Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Load Cases For Typical Piping System Using CAESAR II
Load Cases For Typical Piping System Using CAESAR II
Uploaded by
sj22Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Load Cases For Typical Piping System Using CAESAR II
Load Cases For Typical Piping System Using CAESAR II
Uploaded by
sj22Copyright:
Available Formats
Main objectives of stress analysis is to ensure A.
Structural Integrity (Design adequacy for the pressure of the carrying fluid,Failure against various loading in the life cycle and i!iting stresses belo" code allo"able.# $. %perational Integrity ( i!iting no&&le loads of the connected equip!ent "ithin allo"able values, Avoiding lea'age at joints, i!iting sagging ( displace!ent "ithin allo"able values.# ). %pti!al Design (Avoiding e*cessive fle*ibility and also high loads on supporting structures. Ai! to"ards an opti!al design for both piping and structure.# +o !eet these objectives several load cases are required during stress analysis. +his article "ill guide all the beginners "ith the !ethodology to build several load cases "hich "ill be required for stress analysis. In this article "e "ill use follo"ing notations for building load cases, -- . "ater filled "eight of piping syste!, /0 . /ydrotest 0ressure, - . "eight of pipe including content and insulation, 01 . Internal Design pressure, +1 . %perating te!perature, +2 . Ma*i!u! te!perature, +3 . Mini!u! te!perature, -I41, -I42, -I43 A4D -I45, "ind loads acting in so!e specific direction, 61, 62, 63 A4D 65, unifor! (seis!ic# loads acting in so!e specific direction. -hile analysis at a !ini!u! the stress chec' is required for the belo" !entioned cases, a. Hydrotesting case: 0ipelines are nor!ally hydrotested before actual operation to ensure absence of lea'age. -ater is used as the testing !ediu!. So during this situation pipe "ill be subjected to "ater "eight and hydrotest pressure. Accordingly our first load case in )aesar II "ill be as !entioned belo" 1. --7/0 /8D
b. Operating case: -hen operation starts "or'ing fluid "ill flo" through the piping at a te!perature and pressure. So accordingly our operating load cases "ill be as !entioned belo",
2. 3. 5.
-7+1701 -7+2701 -7+3701
%09 %09 %09
for operating te!perature case for !a*i!u! syste! te!perature case for !ini!u! syste! te!perature case
c. Sustained Case: Sustained loads "ill e*ist throughout the plant operation. -eight and pressure are 'no"n as sustained loads. So our sustained load case "ill be as follo"s, :. -701 S6S
d. Occasional Cases: 0iping !ay be subjected to occassional "ind and seis!ic forces. So to chec' stresses in those situations "e have to build the follo"ing load cases, ;. =. ?. @. 1A. 11. 12 13 -7+17017-I41 -7+17017-I42 -7+17017-I43 -7+17017-I45 -7+1701761 -7+1701>61 -7+1701762 -7+1701>62 %09 %09 %09 %09 %09 %09 %09 %09 )onsidering "ind fro! 7< direction )onsidering "ind fro! >< direction )onsidering "ind fro! 7& direction )onsidering "ind fro! 7& direction )onsidering seis!ic fro! 7< direction )onsidering seis!ic fro! 7< direction )onsidering seis!ic fro! 7< direction )onsidering seis!ic fro! 7< direction
-hile stress analysis the above load cases for! load case ; to load case 13 is generated only to chec' loads at node points. +o find occasional stresses "e need to add pure occassional cases "ith sustained load and then co!pare "ith code allo"able values. Follo"ing sets of load cases are built for that purpose. 15. ;> 2 %)) 0ure "ind fro! 7< direction 1:. => 2 %)) 0ure "ind fro! >< direction 1;. ?> 2 %)) 0ure "ind fro! 7& direction 1=. @> 2 %)) 0ure "ind fro! >& direction 1?. 1A> 2 %)) 0ure seis!ic fro! 7< direction 1@. 11> 2 %)) 0ure seis!ic fro! >< direction 2A. 12> 2 %)) 0ure seis!ic fro! 7& direction 21. 13> 2 %)) 0ure seis!ic fro! >& direction 22. 157 : %)) 0ure "ind7Sustained 23. 1:7 : %)) 0ure "ind7Sustained 25. 1;7 : %)) 0ure "ind7Sustained 2:. 1=7 : %)) 0ure "ind7Sustained 2;. 1?7 : %)) 0ure seis!ic7Sustained 2=. 1@7 : %)) 0ure seis!ic7Sustained 2?. 2A7 : %)) 0ure seis!ic7Sustained 2@. 217 : %)) 0ure seis!ic7Sustained oad cases fro! 22 to 2@ "ill be used for chec'ing occasional stresses "ith respect to code $ 31.3 allo"able (.1.33 ti!es Sh value fro! code#. 6se scalar co!bination for load cases 22 to 2@ above and algebraic co!bination for others as sho"n in figure attached belo",
e. Expansion Case: Follo"ing load cases are required for chec'ing e*pansion stress range as per code 3A. 31. 32. 33. 2> 3> 5> 3> : : : 5 9<0 9<0 9<0 9<0
for co!plete stress range
+he above load cases (fro! 3A to 33# are used to chec' e*pansion stress +he above !entioned load cases are !ini!u! required load cases to analysis any stress syste!. %ut of the above load cases the load cases !entioned in point nu!ber 1, :, and 22>33 are used for stress chec'. And load cases !entioned in point nu!ber 1 to 13 are used for chec'ing restraint forces, displace!ents and no&&le load chec'ing. Fe" additional load cases !ay be required for 0SB connected syste!s, Cotary equip!ent connected syste!s. Seis!ic and -ind analysis !ay not be required every ti!e. So those load cases can be deleted if the piping syste! does not fall under the purvie" of seis!ic and "ind analysis by project specification. /o"ever to perfor! "ind and seis!ic analysis proper related data !ust have to be entered in )aesar II spreadsheet (-ill be discussed in !y future posts#. If the stress syste! involves use of i!posed displace!ents (D# and forces (F# then those have to be added "ith the above load cases in the for! of D1, D2 or F1, F2 as applicable.
It is a better practice to keep 1. Hydro and sustained stresses below 60 o! code allowable o! code allowable
". Expansion and occasional stresses below #0
$. Sustained sagging below 10 %% !or process lines and below $ %% !or stea%& two p'ase and !lare lines (. )esign*+axi%u% displace%ent below ,- %% !or unit piping and below "00 %% in rack piping.
You might also like
- FM 1614 FRC Pipe and Fittings For UG FP Service 2017Document28 pagesFM 1614 FRC Pipe and Fittings For UG FP Service 2017andyNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between B31.3 & en 13480Document84 pagesComparison Between B31.3 & en 13480sj2283% (6)
- Flare Line Stress AnalysisDocument7 pagesFlare Line Stress Analysisdhurjatibhutesh100% (1)
- 4PH1 2PR Rms 20200305 PDFDocument13 pages4PH1 2PR Rms 20200305 PDFNairit67% (3)
- Load CombinationsDocument3 pagesLoad Combinationserikoh100% (1)
- Must Have Load Cases For Stress Analysis of A Typical Piping System Using Caesar IIDocument4 pagesMust Have Load Cases For Stress Analysis of A Typical Piping System Using Caesar IIKaliya Perumal100% (3)
- Fatigue Analysis in Caesar IIDocument4 pagesFatigue Analysis in Caesar IIsj22100% (2)
- Load CasesDocument15 pagesLoad CasesVishnu Menon100% (2)
- Column Piping Stress AnalysisDocument6 pagesColumn Piping Stress Analysissj22No ratings yet
- Dynamic Load in Piping SystemDocument3 pagesDynamic Load in Piping SystemAMITDEWANGAN1991100% (1)
- How To Export - Import Displacement File From - Into CAESAR IIDocument4 pagesHow To Export - Import Displacement File From - Into CAESAR IIGem GemNo ratings yet
- Piping Stress Analysis Pipeline System in Offshore PlatformDocument2 pagesPiping Stress Analysis Pipeline System in Offshore Platformgpskumar22100% (1)
- CAESAR II Software BasicsDocument28 pagesCAESAR II Software Basicsanishsr100% (1)
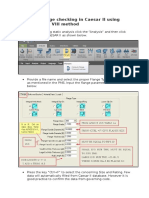
- Step by Step Methods For WRC 107 and WRC 297 Checking in Caesar IIDocument13 pagesStep by Step Methods For WRC 107 and WRC 297 Checking in Caesar IIMiguel Dominguez100% (1)
- Pipe Stresses and B31.3 Effects of Pipe StressDocument22 pagesPipe Stresses and B31.3 Effects of Pipe Stress20jose12luis100% (1)
- Algebraic and ScalarDocument4 pagesAlgebraic and Scalardtr17No ratings yet
- Jacketed PipingDocument4 pagesJacketed Pipingbinukumar100100% (1)
- Fatigue Analysis W - CIIDocument10 pagesFatigue Analysis W - CIInaeand100% (1)
- Pipe Stress AnalysisDocument15 pagesPipe Stress Analysispvmsson100% (1)
- Acoustic Pipe SupportsDocument6 pagesAcoustic Pipe Supportsnamdq-1No ratings yet
- Trunnion Checking or Dummy Checking During Stress Analysis of A Piping SystemDocument2 pagesTrunnion Checking or Dummy Checking During Stress Analysis of A Piping SystemAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nozzle LoadDocument8 pagesNozzle LoadDam VoNo ratings yet
- Flare PipingDocument1 pageFlare Pipingsenthilask_81No ratings yet
- Harmonic Analysis REV. 1Document7 pagesHarmonic Analysis REV. 1Amro SalahNo ratings yet
- Modeling Procedure of Rigid Strut in Caesar IIDocument5 pagesModeling Procedure of Rigid Strut in Caesar IIHmd MokhtariNo ratings yet
- Zinq - AnalysisDocument116 pagesZinq - AnalysisAimiNo ratings yet
- Slug Flow Analysis Using Dynamic Spectrum Method in Caesar IIDocument7 pagesSlug Flow Analysis Using Dynamic Spectrum Method in Caesar IIJ A S JAS100% (1)
- 01 E02STB007-W146693-03-0 - BC - Stress UpdateDocument1 page01 E02STB007-W146693-03-0 - BC - Stress Update86tejas100% (1)
- Nozzle Loads - Part 1 - Piping-EngineeringDocument5 pagesNozzle Loads - Part 1 - Piping-EngineeringShaikh Aftab100% (1)
- Pipeline Stress Analysis With Caesar IIDocument16 pagesPipeline Stress Analysis With Caesar IISharbel WgNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Training - Caesar IIDocument2 pagesStress Analysis Training - Caesar IIKehinde Adebayo100% (2)
- Bourdon Effect in CAESAR II: Intergraph CASDocument3 pagesBourdon Effect in CAESAR II: Intergraph CASAnonymous Iev5ggSR100% (2)
- Load Cases in CAESARDocument1 pageLoad Cases in CAESARmasoud132No ratings yet
- Fatigue Analysis Using CAESAR IIDocument7 pagesFatigue Analysis Using CAESAR IIayounga100% (1)
- What Is A Piping System?Document20 pagesWhat Is A Piping System?SARA VijayNo ratings yet
- Expansion Loop IDocument50 pagesExpansion Loop IDar Fall100% (1)
- CEASAR and PDMS SoftwareDocument10 pagesCEASAR and PDMS Softwarehayatmdazhar100% (1)
- Case Study For Fatigue Analysis in Caesar IIDocument3 pagesCase Study For Fatigue Analysis in Caesar IIamlanfacebookNo ratings yet
- How Do You Carry Out Estimation? Ans: 1. Input From BidDocument21 pagesHow Do You Carry Out Estimation? Ans: 1. Input From BidSunil ShaNo ratings yet
- Sample CalculationDocument35 pagesSample CalculationYoesbar Sofyan100% (1)
- Snubber Modelling in Caesar IIDocument2 pagesSnubber Modelling in Caesar IISamNo ratings yet
- Snubber Modelling in Caesar IIDocument2 pagesSnubber Modelling in Caesar IIanup15balagarhNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Thermal Movement and Evaluation Sheet For VesselDocument27 pagesNozzle Thermal Movement and Evaluation Sheet For VesselJ A S JASNo ratings yet
- Stress QuizDocument8 pagesStress QuizNagarjuna Seella100% (1)
- The Art of Designing Pipe Support SystemsDocument6 pagesThe Art of Designing Pipe Support Systemsguluu100% (1)
- Check List For General Arrangement DrawingsDocument1 pageCheck List For General Arrangement DrawingsenjoygurujiNo ratings yet
- 14.experimental and Stress Analysis of Pipe Routing at Various Temperature and Pressure by Changing The Various Material and SupportDocument54 pages14.experimental and Stress Analysis of Pipe Routing at Various Temperature and Pressure by Changing The Various Material and Supporteshu100% (2)
- Flare Piping Stress NalysisDocument7 pagesFlare Piping Stress Nalysisgpskumar22100% (1)
- Basics For Stress Analysis of Underground Piping Using Caesar IIDocument4 pagesBasics For Stress Analysis of Underground Piping Using Caesar IIzektor_angel100% (1)
- StressISO TroubleshootingDocument31 pagesStressISO TroubleshootingDarren Kam100% (1)
- Overview of GRP PipesDocument14 pagesOverview of GRP PipesMD IBRARNo ratings yet
- CAESAR II NonconvergenceDocument11 pagesCAESAR II NonconvergenceJohn Brindley100% (1)
- Flange Leakage Checking in Caesar II Using ASME Section VIII MethodDocument6 pagesFlange Leakage Checking in Caesar II Using ASME Section VIII Methodwisesa100% (1)
- The Basics of Pipe Thermal ExpansionDocument7 pagesThe Basics of Pipe Thermal Expansionmohdnazir100% (1)
- Procedure For Column Line Stress AnalysisDocument6 pagesProcedure For Column Line Stress AnalysisNilesh Gohel100% (1)
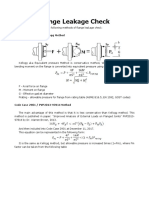
- Flange Leakage Check: Equivalent Pressure / Kellogg MethodDocument3 pagesFlange Leakage Check: Equivalent Pressure / Kellogg Methodtom hNo ratings yet
- Example From Theory To Caesar II PDFDocument12 pagesExample From Theory To Caesar II PDFIskandar Hasibuan100% (1)
- SIF Calculation For Piping ConnectionsDocument6 pagesSIF Calculation For Piping ConnectionsManuel100% (1)
- Jacketed Piping CalculationDocument9 pagesJacketed Piping CalculationKamran Shaikh0% (1)
- 01 - Chapter 1Document37 pages01 - Chapter 1Eko Idris Hutagaol100% (1)
- Metal Valves & Pipe Fittings World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandMetal Valves & Pipe Fittings World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- ST LLC 0702 PresDocument65 pagesST LLC 0702 PresSubhadip SadhukhanNo ratings yet
- Pressure Test in Piping Systems - Hydro and Pneumatic TestsDocument3 pagesPressure Test in Piping Systems - Hydro and Pneumatic Testssj22No ratings yet
- Basics of Pipe Stress AnalysisDocument7 pagesBasics of Pipe Stress Analysissj22No ratings yet
- Fatigue Analysis in Caesar IIDocument4 pagesFatigue Analysis in Caesar IIsj22100% (2)
- Load Cases in Caesar IIDocument4 pagesLoad Cases in Caesar IIsj22No ratings yet
- Pump Piping AnalysisDocument5 pagesPump Piping Analysissj22No ratings yet
- Column Piping Stress AnalysisDocument6 pagesColumn Piping Stress Analysissj22No ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of PSV Connected Piping1Document5 pagesStress Analysis of PSV Connected Piping1sj22100% (1)
- Sample Spring Data Sheet1Document1 pageSample Spring Data Sheet1sj22No ratings yet
- SnubbersDocument1 pageSnubberssj22No ratings yet
- Seismic Data Requirement As Per Different CodesDocument1 pageSeismic Data Requirement As Per Different Codessj22No ratings yet
- Seismic CalculationDocument1 pageSeismic Calculationsj22100% (1)
- Optimization of The Geometrical Parameters of Bonded Composite Wrap For Repairing Cracked PipelinesDocument12 pagesOptimization of The Geometrical Parameters of Bonded Composite Wrap For Repairing Cracked PipelinesjeovanNo ratings yet
- Phased Array Scan Coverage - Ed GinzelDocument17 pagesPhased Array Scan Coverage - Ed GinzelJ.Carrasco100% (2)
- HeliCoil Technical Information Shock Vibration FatigueDocument8 pagesHeliCoil Technical Information Shock Vibration FatigueAce Industrial SuppliesNo ratings yet
- Valve Samson Model 3241 Serial 470 132 B347W701 ENDocument1 pageValve Samson Model 3241 Serial 470 132 B347W701 ENClaudio StadelmannNo ratings yet
- Us1665267 PDFDocument3 pagesUs1665267 PDFmien namNo ratings yet
- Trunnion & Tailing Lug DesignDocument25 pagesTrunnion & Tailing Lug Designvpjagannaath100% (3)
- Example of NanomaterialsDocument8 pagesExample of NanomaterialsKalKatu MaLam79% (14)
- Basic Reservoir EngineeringDocument74 pagesBasic Reservoir EngineeringRizaldiSaputraNo ratings yet
- 枪弹密封剂和拔弹力Sealants and Bullet Pull StrengthDocument6 pages枪弹密封剂和拔弹力Sealants and Bullet Pull StrengthAddison TuNo ratings yet
- Soroako SerpentinisationDocument24 pagesSoroako SerpentinisationadisatriowicaksonoNo ratings yet
- HSC Chemistry 8Document12 pagesHSC Chemistry 8Lubomira Macheva100% (2)
- Chemical KineticsDocument116 pagesChemical KineticsSai Vishnu GainiNo ratings yet
- Astm D6943.36568Document6 pagesAstm D6943.36568Info SecclabNo ratings yet
- Urea Plant Training Program For GTEDocument40 pagesUrea Plant Training Program For GTEnomidangerous100% (1)
- JGR Space Physics - 2023 - Rubtsov - Polarization and Spatial Distribution Features of Pc4 and Pc5 Waves in TheDocument19 pagesJGR Space Physics - 2023 - Rubtsov - Polarization and Spatial Distribution Features of Pc4 and Pc5 Waves in TheYiyang LuoLuoNo ratings yet
- Ds Medaprot 100Document1 pageDs Medaprot 100faridNo ratings yet
- Griffiths QMCH 1 P 8Document2 pagesGriffiths QMCH 1 P 8abc xyzNo ratings yet
- 安川ES165N en 40Document4 pages安川ES165N en 40rockNo ratings yet
- Steel Tables (British) PDFDocument18 pagesSteel Tables (British) PDFdarulrajNo ratings yet
- Pre FormulationDocument15 pagesPre FormulationMeghana JNo ratings yet
- Hysys FileDocument34 pagesHysys FileSyed Saad ShahNo ratings yet
- As 2360.1.2-1993 Measurement of Fluid Flow in Closed Conduits Pressure Differential Methods - Measurement UsiDocument9 pagesAs 2360.1.2-1993 Measurement of Fluid Flow in Closed Conduits Pressure Differential Methods - Measurement UsiSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- FP SlidesDocument14 pagesFP Slidesapi-390422023No ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4-Module 5: Observing Weather ConditionsDocument13 pagesScience: Quarter 4-Module 5: Observing Weather ConditionsMary Grace Gamose IntongNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 10 Biomolecules Chemical Reactions Gas LawsDocument48 pagesQ4 Science 10 Biomolecules Chemical Reactions Gas LawsCriselda EspirituNo ratings yet
- Design & Analysis of A Cogeneration Plant Using WHRDocument5 pagesDesign & Analysis of A Cogeneration Plant Using WHRSrinivas TangellapalliNo ratings yet
- EC3 Steel Design Short CourseDocument3 pagesEC3 Steel Design Short CoursekiplingkipNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure ChemistryDocument3 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure ChemistryAbhisiktaNo ratings yet