Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Joan RabeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Joan RabeCopyright:
Available Formats
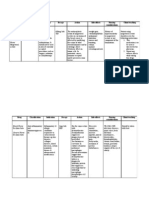
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo.
Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) Felodipine
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
Order: 5mg OD Dosages: Adults Initially, 5mg PO daily; dosage may be gradually increased over at least 14 days. Usual dose is 2.5mg10mg PO daily. Doses greater than 10mg PO daily are associated with an increased risk of peripheral edema. Pediatric Patients Safety and efficacy not established. Geriatic patients or patients with hepatic impairment
Drug Classes: Antihypertensive Calcium channel blocker Therapeutic actions: Inhibits the movement of calcium ion across the membranes of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells; greater selectivity for vascular smooth muscle as compared to cardiac muscle; leads to arterial and coronary artery vasodilation and decreased peripheral vascular resistance.
Essential hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive
Contraindicated with allergy to felodipine or other calcium channel blockers, sick sinus syndrome, heart block(second or third degree), lactation. Use cautiously with pregnancy, impaired hepatic function.
CNS: Dizziness, light-headedness, headache, asthenia, fatigue, lethargy CV: Peripheral Edema, arrhythmias Dermatologic: Flushing, rash GI: Nausea, abdominal discomfort, reflux, constipation.
Assessment History: Allergy to felodipine, impaired hepatic function, sick sinus syndrome, heart block, lactation, pregnancy Physical: Skin lesions, color, edema; P, BP, baseline ECG, peripheral perfusion, auscultation, R, adventitious sounds, Liver evaluation, GI normal output; LFTs, urinalysis Interventions: Have patient swallow tablet whole; do not chew or crush. Monitor patient carefully(BP, Cardiac rhythm and output) while drug is being adjusted to therapeutic dose. Monitor cardiac Rhythm regularly during
Monitor carefully; begin with 2.5mg daily, and do not exceed 10mg daily PO.
stabilization of dosage and periodically during long term therapy Administer drug without regard o meals
Teaching Points Take this drug with meals if upset stomach occurs; swallow tablet whole, do not cut, crush or chew, Do not drink grapefruit juice while using this drug You may experience this side effects: Nausea, vomiting(eat frequent small meals); headache(adjust lighting, noise, and temperature; medication may be ordered if severe). Report irregular heart beat, shortness of breath, swelling of the hands or feet, pronounced dizziness, constipation.
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) Magnesiu m sulfate
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
Dosages: Adults Parenteral Nutrition : 824mEq/day IV. Mild magnesium deficiency: 1 g IM or IV every 6 hour for 4 doses (32.5 mEq/ day) Eclampsia, severe eclampsia: Total initial dose of 10 14 g. May infuse 4-5 g in 250 ml. 5% dextrose injection or 0.09% sodium chloride while giving IM doses up to 10g. ( 5g or 10 ml of undiluted 50% solution in each buttock). Or, may give initial Iv dose of 4 g by diluting
Drug Classes: Antiepileptic Electrolyte Laxative Therapeutic actions: Cofactor of many enzyme systems involved in neurochemical transmission and muscular excitability; prevents or controls seizures by blocking neuromuscular transmission; attracts and retains water in the intestinal lumen and distends the bowel to promote mass movement and relieve constipation.
Acute nephritis(children), to control hypertension IV; hypomagnesemia, replacement therapy IV or IM: Pre-eclampsia or eclampsia PO: short term treatment of constipation PO: evacuation of the colon for rectal and bowel examinations To correct or prevent hypomagnesemia in patients on parenteral nutrition Unlabeled uses : inhibition of premature labor(parenteral), adjunct treatment of exacerbations of acute asthma; treatment torsades de pointes: atypical ventricular arrhythmias.
Contraindicated with allergy to magnesium products; heart block, myocardial damage; abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or other symptoms of appendicitis; acute surgical abdomen, fetal impaction,intestine and biliary tract obstruction, hepatitis. Do not give during two hour preceeding delivery because of risk of magnesium toxicity in the neonate. Use cautiously with renal insufficiency.
CNS: Weakness, Dizziness, Fainting, Sweating(PO) CV: Palpitation GI: Excessive bowel activity, perianal irritation(PO) Metabolic: Magnesium Intoxication(Flush ing, Sweating, Hypotension, Depressed reflexes, Flaccid Paralysis, Hypothermia, Circulatory collapse, Cardiac and CNS depression Parenteral) ; Hypocalcemia with tetany(Secondary to treatment of eclampsia Parenteral)
Assessment History: Allergy to magnesium products; renal insufficiency; heart block, myocardial damage; symptoms of appendicitis; acute surgical abdomen, fecal impaction, intestinal and biliary tract obstruction, hepatitis. Physical: Skin color, texture; muscle tone; orientation, affect, reflexes, peripheral sensation; P, Auscultation, BP, Rhythm strip; abdominal examination, bowel sounds; Renal function test, serum magnesium and calcium(Oral Used) Interventions: Reserved IV used in eclampsia for immediate life threatening
50%solution to 10% or 20% ; may inject diluted fluid ( 4ml of 10- % or 20 mL of 20% solution) IV over 3-4 min. then inject 4-5 g (8 to 10 mL of 50% solution) im into alternate buttocks every 4 hr as needed depending on the patellar reflex and and respiratory function. Or, after initial IV dose, may give 1-2 g/hr by constant IV infusion. Continue until paroxyxms stop. To control seizures, optimal magnesium level is 6mg/100 ml. Do not exceed 30-40 g in 24 hr.
situation Teaching Points Use only as a temporary measure to relieve constipation You may experience diarrhea with oral used Report sweating, flushing, muscle tremors or twitching, inability to move extremnities
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing
Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study Generic Name (Brand Name) Isordil Catapres
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
Order: 5mg OD Dosage/Frequency: Empty stomach w/ full glass of water 20-40mg/day or twice/day after meals Route: PO
Cardiovascular drug
Prevents & long-term treatment of angina-pectoris or post myocardial infarction (MI) angina. Treatment of severe congestive heart failure (CHF) in combination with cardiac glycosides, diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme(ACE) inhibitors, arterial vaso dilators;pulmonary hypertension
Acute myocardial infarction(MI); with low filling pressures, except in intensive care unit (ICU) with continuous haemodynamic monitoring; left heart failure with low filling pressures; very low BP; circulatory collapse; hypertrop hic obstructive cardiomyopathy; constrictive pericarditis; pericardial tamponade; aorticstenosis; mitral stenosis; marked anemia; head trauma; cerebral hemorrhage; close angle glaucoma; hyperthyroidism; concomitant therapy w/ sildenafil
Transient hypoxemia; headache; fall in blood pressure; reflex rise in pulse rate, dizziness &weakness, nausea and vomiting, transient skin disorders & allergic skin reactions may sometimes occur. Rare: Paradoxical nitrate effect and/or marked collapse with cardiac arrhythmias. Nitrate headache erythema. Increase in heart rate at start of treatment. Cerebral ischemia. Headache and dizziness.
Assess for pain: duration, time started, activity being performed, character, intensity. Monitor BP; pulse at baseline & during treatment. Cardiac output, decreased(uses) Knowledge deficit(teaching) Give 1hr before or 2hrsafter meals with 8oz of water. Sustained release tablets should not be chewed, or crushed; tablet should be chewed thoroughly.
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) Ferrous Sulfate ApoFerrous Sulfate (CAN), Feosol, Fer-gensol, Fer-InSol
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
Order: OD Dosages: Daily Requirements Men: 8-11 mg/day Women: 8-18 mg/day PO Pregnant and Lactating women: 10-27 mg/day PO. Replacement in deficiency states 90-300 mg/day(6 mg/kg/day) PO for approximately 6-10 mo may be required.
Drug Classes: Iron preparation Therapeutic actions: Elevates the serum iron concentration, which then helps to form hemoglobin or trapped in the reticuloendotheli al cells for storage and eventual conversion to a usable form of iron.
Prevention and treatment for iron deficiency. Dietary supplement for iron. Unlabeled use:supplemental use during epoetin therapy to ensure proper hematologic response to epoetin.
Contraindicated with allergy to any ingredient; sulfite allergy; hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis, hemolytic anemias. Use cautiously with normal iron balance; peptic ulcer, regional enteritis, ulcerative colitis.
CNS: CNS toxicity, acidosis, coma and death with overdose. GI: GI upset anorexia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, dark stools, temporary staining of the teeth.
Assessment History: Allergy to any ingredient sulfite; hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis, hemolytic anemias; normal iron balnce; peptic ulcer, rehional enteritis, ulcerative colitis. Physical: Skin lesions, color, gums, teeth; Bowelo sounds; CBC, Hgb, Hct, serum ferritin nad iron levels. Interventions: Confirm that pt. does have iron deficiency anemia before treatment. Give drug with meals (avoiding milk, eggs, coffee, tea) if GI discomfort is severe; may slowly increase to build up tolerance. Administer liquid preparations in
water or juice to mask the taste and prevent staining of teeth; have the patient drink the solution with straw. Warn pt. that stool may be dark or green. Arrange for periodic monitoring of Hct and Hgb levels. Teaching Points Do not take this preparation with antacids and tetracyclines. Have periodic blood tests during therapy to determine the appropriate dosage. Report GI upset, lethargy, rapid respirations, constipation.
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) HyoscineNbutylbromi
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
1 amp every 8
hours
Classification: Anti spasmodic
de
Brand Name: Buscopan
Inhibits acetylcholineat receptor sites inautonomic nervoussystem, which controlssecretions, free acidsin stomach.
Glaucoma megacolon,hypers
Dry mouth, dizziness,fatigue,
>Give by direct IVafter diluting
ensitivity,paralytic ileus,tachycardia
rash anorexia,headache
withsterilize water >Monitor I&O ratio,retention commonly causes decreasedurinary output
>Assess for constipation >Assess for toleranceover long
term therapy
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) Cefalexin Also known as Cephalexin
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
250 mg q6, OD
Drug Class: Anti Bacterial Drugs Cephalosporins Cephalexin, like the penicillins, is a beta-lactam antibiotic. By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins(PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, it inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall
For the treatment of respiratory tract infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae And Streptococcus pyogenes
Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins.
Pain at injection site; hypersensitivity; GI disturbances; eosinophilia, neutropenia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia. Potentially Fatal: Anaphylactic reactions; nephrotoxicity.
1. The drug should be taken with or without food. (May be taken with meals to reduce GI discomfort) 2.Before administ ration, ask patient if he is allergic to penicillins or cephalosporins. 3. Tell patient to take entire amount of drug exactly as prescribed, even after he feels better. 4. Advise patient to notif y prescriber if rash develops or signs and symptoms of super infection appear. 5. Inform the client not to chew, or cut extended tablets.
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) Mefenamic acid
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility > assess patients pain before therapy >monitor for possible drug induced adverse reactions >advice patient not to take drug for more than 7 days >advice patient to report immediately persistence or failure torelieve pain
Adult: start with 75-150 mcg BID
Drug Class: Analgesics Aspirin-like drug that has analgesic, antipyretic, & antiinflammatory activities
Relief of pain including muscular, rheumatic, traumatic, dental, postop and postpartum pain, headache, migraine, fever, dysmenorrheal.
Pregnancy & lactation, hypersensitivity, active ulceration or chronic inflammation of either upper or lower GIT, blood disorders, poor platelet function, kidney or liver impairment, children < 14 yrs
If rash occurs, administration should be stopped, asthmatics, Hx of liver and kidney disease Ddverse reaction: GI discomfort, diarrhea or constipation, gas pain, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness.
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) Clonidine hydrochlor ide
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
Individualize dosage. Initial dose is 0.1 mg bid; for maintenanc e dosage, increase in increments of 0.1 or 0.2 mg to reach desired response. Common range is0.20.6 mg/day, in divided doses; maximum dose is2.4 mg/day. Minimize sedation by slowly increasing daily dosage; giving majority of daily dose at bedtime.
Drug Class: Anti hypertensive Sympatholytic (centrally acting), Central analgesic Therapeutic Actions: Clonidine stimulates alpha2receptors in brainstem which results in reduced sympathetic out flow from the CNS and a decrease in peripheral resistance leading o reduced BP and pulse rate. It does not alter normal hemodynamic response to exercise at recommended dosages.
Hypertension, use dalone or as part of combination therapy Treatment of severe pain in cancer patients in combination with opiates; epidural more effective with neuropathic pain (Duraclon) Unlabeled uses: Tourette's syndrome; migraine, decreases severity and frequency; menopausal flushing, decreases severity and frequency of episodes; chronic methadone detoxification; rapid opiate detoxification(in doses up to 17mcg/kg/day); alcohol and benzo diazepine withdrawal treatment; management of hypertensive "urgencies"; (oral clonidine "loading" is used; initial dose of 0.2 mg then 0.1 mg every hour until a dose of 0.7 mg is reached or until BP is controlled)
Hypersensitivity. Disorders of cardiac pacemaker activity and conduction. Pregnancy and lactation.
Dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness, headache, constipation, impotence, vivid dreams, urinary retention; dry, itching, burning sensation in the eye; fluid or electrolyte imbalance, GI upset, paralytic ileus, orthostatic hypotension, weakness, sedation, pruritus, myalgia, urticaria, nausea, insomnia, arrhythmias, agitation. Reduced GI motility at times may cause paralytic ileus..
Assessment History: Hypersensitivity to clonidine or adhesive layer components of the transdermal system; severe coronary insufficiency, recent MI, cerebrovascular dise ase; chronic renal failure; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Body weight; T; skin color, lesions, T; mucous membranes color, lesions; breast examination; orientation, affect, reflexes; ophthalmologic examination; P, BP, orthostatic BP, perfusion, edema, auscultation; bowel sounds, normal output ,liver evaluation, palpation of salivary glands; normal urinary
output, voiding pattern; LFTs, ECG. Nursing Interventions WARNING: Do not discontinue abruptly; discontinue therapy by reducing the dosage gradually over 24 days to avoid rebound hypertension, tachycardia, flushing, nausea, vomiting, cardiac arrhythmias (hypertensive encephalopathy and death have occurred after abrupt cessation of clonidine). Do not discontinue transdermal therapy prior to surgery; monitor BP carefully during surgery; have other BP-controlling drugs readily available. Continue oral clonidine therapy within 4 hr of surgery then resume as soon as possible thereafter. Store epidural injection at room temperature; discard any unused portions. Reevaluate therapy if clonidine tolerance occurs; giving concomitant diuretic
increases the antihypertensive efficacy of clonidine. Monitor BP carefully when discontinuing clonidine; hypertension usually returns within 8 hr.
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) Metoprolol
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
100 mg / day
Drug Class: Beta1-selective adrenergic blocker Antihypertensive Therapeutic actions: Competitively blocks betaadrenergic receptors in the heart and juxtaglomerular apparatus, decreasing the influence of the sympathetic nervous system on these tissues and the excitability of the heart, decreasing cardiac output and the release of renin, and lowering BP; acts in the CNS to reduce sympathetic outflow and vasoconstrictor tone.
- Hypertension, alone or with other drugs, especially diuretics - Immediate-release tablets and injection: Prevention of reinfarction in MI patients who are hemodynamically stable or within 3\u201310 days of the acute MI - Treatment of angina pectoris - Toprol XL only: Treatment of stable, symptomatic CHF of ischemic, hypertensive, or cardiomyopathic origin.
Contraindicated with sinus bradycardia (HR < 45 beats/min), second- or thirddegree heart block (PR interval > 0.24 sec), cardiogenic shock, CHF, systolic BP < 100 mm Hg; lactation. - Use cautiously with diabetes or thyrotoxicosis; asthma or COPD; pregnancy
Allergic: Pharyngitis, erythematous rash, fever, sore throat, laryngospasm CNS: Dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, fatigue, emotional depression, paresthesias, sleep disturbances, hallucinations, disorientation, memory loss, slurred speech CV:CHF, cardiac arrhythmias, peripher al vascular insufficiency, claudication, CVA, pulmonary edema, hypotension Dermatologic: Rash, pruritus, sweating, dry skin EENT: Eye irritation, dry eyes, conjunctivitis, blurred vision GI: Gastric pain, flatulence, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting,anorexia, ischemic colitis, renal
Do not discontinue drug abruptly after long-term therapy (hypersensitivity tocatecholamines may have developed, causing exacerbation of angina, MI, andventricular arrhythmias). Taper drug gradually over 2 wk with monitoring. Ensure that patient swallows the ER tablets whole; do not cut, crush, or chew them. Consult physician about withdrawing drug if patient is to undergo surgery (controversial). Give oral drug with food to facilitate absorption. Provide continual cardiac monitoring for patients receiving IV metoprolol
and mesenteric arterial thrombosis, retroperitoneal fibrosis, hepatomegaly, acute pancreatitis GU: Impotence, decreased libido, Peyronie's disease, dysuria, nocturia, frequent urination Musculoskeletal: Joint pain, arthralgia, muscle cramp Respiratory: Bronchospasm, dyspnea, cough, bronchial obstruction, nasal stuffiness, rhinitis, pharyngitis Other: Decreased exercise tolerance, development of antinuclear antibodies (ANA), hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, elevated serum transaminase, alkaline Phosphatase. .
Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Name & age of Patient: Zipagan, Chatelyn 24 yo. Drug Study
Generic Name (Brand Name) Generic Name Hydralazine Trade Name: Apresoline , NovoHylazin
Dosage Frequency
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
10 mg by IV infusion
Pharmacologic Class Vasodilator Therapeutic Class Antihypertensive
General Indications - Hypertension - Eclampsia .
Concentrations - HypersensitivityCAD- mitral valvular rheumatic heart disease Precaution - with CAVs - increased intracranial pressure - severe hypertension with uremia - advanced renal damage - slow acetylators - lactation - pregnancy - pulmonary hypertension
CNS: Headache, periphera lneuritis, dizziness, tremors, psychotic reactions, characterized by depression, disorientation, anxiety CV: Palpitations, tachycardia, angina pectoris, hypotension, paradoxical pressor response, orthostatic hypotension GI: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, paralyticileus GU: Difficult micturition, impotence Hematologic: Blood dyscrasias Hypersensitivity: Rash, urticaria, pruritus, fever, chills, arthralgia, eosinophilia; rarely, hepatits, obstructive jaundice Other: Nasal congestion,
Before - Check blood pressure. - Arrange for CBC, LE cell preparations, and ANA titers before therapy - Assess for contraindicated conditions. - Observe the 15 rights of drug administration. - Assess bowel sounds. - Assess voiding pattern. During - Give oral drug with food.- Use parenteral drug immediately after opening ampule. - Discard discolored solutions .- Arrange for CBC, LE cell preparations, and ANA titers during prolonged therapy. - Instruct to take drug exactly as prescribed.
flushing, edema, muscle cramps, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, dyspnea, lupus-like syndrome, possible carcinogenesis, lacrimation, conjunctivitis .
After - Withdraw drug gradually. - Discontinue if blood dyscrasias occur. - Arrange for pyridoxine therapy if patient develops symptoms of peripheral neuritis. - Monitor for orthostatic hypotension. - Report persistent or severe constipation, unexplained fever or malaise, muscle or joint aching, chest pain, rash, numbness, tingling. - Do proper documentation
You might also like
- Pond WaterDocument4 pagesPond Waterapi-264011999No ratings yet
- Drug Study Sa PharmaDocument4 pagesDrug Study Sa PharmaKyle De Sagun Oteda100% (1)
- Drug Study Ciprofloxacin QuinosynDocument3 pagesDrug Study Ciprofloxacin QuinosynEmmanuel Margate100% (1)
- Acetaminophen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Drug StudyFrancis Corpuz100% (4)
- Brain Gym ExercisesDocument21 pagesBrain Gym Exercisesapi-380547950% (4)
- Medical English ExercisesDocument54 pagesMedical English ExercisesCarmen100% (1)
- 01b Biomechanic of KAFODocument66 pages01b Biomechanic of KAFOFERYANDA UTAMINo ratings yet
- Gemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsDocument13 pagesGemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsAnna-Tammy HumanNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument12 pagesOB Drug StudyCj AttoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument34 pagesDrug StudyMarco MoralesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyuntoned100% (1)
- Salbutamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalbutamol Drug StudyVinz Khyl G. CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaDocument2 pagesDrug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaFerdinand Sherwin MorataNo ratings yet
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Drug Study.Document9 pagesDrug Study.Chelsea Therese GuevarraNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY New BornDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY New BornNikolai FuncionNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Drug 101Document12 pagesDrug 101Alyzza DagoyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument26 pagesDrug Studyrn msnNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Lung Cancer)Document10 pagesDRUG STUDY (Lung Cancer)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyBadgal BazingaNo ratings yet
- Drug CelexaDocument1 pageDrug CelexaSrkocher100% (1)
- Drug Study (Pedia)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyAthena Irish LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument28 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On AlendronateDocument12 pagesA Drug Study On AlendronateTrio San LuisNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDelivery Room Drug StudyChinimansiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MMMCDocument14 pagesDrug Study MMMCKathleen Pagulayan Intalan-GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CapDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CapABARAJNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Content Class and Mechanism of Action (MOA) Indication/s Contraindication/s Side Effects (Pere System) Nursing ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesName of Drug Content Class and Mechanism of Action (MOA) Indication/s Contraindication/s Side Effects (Pere System) Nursing ConsiderationsJustin John NavarroNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY RANITIDINE, METRONIDAZOLE, CEFUROXIME, KEtorolac NUBainDocument7 pagesDRUGSTUDY RANITIDINE, METRONIDAZOLE, CEFUROXIME, KEtorolac NUBainKyle Cholo CholoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPrincess Ortega Namoc100% (1)
- Paracetamol PODocument3 pagesParacetamol POSheena GallardoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage and Route Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pagesName of Drug Dosage and Route Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTon AgustinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyAika CortesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyemmanuelmyagokayeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Mother TDocument14 pagesDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaNo ratings yet
- © The Mechanism of Action of Anectine Involves What Appears To Be A "Persistent"Document6 pages© The Mechanism of Action of Anectine Involves What Appears To Be A "Persistent"kaye marie100% (1)
- Drug Study - CaDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Casaint_ronald8No ratings yet
- Ivf StudyDocument2 pagesIvf StudyJannine Bensi100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyAl-nazer Azer AlNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Room 104)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Room 104)Maeshe Pryll TanamorNo ratings yet
- Amikacin 2Document2 pagesAmikacin 2Sian AsadaNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument8 pagesDrugAlyzza DagoyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyKristine Joy A. AniNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Advserse Effects (Specify) Nursing InterventionsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Advserse Effects (Specify) Nursing InterventionsKaterina Petrova100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJann Zaniel Allayne RiNo ratings yet
- Erythromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesErythromycin Drug StudyJude LabajoNo ratings yet
- Psychia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPsychia Drug StudyJustin 葉志明 Yap Delapaz100% (1)
- Availability: Classifications: Antiinfective Antitrichomonal Amebicide Antibiotic Pregnancy Category: BDocument5 pagesAvailability: Classifications: Antiinfective Antitrichomonal Amebicide Antibiotic Pregnancy Category: BCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: ALEXA MURIEL L. MOZAR Section: BLOCK 261Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: ALEXA MURIEL L. MOZAR Section: BLOCK 261Alexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug Study PDFDocument2 pagesVit K Drug Study PDFA sisonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyryanNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY PediaDocument5 pagesDRUG-STUDY PediaRhea Jane Bongcato50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyVicenia BalloganNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument6 pagesDexamethasoneapi-3797941100% (1)
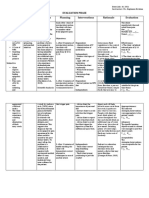
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- Drug TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug TramadolFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (2)
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Blood BankingDocument9 pagesBlood BankingKimverlyn Balanay AgpaloNo ratings yet
- Cognitive P. Chapter 2Document4 pagesCognitive P. Chapter 2May AloNo ratings yet
- K5 K6 - Osteologi Kepala LeherDocument21 pagesK5 K6 - Osteologi Kepala LeherMohammad Nuh Al-hudawy SiraitNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Tests of Thyroid Function - Uses and Limitations PDFDocument16 pagesLaboratory Tests of Thyroid Function - Uses and Limitations PDFMansouri HichemNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular System Complete HandoutDocument65 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular System Complete HandoutNicole LantinNo ratings yet
- DiaDENS-PCM Operations ManualDocument44 pagesDiaDENS-PCM Operations Manualgetdenas100% (7)
- Study of Lipid Profile in Coronary Heart Disease Patients in LibyaDocument9 pagesStudy of Lipid Profile in Coronary Heart Disease Patients in LibyaInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Targets Lower Medulla Oblongata Via Vagus NerveDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Targets Lower Medulla Oblongata Via Vagus NerveBOHR International Journal of Current research in Dentistry (BIJCRID)No ratings yet
- Development of Recommendations For SEMG Sensors and Sensor Placement Procedures - Hermens - 2000Document14 pagesDevelopment of Recommendations For SEMG Sensors and Sensor Placement Procedures - Hermens - 2000EmirDefaNo ratings yet
- ThyagarajDocument1 pageThyagarajrbllaboratoryNo ratings yet
- Medical For Athletes 1Document2 pagesMedical For Athletes 1Peachy FreezyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 2 Unpacking The Self The Physical Self Sexual Self.Document81 pagesLesson 2.1 2 Unpacking The Self The Physical Self Sexual Self.Jonel Maristela100% (1)
- Restoration of GABAA Receptor Function After Benzodiazepine Use - A Meta-AnalysisDocument19 pagesRestoration of GABAA Receptor Function After Benzodiazepine Use - A Meta-AnalysisLucasNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin ElectrophoresisDocument68 pagesHemoglobin Electrophoresisdrafq2000No ratings yet
- 2014 - June 2BR MS PDFDocument11 pages2014 - June 2BR MS PDFSimilar12345No ratings yet
- CAREGIVING NC II - Week7Document12 pagesCAREGIVING NC II - Week7Lignerrac Anipal UtadNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument74 pagesPharmacologyKiara Denise Tamayo100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryAparna RamachandranNo ratings yet
- On Galen in Galenism: Claudius GalenusDocument2 pagesOn Galen in Galenism: Claudius GalenusiamNashix22No ratings yet
- AVAMYSDocument11 pagesAVAMYSgisellapramuditaNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in HumansDocument14 pages(BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in Humansanya desilvaNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument2 pagesSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeRan MaNo ratings yet
- AmoebaDocument10 pagesAmoebaSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- GIT EmbryologyDocument39 pagesGIT Embryologyqnz78swpjmNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaDocument14 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet