2001 Rev 2 - Flange Joint Tightening Inspection Reportdeepa narayan100% (1)
- Comentarios-103 - Parte I - English PDFDocument89 pagesComentarios-103 - Parte I - English PDFSakthivel VNo ratings yet
- Tack WeldDocument1 pageTack Weldbhatti19No ratings yet
- Tightening of Non Preloadable PDFDocument2 pagesTightening of Non Preloadable PDFFaisal MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Heat-Affected ZoneDocument9 pagesPrediction of Heat-Affected ZonePrakhar Deep KulshreshthaNo ratings yet
- Details of Fillet Welds D15M-D15-2002 - Section - 2.1Document40 pagesDetails of Fillet Welds D15M-D15-2002 - Section - 2.1drac_dracNo ratings yet
- A FEDS Structural BoltsDocument6 pagesA FEDS Structural BoltsCrimsonPoshNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument39 pagesShielded Metal Arc Weldingعزت عبد المنعم100% (1)
- Nelson Stud Welding - CJL Reduced Base StudsDocument1 pageNelson Stud Welding - CJL Reduced Base StudsStefan IonitaNo ratings yet
- Quality Control in Design and Supervision Can Eliminate Lamellar TearingDocument5 pagesQuality Control in Design and Supervision Can Eliminate Lamellar Tearingdurandm10No ratings yet
- Welded Joint Design and ProductionDocument116 pagesWelded Joint Design and ProductionGilbertoUGONo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Steel Structure Dent RectificationDocument13 pagesMethod Statement For Steel Structure Dent RectificationPrem ChristianNo ratings yet
- Specification For Plant Access Platforms, Stairs and Ladders Materials and FabricationDocument41 pagesSpecification For Plant Access Platforms, Stairs and Ladders Materials and FabricationRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Fillet Welded Joints - A Review of The Practicalities - Job Knowledge 66Document4 pagesFillet Welded Joints - A Review of The Practicalities - Job Knowledge 66Anuj ShahiNo ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of SS 304 and CP TitaniumDocument39 pagesGas Tungsten Arc Welding of SS 304 and CP TitaniumDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Welding Symbols PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Welding Symbols PDFEarl HarbertNo ratings yet
- Miller - 2010 Welding Heavy Structural Steel SucessfulyyDocument15 pagesMiller - 2010 Welding Heavy Structural Steel SucessfulyyLleiLleiNo ratings yet
- "Stiffner" - Steel Beam Web Stiffener Analysis: Program DescriptionDocument6 pages"Stiffner" - Steel Beam Web Stiffener Analysis: Program DescriptionGustavo PaganiniNo ratings yet
- En10204 Certification For Steel PlatesDocument6 pagesEn10204 Certification For Steel PlatesTree Tawee100% (1)
- Post-Weld Heat Treatment Effects On Hardness and Impact Strength of Aluminum Alloy 6061 Friction Stir Butt WeldDocument5 pagesPost-Weld Heat Treatment Effects On Hardness and Impact Strength of Aluminum Alloy 6061 Friction Stir Butt WeldAliakbar GhaderiNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Erection MSDocument6 pagesFabrication and Erection MSShrikant BudholiaNo ratings yet
- 13 1611Document8 pages13 1611teguh andriantoNo ratings yet
- STS05120Document20 pagesSTS05120JunaidAhmedNo ratings yet
- Steel Connections: Research in Building Tech 3Document10 pagesSteel Connections: Research in Building Tech 3Angelica Marie AzucenaNo ratings yet
- CHS Splice PDFDocument5 pagesCHS Splice PDFKintali VinodNo ratings yet
- Repeated Weld Repair and Its Influence On Welded Carbon SteelDocument9 pagesRepeated Weld Repair and Its Influence On Welded Carbon SteelRabah BrikaNo ratings yet
- HSFG BoltsDocument4 pagesHSFG BoltspajipitarNo ratings yet
- Specification No: LMB-COI-TRG-001 Rev No. R0 Page ofDocument16 pagesSpecification No: LMB-COI-TRG-001 Rev No. R0 Page ofApoorv MathurNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt and Setting TemplateDocument5 pagesAnchor Bolt and Setting Templatemadhu_bgrNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7-16 Practical Seismic DesignDocument21 pagesASCE 7-16 Practical Seismic Designcloudbooks007No ratings yet
- Bolts and TighteningDocument4 pagesBolts and TighteningArassen RunNo ratings yet
- Summers 2008 Structures Congress Modular Blast Resistant Buildings PaperDocument7 pagesSummers 2008 Structures Congress Modular Blast Resistant Buildings PaperJose Luis Velasco Cadavid100% (1)
- QW 381Document1 pageQW 381Waqas WaqasNo ratings yet
- Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) : JointDocument2 pagesProcedure Qualification Record (PQR) : JointBalkishan DyavanapellyNo ratings yet
- SteelWise Specifying MaterialsDocument6 pagesSteelWise Specifying Materialsv100% (1)
- Astm A194-A194m-13 PDFDocument12 pagesAstm A194-A194m-13 PDFjhonnyNo ratings yet
- Astm A 123 - 2013Document8 pagesAstm A 123 - 2013JOSENo ratings yet
- HD Bolts BS - 7419Document5 pagesHD Bolts BS - 7419Deana White100% (1)
- Welding InspectionDocument9 pagesWelding InspectionJackNo ratings yet
- ASME PCC 1 HugoJulien Eng ModDocument2 pagesASME PCC 1 HugoJulien Eng ModTarunNo ratings yet
- Final Inspection ProcedureDocument1 pageFinal Inspection ProcedurePamela ColemanNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Technical Specification For Structural SteelworkDocument11 pages4.4 Technical Specification For Structural SteelworkHazim HaNo ratings yet
- ASTM A131 Steel, Grade DDocument1 pageASTM A131 Steel, Grade DjulianmorantesNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rail GuideDocument227 pagesBridge Rail GuideSakineNo ratings yet
- Deflections PortalsDocument9 pagesDeflections PortalsJim SpsNo ratings yet
- Certification: Structural Steel and Bolting Special Inspector Exam ID: S1Document2 pagesCertification: Structural Steel and Bolting Special Inspector Exam ID: S1Ammar A. AliNo ratings yet
- Steel GlossaryDocument5 pagesSteel GlossaryzaninelloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document11 pagesChapter 7lhorenelNo ratings yet
- Welded ConnectionsDocument15 pagesWelded ConnectionsMax MillianNo ratings yet
- Field Welding Inspection ManualDocument40 pagesField Welding Inspection ManualrosennmNo ratings yet
- GougingDocument6 pagesGougingP Sandana NaraNo ratings yet
- Definitions: I) /60v, Where V Voltage, I Amperage, V Weld Travel Speed (In./min.)Document2 pagesDefinitions: I) /60v, Where V Voltage, I Amperage, V Weld Travel Speed (In./min.)Michael JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Welding Drawings 1Document18 pagesWelding Drawings 1muh2006No ratings yet
- PARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0111550.sorDocument1 pagePARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0111550.sorsojeckNo ratings yet
- 2020 01 06 Nse EqDocument27 pages2020 01 06 Nse EqsojeckNo ratings yet
- PARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0131550.sorDocument2 pagesPARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0131550.sorsojeckNo ratings yet
- PARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0121550.sorDocument1 pagePARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0121550.sorsojeckNo ratings yet
- PARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0031550.sorDocument1 pagePARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0031550.sorsojeckNo ratings yet
- PARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0051550.sorDocument1 pagePARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0051550.sorsojeckNo ratings yet
- PARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0061550.sorDocument1 pagePARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0061550.sorsojeckNo ratings yet
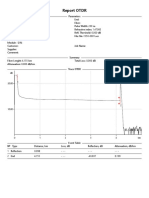
- Report OTDR: Comment: CommentDocument5 pagesReport OTDR: Comment: CommentsojeckNo ratings yet
- PARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0041550.sorDocument1 pagePARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0041550.sorsojeckNo ratings yet
- PARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0021550.sorDocument1 pagePARAMOUNT DRUM ID 7891 0021550.sorsojeckNo ratings yet
- Job Procedure FOR Hydrotesting of Underground Mov (Api 6D Valve)Document6 pagesJob Procedure FOR Hydrotesting of Underground Mov (Api 6D Valve)sojeckNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Shell TestDocument5 pagesHydrostatic Shell TestsojeckNo ratings yet
- Measurement Sheet MOV 5 GI ConduitDocument2 pagesMeasurement Sheet MOV 5 GI ConduitsojeckNo ratings yet
- Report OTDRDocument24 pagesReport OTDRsojeckNo ratings yet
- Balance Joint DetailsDocument3 pagesBalance Joint DetailssojeckNo ratings yet
- Rate QuotationDocument1 pageRate QuotationsojeckNo ratings yet
- Sr. No Date Description Drum No MTR Ch. No Receiver Name Remarks Koyali 2.1 Koyali 5.2 Koyali Koyali Koyali Koyali Koyali Koyali Koyali ?Document5 pagesSr. No Date Description Drum No MTR Ch. No Receiver Name Remarks Koyali 2.1 Koyali 5.2 Koyali Koyali Koyali Koyali Koyali Koyali Koyali ?sojeckNo ratings yet
- OTDR at Bareja, Towards Koyali: Pipe Line Chainage (Approx)Document2 pagesOTDR at Bareja, Towards Koyali: Pipe Line Chainage (Approx)sojeckNo ratings yet
- Al Muaser Petroleum Services PVT LTD Client/Consultant: Indian Oil Corporation Limited Kaspl Pipeline Project Incoming Material Inspection ReportDocument1 pageAl Muaser Petroleum Services PVT LTD Client/Consultant: Indian Oil Corporation Limited Kaspl Pipeline Project Incoming Material Inspection ReportsojeckNo ratings yet
- Resolution of Barricaded Subject Course Overview and Instructional GoalsDocument6 pagesResolution of Barricaded Subject Course Overview and Instructional GoalsAnonymous pOggsIhOMNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing: A Mini-Project ReportDocument8 pagesAdditive Manufacturing: A Mini-Project ReportArchit BathriNo ratings yet
- Niosh Naftas 1550Document6 pagesNiosh Naftas 1550Enrique Alejandro OvandoNo ratings yet
- (Fix) Windows 7 Keeps Checking For Updates For Hours - AskVGDocument9 pages(Fix) Windows 7 Keeps Checking For Updates For Hours - AskVGcornel68No ratings yet
- Platinum Corporate Epicure Enrolment FormDocument2 pagesPlatinum Corporate Epicure Enrolment FormDebabrata DasNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin Amsterdam (Europe) 2013 Speaker and Panelist ScheduleDocument5 pagesBitcoin Amsterdam (Europe) 2013 Speaker and Panelist Schedulem9500No ratings yet
- COO CIO VP Director in Denver CO Resume Dan SwaneyDocument2 pagesCOO CIO VP Director in Denver CO Resume Dan SwaneyDan SwaneyNo ratings yet
- Guide Number 1 OUR Life!: You Will Learn How To: Introduce Yourself. Ask People About Some Specific InformationDocument3 pagesGuide Number 1 OUR Life!: You Will Learn How To: Introduce Yourself. Ask People About Some Specific InformationyamileNo ratings yet
- OptiSystem Getting StartedDocument35 pagesOptiSystem Getting StartedFabricio PedrielNo ratings yet
- Cavendish ManualDocument6 pagesCavendish ManualbertosamNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco Air Compressor Parts CatalogDocument535 pagesAtlas Copco Air Compressor Parts CatalogJR Aguilar100% (3)
- Ceragon 1500p GuideDocument70 pagesCeragon 1500p Guidechong.cheekin8686No ratings yet
- EasyVR Datasheet 2.0Document23 pagesEasyVR Datasheet 2.0owais_36No ratings yet
- Standardi PERFORMANSI U Građenju Engleski ISO 9836 PDFDocument12 pagesStandardi PERFORMANSI U Građenju Engleski ISO 9836 PDFsaban saulic100% (1)
- Pengaruh Kualitas Produk Dan Harga Terhadap Volume Penjualan Pada Distro Popin Pangkal PinangDocument20 pagesPengaruh Kualitas Produk Dan Harga Terhadap Volume Penjualan Pada Distro Popin Pangkal PinangFifi FifiNo ratings yet
- JackDocument85 pagesJackapi-3831626No ratings yet
- Apl Case StudyDocument6 pagesApl Case StudyDeepak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- LMBUS User ManualDocument16 pagesLMBUS User ManualGaspar AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Projector - Manual Infocus IN26Document41 pagesProjector - Manual Infocus IN26COCO00677No ratings yet
- CPD 6 Application FormDocument2 pagesCPD 6 Application FormMj Ong PiersonNo ratings yet
- Congress ProgramDocument10 pagesCongress ProgramGuillermo Garcia HernandezNo ratings yet
- Table 21. Water Supply Fixture Unit Values (WSFU) and DiversityDocument4 pagesTable 21. Water Supply Fixture Unit Values (WSFU) and DiversityMustafa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cape Caribbean Studies Syllabus 2013Document3 pagesCape Caribbean Studies Syllabus 2013Kadek Mardika0% (3)
- QP Turbomachines 2019Document2 pagesQP Turbomachines 2019kuldeep chandrakarNo ratings yet
- GB-distribution Boxes and EnclosuresDocument10 pagesGB-distribution Boxes and EnclosuresVictor Solis BrevisNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Remedial Exam 1Document3 pagesReading and Writing Remedial Exam 1Virgilio Rosario BiagtanNo ratings yet
- Rainbow5 ProductPresentation 5310 117BRX PDFDocument133 pagesRainbow5 ProductPresentation 5310 117BRX PDFngmsilva67% (3)