Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Do Organisms Reproduce
How Do Organisms Reproduce
Uploaded by
Tapas BanerjeeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Do Organisms Reproduce
How Do Organisms Reproduce
Uploaded by
Tapas BanerjeeCopyright:
Available Formats
How Do Organisms Reproduce? 1. What is the importance of the process of reproduction?
Though reproduction is not an essential life process for an individual, it is very necessary for the perpetuation of the species. Increase in the population of a species is possible only by reproduction. Favourable variations from parents to offspring are passed on by reproduction. 2. What is species? A group of similar organisms which can naturally interbreed is called Species. 3. Do organisms produce exact copies of themselves during reproduction? In asexual reproduction there are subtle differences between parent and offspring In sexual reproduction these variations are more pronounced because two different individuals in a population would have quite different patterns of accumulated variations. Combining variations from two individuals would thus create more new combinations or variants. There is also gene recombination during the division leading to gamete formation. 4. What is the importance of variations? Variations increase the survival chance, variation is the raw material for evolution. Successful variations are selected in evolution. 5. Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individuals? Variations can be beneficial or harmful according to the ecological niche of the organism. A variation suitable for the particular niche is selected by nature in evolution. Thus variations are necessary for the survival of the species. Variation is important for evolution of the species. E.g.: A population of heat resistant bacteria in temperature of the water survives, if the temperature of water increases by global warming but most other bacteria would die. 6. What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA is a macromolecule present in the chromosome. Genes are segments of the DNA.. DNA has the information to create proteins which lead to body design of the organism. If a similar individual has to be reproduced, the DNA should replicate to make an exact copy of itself. The process of reproduction results in the production of offsprings which are exactly similar to the parents. DNA copying is accompained by cell division that gives rise to new cells. The exact blue print of body design is inherited in the offsping due to DNA replication in parent cell. 7. What are the different methods of asexual reproduction? a. Fission b. Budding c. Fragmentation d. Spore formation e. Vegetative Propagation 8. Name the following: An organism which reproduces by a. Binary fission - Amoeba
b. Multiple fission - Plasmodium c. Budding - Hydra d. Fragmentation - Spirogyra e. Spore Formation Rhizopus 9. How does binary fission differ from multiple fission? Binary fission consists of divisions of the nucleus followed by the division of cytoplasm producing two cells each having a daughter nucleus. E.g.: Amoeba In multiple fission, the nucleus of the parent cell undergoes repeated divisions to produce many daughter nuclei. The cytoplasm also divides and cleaves around each nucleus forming several daughter cells in the parent cell. In favorable conditions when the parent cell membrane raptures all the daughter individuals are released. E.g.: Plasmodium. 10. How does binary fission in amoeba differ from binary fission in Leishmania? Splitting of the cell into two can take place in any place in amoeba. In Leishmania which has a whip like structure at one end of the cell binary fission occurs in a definite orientation in relation to these structures. 11. How will an organism be benefitted if it reproduces through spores? Spores have thick walls that protect them from unfavorable conditions. Such spores are produced in large numbers. They germinate when favorable conditions return. 12. Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration? Complex organisms have highly differentiated tissues and organs. In this case regeneration of complex individual organism is difficult from a small piece. 13. Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants? a. In plants which do not produce viable seeds it is the only method of reproduction. b. Vegetative propagation is quicker and mature plants can be raised very quickly by this method. c. Genetically similar plants can be produced. This is of great importance in agriculture and gardening. 14. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction? The progeny of asexual reproduction show very little variations. This reduces the chance of survival and evolution of species. Sexual reproduction promotes diversity among the offspring because variations from two parents are coming together. Progeny of sexual reproduction have more chance of survival because of the variations. New combinations of characters thus plays important role in the evolution of species. 15. What is asexual reproduction? Explain briefly various methods of asexual reproduction? Formation of a new organism from a single parent without fusion of reproductive cells is called asexual reproduction. a. Fission: For unicellular organisms, cell division or fission leads to the creation of new individuals. i. Binary fission: The parent cell divides into two equal halves and two new individuals are produced. E.g.: Amoeba, bacteria, Leistmania ii. Multiple fission: The parent cell divides into many daughter cells simultaneously. E.g.: Plasmodium b. Fragmentation: Organisms break up into many pieces upon maturation. These fragments grow into new
individuals. E.g.: Spirogyra c. Regeneration: Simple animals like hydra and planaria can be cut into a number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism. Regeneration is carried out by specialized cells. d. Budding: In hydra, a bud develops as an out-growth due to repeated cell divisions at one specific site. These buds develop into tiny individuals, when full mature they detach from the parent body and start independent existence. e. Spore formation: Organisms like rhizopus produces spores in sporangia. Each spore has a thick wall to protect it. The spore germinates to produce a new organism. f. Vegetative propagation: when a vegetative part like stem, root, and leaf can produce a new organism, it is called vegetative propagation. Natural: i. Stem: Potato, onion ii. Root: Guava iii. Leaf: Bryophyllum Artificial: i. Stem-cutting ii. Grafting iii. Layering iv. Tissue culture 16. How is specific chromosome number maintained in a sexually reproducing organism? A special division takes place in the cells of reproductive organ such that the chromosome number is halved. Diploid mother cell produces haploid gametes. Gametes contain only half the amount of DNA. When gametes fuse during fertilization in the full number of chromosomes is re-established. Two haploid gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote. 17. Draw and label the parts of a flower.
18. What are the functions of the following parts of a flower? a. Sepals & petals: Sepals in the calyx cup protect the flower in the bud stage. They persist in the fruit. Petals of insect pollinated flowers are brightly colored and scented to attract bees and butterflies for pollination. They are colorless and inconspicuous in wind pollinated flowers. b. Stamen: This is the male reproductive part of the flower. The anther produces pollen grains. c. Carpel: It has a swollen bottom part called ovary, a middle elongated part called style and a sticky terminal part called stigma. The ovary contains ovules which contain the female gametes - the eggs. 19. What is pollination? The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is called pollination. If this transfer occurs in the same flower, it is called self-pollination. If the transfer occurs from one flower to another flower, it is called crosspollination. 20. How is the process of pollination differing from fertilization? The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is called Pollination. This occurs in angiosperm plants. The fusion of male and female gametes of all sexually-reproducing organisms is called fertilization. 21. What are the steps involved in fertilization and formation of seeds? a. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma. b. Pollen grains germinate to produce the pollen tube which grows through the style to the ovule in the ovary. c. The pollen tube releases male gametes which fuses with the egg nucleus to form a zygote. d. The zygote divides and develops to an embryo. e. The ovule develops into a seed. f. The ovary develops into the fruit. 22. What are the secondary sexual characteristics seen in males? a. Growth of thick hair on the face b. Cracking of the voice
23. Why are the testis located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum? Sperm production requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature. 24. Draw the female reproductive system and label the parts.
25. What is ovulation? The release of mature ovum from the ovary is called ovulation. This process occurs every month. 26. Draw the longitudinal section of pistil to show pollen grains germination.
27. List the events after fertilization in an angiosperm takes place. a. The zygote divides several times to form an embryo. This embryo develops plumule, radicle and one or two cotyledons. b. The ovule develops a tough coating and becomes a seed. c. The ovary develops into a fruit d. The petals, stamens, style and stigma shrivel and fall off. e. The calyx (of sepals) persists. 28. Draw the male reproductive system and label the parts.
29. What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate glands? The seminal vesicle and the prostate glands add their secretions so that the sperm are in a fluid which makes their transport easier and this fluid also provides nutrition. 30. What are the changes seen in females at the time of puberty? a. The breast size begins to increase with the darkening of the skin of the nipples. b. They begin to menstruate. 31. What happens when the egg is not fertilized?
If the egg is not fertilized, it lives only for a day. Every month the uterus prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg. The lining of the uterus becomes thick, spongy and richly supplied with blood. If the egg is not fertilized, the lining breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous. It usually lasts for 2 8 days. This process is called menstruation . 32. How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mothers body ? The embryo gets nutrition from the mothers blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. This is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryos side of the tissue. On the mothers side are blood spaces. This provides a large surface area for diffusion of glucose, oxygen and other nutrients from the mother to the embryo. 33. What are the contraceptive methods taken to avoid pregnancy? a. Creating a mechanical barrier so that the sperms do not reach the egg. This is done with a condom which is worn around the penis or a similar device that is placed in the vagina. b. Changing the hormonal balance of the body so that fertilization cannot occur. This is done with the help of oral contraceptive pills. c. Contraceptive devices like loop or copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. d. Surgical methods like vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females. 34. If a woman is using copper-T, will it help in protecting her from sexually-transmitted diseases? No. Copper-T which is placed in the uterus prevents pregnancy. It cannot prevent sexually-transmitted diseases. 35. What are the functions performed by the testis in males? a. Testis produces sperms. b. Testis produces male hormones called testosterone. This hormone helps the male to develop secondary sexual characteristics. It gives maleness and male feelings 36. How are the modes of reproduction different in unicellular and multi-cellular organisms? For unicellular organisms, cell division or fission leads to the creation of new individuals. In multi-cellular organisms with relatively simple body organization like spirogyra, simple reproductive methods can work. True multi-cellular organisms cannot divide cell by cell. They have specialized tissues and organs placed at definite positions in the body. So multi-cellular organisms have tissues and organs specially differentiated for reproduction 37. How does reproduction help in providing stability to population of species? Populations of organisms with well defined places in the ecosystem use their ability to reproduce. The consistency of DNA copying during reproduction is important for the maintenance of the body design features that allow the organism to use the particular niche. Reproduction is therefore linked to the stability of population of species. 38. What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods? Pregnancy will make major demands on the body and mind of the woman and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected. By adopting contraceptive methods, frequent and unwanted pregnancies can be avoided. Moreover, population can be controlled to improve the standard of living. More children bring financial constraints on the parents to feed, clothe and educate them. So to control the size of the family, contraceptive methods are adopted. Some of the contraceptive devices like condoms prevent sexually-transmitted diseases as well.
(i) Fossils are the remains or expressions of organisms that existed in the past, allow us tostudy organ structure of organisms that are no longer alive. Comparing their organ structure of present day organisms will also enable us to trace evolutionary relationships.. (ii) To estimate the age of fossils is known as fossil dating. Importance of Study of Fossils : (a) Fossils represent modes of preservation of ancient species. (b) Fossils help in establishing evolutionary traits among organisms and their ancestors. (c) Fossils help in establishing the time period in which organisms lived. Fossils are preserved traces of living organisms, that got buried deep inside the earth million of years ago. Two uses of fossils : (i) Racial history of plants. (ii) Past climatic conditions of earth. About the process of evolution the fossils indicates that : (i) Fossils helps to identify an evolutionary relationship between apparently different species. (ii) The fossils present in the bottom rocks are simple while the most recent fossil found in the upper strata are highly complex. This geographical succession completely agrees with the concept of evolution 5. (a) Leishmania reproduce by Binary fission. Plasmodium reproduce by Multiple fission. (b) Binary fission occurs under favourable conditions and gives rise to two individuals. Multiple fission occurs both under favourable and unfavourable conditions and gives rise to many individuals. Spore formation in Rhizopus : This is an asexual method of reproduction in bacteria and fungi. Spores are unicellular bodies formed by cell division in a parent organism. After detaching from the parent, and if conditions are suitable, they germinate, directly or indirectly develops into a new individual.
Sporangium Spores Hyphae
Spore formation in Rhizopus
Advantages : 2 (i) It is a rapid mode of multiplication. (ii) It produces identical organisms generation after generation. Secondary Sexual Characters : Male : 1. Hair growth on face, chest, armpit and over pubis. 2. Voice becomes deep and harsh due to growth of larynx called Adams apple. 3. Body becomes muscular. Female : 1. Growth of breasts and hair in axillae and over pubis. 2. Pelvis region becomes broad and buttocks become heavy due to deposition of fat. 3. Development of accessory sex organs. Functions of Fallopian Tube : (i) They are thin tubes that carry the egg from ovary to uterus. (ii) It is a site of fertilization
Fossils provide evidence for evolution: - The remains (or impressions) of dead animals or plants that lived in the remote past are known as fossils. The fossils provide evidence for evolution. For example, a fossil bird called Archaeopteryx looks like a bird it has many other features which are found in the reptiles. This is because Archaeopteryx has feathered wings like those of birds but teeth and tail like those of reptiles. Archaeopteryx is, therefore, a connecting link between the evolved from the reptiles. Thus, fossils provide the evidence that the present animals (and plants) have originated from the previously existing ones through the process of continuous evolution. Advantages of vegetative propagation: The main advantages of vegetative propagation are listed below: 1. It is a cheap and easy method of reproducing the plants. 2. The plants that do not produce viable seeds are easily propagated by this method. 3. It is the only method of producing and preserving two plant types during cross-pollination. 4. This method is used to produce a large number of selected strains of plants without loosing any desirable character
You might also like
- Delhi Public School, Harni: Subject - Biology (Science) Class - X Chapter-6 Life ProcessesDocument54 pagesDelhi Public School, Harni: Subject - Biology (Science) Class - X Chapter-6 Life ProcessesAnin BertNo ratings yet
- Final Practice Examination Answer Key: Rade HysicsDocument40 pagesFinal Practice Examination Answer Key: Rade HysicsNenbon NatividadNo ratings yet
- Science Papers - Grade 6Document4 pagesScience Papers - Grade 6Mallindu Perera100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 8 How Do Organism ReproduceDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 8 How Do Organism ReproduceAll Rounder HindustanNo ratings yet
- Important Question For Class 10 Science Our Environment PDF - LearnCBSE - inDocument6 pagesImportant Question For Class 10 Science Our Environment PDF - LearnCBSE - inBinode Sarkar100% (1)
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction in Animalsbinu_praveenNo ratings yet
- Allen CONTROL AND CO-ORDINATIONS IOQJSDocument14 pagesAllen CONTROL AND CO-ORDINATIONS IOQJSAtharv Aggarwal100% (1)
- Control & Coordination - Expected Q&ADocument15 pagesControl & Coordination - Expected Q&Apallab mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- CH.3 PLANT AND ANIMAL TISSUES Class 9 Notes IcseDocument5 pagesCH.3 PLANT AND ANIMAL TISSUES Class 9 Notes IcseFebin GeorgeNo ratings yet
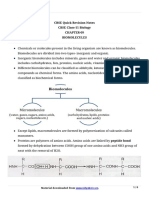
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesHARSH PahwaNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms: Friend or FoeDocument14 pagesMicroorganisms: Friend or FoeGeetika100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice QuestionsBasavarajNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10Document11 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10Pranay Kumar60% (5)
- Class-VII Science 2022Document4 pagesClass-VII Science 2022Mamta Shrivastava100% (1)
- Tissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeDocument31 pagesTissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeAyushi VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Fundamental Unit of Life Practice Worksheet: (B) Golgi Apparatus (C) Cell Wall (D) Cytoplasm (E) NucleoplasmDocument3 pagesChapter 5: Fundamental Unit of Life Practice Worksheet: (B) Golgi Apparatus (C) Cell Wall (D) Cytoplasm (E) NucleoplasmSarwan KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology Holiday HomeworkDocument2 pagesBiology Holiday Homeworkdaisy pNo ratings yet
- New CBSE Classcheme All Subjects Maths, Science, Social ScienceDocument1 pageNew CBSE Classcheme All Subjects Maths, Science, Social ScienceMihica KhareNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination PDFDocument24 pagesControl and Coordination PDFMUZEER PASHANo ratings yet
- New Horizon Public School, Airoli: Grade VIII: Science: Chapter 2: The Microbial WorldDocument3 pagesNew Horizon Public School, Airoli: Grade VIII: Science: Chapter 2: The Microbial WorldMann Gosar100% (1)
- Microorganism Friend and FoeDocument7 pagesMicroorganism Friend and FoeNEIL GAROONo ratings yet
- Physics Form 2 NotesDocument35 pagesPhysics Form 2 NotesLeon MzarabaniNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument37 pagesPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionved bhaskerNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive Sysytem Icse BoardDocument40 pagesHuman Digestive Sysytem Icse BoardJagrity SinghNo ratings yet
- VIII Science-Worksheets Session 2012 2013Document26 pagesVIII Science-Worksheets Session 2012 2013Jai Gupta100% (1)
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFDocument12 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFSomik JainNo ratings yet
- Gr-8 CEll - Structure and Function Answer KeyDocument5 pagesGr-8 CEll - Structure and Function Answer KeyT. Dharshini100% (1)
- Case Study Based Questions Grade 9cbse BiologyDocument1 pageCase Study Based Questions Grade 9cbse BiologySrijita Roy0% (1)
- Absorption by RootsDocument7 pagesAbsorption by RootsSaswatNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Biology Life Processes NotesDocument18 pagesCBSE Class 10 Biology Life Processes NotesSuresh Raghav50% (2)
- Nutrition in Plants Worksheet 28 AprilDocument1 pageNutrition in Plants Worksheet 28 AprilPulkit Sabharwal100% (1)
- Grade 7 Student Worksheet 1 Ch-1,2 - Nutrition in Plants and AnimalsDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Student Worksheet 1 Ch-1,2 - Nutrition in Plants and AnimalsRaghvendra Shrivastava100% (3)
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - TissuesDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - Tissuesankit anand100% (1)
- CBSE Class X Science How Do Organisms Reproduce ConceptsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class X Science How Do Organisms Reproduce ConceptsLamikso SawadenNo ratings yet
- Subject: Biology Fundamental Unit of Life Class - Ix WorksheetDocument3 pagesSubject: Biology Fundamental Unit of Life Class - Ix WorksheetVedant SinghalNo ratings yet
- CH2Document9 pagesCH2dhivya sankarNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Mumbai Region: Sample Question PaperDocument4 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Mumbai Region: Sample Question PaperYash BhagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Science-9 CombinedDocument20 pagesChapter Science-9 CombinedAnushkaNo ratings yet
- X-7-Control and CoordinationDocument30 pagesX-7-Control and CoordinationArohan BuddyNo ratings yet
- KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument16 pagesKSEEB SSLC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationssumeshmirashiNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Class Notes - Warrior-Life Processes (Samridhi Mam) WarriorDocument162 pagesLife Processes - Class Notes - Warrior-Life Processes (Samridhi Mam) Warriorsiddhesht104100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in AnimalsDocument6 pagesSexual Reproduction in AnimalsRahul Ecka100% (1)
- Chapter - 13: Why Do We Fall IllDocument10 pagesChapter - 13: Why Do We Fall Illuma mishraNo ratings yet
- 07 Science Ws Ch17 01 MZDocument3 pages07 Science Ws Ch17 01 MZrjoisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Tissues: Plant and Animal Tissues ExerciseDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - Tissues: Plant and Animal Tissues ExerciseArpan KaurNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Science - LightDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science - LightAnonymous JamqEgqqh1100% (2)
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Name: Class & Sec: DateDocument5 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Name: Class & Sec: DateSujay100% (1)
- Animal Kingdom PPT 3 - Class 9Document32 pagesAnimal Kingdom PPT 3 - Class 9vidushi rathi100% (1)
- Notes of CH 9 Heredity and Evolution Class 10th ScienceDocument17 pagesNotes of CH 9 Heredity and Evolution Class 10th SciencenabshanahshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Nutrition in Animals: Fill in The BlanksDocument1 pageChapter 2: Nutrition in Animals: Fill in The Blankssifat mongaNo ratings yet
- Psychology XII All PYQs & Previous SQPs @CUET - CBSE - 12thDocument122 pagesPsychology XII All PYQs & Previous SQPs @CUET - CBSE - 12th76kumarjatin100% (1)
- Topic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsDocument56 pagesTopic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsAhmed IqbalNo ratings yet
- UCTO-Sample-Papers-for-Class-6 CriticalthinkingDocument4 pagesUCTO-Sample-Papers-for-Class-6 CriticalthinkingSamiksha MahajanNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument25 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceSubrata MallickNo ratings yet
- Saraswati Vidya Niketan Human and Social Biology Name: Form: Instructions: Answer All Questions. Time: 30 MinsDocument2 pagesSaraswati Vidya Niketan Human and Social Biology Name: Form: Instructions: Answer All Questions. Time: 30 Minsnehru09No ratings yet
- 638dba179fd2e400bf4af02f - ## - The Fundamental Unit of Life: Class Notes - SprintDocument45 pages638dba179fd2e400bf4af02f - ## - The Fundamental Unit of Life: Class Notes - SprintShivam RajNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Chapter 2 - Nutrition in AnimalsDocument5 pagesClass 7 - Chapter 2 - Nutrition in AnimalskishanrwtNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce - Class 10th Science Study RankersDocument10 pagesNotes of CH 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce - Class 10th Science Study RankerssamyNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Document11 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Varshini PeraNo ratings yet
- 31 4 3 ScienceDocument24 pages31 4 3 ScienceTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 31 6 3 ScienceDocument32 pages31 6 3 ScienceTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 31 6 2 ScienceDocument32 pages31 6 2 ScienceTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 25Document11 pagesCbjescpu 25Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 12Document10 pagesCbjescpu 12Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 17Document11 pagesCbjescpu 17Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 05Document11 pagesCbjescpu 05Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 29Document12 pagesCbjescpu 29Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 11Document12 pagesCbjescpu 11Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 04Document10 pagesCbjescpu 04Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 23Document10 pagesCbjescpu 23Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 24Document10 pagesCbjescpu 24Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 21Document10 pagesCbjescpu 21Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 18Document10 pagesCbjescpu 18Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 13Document12 pagesCbjescpu 13Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 22Document9 pagesCbjescpu 22Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 19Document10 pagesCbjescpu 19Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 30Document10 pagesCbjescpu 30Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 09Document9 pagesCbjescpu 09Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 26Document12 pagesCbjescpu 26Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 28Document9 pagesCbjescpu 28Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 16Document13 pagesCbjescpu 16Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- FlowersDocument10 pagesFlowersAmina Zeghar BNo ratings yet
- Why Is Biodiversity ImportantDocument21 pagesWhy Is Biodiversity ImportantAishwarya BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Soal OSN Bhs Inggris Edisi 4Document3 pagesSoal OSN Bhs Inggris Edisi 4Anonymous QJNovaWNo ratings yet
- PSLE Science SketchnotesDocument75 pagesPSLE Science SketchnotesANGIE NGNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument13 pagesREPRODUCTIONDana HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment of Angiosperm PlantDocument4 pagesExperiment of Angiosperm Plantganu8950% (2)
- Ms PrincyMolAP PalynologyDocument100 pagesMs PrincyMolAP PalynologyRekha guptaNo ratings yet
- BotanyLessonSixrColor 1 5 13Document16 pagesBotanyLessonSixrColor 1 5 13Daniel AbadNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit 1 SpeedrunDocument178 pagesCape Biology Unit 1 SpeedrunBrado BradoNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKDocument16 pagesGrade 5 - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKMeera Joy Deboma Blanco100% (1)
- So Lesson Plan 2 TechnologyDocument22 pagesSo Lesson Plan 2 Technologyapi-309886906No ratings yet
- Nonfiction Reading Comprehension Test HummingbirdsDocument3 pagesNonfiction Reading Comprehension Test HummingbirdsPutri chanelNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Review 1st Endterm 23-24Document16 pagesScience 8 Review 1st Endterm 23-24johnvo31052010No ratings yet
- Beemaster's Beekeeping CourseDocument116 pagesBeemaster's Beekeeping Coursedvskiwi100% (4)
- Microfossils Description Paper: Palaeontology Practical: KalpanadekakalitaDocument32 pagesMicrofossils Description Paper: Palaeontology Practical: Kalpanadekakalitarikalave ramanNo ratings yet
- Compare The Features of Insect Pollinated and Wind Pollinated FlowerDocument1 pageCompare The Features of Insect Pollinated and Wind Pollinated Flowersuma deviNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science NotesDocument17 pagesIntegrated Science NotesannmarieNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Statics 4Th Edition Pytel Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesEngineering Mechanics Statics 4Th Edition Pytel Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFrichard.eis609100% (10)
- Xam Idea Biology Class 12Document517 pagesXam Idea Biology Class 12ssshuuushhhNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plant Life CycleDocument5 pagesFlowering Plant Life CycleTze XienNo ratings yet
- Pollination Drops, Pollen, and Insect Pollination of Mesozoic Gymnosperms 2007Document33 pagesPollination Drops, Pollen, and Insect Pollination of Mesozoic Gymnosperms 2007danytiNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants High Yield MCQs For NEETDocument11 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants High Yield MCQs For NEETruhaniarora222No ratings yet
- Sweet Potato SEM IndonesiaDocument8 pagesSweet Potato SEM IndonesiaGalhaadisNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerDocument7 pagesChapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Wild FlowersAn Aid To Knowledge of Our Wild Flowers and Their Insect Visitors by Blanchan, Neltje, 1865-1918Document330 pagesWild FlowersAn Aid To Knowledge of Our Wild Flowers and Their Insect Visitors by Blanchan, Neltje, 1865-1918Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Sksu Searice Terminal ReportDocument66 pagesSksu Searice Terminal ReportGAYATIN PRINCESS SHEINENo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) June 2011: International GCSE Biology (4BI0) Paper 1B Science Double Award (4SC0) Paper 1BDocument18 pagesMark Scheme (Results) June 2011: International GCSE Biology (4BI0) Paper 1B Science Double Award (4SC0) Paper 1BAbdulrahman AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Allergies Getting Worse Blame The Global Warming.Document2 pagesAllergies Getting Worse Blame The Global Warming.Daryl SeraficaNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Plants: Unit 3 - Science FusionDocument12 pagesLife Cycle of Plants: Unit 3 - Science FusionFebrymaria LimbongNo ratings yet
- Bee Pollen Benefits - Facts of Bee PollenDocument2 pagesBee Pollen Benefits - Facts of Bee PollenreenakotakNo ratings yet