Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Exam Set A
Final Exam Set A
Uploaded by
Atikah JCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Rvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesRvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 13.differentiation and Integration of Power Series PDFDocument11 pages13.differentiation and Integration of Power Series PDFAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Info Booklet, Revised 2011Document27 pagesInfo Booklet, Revised 2011ordinanceNo ratings yet
- Name of The Student: Branch: Unit - I (Fourier Series) : Engineering Mathematics MaterialDocument11 pagesName of The Student: Branch: Unit - I (Fourier Series) : Engineering Mathematics Materialsabarish001No ratings yet
- MA2211 NotesDocument145 pagesMA2211 NotesBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Formulae:: Quadratic FormulaDocument6 pagesSome Basic Formulae:: Quadratic FormulaBlazingStudiosNo ratings yet
- 2.odd Even Function1Document12 pages2.odd Even Function1Atikah JNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesDocument13 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesCM Zain CrcoNo ratings yet
- GATE Mathematics Paper-2007Document11 pagesGATE Mathematics Paper-2007RajkumarNo ratings yet
- GATE Mathematics Paper 2011Document8 pagesGATE Mathematics Paper 2011RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesFourier SeriesPurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Misrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97Document26 pagesMisrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97bhagyagr8No ratings yet
- Advanced Computational Methods: Numerical IntegrationDocument59 pagesAdvanced Computational Methods: Numerical IntegrationMohammed HamdyNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument31 pagesFourier SeriesSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- Final Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinal Formula SheetwhatnononoNo ratings yet
- Function: X Is Chosen at Random From The First 1000 Natural Numbers. If (.) Denotes TheDocument4 pagesFunction: X Is Chosen at Random From The First 1000 Natural Numbers. If (.) Denotes TheShrey PandeyNo ratings yet
- DRM SolutionsDocument116 pagesDRM SolutionsCésar TapiaNo ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- 2008 Ext1 PDFDocument3 pages2008 Ext1 PDFBrandi RoseNo ratings yet
- Kcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Document13 pagesKcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Kamalesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Https Doc 00 7g Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocument7 pagesHttps Doc 00 7g Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentVignesh RavishankarNo ratings yet
- Eamcet 2014 Engineering Key SolutionsDocument42 pagesEamcet 2014 Engineering Key Solutionsandhracolleges100% (1)
- (A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Document15 pages(A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Heather JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Engineering MathsDocument8 pagesEngineering MathsSanthosh SanNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- $RM3GFU6Document14 pages$RM3GFU6bacchuskevin10No ratings yet
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDocument12 pagesHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument6 pagesFormula RioJorge Laura GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Narayana Grand Test - 8Document12 pagesNarayana Grand Test - 8Meet ShahNo ratings yet
- Solutions: S - 1 5 Mathematics-III (May-2012, Set-2) JNTU-KakinadaDocument10 pagesSolutions: S - 1 5 Mathematics-III (May-2012, Set-2) JNTU-KakinadaSri DNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboNo ratings yet
- Ajc h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesAjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer Scheme MAT 565/480 (Advanced Differential Equation) JANUARY 2012Document4 pagesSuggested Answer Scheme MAT 565/480 (Advanced Differential Equation) JANUARY 2012Fakhrur RaziNo ratings yet
- Math54 Teleman Final 2011spring SolnDocument3 pagesMath54 Teleman Final 2011spring SolntehkronosNo ratings yet
- B.E. Degree Examinations: April/May 2011Document4 pagesB.E. Degree Examinations: April/May 2011Dhanabal Palanisamy PNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDocument110 pagesEe602 Fourier SeriesArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- MST209 2005solutionsDocument6 pagesMST209 2005solutionsrashismart2000No ratings yet
- GATE Mathematics Paper-2003Document13 pagesGATE Mathematics Paper-2003RajkumarNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Maths SolutionsDocument7 pagesIIT JEE Maths SolutionsVishal GaudNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Computer Science Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesTheoretical Computer Science Cheat SheetRosa GonzalezNo ratings yet
- X Senx Senx y DX Dy X X DZ Xtagx DX Dy: Cos 2 Cos 1Document3 pagesX Senx Senx y DX Dy X X DZ Xtagx DX Dy: Cos 2 Cos 1Gabriel Irigoin CordovaNo ratings yet
- JC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Document10 pagesJC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Huixin LimNo ratings yet
- Cape Pure Mathematics Unit 2module 2: Sequences, Series and ApproximationsDocument39 pagesCape Pure Mathematics Unit 2module 2: Sequences, Series and ApproximationsCarlon BairdNo ratings yet
- MATH 1432 (Cal II) Final Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesMATH 1432 (Cal II) Final Exam Reviewyvcala456No ratings yet
- Differentiation of Continuous Functions: X X X F X X F X F XDocument13 pagesDifferentiation of Continuous Functions: X X X F X X F X F XFrancisco FalconNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- 8.half Range (Exercise)Document1 page8.half Range (Exercise)Atikah JNo ratings yet
- X F X F: Even Function Half Range Series: A Series That IsDocument1 pageX F X F: Even Function Half Range Series: A Series That IsAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 12b) Power Series in XDocument6 pages12b) Power Series in XAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 7.half Range SeriesDocument9 pages7.half Range SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 5.periodic FunctionDocument7 pages5.periodic FunctionAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 6.periodic FuncDocument1 page6.periodic FuncAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 2.odd Even Function1Document12 pages2.odd Even Function1Atikah JNo ratings yet
- 1.fourier SeriesDocument11 pages1.fourier SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 4.odd N Even (Exercise)Document1 page4.odd N Even (Exercise)Atikah JNo ratings yet
- 7.quotient Test (Ratio Test)Document4 pages7.quotient Test (Ratio Test)Atikah JNo ratings yet
- 5 P-SeriesDocument3 pages5 P-SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 8.root TestDocument2 pages8.root TestAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Slide 2nd Order ODEDocument15 pagesSlide 2nd Order ODEAtikah JNo ratings yet
- The Integral Test PDFDocument8 pagesThe Integral Test PDFAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Application 1st OrderDocument3 pagesApplication 1st OrderAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformationDocument13 pagesLaplace TransformationAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Find The Laplace Transform. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L)Document1 pageFind The Laplace Transform. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L)Atikah JNo ratings yet
- Application 2nd OrderDocument3 pagesApplication 2nd OrderAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Theorem 3: MultiplyDocument2 pagesTheorem 3: MultiplyAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 3.telescope SeriesDocument3 pages3.telescope SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Inverse LaplaceDocument2 pagesInverse LaplaceAtikah JNo ratings yet
- S1: Determine A and F (X) - S2: Find The Complimentary SolutionDocument2 pagesS1: Determine A and F (X) - S2: Find The Complimentary SolutionAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Undetermined CofDocument4 pagesUndetermined CofAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Theorem 1: LinearityDocument2 pagesTheorem 1: LinearityAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Theorem 2: First ShiDocument2 pagesTheorem 2: First ShiAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 1 .2nd ODE - Homogeneous EquationDocument2 pages1 .2nd ODE - Homogeneous EquationAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Table of Particular IntegralDocument1 pageTable of Particular IntegralAtikah JNo ratings yet
Final Exam Set A
Final Exam Set A
Uploaded by
Atikah JOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Exam Set A
Final Exam Set A
Uploaded by
Atikah JCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA
FINAL EXAMINATION
SEMESTER II
SESSION 2012/2013
COURSE NAME : CIVIL ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS II
COURSE CODE : BFC 14003
PROGRAMME : 1 BFF, 2 BFF
EXAMINATION DATE : JUNE 2013
DURATION : 3 HOURS
INSTRUCTION : ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN PART A
AND THREE (3) QUESTIONS IN PART B
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF SIX (6) PAGES
CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL
BFC 14003
2
PART A
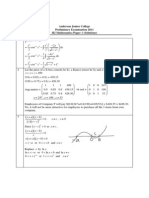
Q1 A periodic function is defined by
2 , 0
( )
2 , 0
x
f x
x x
t t
t
< <
=
< <
( ) t 2 ) ( + = x f x f .
(a) Sketch the graph of the function over x t t < < .
(2 marks)
(b) Determine whether the function is even, odd or neither.
(1 marks)
(c) Show that the Fourier series of the function ) (x f
is
( )
( ) ( )
2
1 1
1 1
3 1
2 cos 2 sin
2
n
n n
nx nx
n n
t
t
= =
(
+ E E .
(17 marks)
Q2 (a) Given that + + =
! 6 ! 4 ! 2
1 cos
6 4 2
x x x
x .
(i) Find the first three nonzero terms of a power series for
x
x sin
.
(ii) Hence, evaluate dx
x
x
}
1
0
sin
by using the series expansion.
(6 marks)
(b) (i) Determine whether the series
=1
2
n
n
e
n
converges or diverges by
using ratio test.
(ii) Determine whether the series
1
) 1 (
n
n
n
converges
absolutely, converges conditionally, or diverges by using a
suitable convergence test.
(8 marks)
(c) Find the radius of convergence of
0
3( 2)
n
n
x
.
(6 marks)
BFC 14003
3
PART B
Q3 (a) Solve the differential equation by using the method of separation of variables,
( ) 1 1
dy
x x y
dx
+ = .
Hence, find the particular solution when (1) 0 y = .
(7 marks)
(b) By using the substitution of and ,
dy dv
y xv x v
dx dx
= = + find the solution of
2 2
.
3
dy x y
dx xy
+
=
(6 marks)
(c) In a certain culture of bacteria, the rate of increase is proportional to the
number of present. If it is found that the number doubles in 4 hours, how many
may expected at the end of 12 hours?
(Hints:
dN
kN
dt
= , where N denotes the number of bacteria at time, t hours
and k is the proportionality factor.)
(7 marks)
Q4 (a) Use the method of variation of parameters to solve
sec tan y y x x '' + = ,
which satisfies the initial conditions (0) 0 y = and (0) 2 y' = .
(Hints: 1 tan sec
2 2
= + x x ,
2
sec tan .) x dx x =
}
(10 marks)
(b) A spring is stretched 0.1 m ( ) l = A when a 4 kg mass ( ) M = is attached. The
weight is then pulled down an additional 0.2 m and released with an upward
velocity of 4 m/s. Neglect damping, c. If the general equation describing the
spring-mass system is
BFC 14003
4
0, Mu cu ku '' ' + + =
find an equation for the position of the spring at any time t.
(Hints: weight, , 9.8, .
W
W Mg g k
l
= ~ =
A
)
(10 marks)
Q5 (a) Find
(i)
3 2
5
4
.
t
t
e t
e
+
`
)
(ii)
{ }
3
cosh4 ( 3) . t t t t o +
(iii)
{ }
3
sinh(3 ) ( 3) .
t
t e H t +
(10 marks)
(b) By using Laplace transform, solve
2 , (0) 2, (0) 3.
t
y y y e y y '' ' ' + = = =
(10 marks)
Q6 (a) Find
(i)
1
2 2
5 6
.
4 ( 2) 4
s
s s
+
`
+
)
(ii)
2
1
2
16
.
( 3)( 1)
s
s s
`
+
)
(10 marks)
(b) Find the general solution for the second order differential equation
2
3 2 2 5sin , y y y x x '' ' + = +
by using the undetermined coefficient method.
(10 marks)
BFC 14003
5
FINAL EXAMINATION
SEMESTER / SESSION : SEM II / 2012/2013 COURSE : 1 BFF / 2 BFF
SUBJECT : CIVIL ENGINEERING MATHEMATIC II SUBJECT CODE : BFC 14003
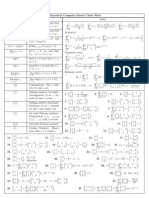
FORMULA
Second-order Differential Equation
The roots of characteristic equation and the general solution for differential equation
. 0 = + ' + ' ' cy y b y a
Characteristic equation: . 0
2
= + + c bm am
Case The roots of characteristic equation General solution
1.
Real and different roots:
1
m and
2
m
x m x m
Be Ae y
2 1
+ =
2.
Real and equal roots:
2 1
m m m = =
mx
e Bx A y ) ( + =
3.
Complex roots: i m | o + =
1
, i m | o =
2
) sin cos ( x B x A e y
x
| |
o
+ =
The method of undetermined coefficients
For non-homogeneous second order differential equation ( ), ay by cy f x '' ' + + = the particular
solution is given by ( )
p
y x :
( ) f x
( )
p
y x
1
1 1 0
( )
n n
n n n
P x A x A x Ax A
= + + + +
1
1 1 0
( )
r n n
n n
x B x B x B x B
+ + + +
x
Ce
o
( )
r x
x Pe
o
cos or sin C x C x | |
( cos sin )
r
x P x Q x | | +
( )
x
n
P x e
o
1
1 1 0
( )
r n n x
n n
x B x B x B x B e
o
+ + + +
cos
( )
sin
n
x
P x
x
|
|
1
1 1 0
1
1 1 0
( ) cos
( )sin
r n n
n n
r n n
n n
x B x B x B x B x
x C x C x C x C x
|
|
+ + + + +
+ + + +
cos
sin
x
x
Ce
x
o
|
|
( cos sin )
r x
x e P x Q x
o
| | +
cos
( )
sin
x
n
x
P x e
x
o
|
|
1
1 1 0
1
1 1 0
( ) cos
( ) sin
r n n x
n n
r n n x
n n
x B x B x B x B e x
x C x C x C x C e x
o
o
|
|
+ + + + +
+ + + +
Note : r is the least non-negative integer (r = 0, 1, or 2) which determine such that there
is no terms in particular integral ) (x y
p
corresponds to the complementary function
) (x y
c
.
The method of variation of parameters
If the solution of the homogeneous equation 0 = + ' + ' ' cy y b y a is ,
2 1
By Ay y
c
+ = then the
particular solution for ) (x f cy y b y a = + ' + ' ' is
,
2 1
vy uy y + =
where ,
) (
2
A dx
aW
x f y
u + =
}
B dx
aW
x f y
v + =
}
) (
1
and
1 2 2 1
2 1
2 1
y y y y
y y
y y
W ' ' =
' '
= .
BFC 14003
6
FINAL EXAMINATION
SEMESTER / SESSION : SEM II / 2012/2013 COURSE : 1 BFF / 2 BFF
SUBJECT : CIVIL ENGINEERING MATHEMATIC II SUBJECT CODE : BFC 14003
Laplace Transform
L
}
= =
0
) ( ) ( )} ( { s F dt e t f t f
st
) (t f ) (s F ) (t f ) (s F
a
s
a
) ( a t H
s
e
as
at
e
a s
1
) ( ) ( a t H a t f
) (s F e
as
at sin
2 2
a s
a
+
) ( a t o
as
e
at cos
2 2
a s
s
+
( ) ( ) f t t a o
( )
as
e f a
at sinh
2 2
a s
a
0
( ) ( )
t
f u g t u du
}
) ( ) ( s G s F
at cosh
2 2
a s
s
( ) y t ) (s Y
n
t , ... , 3 , 2 , 1 = n
1
!
+ n
s
n
( ) y t ' ) 0 ( ) ( y s sY
) (t f e
at
) ( a s F ( ) y t ''
) 0 ( ) 0 ( ) (
2
y sy s Y s '
) (t f t
n
, ... , 3 , 2 , 1 = n ) ( ) 1 ( s F
ds
d
n
n
n
Fourier Series
Fourier series expansion of periodic
function with period L 2
0
1 1
1
( ) cos sin
2
n n
n n
n x n x
f x a a b
L L
t t
= =
= + +
where
}
=
L
L
dx x f
L
a ) (
1
0
}
=
L
L
n
dx
L
x n
x f
L
a
t
cos ) (
1
}
=
L
L
n
dx
L
x n
x f
L
b
t
sin ) (
1
Fourier half-range series expansion
=
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
L
x n
b
L
x n
a a x f
t t
where
}
=
L
dx x f
L
a
0
0
) (
2
}
=
L
n
dx
L
x n
x f
L
a
0
cos ) (
2 t
}
=
L
n
dx
L
x n
x f
L
b
0
sin ) (
2 t
BFC 14003
7
Marking Scheme
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
Q1
(a)
A2
2
Q1
(b)
Neither A1
1
Q1
(c)
2 x T x t + = +
2 T L =
2 2L t =
L t =
0
1
( )
L
L
a f x dx
L
( = }
0
0
1
2 2 dx xdx
t
t
t
t
( = } + }
| |
0
2
0
1
2 x x
t
t
t
t
(
( = +
(
2 2
1
2t t
t
( = +
3t =
1
( ) cos
L
n L
n x
a f x dx
L L
t
(
= }
(
0
0
1
2 cos( ) 2 cos( ) nx dx x nx dx
t
t
t
t
( = } + }
A1
M1
A1
A1
A1
M1
17
BFC 14003
8
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
u dv
2x cos( ) nx
2 1
sin( ) nx
n
0
2
1
cos( ) nx
n
0
2
0
1 2 2 2
sin( ) sin( ) cos( )
x
nx nx nx
n n n
t
t
t
t
(
( (
= + +
(
( (
(
2 2
1 2 2
cos( ) n
n n
t
t
(
=
(
1
( )sin
L
n L
n x
b f x dx
L L
t
(
= }
(
0
0
1
2 sin( ) 2 sin( ) nx dx x nx dx
t
t
t
t
( = } + }
u dv
2x sin( ) nx
2 1
cos( ) nx
n
0
2
1
sin( ) nx
n
0
2
0
1 2 2 2
cos( ) cos( ) sin( )
x
nx nx nx
n n n
t
t
t
t
(
( (
= + +
(
( (
(
2
n
=
( )
2 2
1
3 1 2 2 2
( ) cos( ) cos( ) sin
2
n
f x n nx nx
n n n
t
t
t
=
(
(
= + E
(
(
M1
A1
A1
M1
M1
A1
A1
A1M1
BFC 14003
9
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
{ }
2
1
3 2 2
( 1) 1 cos( ) sin( )
2
n
n
nx nx
n n
t
t
=
(
= + E
(
( )
( ) ( )
2
1 1
1 1
3 1
2 cos 2 sin
2
n
n n
nx nx
n n
t
t
= =
(
= + E E
A1
A1
Q2
(a) (i)
| |
+ + =
(
(
+ + =
(
(
+ + =
=
120 6
! 6
6
! 4
4
! 2
2
! 6 ! 4 ! 2
1
cos sin
5 3
5 3
6 4 2
x x
x
x x x
x x x
dx
d
x
dx
d
x
So,
+ + =
+ +
=
120 6
120 6
sin
2 / 9 2 / 5
5 3
x x
x
x
x x
x
x
x
M1
A1
A1
3
Q2
(a)
(ii)
. 621 . 0
1320
2
42
2
3
2
1320
2
42
2
3
2
120 6
sin
1
0
2 / 11 2 / 7 2 / 3
1
0
2 / 9 2 / 5
1
0
=
+ + =
(
+ + =
+ + =
} }
x x x
dx
x x
x dx
x
x
M1
A1
A1
3
Q2
(b) (i)
=1
2
n
n
e
n
2
2
1
2 1 2
2 2
( 1)
( 1)
lim lim
1 1 1 1
lim lim 1
1
1 ; the series converges.
n
n
n
n n
n
n n
n
e n
e
n e n
e
n
e n e n
e
+
+
+ +
+ +
+
+
= =
+ | | | |
= = +
| |
\ . \ .
= <
M1
A1A1
3
BFC 14003
10
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
Q2
(b)
(ii)
+ + + =
=
5
1
4
1
3
1
2
1
1
) 1 (
1 n
n
n
Use alternating series test:
(a) + > > > >
5
1
4
1
3
1
2
1
1
(b) 0
1
lim =
+ n n
the series converges.
Use p-series:
2
1
= p ( ) 1 0 s < p
the series diverges.
Conclusion, the series converges conditionally.
M1
A1
M1
A1
A1
5
Q2
(c)
For 2 = x , let
n
n
x u ) 2 ( 3 = .Then
| 2 |
| 2 | lim
) 2 ( 3
) 2 ( 3
lim lim
1
1
=
=
=
+
+
x
x
x
x
u
u
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
Thus, the series converges absolutely if
| 2| 1 x < or 1 3 x < < .
The series diverges if 1 x < or 3 x >
Therefore, the radius of convergence of the series is 1 = R .
M1
M1
A1
M1
A1
A1
6
Q3
(a)
( ) 1 1
dy
x x y
dx
+ =
1 1
dy x
dx
x y
=
+
1
1 1
x
dy dx
x y
} = }
+
2 1 ln(x 1) k y x = + + , k is constant
Given (1) 0 y = , so
A1
M1
M2
A1
7
BFC 14003
11
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
ln(2) 3 k =
2 1 ln(x 1) ln(2) 3 y x = + +
A1
A1
Q3
(b)
2 2
3
dy x y
dx xy
+
=
2 2 2
3 ( )
dv x x v
x v
dx x xv
+
+ =
2
1
3
v
v
+
=
2
1
3
dv v
x v
dx v
+
=
2
1 2
3
v
v
=
2
3 1
1 2
v
dv dx
v x
=
2
3 1
1 2
v
dv dx
v x
} = }
assume
2
1 2 a v =
4
da
v
dv
=
1
4
da vdv =
3 1 1
4
da dx
a x
} = }
2
3
ln 1 2 ln
4
v x k = +
2
3
ln 1 2 ln
4
y
x k
x
| |
= +
|
\ .
A1
M1
A1
M1
A1
A1
6
Q3
(c)
at 0, t =
0
N N = ; 4 t = ,
0
2 N N = ; 12 t = , ? N =
dN
kN
dt
=
7
BFC 14003
12
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
dN
kdt
N
=
1
dN kdt
N
} = }
ln | | N kt c = + , c is constant
kt
N Ae = ,
c
A e =
at 0, t =
0
A N =
So
0
kt
N N e =
at 4 t = ,
4
0 0
2
k
N N e =
4
2
k
e =
4 ln | 2| k =
1
ln | 2|
4
k =
So
1
ln|2|
4
0
t
N N e =
at 12 t = ,
3ln|2|
0
N N e =
0
8N =
At the end of 12 hours, the number of bacteria is 8 times of the
original number.
M1
A1
A1
A1
A1
M1
A1
Q4
(a)
Step 1:
1, ( ) sec tan a f x x x = =
Step 2:
2
1 2
1 2
1 0
Thus,
cos sin
cos sin
sin cos
h
m
m i
y A x B x
y x y x
y x y x
+ =
=
= +
= =
' ' = =
M1
A1
10
BFC 14003
13
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
Step 3:
2 2
cos sin
cos sin 1.
sin cos
x x
W x x
x x
= = + =
Step 4:
2
2
sin sec tan
tan
1 sec
( tan )
u x x x dx
x dx
x dx
x x C
=
=
=
= +
}
}
}
cos sec tan
tan
sin
cos
sin
sin
1
ln | cos |
v x x x dx
x dx
x
dx
x
x du
u x
du
u
x D
=
=
=
=
=
= +
}
}
}
}
}
Step 5:
1 2
(tan ) cos ( ln | cos |) sin
cos sin sin cos sin ln | cos |
sin cos cos sin cos sin tan
cos ln | cos |
y uy vy
x x C x D x x
C x D x x x x x x
y C x D x x x x x x x
x x
= +
= + +
= + +
' = + + + +
When (0) 0, y =
0. C =
When (0) 2, y' =
2. D =
Thus,
2sin sin cos sin ln | cos | . y x x x x x x = +
M1A1
M1
A1
M1
A1
A1
A1
BFC 14003
14
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
Q4
(b)
4(9.8) 39.2
39.2
392
0.1
0
W mg
W
k
l
c
= = =
= = =
A
=
Thus, from 0, mu cu ku '' ' + + =
We get 4 392 0 u u '' + = or 98 0. u u '' + =
The characteristic equation is
2
98 0. m + =
So, 7 2 . m i =
Therefore, ( ) cos(7 2 ) sin(7 2 ). u t A t B t = +
or ( ) cos(9.9 ) sin(9.9 ). u t A t B t = +
( ) 7 2 sin(7 2 ) 7 2 cos(7 2 ). u t A t B t ' = +
The spring is released after pulling it down 0.2 m.
So, we have (0) 0.2 u = .
Since its set in motion with an upward velocity of 4 m/s,
we have (0) 4 u' = . (upward is negative)
These initial conditions give us the equation for the position of the
spring at any time t as
( ) 0.2cos(7 2 ) 0.4041sin(7 2 ). u t t t =
or
1 2 2
( ) cos(7 2 ) sin(7 2 ).
5 7
u t t t =
A1
A1
A1
M1
A1
A1
A1
A1
A1
A1
10
Q5(a)
(i)
{ } { }
3 2
5
3 2 5
3
4
4
2 4
( 3) 5
t
t
t t
e t
e
e t e
s s
+
`
)
= +
= +
+
M1
A1A1
3
Q5(a)
(ii)
{ }
{ } { }
3
3
2
3
2 2
cosh 4 ( 3)
cosh 4 ( 3)
16
27
( 16)
s
t t t t
t t t t
s
e
s
o
o
+
= +
+
= +
M1
A1A1
3
BFC 14003
15
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
Q5(a)
(iii)
{ }
{ } { }
{ } { }
{ } { }
3
3
3[( 3) 3]
9 3( 3)
9 3
2
sinh(3 ) ( 3)
sinh(3 ) ( 3)
sinh(3 ) ( 3)
sinh(3 ) ( 3)
3
9 3
t
t
t
t
s
t e H t
t e H t
t e H t
t e e H t
e
s s
+
+
= +
= +
= +
= +
M1
A1
A1A1
4
Q5(b)
{ } { } { } { }
( )
( )
2
2
2
2
3 2 2
3
2 , (0) 2, (0) 3
2
1
( ) (0) (0) 2 ( ) (0) ( )
1
1
( ) 2 3 2 ( ) 4 ( )
1
1
2 1 ( ) 2 1
1
1
( 1) ( ) 2 1
1
1 2 1
( )
( 1) ( 1) ( 1)
1 2
( )
( 1)
t
t
y y y e y y
y y y e
s Y s sy y sY s y Y s
s
s Y s s sY s Y s
s
s s Y s s
s
s Y s s
s
s
Y s
s s s
Y s
s
'' ' ' + = = =
'' ' + =
' + =
+ + + =
+ = +
= +
= +
= +
{ }
2
2 2
1
1
3 2
2
1
( 1)
Byusing partial fraction,
2 1
( 1) 1 ( 1)
2, 1
( ) ( )
1 2 1
( 1) 1 ( 1)
1
2
2
t t t
s
s
s A B
s s s
A B
y t Y s
s s s
e t e e t
+
= +
= =
=
=
`
)
=
M1
A1
A1
M1
A1
M1
A1
A1A1A1
10
Q6(a)
(i)
1
2 2
1 1
2 2
2
5 6
4 ( 2) 4
6
5
4 ( 2) 4
5cosh 2 3 sin 2
t
s
s s
s
s s
t e t
+
`
+
)
= +
` `
+
)
)
= +
M1
A1A1
3
BFC 14003
16
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
Q6(a)
(ii)
2
1
2
2
2 2
2 2
2 2
2
1
2
1 1
16
( 3)( 1)
Bypartial fraction,
16
( 3)( 1) 3 1 ( 1)
16 ( 1) ( 1)( 3) ( 3)
16 ( ) (2 2 ) ( 3 3 )
9, 7, 4
16
( 3)( 1)
9 7
3 1
s
s s
s A B C
s s s s s
s A s B s s C s
s A B s A B C s A B C
A B C
s
s s
s s
`
+
)
= + +
+ + +
= + + + +
= + + + +
= = =
`
+
)
= +
`
+
)
1
2
3
4
( 1)
9 7 4
t t t
s
e e e t
` `
+
)
)
= +
M1
M1
A1
A1
A1A1A1
7
BFC 14003
17
(M method, A answer) Mark Total
Q6(b)
2
2
1 2
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
1
1
2
1 1 1
3 2 2 5sin , (0) 0, (0) 2
3 2 0
2, 1
( ) 2
0 .......(i)
Compare with , no termalike, accept (i)
2
2
3 2 2
2 3(2
x x
h
r
p
p
h
p
p
p p p
y y y x x y y
m m
m m
y Ae Be
f x x
y x Cx Dx E
r y Cx Dx E
y
y Cx D
y C
y y y x
C C
'' ' ' + = + = =
+ =
= =
= +
= +
( = + +
= = + +
' = +
'' =
'' ' + = +
| |
2 2
2 2
2
1
2
2
2
2
) 2( ) 2
2 ( 6 2 ) (2 3 2 3) 2
1 3 11
, ,
2 2 4
1 3 11
2 2 4
( ) 5sin
cos sin
0 cos sin ............(ii)
Compare with , no termalike, accept (ii)
sin cos
p
r
p
p
h
p
x D Cx Dx E x
Cx C D x C D E x
C D E
y x x
f x x
y x K x L x
r y K x L x
y
y K x L
+ + + + = +
+ + + + = +
= = =
= + +
=
= +
= = +
' = +
2
2 2 2
2
2 2
cos sin
3 2 5sin
cos sin 3( sin cos ) 2( cos sin ) 5sin
( 3 ) cos (3 ) sin 5sin
3 1
,
2 2
3 1
cos sin
2 2
1 3 11 3 1
cos sin
2 2 4 2 2
p
p p p
p
x x
x
y K x L x
y y y x
K x L x K x L x K x L x x
K L x K L x x
K L
y x x
y Ae Be x x x x
'' =
'' ' + =
+ + + =
+ + =
= =
=
= + + + +
M1
A1
M1
A1
A
1
2
A1
M1
A1
A
1
2
A1
A1
10
You might also like
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Rvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesRvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 13.differentiation and Integration of Power Series PDFDocument11 pages13.differentiation and Integration of Power Series PDFAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Info Booklet, Revised 2011Document27 pagesInfo Booklet, Revised 2011ordinanceNo ratings yet
- Name of The Student: Branch: Unit - I (Fourier Series) : Engineering Mathematics MaterialDocument11 pagesName of The Student: Branch: Unit - I (Fourier Series) : Engineering Mathematics Materialsabarish001No ratings yet
- MA2211 NotesDocument145 pagesMA2211 NotesBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Formulae:: Quadratic FormulaDocument6 pagesSome Basic Formulae:: Quadratic FormulaBlazingStudiosNo ratings yet
- 2.odd Even Function1Document12 pages2.odd Even Function1Atikah JNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesDocument13 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesCM Zain CrcoNo ratings yet
- GATE Mathematics Paper-2007Document11 pagesGATE Mathematics Paper-2007RajkumarNo ratings yet
- GATE Mathematics Paper 2011Document8 pagesGATE Mathematics Paper 2011RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesFourier SeriesPurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Misrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97Document26 pagesMisrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97bhagyagr8No ratings yet
- Advanced Computational Methods: Numerical IntegrationDocument59 pagesAdvanced Computational Methods: Numerical IntegrationMohammed HamdyNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument31 pagesFourier SeriesSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- Final Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinal Formula SheetwhatnononoNo ratings yet
- Function: X Is Chosen at Random From The First 1000 Natural Numbers. If (.) Denotes TheDocument4 pagesFunction: X Is Chosen at Random From The First 1000 Natural Numbers. If (.) Denotes TheShrey PandeyNo ratings yet
- DRM SolutionsDocument116 pagesDRM SolutionsCésar TapiaNo ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- 2008 Ext1 PDFDocument3 pages2008 Ext1 PDFBrandi RoseNo ratings yet
- Kcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Document13 pagesKcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Kamalesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Https Doc 00 7g Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocument7 pagesHttps Doc 00 7g Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentVignesh RavishankarNo ratings yet
- Eamcet 2014 Engineering Key SolutionsDocument42 pagesEamcet 2014 Engineering Key Solutionsandhracolleges100% (1)
- (A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Document15 pages(A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Heather JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Engineering MathsDocument8 pagesEngineering MathsSanthosh SanNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- $RM3GFU6Document14 pages$RM3GFU6bacchuskevin10No ratings yet
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDocument12 pagesHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument6 pagesFormula RioJorge Laura GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Narayana Grand Test - 8Document12 pagesNarayana Grand Test - 8Meet ShahNo ratings yet
- Solutions: S - 1 5 Mathematics-III (May-2012, Set-2) JNTU-KakinadaDocument10 pagesSolutions: S - 1 5 Mathematics-III (May-2012, Set-2) JNTU-KakinadaSri DNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboNo ratings yet
- Ajc h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesAjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer Scheme MAT 565/480 (Advanced Differential Equation) JANUARY 2012Document4 pagesSuggested Answer Scheme MAT 565/480 (Advanced Differential Equation) JANUARY 2012Fakhrur RaziNo ratings yet
- Math54 Teleman Final 2011spring SolnDocument3 pagesMath54 Teleman Final 2011spring SolntehkronosNo ratings yet
- B.E. Degree Examinations: April/May 2011Document4 pagesB.E. Degree Examinations: April/May 2011Dhanabal Palanisamy PNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDocument110 pagesEe602 Fourier SeriesArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- MST209 2005solutionsDocument6 pagesMST209 2005solutionsrashismart2000No ratings yet
- GATE Mathematics Paper-2003Document13 pagesGATE Mathematics Paper-2003RajkumarNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Maths SolutionsDocument7 pagesIIT JEE Maths SolutionsVishal GaudNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Computer Science Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesTheoretical Computer Science Cheat SheetRosa GonzalezNo ratings yet
- X Senx Senx y DX Dy X X DZ Xtagx DX Dy: Cos 2 Cos 1Document3 pagesX Senx Senx y DX Dy X X DZ Xtagx DX Dy: Cos 2 Cos 1Gabriel Irigoin CordovaNo ratings yet
- JC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Document10 pagesJC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Huixin LimNo ratings yet
- Cape Pure Mathematics Unit 2module 2: Sequences, Series and ApproximationsDocument39 pagesCape Pure Mathematics Unit 2module 2: Sequences, Series and ApproximationsCarlon BairdNo ratings yet
- MATH 1432 (Cal II) Final Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesMATH 1432 (Cal II) Final Exam Reviewyvcala456No ratings yet
- Differentiation of Continuous Functions: X X X F X X F X F XDocument13 pagesDifferentiation of Continuous Functions: X X X F X X F X F XFrancisco FalconNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- 8.half Range (Exercise)Document1 page8.half Range (Exercise)Atikah JNo ratings yet
- X F X F: Even Function Half Range Series: A Series That IsDocument1 pageX F X F: Even Function Half Range Series: A Series That IsAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 12b) Power Series in XDocument6 pages12b) Power Series in XAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 7.half Range SeriesDocument9 pages7.half Range SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 5.periodic FunctionDocument7 pages5.periodic FunctionAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 6.periodic FuncDocument1 page6.periodic FuncAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 2.odd Even Function1Document12 pages2.odd Even Function1Atikah JNo ratings yet
- 1.fourier SeriesDocument11 pages1.fourier SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 4.odd N Even (Exercise)Document1 page4.odd N Even (Exercise)Atikah JNo ratings yet
- 7.quotient Test (Ratio Test)Document4 pages7.quotient Test (Ratio Test)Atikah JNo ratings yet
- 5 P-SeriesDocument3 pages5 P-SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 8.root TestDocument2 pages8.root TestAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Slide 2nd Order ODEDocument15 pagesSlide 2nd Order ODEAtikah JNo ratings yet
- The Integral Test PDFDocument8 pagesThe Integral Test PDFAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Application 1st OrderDocument3 pagesApplication 1st OrderAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformationDocument13 pagesLaplace TransformationAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Find The Laplace Transform. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L)Document1 pageFind The Laplace Transform. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L)Atikah JNo ratings yet
- Application 2nd OrderDocument3 pagesApplication 2nd OrderAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Theorem 3: MultiplyDocument2 pagesTheorem 3: MultiplyAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 3.telescope SeriesDocument3 pages3.telescope SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Inverse LaplaceDocument2 pagesInverse LaplaceAtikah JNo ratings yet
- S1: Determine A and F (X) - S2: Find The Complimentary SolutionDocument2 pagesS1: Determine A and F (X) - S2: Find The Complimentary SolutionAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Undetermined CofDocument4 pagesUndetermined CofAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Theorem 1: LinearityDocument2 pagesTheorem 1: LinearityAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Theorem 2: First ShiDocument2 pagesTheorem 2: First ShiAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 1 .2nd ODE - Homogeneous EquationDocument2 pages1 .2nd ODE - Homogeneous EquationAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Table of Particular IntegralDocument1 pageTable of Particular IntegralAtikah JNo ratings yet