Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design
Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design
Uploaded by
Michael ButlerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Fea Assignment - IDocument13 pagesFea Assignment - Isakthivel balamuruganNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis Questions OnlyDocument9 pagesFinite Element Analysis Questions OnlyAeronaughtycs Hamdan100% (1)
- Pet'n For Coroner's InquestDocument14 pagesPet'n For Coroner's InquestScott MagruderNo ratings yet
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument3 pagesEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Designselvithimmarajan@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Mtech. Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 pagesMtech. Finite Element Analysissimalaravi100% (2)
- Rr311403 Finite Element MethodDocument7 pagesRr311403 Finite Element MethodDestinifyd MydestinyNo ratings yet
- FEA Model PAperDocument6 pagesFEA Model PApersmg26thmayNo ratings yet
- Ed9221-Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design-R8Document2 pagesEd9221-Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design-R8Bakkiya RajNo ratings yet
- Me 2353 - Finite Element AnalysisDocument4 pagesMe 2353 - Finite Element AnalysiscprabhakaranNo ratings yet
- P.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya - 571 401Document2 pagesP.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya - 571 401coolmagaNo ratings yet
- 07a51402-Finite Element MethodsDocument8 pages07a51402-Finite Element Methodswebs6000No ratings yet
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument4 pagesEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods April May 2007 Question PaperDocument6 pagesFinite Element Methods April May 2007 Question PaperelimelekNo ratings yet
- r05311402 Finite Element MethodsDocument6 pagesr05311402 Finite Element MethodsSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Me, Ae, MSNT)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Me, Ae, MSNT)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Fea QP CT3Document2 pagesFea QP CT3yuvashreesharmiNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1Document31 pagesSet No. 1dodda12345No ratings yet
- Me6603 Fea Rejinpaul Iq Am19Document5 pagesMe6603 Fea Rejinpaul Iq Am19shivesh rockesNo ratings yet
- Question Paper CodeDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Codekarthikeyankv.mech DscetNo ratings yet
- Anna University Fea Question PaperDocument3 pagesAnna University Fea Question PaperAnand RasNo ratings yet
- Question Paper-1 - FEA Model ExamDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper-1 - FEA Model ExamS A ABDUL SUKKURNo ratings yet
- FEA Question BankDocument6 pagesFEA Question Bankmenmoli2012No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument21 pagesQuestion BankmoinNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis AE2351Document5 pagesFinite Element Analysis AE2351Aghil BuddyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To AE, MSNT, ME)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To AE, MSNT, ME)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Rr311403 Finite Element MethodDocument8 pagesRr311403 Finite Element MethodSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Gayatri Vidya Parishad College of Engineering (Autonomous)Document3 pagesGayatri Vidya Parishad College of Engineering (Autonomous)Lakshmi Ganesh SudikondaNo ratings yet
- 9A21701 Finite Element & Modeling MethodsDocument4 pages9A21701 Finite Element & Modeling MethodssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Fea Fm2018.711met03Document2 pagesFea Fm2018.711met03AC20UME061 Ragul vanthanNo ratings yet
- 09-Finite Element Analysis March 2010Document2 pages09-Finite Element Analysis March 2010simalaraviNo ratings yet
- Essay Questions FEMDocument21 pagesEssay Questions FEMharshamech360No ratings yet
- FEA TutorialsDocument14 pagesFEA Tutorialsbalusharma1212No ratings yet
- CAE Question Bank Unit 3Document4 pagesCAE Question Bank Unit 3Sandesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodsDocument12 pagesFinite Element Methodspraneeth4a100% (1)
- Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham: ME401 - Finite Element MethodsDocument2 pagesAmrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham: ME401 - Finite Element MethodsPramod GowdaNo ratings yet
- Q&a FeaDocument19 pagesQ&a FeaKishoreNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Venkat.G SuryaNo ratings yet
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument4 pagesEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignRajesh KannanNo ratings yet
- Vallurupalli Nageswara Rao Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDocument48 pagesVallurupalli Nageswara Rao Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering and TechnologyRathod VakilNo ratings yet
- FINITE ELEMENT METHODS - Model PaperDocument3 pagesFINITE ELEMENT METHODS - Model PaperUpendra NeravatiNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods: Code: ME7T3Document3 pagesFinite Element Methods: Code: ME7T3Radha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis 2010Document2 pagesFinite Element Analysis 2010simalaraviNo ratings yet
- Fea QBDocument11 pagesFea QBPradeepNo ratings yet
- III and IV UnitDocument3 pagesIII and IV Unitbalusharma1212No ratings yet
- Finite Element Model Question PaperDocument4 pagesFinite Element Model Question PaperSrinivasan SriniNo ratings yet
- Aae009 - Fem - Model Paper - IDocument6 pagesAae009 - Fem - Model Paper - IChekka SudheerNo ratings yet
- Fea Model - Iset IDocument3 pagesFea Model - Iset IKishoreNo ratings yet
- APRMAY18Document6 pagesAPRMAY18fantin amirtharajNo ratings yet
- RR410104-Finite Element MethodsDocument8 pagesRR410104-Finite Element MethodsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- ME 6603 Question Bank: Unit I - Introduction Part-A (2-Marks)Document6 pagesME 6603 Question Bank: Unit I - Introduction Part-A (2-Marks)Bharathi KannaNo ratings yet
- rr420302 Finite Element MethodsDocument7 pagesrr420302 Finite Element MethodsSrinivasa Rao G100% (3)
- A0404 - Finite Element AnalysisDocument2 pagesA0404 - Finite Element Analysishari0118No ratings yet
- Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 pagesFinite Element Analysiskumbharashish37No ratings yet
- QBank FEMDocument12 pagesQBank FEMShivam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Jalpaiguri Government Engineering College COE/B.TECH./ ME /ME605A/2017-18 2018 Finite Element MethodsDocument2 pagesJalpaiguri Government Engineering College COE/B.TECH./ ME /ME605A/2017-18 2018 Finite Element Methodsaarav aggarwalNo ratings yet
- R7410303-Finite Element MethodsDocument4 pagesR7410303-Finite Element MethodssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Practical Finite Element Modeling in Earth Science using MatlabFrom EverandPractical Finite Element Modeling in Earth Science using MatlabNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- Pawan Puthra To Swabhumi 2Document1 pagePawan Puthra To Swabhumi 2Michael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Ranchi To JamshedpurDocument3 pagesRanchi To JamshedpurMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Program To AirportDocument3 pagesProgram To AirportMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Chennai Institute of Technology: Robotics and AutomationDocument2 pagesChennai Institute of Technology: Robotics and AutomationMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Pawan Puthra To SwabhumiDocument1 pagePawan Puthra To SwabhumiMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Sarathy Nagar, Pudupedu, Chennai - 600 069. 18/10/2016 100 Marks Me6501 Computer Aided Design 3 Hrs MechanicalDocument2 pagesSarathy Nagar, Pudupedu, Chennai - 600 069. 18/10/2016 100 Marks Me6501 Computer Aided Design 3 Hrs MechanicalMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Name ListDocument1 pageName ListMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Me 6501 Computer Aided Design BRANCH: Mechanical Department Year / Sem: III / VDocument3 pagesMe 6501 Computer Aided Design BRANCH: Mechanical Department Year / Sem: III / VMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering May June 2013 Question PaperDocument2 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering May June 2013 Question PaperMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- B-Tech. Mechanical UNIT-1: Bme 206 Manufacturing Technology - 1Document6 pagesB-Tech. Mechanical UNIT-1: Bme 206 Manufacturing Technology - 1Michael ButlerNo ratings yet
- ME 2253 Nov - Dec 2011Document3 pagesME 2253 Nov - Dec 2011Michael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument4 pagesEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- PPC Question BankDocument4 pagesPPC Question BankMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii Engine Exhaust Emission ControlDocument46 pagesUnit - Iii Engine Exhaust Emission ControlMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii Engine Exhaust Emission ControlDocument46 pagesUnit - Iii Engine Exhaust Emission ControlMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Emily DickinsonDocument3 pagesEmily DickinsonAnthony RivasNo ratings yet
- Response Sheet For SCQDocument7 pagesResponse Sheet For SCQChandresh Gambhir100% (1)
- The Role of Nursing Informatics On Promoting Quality of Health Care and The Need For Appropriate EducationDocument7 pagesThe Role of Nursing Informatics On Promoting Quality of Health Care and The Need For Appropriate EducationBasrin NasirinNo ratings yet
- The Great DictatorDocument2 pagesThe Great DictatoralmariveraNo ratings yet
- 1960s To Present Day Fashion HistoryDocument45 pages1960s To Present Day Fashion HistoryAreda100% (1)
- English 8 Course OutlineDocument7 pagesEnglish 8 Course OutlineYhel LantionNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Atrophaeus: (Atcc 9372™)Document2 pagesBacillus Atrophaeus: (Atcc 9372™)lenongnikaimutNo ratings yet
- Code VBA Untuk Gerak ShapesDocument4 pagesCode VBA Untuk Gerak Shapesamirlatip76No ratings yet
- Dairy Management Dr.a.deyDocument45 pagesDairy Management Dr.a.deyavijitcirbNo ratings yet
- Duty To ReportDocument3 pagesDuty To ReportJeffrey FawcettNo ratings yet
- Et 101 (B)Document5 pagesEt 101 (B)PUSHPA SAININo ratings yet
- Present Simple 1Document5 pagesPresent Simple 1Luis FelipeNo ratings yet
- The Architects of Islamic CivilizationDocument372 pagesThe Architects of Islamic Civilizationlazut273No ratings yet
- Sirs & ModsDocument26 pagesSirs & Modsnerlyn silao50% (2)
- Wade 1Document3 pagesWade 1api-609396716No ratings yet
- How To Use Friends As A Reference (Plus How To Ask Them)Document6 pagesHow To Use Friends As A Reference (Plus How To Ask Them)josieliraychanNo ratings yet
- TeratomaDocument13 pagesTeratomaGoncang Setyo PambudiNo ratings yet
- 118ConvoList 16.06.2021Document6,661 pages118ConvoList 16.06.2021Sandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Notes On Religious Knowledge Systems (Part 2)Document4 pagesNotes On Religious Knowledge Systems (Part 2)xNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1: NAME: Zariq Ahmed KhanDocument15 pagesAssignment # 1: NAME: Zariq Ahmed KhanSha KhNo ratings yet
- Bryan Hloom: Address: 1234 Park Avenue, Redwood City, CA 94063Document2 pagesBryan Hloom: Address: 1234 Park Avenue, Redwood City, CA 94063aykutNo ratings yet
- Problems of Parenthood + Leadership Functions + Security Tips in The SchoolDocument8 pagesProblems of Parenthood + Leadership Functions + Security Tips in The SchoolAminu SaniNo ratings yet
- Sample of Equipment ProposalDocument2 pagesSample of Equipment ProposalJeasa Mae Jagonia MiñozaNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Latihan Peregangan Terhadap PenDocument20 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Latihan Peregangan Terhadap PenBang DeanNo ratings yet
- Lebato-Pr2Document6 pagesLebato-Pr2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument1 pageReaction PaperMarie SollanoNo ratings yet
- (1900) The Game Birds and Wild Fowl of The British IslesDocument594 pages(1900) The Game Birds and Wild Fowl of The British IslesHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (2)
- From Court of Dar Es at Kisutu in Civil Application No. 107 2022)Document17 pagesFrom Court of Dar Es at Kisutu in Civil Application No. 107 2022)Emmanuel ShekifuNo ratings yet
- Discworld - One in A Million - 2nd Edition - LowRes PDFDocument27 pagesDiscworld - One in A Million - 2nd Edition - LowRes PDFjordi-timonNo ratings yet
Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design
Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design
Uploaded by
Michael ButlerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design
Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design
Uploaded by
Michael ButlerCopyright:
Available Formats
Reg. No.
Question Paper Code :
77708
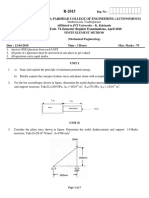
M.E. DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY 2011 Second Semester Engineering Design
ED 9221 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS IN MECHANICAL DESIGN (Common to M.E. Computer Aided Design and M.E. Product Design and Development) Time : Three hours Answer ALL questions Maximum : 100 marks
PART A (10 2 = 20 marks) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is the essence of finite element method?
What is the need to perform a patch test? How is it done? Mention the basic steps of Galerkins method.
Distinguish between one dimensional and two dimensional elements. Specify the Jacobian matrix for CST element. What is a Mindlin plate element? Specify the mass matrix for a truss element having four degrees of freedom. State the required condition for solving dynamic problems as specified by characteristic polynomial method. Mention two examples for contact non-linearity. State the essential difference between nonlinear elastic material and elasticplastic material.
21
9. 10.
21
21
PART B (5 16 = 80 marks) 11. (a) Using direct method, formulate the stiffness matrix for a simple plane beam element. Or (b)
A horizontal rod (E = l, A = 1, L = l) fixed at both ends is subjected to an axially varying body force, f = x3 N/m. Using a quadratic displacement
(All the quantities have units which must be taken suitably). 12. (a)
Describe Galerkins method of formulation for solving a one dimensional structural problem with an illustrative example. Or
(b)
Establish the shape functions for the eight node quadrilateral element belonging to serendipity family.
Evaluate the stress at the centroid of the element, assuming plane stress condition. Take Youngs modulus and Poissons ratio as 30 106 N/m2 and 0.3 respectively.
(b)
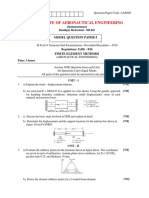
For a one dimensional composite bar shown in Fig. 1, determine the interface temperatures. For element 1, let Kxx = 200W/mC; for element 2, let Kxx = 100 W/mC; and for element 3, let Kxx = 50W//mC; Let A = 0.1m2. The left end has a constant temperature of 100C and the right end has a constant temperature of 300C.
21 4
4
Or Fig. 1 2
21
13.
(a)
A rectangular element is defined by nodal coordinates (in m) as 1(0,0), 2(2,0), 3(2,2) and 4(0,2). The nodal displacement vector is given by q = [0,0,0.002,0.003,0.006,0.0032,0,0]T.
field, determine the displacement u(x) and stress (x) in the rod.
21
77708
14.
(a)
A pin jointed truss defined by coordinates P (0,0), Q(1000,0) and R(500, 1700) is fixed at P and Q. The links are of 8 mm diameter and made of steel (E = 2 105 N/mm2, density = 7800 kg/m3). Using the lumped mass matrix, determine the natural frequencies of the truss. Or
15.
(a)
Explain, with examples, the solution algorithms for performing non-linear analysis. Or
(b)
Explain stress stiffening and its use in linear buckling analysis and non-linear analysis.
21
3
4
77708
21
(b)
Explain the central difference method for determining the transient dynamic response of a structure.
21
You might also like
- Fea Assignment - IDocument13 pagesFea Assignment - Isakthivel balamuruganNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis Questions OnlyDocument9 pagesFinite Element Analysis Questions OnlyAeronaughtycs Hamdan100% (1)
- Pet'n For Coroner's InquestDocument14 pagesPet'n For Coroner's InquestScott MagruderNo ratings yet
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument3 pagesEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Designselvithimmarajan@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Mtech. Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 pagesMtech. Finite Element Analysissimalaravi100% (2)
- Rr311403 Finite Element MethodDocument7 pagesRr311403 Finite Element MethodDestinifyd MydestinyNo ratings yet
- FEA Model PAperDocument6 pagesFEA Model PApersmg26thmayNo ratings yet
- Ed9221-Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design-R8Document2 pagesEd9221-Finite Element Methods in Mechanical Design-R8Bakkiya RajNo ratings yet
- Me 2353 - Finite Element AnalysisDocument4 pagesMe 2353 - Finite Element AnalysiscprabhakaranNo ratings yet
- P.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya - 571 401Document2 pagesP.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya - 571 401coolmagaNo ratings yet
- 07a51402-Finite Element MethodsDocument8 pages07a51402-Finite Element Methodswebs6000No ratings yet
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument4 pagesEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods April May 2007 Question PaperDocument6 pagesFinite Element Methods April May 2007 Question PaperelimelekNo ratings yet
- r05311402 Finite Element MethodsDocument6 pagesr05311402 Finite Element MethodsSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Me, Ae, MSNT)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Me, Ae, MSNT)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Fea QP CT3Document2 pagesFea QP CT3yuvashreesharmiNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1Document31 pagesSet No. 1dodda12345No ratings yet
- Me6603 Fea Rejinpaul Iq Am19Document5 pagesMe6603 Fea Rejinpaul Iq Am19shivesh rockesNo ratings yet
- Question Paper CodeDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Codekarthikeyankv.mech DscetNo ratings yet
- Anna University Fea Question PaperDocument3 pagesAnna University Fea Question PaperAnand RasNo ratings yet
- Question Paper-1 - FEA Model ExamDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper-1 - FEA Model ExamS A ABDUL SUKKURNo ratings yet
- FEA Question BankDocument6 pagesFEA Question Bankmenmoli2012No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument21 pagesQuestion BankmoinNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis AE2351Document5 pagesFinite Element Analysis AE2351Aghil BuddyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To AE, MSNT, ME)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To AE, MSNT, ME)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Rr311403 Finite Element MethodDocument8 pagesRr311403 Finite Element MethodSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Gayatri Vidya Parishad College of Engineering (Autonomous)Document3 pagesGayatri Vidya Parishad College of Engineering (Autonomous)Lakshmi Ganesh SudikondaNo ratings yet
- 9A21701 Finite Element & Modeling MethodsDocument4 pages9A21701 Finite Element & Modeling MethodssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Fea Fm2018.711met03Document2 pagesFea Fm2018.711met03AC20UME061 Ragul vanthanNo ratings yet
- 09-Finite Element Analysis March 2010Document2 pages09-Finite Element Analysis March 2010simalaraviNo ratings yet
- Essay Questions FEMDocument21 pagesEssay Questions FEMharshamech360No ratings yet
- FEA TutorialsDocument14 pagesFEA Tutorialsbalusharma1212No ratings yet
- CAE Question Bank Unit 3Document4 pagesCAE Question Bank Unit 3Sandesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodsDocument12 pagesFinite Element Methodspraneeth4a100% (1)
- Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham: ME401 - Finite Element MethodsDocument2 pagesAmrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham: ME401 - Finite Element MethodsPramod GowdaNo ratings yet
- Q&a FeaDocument19 pagesQ&a FeaKishoreNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Venkat.G SuryaNo ratings yet
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument4 pagesEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignRajesh KannanNo ratings yet
- Vallurupalli Nageswara Rao Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDocument48 pagesVallurupalli Nageswara Rao Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering and TechnologyRathod VakilNo ratings yet
- FINITE ELEMENT METHODS - Model PaperDocument3 pagesFINITE ELEMENT METHODS - Model PaperUpendra NeravatiNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods: Code: ME7T3Document3 pagesFinite Element Methods: Code: ME7T3Radha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis 2010Document2 pagesFinite Element Analysis 2010simalaraviNo ratings yet
- Fea QBDocument11 pagesFea QBPradeepNo ratings yet
- III and IV UnitDocument3 pagesIII and IV Unitbalusharma1212No ratings yet
- Finite Element Model Question PaperDocument4 pagesFinite Element Model Question PaperSrinivasan SriniNo ratings yet
- Aae009 - Fem - Model Paper - IDocument6 pagesAae009 - Fem - Model Paper - IChekka SudheerNo ratings yet
- Fea Model - Iset IDocument3 pagesFea Model - Iset IKishoreNo ratings yet
- APRMAY18Document6 pagesAPRMAY18fantin amirtharajNo ratings yet
- RR410104-Finite Element MethodsDocument8 pagesRR410104-Finite Element MethodsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- ME 6603 Question Bank: Unit I - Introduction Part-A (2-Marks)Document6 pagesME 6603 Question Bank: Unit I - Introduction Part-A (2-Marks)Bharathi KannaNo ratings yet
- rr420302 Finite Element MethodsDocument7 pagesrr420302 Finite Element MethodsSrinivasa Rao G100% (3)
- A0404 - Finite Element AnalysisDocument2 pagesA0404 - Finite Element Analysishari0118No ratings yet
- Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 pagesFinite Element Analysiskumbharashish37No ratings yet
- QBank FEMDocument12 pagesQBank FEMShivam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Jalpaiguri Government Engineering College COE/B.TECH./ ME /ME605A/2017-18 2018 Finite Element MethodsDocument2 pagesJalpaiguri Government Engineering College COE/B.TECH./ ME /ME605A/2017-18 2018 Finite Element Methodsaarav aggarwalNo ratings yet
- R7410303-Finite Element MethodsDocument4 pagesR7410303-Finite Element MethodssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Practical Finite Element Modeling in Earth Science using MatlabFrom EverandPractical Finite Element Modeling in Earth Science using MatlabNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- Pawan Puthra To Swabhumi 2Document1 pagePawan Puthra To Swabhumi 2Michael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Ranchi To JamshedpurDocument3 pagesRanchi To JamshedpurMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Program To AirportDocument3 pagesProgram To AirportMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Chennai Institute of Technology: Robotics and AutomationDocument2 pagesChennai Institute of Technology: Robotics and AutomationMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Pawan Puthra To SwabhumiDocument1 pagePawan Puthra To SwabhumiMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Sarathy Nagar, Pudupedu, Chennai - 600 069. 18/10/2016 100 Marks Me6501 Computer Aided Design 3 Hrs MechanicalDocument2 pagesSarathy Nagar, Pudupedu, Chennai - 600 069. 18/10/2016 100 Marks Me6501 Computer Aided Design 3 Hrs MechanicalMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Name ListDocument1 pageName ListMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Me 6501 Computer Aided Design BRANCH: Mechanical Department Year / Sem: III / VDocument3 pagesMe 6501 Computer Aided Design BRANCH: Mechanical Department Year / Sem: III / VMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering May June 2013 Question PaperDocument2 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering May June 2013 Question PaperMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- B-Tech. Mechanical UNIT-1: Bme 206 Manufacturing Technology - 1Document6 pagesB-Tech. Mechanical UNIT-1: Bme 206 Manufacturing Technology - 1Michael ButlerNo ratings yet
- ME 2253 Nov - Dec 2011Document3 pagesME 2253 Nov - Dec 2011Michael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument4 pagesEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- PPC Question BankDocument4 pagesPPC Question BankMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii Engine Exhaust Emission ControlDocument46 pagesUnit - Iii Engine Exhaust Emission ControlMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii Engine Exhaust Emission ControlDocument46 pagesUnit - Iii Engine Exhaust Emission ControlMichael ButlerNo ratings yet
- Emily DickinsonDocument3 pagesEmily DickinsonAnthony RivasNo ratings yet
- Response Sheet For SCQDocument7 pagesResponse Sheet For SCQChandresh Gambhir100% (1)
- The Role of Nursing Informatics On Promoting Quality of Health Care and The Need For Appropriate EducationDocument7 pagesThe Role of Nursing Informatics On Promoting Quality of Health Care and The Need For Appropriate EducationBasrin NasirinNo ratings yet
- The Great DictatorDocument2 pagesThe Great DictatoralmariveraNo ratings yet
- 1960s To Present Day Fashion HistoryDocument45 pages1960s To Present Day Fashion HistoryAreda100% (1)
- English 8 Course OutlineDocument7 pagesEnglish 8 Course OutlineYhel LantionNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Atrophaeus: (Atcc 9372™)Document2 pagesBacillus Atrophaeus: (Atcc 9372™)lenongnikaimutNo ratings yet
- Code VBA Untuk Gerak ShapesDocument4 pagesCode VBA Untuk Gerak Shapesamirlatip76No ratings yet
- Dairy Management Dr.a.deyDocument45 pagesDairy Management Dr.a.deyavijitcirbNo ratings yet
- Duty To ReportDocument3 pagesDuty To ReportJeffrey FawcettNo ratings yet
- Et 101 (B)Document5 pagesEt 101 (B)PUSHPA SAININo ratings yet
- Present Simple 1Document5 pagesPresent Simple 1Luis FelipeNo ratings yet
- The Architects of Islamic CivilizationDocument372 pagesThe Architects of Islamic Civilizationlazut273No ratings yet
- Sirs & ModsDocument26 pagesSirs & Modsnerlyn silao50% (2)
- Wade 1Document3 pagesWade 1api-609396716No ratings yet
- How To Use Friends As A Reference (Plus How To Ask Them)Document6 pagesHow To Use Friends As A Reference (Plus How To Ask Them)josieliraychanNo ratings yet
- TeratomaDocument13 pagesTeratomaGoncang Setyo PambudiNo ratings yet
- 118ConvoList 16.06.2021Document6,661 pages118ConvoList 16.06.2021Sandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Notes On Religious Knowledge Systems (Part 2)Document4 pagesNotes On Religious Knowledge Systems (Part 2)xNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1: NAME: Zariq Ahmed KhanDocument15 pagesAssignment # 1: NAME: Zariq Ahmed KhanSha KhNo ratings yet
- Bryan Hloom: Address: 1234 Park Avenue, Redwood City, CA 94063Document2 pagesBryan Hloom: Address: 1234 Park Avenue, Redwood City, CA 94063aykutNo ratings yet
- Problems of Parenthood + Leadership Functions + Security Tips in The SchoolDocument8 pagesProblems of Parenthood + Leadership Functions + Security Tips in The SchoolAminu SaniNo ratings yet
- Sample of Equipment ProposalDocument2 pagesSample of Equipment ProposalJeasa Mae Jagonia MiñozaNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Latihan Peregangan Terhadap PenDocument20 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Latihan Peregangan Terhadap PenBang DeanNo ratings yet
- Lebato-Pr2Document6 pagesLebato-Pr2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument1 pageReaction PaperMarie SollanoNo ratings yet
- (1900) The Game Birds and Wild Fowl of The British IslesDocument594 pages(1900) The Game Birds and Wild Fowl of The British IslesHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (2)
- From Court of Dar Es at Kisutu in Civil Application No. 107 2022)Document17 pagesFrom Court of Dar Es at Kisutu in Civil Application No. 107 2022)Emmanuel ShekifuNo ratings yet
- Discworld - One in A Million - 2nd Edition - LowRes PDFDocument27 pagesDiscworld - One in A Million - 2nd Edition - LowRes PDFjordi-timonNo ratings yet