Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
Uploaded by
aravindOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
Uploaded by
aravindCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9 Life Span Development Developmental Psychology: the study of how people change throughout their life span
Ways to study developmental psychology o Cross-sectional study:
o Cohort effects
o Longitudinal studies
o Biographical study Prenatal development: development from conception to birth Fertilized egg embryo fetus
Critical period: when the fetus can be affected by harmful substances Fetal alcohol syndrome
New born babies (neonates) Newborns have many reflexes such as: Rooting reflex
Sucking reflex
Swallowing reflex
Grasping reflex
Stepping reflex:
Temperament Easy
Difficult
Slow to warm up
Shy
Perceptual abilities of infants Vision
Depth Perception
Other Senses
Infancy and Childhood Physical Development
Motor Development
Occurs in a proximodistal fashion
Cognitive Development Piagets Stages of Cognitive Development Sensory motor stage (birth to about 2)
Development of object permanence
Mental representations
Preoperational stage (about 2 to about 7)
Egocentric
Concrete operational stage (about 7 to about 11) Principle of conservation
Formal operational stage
Criticisms of Piagets theory
Moral Development: Kohlberg Preconventional
Conventional
Post conventional
Criticisms of Kohlberg
Language Development
Theories of Language Development Skinners reinforcement view
Chromskys language acquisition device
Social Development Parent-child relationships in infancy: Development of attachment
Humans dont imprint , they form attachments
Erik Erikson
Trust vs mistrust
Autonomy
Socialization
Parent child relationships in childhood Authoritarian
Permissive
Authoritative
Relationships with other children Different play styles o Solitary play
Parallel play
o Cooperative play
Sex-role Development Gender identity
Gender Constancy
Gender role awareness
Gender stereotypes
Sex-typed behavior
Television and children
Adolescence Physical changes Sexual development Puberty
Menarche
Early and Late Developers
o Adolescent sexual activity
Cognitive changes o Imaginary audience
o Personal fable
Personality and social development o How stormy and stressful is adolescence?
o Forming an identity Identity formation
Identity crisis
Moratorium
Identity diffusion
o Relationships with peers Cliques
o Relationships with parents
Some problems of adolescence
o Depression and suicide
o Youth Violence Warning signs of potential violence Lack of connection Masking emotions Withdrawal Silence Rage Increased lying Trouble with friends Hypervigilance Cruelty to other children and animals Other causes for concern regarding acting out violently If they come from a family with a history of criminal violence Child has been abused Belongs to a gang Abuses drugs or alcohol Problems at school Young and Middle Adulthood o Forming partnerships
o Parenthood
o Divorce
The World of Work o Dual-career families
Cognitive changes
Personality changes o Midlife crisis
o Midlife transition
The change of life
Late Adulthood Social Changes: gradually occur in 3 stages o Shrinkage of life space
o Increased individuality
o Acceptance
Cognitive Changes
Facing the end of life o Stages of dying o Denial o Anger o Bargaining o Depression o Acceptance
You might also like
- Women Who Become Men Albanian Sworn Virgins - Antonia YoungDocument195 pagesWomen Who Become Men Albanian Sworn Virgins - Antonia Youngdhcruz100% (3)
- Guide To Adult Dating PDFDocument22 pagesGuide To Adult Dating PDFNishthaNo ratings yet
- Slaying The DragonDocument5 pagesSlaying The DragonMarkus ChNo ratings yet
- Perdev AdolescenceDocument32 pagesPerdev AdolescenceandrewNo ratings yet
- Edpc 238 Student Human Growth and Development 2020Document109 pagesEdpc 238 Student Human Growth and Development 2020Naomi ChepkoechNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides Module13Document51 pagesLecture Slides Module13Lucas Coleta AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Physical and CognitiveDocument30 pagesAdolescent Physical and CognitivekasinarayananjrNo ratings yet
- Psychological and Social AspectsDocument16 pagesPsychological and Social AspectsHemangi NarvekarNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentDocument34 pagesDevelopmentFardin RahmanNo ratings yet
- AdolescentDocument34 pagesAdolescentShiney N ChristyNo ratings yet
- ADOLESCENCEDocument15 pagesADOLESCENCEEdmund G. VillarealNo ratings yet
- علوم وسلوكيه فكري &تسنيمDocument96 pagesعلوم وسلوكيه فكري &تسنيمnaji0mohammed80No ratings yet
- The Infants, Toddler, and PreschoolerDocument128 pagesThe Infants, Toddler, and PreschoolerPiao Liang Jing100% (2)
- Child Psychology and ManagementDocument94 pagesChild Psychology and ManagementJacob ThomasNo ratings yet
- 7 AdolescentDocument40 pages7 Adolescentharutochoky8No ratings yet
- Adolescent Mental HealthDocument38 pagesAdolescent Mental HealthblairNo ratings yet
- Teen PPT PresentationDocument18 pagesTeen PPT PresentationSantosh YadavNo ratings yet
- Development ArmDocument51 pagesDevelopment ArmVukashin.meNo ratings yet
- Physical ChangeDocument55 pagesPhysical ChangeChia TanNo ratings yet
- Theories of Development HANDOUTSDocument20 pagesTheories of Development HANDOUTSShirlyn Kate AsidoyNo ratings yet
- PER DEV and ORAL COMM ReviewerDocument11 pagesPER DEV and ORAL COMM ReviewerHeeseung SimpNo ratings yet
- Identity and PersonalityDocument14 pagesIdentity and PersonalityCherry Grace Articulo DabuconNo ratings yet
- Myers AP - Unit 09 NotesDocument150 pagesMyers AP - Unit 09 NotesHuyen-Yen HoangNo ratings yet
- Adolescent 150219082715 Conversion Gate01Document52 pagesAdolescent 150219082715 Conversion Gate01andrewNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Chapter 5Document53 pagesPersonal Development Chapter 5Edilene Rosallosa CruzatNo ratings yet
- 300 QuestionsDocument1,054 pages300 QuestionsJrure TE33% (3)
- Health Promotion of The Adolescent and FamilyDocument31 pagesHealth Promotion of The Adolescent and FamilyVanisa NurmaheriNo ratings yet
- 2 Psi 101 Developmental Psy - OnlineDocument18 pages2 Psi 101 Developmental Psy - Onlineew weNo ratings yet
- The Transition Period From Childhood To AdulthoodDocument26 pagesThe Transition Period From Childhood To AdulthoodAiyanah Sofia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Life Pro Cess From Bir TH To Old AgeDocument145 pagesLife Pro Cess From Bir TH To Old AgeDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- Human DevelopmentDocument7 pagesHuman DevelopmentXiola BleuNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec FinalsDocument36 pagesMCN Lec FinalsShainaChescaEvansNo ratings yet
- Su+1 Psyc+211 NwuDocument16 pagesSu+1 Psyc+211 Nwuretlametswe42No ratings yet
- Psychology Lecture 05 - Developmental PsychologyDocument65 pagesPsychology Lecture 05 - Developmental Psychologygod_26No ratings yet
- Human Development: Adolesence: By: C. Settley 2016Document43 pagesHuman Development: Adolesence: By: C. Settley 2016loraine cloresNo ratings yet
- Child PsychologyDocument49 pagesChild PsychologydrshreyabagrawalNo ratings yet
- SESSION 2 The Metamorphosis of A PersonDocument19 pagesSESSION 2 The Metamorphosis of A PersonJan Robert GazaNo ratings yet
- Freud's Stages of Psychosexual Development & Defence MechanismsDocument68 pagesFreud's Stages of Psychosexual Development & Defence MechanismsHaris PeaceNo ratings yet
- ch01 Sigelman9e PPTDocument64 pagesch01 Sigelman9e PPTNatasha CarstensNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Intellectual RevolutionDocument43 pages3.1 Intellectual RevolutionMax TooperNo ratings yet
- March 2023 New Curriculum TopicsDocument40 pagesMarch 2023 New Curriculum Topicsjoseglennbalondro4No ratings yet
- Psychology II, Mrs. Hart: Some Slides Are Adopted FromDocument41 pagesPsychology II, Mrs. Hart: Some Slides Are Adopted FromDennis PereyraNo ratings yet
- 1 Psychoanalytic Theory LecturesDocument56 pages1 Psychoanalytic Theory LecturesMaribel Pascual FloresNo ratings yet
- Human DevelopmentDocument56 pagesHuman DevelopmentArjel Ranile100% (1)
- Adolescent Development: DR Ajayi A.HDocument40 pagesAdolescent Development: DR Ajayi A.HAdepeju Adedokun AjayiNo ratings yet
- PSY2071 Topic 5 Adolescence and Emerging AdulthoodDocument47 pagesPSY2071 Topic 5 Adolescence and Emerging AdulthoodEllie LEENo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent DevelopmentDocument109 pagesChild and Adolescent DevelopmentEBO, JOHN KYLE B.No ratings yet
- Developmental StagesDocument60 pagesDevelopmental StagesAngel DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Psychology and SociologyDocument20 pagesPsychology and SociologykwagalaenochkeaneNo ratings yet
- Perdev AlfredDocument7 pagesPerdev AlfredRhamyllia Kyla C. MaghanoyNo ratings yet
- Child Development Theories and TheoristsDocument61 pagesChild Development Theories and TheoristsBenard NNo ratings yet
- 02 Human DevevelopmentDocument25 pages02 Human DevevelopmentShaina Wyn TubaNo ratings yet
- Learners DevelopmentDocument36 pagesLearners DevelopmentLyka AldayaNo ratings yet
- Development (1) - CopyDocument8 pagesDevelopment (1) - Copyasmaalbuloshi98No ratings yet
- Psychology 223 Chapter 1-3Document29 pagesPsychology 223 Chapter 1-3kyramoosthuizenNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroDocument34 pages01 IntroJoe-L ZadaniNo ratings yet
- Psychologyunit VI 200611074008Document63 pagesPsychologyunit VI 200611074008DeepaPandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 - Adolescence and AdulthoodDocument5 pagesChapter 04 - Adolescence and AdulthoodKiprono Matui Arap KogoNo ratings yet
- Human Personality 12345Document12 pagesHuman Personality 12345Kavi rajputNo ratings yet
- Human DevelopmentDocument70 pagesHuman DevelopmentAsher WayneNo ratings yet
- Theories of PersonalityDocument51 pagesTheories of PersonalityOyedele OluwaseunNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Human BehaviorDocument67 pagesDeterminants of Human BehaviorMARK EVANSNo ratings yet
- Know the Personality of Your Child: Using the Science of Numbers (Numerology)From EverandKnow the Personality of Your Child: Using the Science of Numbers (Numerology)No ratings yet
- 100 Power Tips For FPGA Designers Stavinov EvgeniDocument213 pages100 Power Tips For FPGA Designers Stavinov EvgeniAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Examination Centre ListDocument54 pagesExamination Centre Listrkthbd58450% (3)
- IGNOU Prospectus and Application Form 2014 July SessionDocument180 pagesIGNOU Prospectus and Application Form 2014 July SessionAnweshaBoseNo ratings yet
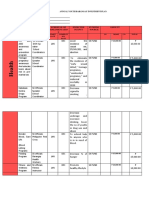
- 278-316 CH08 61939Document39 pages278-316 CH08 61939aravind100% (2)
- ABYIPDocument15 pagesABYIPShiela Mae Urgel100% (2)
- 2019 AUSL Pre Week Notes Civil Law PDFDocument59 pages2019 AUSL Pre Week Notes Civil Law PDFJDR JDRNo ratings yet
- The Physical Self: The Human Body Is The Best Work of Art. ' - Jess C. ScottDocument15 pagesThe Physical Self: The Human Body Is The Best Work of Art. ' - Jess C. ScottJaycee TualaNo ratings yet
- Induced Spawning Techniques Practised at Batu Berendam, Melaka, MalaysiaDocument11 pagesInduced Spawning Techniques Practised at Batu Berendam, Melaka, MalaysiaKaio BarrosNo ratings yet
- Prbs Update Form: Transferee/Survivor (Relationship)Document1 pagePrbs Update Form: Transferee/Survivor (Relationship)Doris Joy Valde89% (9)
- Conjugation and TransformationDocument11 pagesConjugation and Transformationexploreriku100% (1)
- What WartDocument32 pagesWhat Wartsundae650% (4)
- Namma Kalvi 12th Zoology Chapter 3 Sura English Medium GuideDocument9 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Zoology Chapter 3 Sura English Medium GuideAakaash C.K.100% (1)
- Legal Threat From Steve JonesDocument2 pagesLegal Threat From Steve JonesCharles Davis0% (1)
- Catharine R. Stimpson - 'Zero Degree Deviancy - The Lesbian Novel in English', Critical Inquiry, 8 (2), 'Writing and Sexual Difference', 1981 PDFDocument18 pagesCatharine R. Stimpson - 'Zero Degree Deviancy - The Lesbian Novel in English', Critical Inquiry, 8 (2), 'Writing and Sexual Difference', 1981 PDFscottbrodie100% (1)
- Chapter 1 and 2Document6 pagesChapter 1 and 2Emmanuel AzuelaNo ratings yet
- Offensive Advertising An Legal Environment Project by Mansi Bengali 103 TybmmDocument14 pagesOffensive Advertising An Legal Environment Project by Mansi Bengali 103 TybmmKatie1901No ratings yet
- ANALYSIS Pynchon, Thomas The Crying of Lot 49 (1966) Analysis by ChapterDocument17 pagesANALYSIS Pynchon, Thomas The Crying of Lot 49 (1966) Analysis by ChapterMax PowelNo ratings yet
- Tar Baby: Tar Baby (1981) Is Set On An Imaginary Caribbean Island and Involves TheDocument34 pagesTar Baby: Tar Baby (1981) Is Set On An Imaginary Caribbean Island and Involves Thesar0000No ratings yet
- Cherry (1999) - The Female Horror Film Audience - Viewing Pleasures and Fan PracticesDocument285 pagesCherry (1999) - The Female Horror Film Audience - Viewing Pleasures and Fan PracticesHerbie CuffeNo ratings yet
- Hope For TransgressorsDocument6 pagesHope For TransgressorsPizzaCow100% (1)
- LGBTQ ThesisDocument5 pagesLGBTQ Thesismilkshake07No ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce PDFDocument25 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce PDFBala VisaNo ratings yet
- Epididymo-Orchitis: Epididymo-Orchitis in Heterosexual Men What Is Epidiymo-Orchitis?Document4 pagesEpididymo-Orchitis: Epididymo-Orchitis in Heterosexual Men What Is Epidiymo-Orchitis?Letchumanan L MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Fred Pugh Timeline of EventsDocument4 pagesFred Pugh Timeline of EventsCherylNo ratings yet
- Statement by Pam Palmer, Mother of Sovereign Grace Abuse Lawsuit PlaintiffDocument1 pageStatement by Pam Palmer, Mother of Sovereign Grace Abuse Lawsuit PlaintiffwatchkeepNo ratings yet
- Plant Nosodes - According To DR John Henry ClarkeDocument29 pagesPlant Nosodes - According To DR John Henry Clarkemelos24No ratings yet
- The Unheard Voices: Street Children in Kenya From A Local and Global PerspectiveDocument18 pagesThe Unheard Voices: Street Children in Kenya From A Local and Global Perspectivemaryg08No ratings yet
- Men, Women and RelationshipsDocument25 pagesMen, Women and Relationshipsfreeman_bruce6274No ratings yet
- GIDYQ-AA (Female Adult Version)Document2 pagesGIDYQ-AA (Female Adult Version)jadeNo ratings yet
- 6.3 MeiosisDocument24 pages6.3 MeiosisPratika MNo ratings yet
- Plaintiff's Complaint With Jury Demand: Ature of ActionDocument34 pagesPlaintiff's Complaint With Jury Demand: Ature of ActionWKYC.comNo ratings yet