Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plants
Plants
Uploaded by
Shapee ManzanitasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plants
Plants
Uploaded by
Shapee ManzanitasCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 15 Complete this chart by listing the parts of a flower.
Parts of a flower
Male parts
Female parts
Other parts
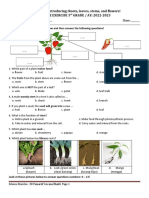
Identify the following. Choose the correct answer below. Stamen Pistil Petals Sepals Stigma Calyx Style Corolla Filament Anther Fruits Seeds Seed Receptacle
Flower Ovules Peduncle Pollen Grains Pollen Tube Gumamela
________________ 1. Reproductive structure of many kinds of plants. ________________ 2. Female reproductive part of a flower. ________________ 3. Male reproductive part of a flower. ________________ 4. Group of sepals. ________________ 5. Part of a flower that becomes a fruit. ________________ 6. Female flower cells. ________________ 7. Group of petals ________________ 8. Male flower cells. ________________ 9. A leaflike parts at the base of a flower that cover the bud. ________________ 10. The colored parts which attract insects. ________________ 11. It holds the anther. ________________ 12. It contains the pollen grains. ________________ 13. Tube below the pistil. ________________ 14. The sticky part on top of the pistil where pollen grains enter. ________________ 15. Tiny tube inside the style that serves as passageway for pollen grains to reach the ovary. ________________ 16. The stalk of a single flower. ________________ 17. Example of a complete flower. ________________ 18. When the ovary matures or ripens it becomes the ___________. ________________ 19. While the ovules becomes the ____________. ________________ 20. The tip to which the floral organs are attached.
LESSON 16 Identify the following terms. Write the letter on the blank. _____ 1. It refers to the transfer of pollen grains into the stigma of a flower? _____ 2. Is the transfer of pollen grains into the stigma of the same flower. _____ 3. Is the transfer of pollen grains into the stigma of another flower. _____ 4. The union of pollen grain and ovule. _____ 5. Refers to the male reproductive cell of a flower. _____ 6. Agent of pollination. _____ 7. Example of plants that produce seeds that are hard and tough. _____ 8. Example of plants that produce soft and moist seeds. _____ 9. Example of plants that produce one seed _____ 10. Example of plants that produce many seeds. LESSON 17 Circle the correct answer. 1. It is the part of a plant from which a new plant grows. 2. It serves as the food container . 3. The hard outer covering of a seed. 4. The baby plant inside a seed. 5. Plants that contain one cotyledon are called ____. 6. Plants that contain two cotyledon are called ____. 7. It develops into the primary root. 8. Part of the stem below the cotyledon. 9. Part of the stem above the cotyledon. 10. The food container or storage. 11. Seeds grow into new plants during the process called _____. Write TRUE if the statement is correct, and FALSE if is not. ______ 1. Seeds are produced as soon as a pollen grain fertilizes the ovules. ______ 2. All plants come from seeds. ______ 3. The embryo is the baby plant that contains an immature stem and root. ______ 4. The cotyledon is the hard outer covering of a seed. ______ 5. Plants with seeds containing one cotyledon are called dicots. Label the parts of the seed. ( seed, testa, embryo) ( testa, cotyledon, embryo) ( seed, testa, embryo) ( seed, seed coat, embryo) ( monocots, dicots, radicle ) (monocots, dicots, radicle ) ( radicle, epicotyls, hypocotyls ) ( radicle, epicotyls, hypocotyls ) ( radicle, epicotyls, hypocotyls ) ( testa, embryo, cotyledon ) ( Pollination, Germination ) A. Mango B. Fertilization C. Cross pollination D. Tamarind E. Bee F. Pollen grains G. Coconut H. Papaya J. Pollination K. Self pollination
1. __________________ 2. ___________________ 3. ___________________
Write on the blank the letter that represents the correct answer. _____ 1. Which refers to the production of another organism similar to the parent organism? a. Fertilization b. molting c. reproduction d. respiration _____ 2. Which of the following animals undergoes asexual reproduction? a. Cockroach b. sea urchin c. sponge d. toad _____ 3. Which of the following animals undergoes incomplete metamorphosis? a. Bee b. moth c. mosquito d. tree hopper _____ 4. How many stages are involved in a complete metamorphosis? a. Two b. three c. four d. five _____ 5. Which of the following pair of animals have skin that is used in making shoes, wallets, belts and bags? a. alligators and snakes c. lions and tigers b. Butterflies and dragonflies d. pigeons and eagles _____ 6. Which of the following sets of animals is a source of milk? a. Cow, carabao, goat c. cow, ewe, tiger b. Cow, carabao, dogs d. ewe, horse, ostrich _____ 7. How can we exterminate dengue-carrying mosquitoes? a. Keep water containers tightly closed. b. Keep the surroundings clean and fumigate breeding areas of mosquitoes. c. Remove empty bottles and cans that may collect rain water. d. All of the above. _____ 8. Most likely, at about what time of the day does a dengue-carrying mosquito bite? a. One hour before sunrise and sunset. b. At noontime when the sun is directly overhead. c. At nighttime especially when the moon is out of sight d. At 9:00 oclock a.m. and 3:00 oclock p.m. _____ 9. Which of the following series of stages shows the possible development of a beetle? a. Egg, pupa, grub, adult c. Pupa, adult, grub, egg b. Egg, grub, pupa, adult d. Grub, egg, pupa, adult _____ 10. Which of the proper way of handling animals? a. Keep your pets in a cage. c. Give them food and water. b. Take them for a walk during the day. d. all of the above _____ 11. What is produced when the ovule and the pollen of a flower meet? a. Flower b. leaf c. root d. seed _____ 12. What happens when the pollen grains of a flower enter the stigma of another flower? a. Germination starts. c. Self pollination occurs. b. Fertilization takes place. d. Cross pollination happens. _____ 13. Which of the following plants has seeds that will grow into new plants when they fall on the ground? a. pineapple b. banana c. siniguelas c. mango _____ 14. Why do flowers usually have attractive colors? a. To encourage people to plant more of them b. To make the plant beautiful c. To attract insects d. To differentiate them from animals _____ 15. Which of these plants has seeds that are dispersed by wind? a. Corn b. coconut c. guava d. mahogany _____ 16. Where does the growing plant get its food? a. Cotyledon b. epicotyl c. hilum d. hypocotyls _____ 17. Which of these plants grouped in threes have fruits that burst or explode because of heat? a. Guava, aratiles, mango c. tomato, coconut, eggplant b. Bean, ipil-ipil, madre de cacao d. Papaya, kalabasa, patola _____ 18. Which group of plants can be reproduced asexually? a. Banana, onion, camote c. okra, guava, red pepper b. Squash, tomato, okra d. tomato, onion, squash
_____ 19. Which of the following statements describes the process of fertilization in flowers? a. The pollen grains continue growing until it reaches the ovary. b. The sperm cell traveling through the pollen tube unites with the ovule. c. The pollen tube enlarges to accommodate several pollen grains. d. The pollen grain from the anther falls into the stigma. _____ 20. A potato is cut into pieces to produce new plants. each piece should have an eye. Where does the growing potato get its food? a. From the water c. from the potato b. From the soil d. from sunlight Tell how the following plants are propagated. Write your answer on the blank. ________________ 1. Cassava ________________ 2. Banana ________________ 3. Garlic ________________ 4. African violets ________________ 5. Potato ________________ 6. Sampaguita ________________ 7. Kataka-taka ________________ 8. Onion ________________ 9. Rose plant ________________ 10. Strawberry
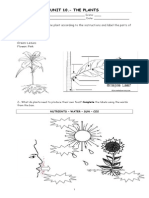
Identify what is being described. Write the answer on the blank. Layering Plant propagation Rhizomes Mound layering Stock Suckers Asexual or vegetative propagation Air layering or marcotting Cutting Grafting Tubers Stolons Budding Scion Bulbs
________________ 1. Means to continue and increase the production of plants. ________________ 2. Underground stem that looks like a swollen root. ________________ 3. Method of joining two different plants of the same kind. It has a stock and a scion. ________________ 4. Method of propagating plants where roots are allowed to grow on a stem or branch still attached to the parent plant ________________ 5. it is done by attaching a small piece of bark or rind containing a scion to the part of the stock. ________________ 6. Parts of the plants with roots ________________ 7. Its the part with leaves ________________ 8. The fastest, easiest and cheapest method of asexual propagation. ________________ 9. Production of new plants form their parts such as leaves, stems or roots. ________________ 10. Done by bending the shoot or branch so that the bark and the tissues will split. ________________ 11. A very short underground stems with fleshy leaves. ________________ 12. Are fleshy and rounded underground stems ________________ 13. Are shoots form the roots or lower part of the stem of a plant. ________________ 14. A modified stems that grow along the soil surface. ________________15. It is done by making an upward cut or slit just below a leafstalk.
You might also like
- MCQs From Cruciferae, Compositae, Graminae & MalvaceaeDocument5 pagesMCQs From Cruciferae, Compositae, Graminae & Malvaceaesajjan1506dbg8052100% (2)
- SC - Plants ExerciseDocument3 pagesSC - Plants ExerciseDewi100% (2)
- The PlantsDocument8 pagesThe PlantsXantal GarciaNo ratings yet
- 4 Science Habitats Communities QuizDocument2 pages4 Science Habitats Communities Quizpianosheetmusic1216No ratings yet
- Variables Constants and Controls Worksheet - electronic.WITH Answers PDFDocument2 pagesVariables Constants and Controls Worksheet - electronic.WITH Answers PDFJinali PatelNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Function: Interpreting DiagramsDocument4 pagesPlant Structure and Function: Interpreting DiagramsWayne CasanovaNo ratings yet
- More About Plants: I. Write (T) If The Statement Is True' and (F) If The Statement Is False'Document5 pagesMore About Plants: I. Write (T) If The Statement Is True' and (F) If The Statement Is False'seemaNo ratings yet
- Hand Out EcosystemDocument6 pagesHand Out EcosystemEvan GamingNo ratings yet
- Flower WorksheetDocument1 pageFlower Worksheetkaryn100% (13)
- Primary 5 ScienceDocument23 pagesPrimary 5 ScienceKyipyarNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Plants: Chapter 1 Plant ClassificationDocument35 pagesAquatic Plants: Chapter 1 Plant ClassificationSaanviNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Grade §ion: - ScoreDocument5 pagesName: - Date: - Grade §ion: - ScoreJe BeeNo ratings yet
- Plants Our Green Friends Worksheet - FLOWERSDocument3 pagesPlants Our Green Friends Worksheet - FLOWERSMeofcourseNo ratings yet
- Flower Parts & Pollination Worksheet: NameDocument1 pageFlower Parts & Pollination Worksheet: NameRaquel Tellez MamarilNo ratings yet
- Evolution Review WorksheetDocument5 pagesEvolution Review WorksheetRobert KarovicNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ST 1Document3 pagesScience 5 ST 1Nila Mae CalpoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Parts of A Plant - Answer KeyDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Parts of A Plant - Answer Keycoolandcrazy44No ratings yet
- m9S1oE HMW 1598176311 L-5 Plants Around Us 5Document3 pagesm9S1oE HMW 1598176311 L-5 Plants Around Us 5Mehaboob Basha0% (1)
- WORKSHEET 6.7 Photosynthesis - Leaf Structure (New)Document4 pagesWORKSHEET 6.7 Photosynthesis - Leaf Structure (New)netiiyah netiiNo ratings yet
- 2ND Pe Science 1 MatthewDocument3 pages2ND Pe Science 1 MatthewLlana Marie CampulloNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 & 7 Cell EnergyDocument17 pagesUnit 6 & 7 Cell EnergyRut ChristineNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Final Revision (Answers) )Document6 pagesYear 5 Final Revision (Answers) )M7G RoyalNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Document12 pagesPaper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Hisham AlEnaiziNo ratings yet
- First-Term Final Revision Grade 4Document14 pagesFirst-Term Final Revision Grade 4Ahmed SalemNo ratings yet
- STD Iv Sci WS 6Document2 pagesSTD Iv Sci WS 6Manit ShahNo ratings yet
- States of Matter QuizDocument1 pageStates of Matter Quizapi-294707707No ratings yet
- Plant Unit Test: Name: - DateDocument2 pagesPlant Unit Test: Name: - Dateapi-375119310No ratings yet
- Plant Worksheet PracticeDocument4 pagesPlant Worksheet PracticesenjicsNo ratings yet
- Classifying Vertebrates and InvertebratesDocument6 pagesClassifying Vertebrates and InvertebratesEliana CrespoNo ratings yet
- Grade IV - SST - The Northern Mountains - WS01.pdf - Ic44222Document1 pageGrade IV - SST - The Northern Mountains - WS01.pdf - Ic44222swatigoahead100% (1)
- Mt. of Olives Blessed School Inc. Lot 4 BLK 4 Remedios Country Homes Brgy. Bubukal, Sta - Cruz, LagunaDocument2 pagesMt. of Olives Blessed School Inc. Lot 4 BLK 4 Remedios Country Homes Brgy. Bubukal, Sta - Cruz, LagunaDiane MaryNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition Worksheets: - ObjectivesDocument8 pagesPlant Nutrition Worksheets: - Objectiveslaura martinez lunaNo ratings yet
- The Human Impact On The Environment: Interpreting DiagramsDocument4 pagesThe Human Impact On The Environment: Interpreting DiagramsWayne CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 2Document5 pagesScience Grade 2Roland Garcia Pelagio Jr.No ratings yet
- Ffa History-2Document2 pagesFfa History-2api-533680592No ratings yet
- Std. III Ch.15. Food WS-1 (22-23)Document2 pagesStd. III Ch.15. Food WS-1 (22-23)Pinky PatelNo ratings yet
- Charactristics of Living and Non Living ThingsDocument2 pagesCharactristics of Living and Non Living ThingsKristine Taroma100% (1)
- Plant Taxonomy and Reproduction WorksheetDocument2 pagesPlant Taxonomy and Reproduction WorksheetMr. C TylerNo ratings yet
- 4-Plant Structure and FunctionDocument7 pages4-Plant Structure and FunctionfebrimetrinNo ratings yet
- Biology 2nd 9 Weeks Week 2 2-2 3 Homework 3 Exam 2-3 ReviewDocument3 pagesBiology 2nd 9 Weeks Week 2 2-2 3 Homework 3 Exam 2-3 Reviewapi-262368188No ratings yet
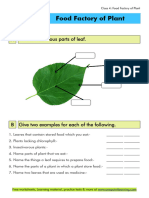
- Food Factory of Plants CDocument3 pagesFood Factory of Plants CNachammai SNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Science Weeks 5-8 Worksheets - Term 1Document26 pagesGrade 1 Science Weeks 5-8 Worksheets - Term 1Sowmya JogimuttNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pages4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsYu HasNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 PDFDocument4 pagesGrade 3 PDFCecille GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Plant Life: Revision AssignmentDocument2 pagesPlant Life: Revision AssignmentRajalaxmiNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Science Weeks 1-6 Worksheets - Term 3Document43 pagesGrade 4 Science Weeks 1-6 Worksheets - Term 3Prinsesa Tråčý Ruthan AbiolaNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Grade 1 Science FinalDocument24 pagesQ1 - Grade 1 Science FinalAURORA BAUTISTA100% (1)
- Science Class 3 Topic: Rocks and Soil Reinforcement WorksheetDocument5 pagesScience Class 3 Topic: Rocks and Soil Reinforcement WorksheetPranjalNo ratings yet
- Plant Structures Quiz - Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPlant Structures Quiz - Answer Keyapi-254428474100% (1)
- Math Study Material1Document24 pagesMath Study Material1subhasish03ee6301100% (1)
- Grade 5 Science Question SampleDocument3 pagesGrade 5 Science Question SampleAnjan SapkotaNo ratings yet
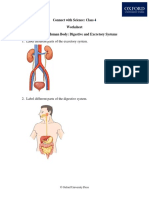
- CWS Class 4 Chapter 3 Human Body Digestive and Excretory SystemsDocument1 pageCWS Class 4 Chapter 3 Human Body Digestive and Excretory SystemsmdevjyotiNo ratings yet
- Food Chain Stage 3 Draft 1Document5 pagesFood Chain Stage 3 Draft 1api-281198656No ratings yet
- 3 RD Grade Daily Skills Week OneDocument3 pages3 RD Grade Daily Skills Week OneOksanaBilenkaNo ratings yet
- Possessive Nouns Circling Re Writing P 1 Intermediate PDFDocument1 pagePossessive Nouns Circling Re Writing P 1 Intermediate PDFmariaNo ratings yet
- Monocot Dicot ColoringDocument3 pagesMonocot Dicot ColoringMashgol KarimNo ratings yet
- Science3 Q2 Mod11 LivingThingsAndTheirInvironment V4Document30 pagesScience3 Q2 Mod11 LivingThingsAndTheirInvironment V4Alzen GalaponNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction QuestionsDocument3 pagesPlant Reproduction QuestionsBenjamin YapNo ratings yet
- English Worksheets Class 3 Session 2021 22Document40 pagesEnglish Worksheets Class 3 Session 2021 22Renu SyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesChapter - Reproduction in PlantsSarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Quarter Test Science 5 Quarter 2Document3 pagesQuarter Test Science 5 Quarter 2Lellaine G. Canieso LptNo ratings yet
- Music 1ST QTRDocument4 pagesMusic 1ST QTRShapee Manzanitas100% (2)
- Arts - Long Test Read and Circle The Correct Answer. Letter OnlyDocument5 pagesArts - Long Test Read and Circle The Correct Answer. Letter OnlyShapee ManzanitasNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 1ST QTRDocument4 pagesPhysical Education 1ST QTRShapee ManzanitasNo ratings yet
- Circle The Correct Answer.: ComputerDocument2 pagesCircle The Correct Answer.: ComputerShapee ManzanitasNo ratings yet
- Christopher S. Campbell Craig W. Greene Benedict F. Neubauer Jean M. HigginsDocument8 pagesChristopher S. Campbell Craig W. Greene Benedict F. Neubauer Jean M. HigginsВоја ВојводаNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument28 pagesReproduction in PlantsMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet 9 Updated FlowerDocument2 pagesLab Worksheet 9 Updated FlowerEnrique F. OcampoNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSri DharshanNo ratings yet
- Botany111 Lecture Report # 07Document77 pagesBotany111 Lecture Report # 07api-3767323No ratings yet
- Documentation of Flower Morphology and Male Gametophyte Development of Cassia Alata L. Through The Usage of Micro TechniqueDocument25 pagesDocumentation of Flower Morphology and Male Gametophyte Development of Cassia Alata L. Through The Usage of Micro TechniqueRobi Goco100% (1)
- SRFP Neet 2024Document53 pagesSRFP Neet 2024subu231201No ratings yet
- Monocots and Dicots: Chart Showing Differences Monocot DicotDocument3 pagesMonocots and Dicots: Chart Showing Differences Monocot DicotCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Biology of AngiospermDocument6 pagesReproductive Biology of AngiospermSarojiniNo ratings yet
- Science - 111120 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesScience - 111120 - Reproduction in PlantsDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal PAT XI 2021Document5 pagesLatihan Soal PAT XI 2021Yusuf Puno AbasNo ratings yet
- Science Reading Comprehension - Weeds and SeedsDocument3 pagesScience Reading Comprehension - Weeds and SeedsCristina AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 21 1Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 21 1femie hemilgaNo ratings yet
- A Flower in L. S. Showing Position of Different Whorls On ThalamusDocument30 pagesA Flower in L. S. Showing Position of Different Whorls On ThalamusDr AwanishNo ratings yet
- Pollination Assignment: A. Choose The Correct Answer:-1x15 15Document3 pagesPollination Assignment: A. Choose The Correct Answer:-1x15 15Shamik DharNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Comparing Flowering PlantsDocument19 pagesGrade 7 Comparing Flowering PlantsGadgetGlitchKillNo ratings yet
- LT Adm 13.2Document9 pagesLT Adm 13.2Bayani VicencioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Insect PollinationDocument4 pagesInsect PollinationStormbringerNo ratings yet
- TOP Science Grade 5 Worksheets Chapter 1Document11 pagesTOP Science Grade 5 Worksheets Chapter 1agustina simorangkirNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Development LAB EXERCISEDocument6 pagesReproduction and Development LAB EXERCISESophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Class XI Liliaceae FamilyDocument17 pagesClass XI Liliaceae FamilySachin PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraNo ratings yet
- Biology CL 12 - Chapter 2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument47 pagesBiology CL 12 - Chapter 2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsjackieaj093No ratings yet
- Ebook Improving Performance How To Manage The White Space On The Organization Chart 3Rd Edition Geary A Rummler Alan P Brache Online PDF All ChapterDocument23 pagesEbook Improving Performance How To Manage The White Space On The Organization Chart 3Rd Edition Geary A Rummler Alan P Brache Online PDF All Chapterraymond.mckay623100% (8)
- Class 6 - Chapter 7 - Getting To Know PlantsDocument4 pagesClass 6 - Chapter 7 - Getting To Know PlantskishanrwtNo ratings yet
- WS For Paper - 4Document17 pagesWS For Paper - 4MotiourNo ratings yet
- Relationships Among Flowers Fruits and SeedsDocument23 pagesRelationships Among Flowers Fruits and Seedsánh nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Xii - 2022-23 - Biology - RaipurDocument219 pagesXii - 2022-23 - Biology - Raipursuresh babu0% (1)