Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integral Calculus Finals Reviewer
Integral Calculus Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jaimee NavarroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Integral Calculus Finals Reviewer
Integral Calculus Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jaimee NavarroCopyright:
Available Formats
INTEGRAL CALCULUS FINALS REVIEWER (2 Sem 11-12) INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES I. Integration by Parts udv = uv vdu 1.
lnxdx
*First, determine u and dv. Yung dv, dapat laging kasama yung dx sa formula. For u, an easier way to find that is by using the code LIPET: Logarithm, Inverse, Polynomial, Exponential, Trigonometric. Kumbaga parang yan yung hierarchy ng pagpipilian mo kung ano yung gagawin mong u. Logarithm being the highest and Trigonometric the lowest u = lnx dv = dx dx du = x v=x *substitute these values sa formula na udv = uv vdu
nd
4. sec xdx
3
= sec xsecxdx
2
u = secx du = secxtanxdx
dv = sec2xdx v = tanx
2
= secxtanx secxtan xdx = secxtanx secx(sec x 1)dx
2
= secxtanx (sec x secx)dx
3
= secxtanx sec xdx + secx
3
*transpose sec3xdx kasi same siya nung sa other side
2 sec xdx = secxtanx + secx 1 sec3xdx = 2 (secxtanx + ln(secx + tanx)) + c
3
lnxdx = xlnx x
= xlnx x + c 2. x lnxdx
2
dx x
5. e cos2xdx
x
u = ex du = e dx dv = x dx x3 v= 3
2 x
dv = cos2xdx 1 v = 2 sin2x
u = lnx dx du = x
1 x 1 x = 2 e sin2x 2 e sin2xdx
u = ex du = e dx
x
1 1 dx x2lnx dx = 3 x3lnx 3 x3 x 1 3 1 2 = 3 x lnx 3 x dx
u = x2 du = 2xdx dv = dx v=x
dv = sin2xdx 1 v = 2 cos2x
1 x 1 1 x 1 x = 2 e sin2x 2 2 e cos2x 2 e cos2xdx 1 x 1 x 1 x = 2 e sin2x + 4 e cos2x 4 e cos2xdx
*transpose exsin2xdx kasi same siya nung sa other side
1 3 1 3 2 = 3 x lnx 3 [x 2 x dx] 1 3 1 3 2 x = 3 x lnx 3 x + 3 3 3 1 3 1 3 2x = 3 x lnx 3 x + 9 + c 1 3 2 = 3 x lnx 1 + 3 + c 1 3 1 = 3 x lnx 3 + c 3. x e dx
3 x 3
excos2xdx + 4 excos2xdx = 2 exsin2x + 4 excos2x
5 x 1 x 1 4 e cos2xdx = 2 e sin2x + 2 cos2x 2 1 excos2xdx = 5 ex sin2x + 2 cos2x + c 6. (x + sinx) dx
2
u = x3 du = 3x2dx
dv = exdx v = ex
x3exdx = x3ex 3 x2exdx
u = x2 du = 2xdx dv = exdx v = ex
x
= x e 3 * x e 2 xe dx ]
3 x 2 x
u=x du = dx
3 x 2 x x x
dv = exdx v = ex
= (x + 2xsinx + sin x)dx 3 x 2 = 3 + 2xsinxdx + sin xdx 3 x 1 = 3 + 2xsinxdx + 2 (1 cos2x)dx 3 x 1 1 = 3 + 2 x 2 sin2x + 2xsinxdx 3 x 1 1 = 3 + 2 x 4 sin2x+ 2xsinxdx
2 2
= x e 3x e + 6[ xe e dx ] 3 x 2 x x x = x e 3x e + 6xe 6e + c
x 1 1 = 3 + 2 x 4 sin2x+ 2 *xcosx +cosxdx] 3 x 1 1 = 3 + 2 x 4 sin2x+ 2 *xcosx + sinx + 3 x 1 1 = 3 + 2 x 4 sin2x 2xcosx + 2sinx + c
u=x du = dx
dv = sinxdx v = cosx
7.
t dt 2 1 + 3t =
t1+t dt 3t
u = t2 du = 2tdt
dv = (1 + 3t2)-1/2tdt 1 1 v = 6 2(1 + 3t2)1/2= 3 (1 + 3t2)1/2 use u du
n
3 3 2 2 4/3 2 3 = 8 (1 x ) x + 7 7 x 3 4 3 2 4/3 2 = 8 (1 x ) 7 x + 7 3 2 4/3 2 = 56 (1 x ) (4x + 3) + c
-11 11. Sec x dx
1 2 2 2 2 = 3 t 1 + 3t 3 1 + 3t tdt
u = 1 + 3t2 du = 6tdt
1 u = Sec-1x du = dx x2 1 x dx x2 1 x 1 x2 x2 dx x2 1 x2 1
dv = dx
1 2 2 1 2 2 2 3/2 = 3 t 1 + 3t 3 6 3 (1 + 3t ) 1 2 2 2 2 3/2 = 3 t 1 + 3t 27 (1 + 3t ) + c 8. xCsc xdx
-1
v=x
= u = Csc-1x dx du = x x2 1 dv = xdx x2 v= 2
1 2 -1 1 2 dx = 2 x Csc x + 2 x 2 x x 1 1 2 -1 1 = 2 x Csc x + 2
xdx 2 x 1
=1 1 2 xx 1x dx = 1 x2
-11 = xSec x +
1 2 -1 1 2 -1/2 = 2 x Csc x + 2 (x 1) xdx use undu 1 2 -1 1 2 1/2 = 2 x Csc x + 2 (x 1) + c 9. sin x dx
y= x y2 = x 2ydy = dx
xdx 2 1x 1 2 -11 2 1/2 = xSec x + 2 1 (1 x ) + c -11 2 = xSec x + 1 x + c 12.
use undu
ln3xdx
u = ln3x 3ln2xdx du = x dv = dx v=x
= siny 2ydy = 2ysinydy
u=y du = dy dv = sinydy v = cosy
= xln x 3
3
= 2 * ycosy + cosydy ] = 2ycosy + 2siny + c
*substitute
3
x ln xxdx
2
= xln x 3 ln xdx
u = ln2x 2lnxdx du = x dv = dx v=x
x back sa mga y
2 1/3 2 2 1/3
= 2 x cos x + 2sin x + c 10. x (1 x ) dx x x(1 x ) dx
u=x
2
du = 2xdx
dv = (1 x ) xdx 1 3 v = 2 4 (1 x2)4/3 use undu
2 1/3
= xln x 3 [xln x 2 x
3 3 2 2
lnxdx x
= xln x 3xln x + 6 lnxdx
u = lnx dx du = x dv = dx v=x
3 2 2 4/3 3 2 4/3 = 8 x (1 x ) + 8 (1 x ) xdx 3 2 2 4/3 3 1 3 2 7/3 = 8 x (1 x ) + 4 2 7 (1 x ) 3 2 9 2 4/3 2 7/3 = 8 x (1 x ) + 56 (1 x ) 3 2 4/3 2 3 2 = 8 (1 x ) x + 7 (1 x )
dx 3 2 = xln x 3xln x + 6 *xlnx x x ] = xln x 3xln x + 6 *xlnx dx] 3 2 = xln x 3xln x + 6xlnx 6x + c
3 2
13.
sin xdx sin xsinxdx
u = sin4x du = 4sin3xcosxdx dv = sinxdx v = cosxdx
c. sinxcosx recall the identity sin2x = 2sinxcosx. Just transpose 2 to the other 1 side. So youll get 2 sin2x = sinxcosx
= sin xcosx + 4 sin xcos xdx
4 4 4 4 3 3 2
= sin xcosx + 4 sin x(1 sin x)dx
2
sin 2x dx 5 sin 2x 2 6 8 sin 2xcos 2x
7 3
= sin xcosx + 4 (sin x sin x) dx
3 5
use undu
= sin xcosx + 4sin xdx 4sin xdx
3 5
=8
2x dx sin sin 2x cos 2x
6 4 6
*transpose sin xdx kasi same siya nung sa other side
5
4sin xdx +sin xdx = sin xcosx + 4sin xdx
5 5 5 4 3
= 8 sin 2xcos 2xdx
dy *represent 2x as y. so y = 2x. And dy = 2dx. So dx = 2
5sin xdx = sin xcosx + 4sin xdx
4 3
u = sin2x du = 2sinxcosxdx
dv = sinxdx v = cosxdx
1 4 6 = 8 2 sin ycos ydy *change the limits. To do that, substitute x sa y = 2x.
x y 0 0 4 2
sin5xdx = 5 (sin4xcosx + 4sin3xdx)
4 6 2 cos x cos x = sin xcosx + 4 4 + 6 ] 0 4
=4
sin ycos ydy
ADDITIONAL FORMULA: WALLIS FORMULA
*only works when the upper and lower limits are 2 and 0.
2
sin xcos xdx =
[(m-1)(m-3)2 or 1+*(n-1)(n-3)2 or 1+ (m+n)(m+n-2)(m+n-4)2 or 1
where: = 2 , if both m and n are EVEN = 1, if other wise *yung 2 or 1, ibig sabihin yung subtraction blah, yung value nun diba paliit nang paliit. Basta until maging 2 OR 1 ka magsstop.
4
*use Wallis formula [(4-1)(4-3)][(6-1)(6-3)(6-5)] = 4 (6+4)(6+4-2)(10-4)(10-6)(10-8) 2 (31)(531) = 4 108642 2 3 = 27 II. Substitution Methods A. Substitution of Functions 1. x 1 + x dx
u=1+x x=u1 dx = du *substitute all xs with us
1.
(1 cos 2x) dx 4 2 tan 2xcsc 4xsinxcosx
7/2
sin 2x
4
(sin 2x) dx 1 1 4 2 2 cos 2x 4sin 2xcos 2x 2 sin2x
7/2
= (u 1)u du
1/2
*okay so isa-isahin natin yung mga chuchu sa denominator: a. tan42x sinx sin42x recall sa identities na tanx = cosx . Kaya naging tan42x= cos42x yay 1 b. csc24x sin24x 1 recall the trigonometric transformation formula sinxcosx = 2 sin2x. So ang main agenda mo is to get sin24x 1 sinxcosx = 2 sin2x
*i-double mo yung angle ng right side. so pag dinouble mo yung angle sa right side, double the angle sa left as well
= (u u )du 2 5/2 2 3/2 =5u 3u +c 5/2 3/2 6u 10u = +c 15 2 3/2 = 15 u (3u 5) + c 2 3/2 = 15 (1 + x) [3(1 + x) 5] + c 2 3/2 = 15 (1 + x) (3x 2) + c
3/2 1/2
1 sin2xcos2x = 2 sin4x
*square both sides
1 sin22xcos22x = 4 sin24x 4sin22xcos22x = sin24x
1 *transpose 4
tadaaaaa yay you
x dx x xdx 2. (x2 + a2)3 (x2 + a2)3
u = x2 + a2 x2 = u a2 2xdx = du *substitute all xs with us
B. Algebraic Substitution 1. x 1 + x dx
u= 1+x u2 = 1 + x x = u2 1 dx = 2udu
1 =2
(u - ua )du
3 -1 2 -2
= 2(u 1) u udu
2
1 -2 2 -3 = 2 (u a u )du 1 u au = 2 -1 -2 + c 2 1 1 a = 2 u + 2u2 + c 2 1 -2u + a = 2 2u2 +c
*substitute the value of u back to x2 + a2
= 2u (u 1)du
2 2
1 -2(x + a ) + a = 2 2(x2 + a2)2 + c 1 2 2 2 = 4(x2 + a2)2 [a 2(x + a )] + c 1 2 2 = 4(x2 + a2)2 (2x + a ) + c y +3 x xdx 3. (3 - 2y)2/3 dy (x2 + a2)3
u = 3 2y 2y = 3 u 2dy = du
= 2 (u u )du 5 3 u u = 2 5 3 + c 5 3 3u 5u +c = 2 15 2 3 2 = 15 u (3u 5) + c 2 3/2 = 15 (1 + x) [3(1 + x) 5] + c 2 2/3 = 15 (1 + x) (3x 2) + c
4 2
2.
3 3 2 2
dy 1/3 y - y dy
u = y1/3 u3 = y 3u2du = dy
1 =2 1 -2/3 = 4 (9 u)u du 1 -2/3 1/3 = 4 (9u u )du 1/3 4/3 1 3 9u 3u =4 1 4 +c 3 1/3 = 16 u (36 u) + c 3 1/3 = 16 (3 2y) (2y + 33) + c
3-u+6 2 2/3 du u
u du = 3u(u - 1) udu = 3 u - 1
u du = 3 u3 - u
2 2 2
= 3ln(u 1) 3 2/3 = 2 ln(y 1)
3 3 2 2
3 3 = 2 (ln2 ln1) = 2 ln2 7 dx 3. 0 1+3 x+1
u=3 x+1 u3 = x + 1 3u2du = dx
u du =3 1+u 1 = 3u - 1 + u + 1 du
*divide u2 by 1 + u
**change the limits. To do that, substitute x sa u = 3 x + 1 x 0 7 1 2 y
u = 3 2 + u + ln(u + 1) 1 3 = 32 + ln2
1 2
4.
ln2 0
e dx e e dx x x 1+e 1+e
u = 1 + ex u2 = 1 + ex ex = u2 1 2udu = exdx
2x
ydy 2 -1/2 ydy 2 (1 y ) 1-y
=2
1)udu (u - u
2
1 **change the limits. To do that, substitute x sa x = y x 5/3 5/4 3/5 4/5 u
= 2(u 1)du *change the limits. To do that, substitute x sa u = 1 + ex
x u
3
1 2 1/2 = 2 1 (1 y) = 9 1 - 25
3/5 4/5
0 2
ln2 3
3 2
16 1 1 - 25 = 5
u = 2 3 - u
3.
1 2 2 = 33 (3 3 - 2 2 ) - ( 3 - 2 ) = 3
dx x 2x -x dy = 25y - 1
2 2
C. Reciprocal Substitution *use this when you see equations like this: dx 1 dy and substitute x = y & dx = y2 x ax + bx + c
2
u = 5y du = 5dy 1 5
a=1
du u2 - a2
1 5+ = 5 ln
25 - x x
+c
1.
x
=
1
y
dx 2 2x - x dy 2 y 2 1 2 y -y dy 2 y
1 dy *substitute x = y & dx = y2
D. Trigonometric Substitution
If you see this combination:
Substitute these: u =asin u = atan u = asec
a u a +u u a
2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2y - 1 2 y y dy 2 y = 1 2 y 2y -1
2ax - x
x = 2asin x = 2atan x = 2asec
2 2
2ax + x
2
x - 2ax
dy 2y - 1
-1/2
1.
u du -a
2
= (2y 1) dy 1 2 1/2 = 2 1 (2y 1) + c =
5/3 5/4
u = asec du = atansecd
2 x -1+c dx 2 x x -1 dy 2 y
2 2
2.
1
y
a tansecd = a sec - 1 1 tansecd = a tan 1 secd = a tan
tansecd = a a2sec2 - a2
2 2 2
1 2 y -1
1 = a cscd 1 = a ln |csc cot| + c
*going back to u = aseci-draw mo sa right triangle hyp *so diba csc, which is opp so magiging = a u2 - a2 u u2 - a2 . and cot
E. Half-Angle Substitution *use this when you see trigo functions 1 z = tan2 (nx) 2z tan(nx) = 1 - z2 1-z cos(nx) = 1 + z2 1. dx 1 + sinx + cosx =
2dz 1 + z2 2z 1 - z2 1 +1 + z2 + 1 + z2 2dz 1 + z2 1 + z2 + 2z + 1 - z2 1 + z2 n=1
2
1 2dz dx = n 1 + z2 2z sin(nx) = 1 + z2
1 = a ln
1 = a ln
u a 2 2 2 2 u -a u -a u-a 2 2 +c u -a
+c
*i-square yung fraction para mawala yung square root at may ma-cancel hihi
1 (u - a)(u - a) = a ln (u - a)(u + a) + c 1 u-a = a ln u + a + c 2.
2 0
2 2
4 - x dx (2) - (x) dx
2 2
= x
u = asin x = 2sin dx = 2cosd
dz 22dz + 2z = 1 + z
= (2sin)
2
4 - (2sin) 2cosd
2
= 24 sin 4 - 4sin cosd
2
= 8 sin 2
2 2 2
1 - sin cosd
2
2.
= ln (1 + z) + c 1 = ln (1 + tan2 x) + c /2 dx 3 + cos2x 0 =
n=2
= 16 sin cos cosd = 16 sin cos d *change the limits. To do that, substitute x sa x = 2sin
x u 0 0
2 2
1 2dz 2 1 + z2 1 - z2 3 + 1 + z2
2 2
2 2
= 16
/2 0
sin cos d
3 + 3z2dz +1-z 1 2dz 1 dz = 2 4 + 2z = 2 2 + z
1 =2
2
du a2 + u 2
*use Wallis Formula (1)(1) = 16 (4)(2) 2 = 3.
2a 0
= =
1 2 2 1
Tan Tan
-1
z 2
/2 0
1 tan2 (nx) -1
2ax - x dx
2
x = 2asin dx = 4asincosd
= (2asin ) 2a(2asin ) - (2asin ) 4asincosd
2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 1 tanx -1 = Tan 2 2 2
]
0
/2 0
/2
= 3. =
= 4a4a = 16a
3
sin4
4a sin - 4a sin sincosd
Tan 2 2
1
/2 0
tan2 -1 2
- Tan
-1tan0
= 4 2
sin4 4a2sin2(1 - sin2) sincosd 3 4 2 = 16a sin 2asin cos sincosd 4 6 2 = 32a sin cos d
*change the limits. To do that, substitute x sa x =
2asin2
4
dx 12 + 13cosx
2dz 1 + z2 1 - z2 12 + 13 1 + z2
2 2
= 32a sin cos d *use wallis 0 4 4 32a (5 x 3 x 1)(1) 5a = 8x6x4x2 2 = 8
/2
12 + 12z 2z + 13 - 13z dz dx = 225 - z = 2(5) - (z)
=
2 2
z = 5sin, dz = 5cosd
5cosd = 225(1 - sin ) 2 cosd 2 d 2 = 5 cos = 5 cos = 5 secd
5cosd = 2 25 - 25sin2
2 2
2.
+ 8x - 12 3x + 8x - 12 x3x+ 7x + 12x = x(x + 4)(x + 3) dx A B C = x + x + 4 + x + 3 dx
3 2
= Alnx + Bln(x + 4) + Cln(x + 3)
Equating Coefficients: 3x2 + 8x 12 = A(x + 4)(x + 3) + Bx(x + 3) + Cx(x + 4) 3x2 + 8x 12 = A(x2 + 7x + 12) + B(x2 + 3x) + C(x2 + 4x) x2: 3 = A + B + C x: 8 = 7A + 3B + 4C c: -12 = 12A A = -1 *using system of equations: (3 = -1 + B + C) 3 -12 = -3B 3C 8 = -7 + 3B + 4C 15 = 3B + 4C 3=C 3=A+B+C B = 3 (-1) 3 B = 1
2 = 5 ln (sec + tan) 2 1 sin 2 1 + sin = 5 ln cos + cos = 5 ln cos
*going back to z = 5sini-draw mo sa right triangle hyp *so diba sin, which is opp so z magiging5 . and cos 25 - z2 = 5
= -lnx + ln(x + 4) + 3ln(x + 3) + lnc = ln B. Linear, Repeated Factors
c(x + 4)(x + 3) x
2 = 5 ln
z 1+5 25 - z 5
2
2 = 5 ln
5+z 2 25 - z
1.
C D A B x(x(x- 2)dx + 3) = x + x + x + 3 + (x + 3) dx
2 2 2 2
*square and get the square root of the fraction. Squinare and kinuha yung sqrt para parang walang damage na nangyari. It was as if you raised the fraction to the first power. Pero diba pag may exponent yung base ng ln, pwede mo siyang i-lagay and imultiply 2 with 5 .
B D = Alnx + x + Cln(x + 3) + x + 3 + E
Equating Coefficients: x 2 = Ax(x + 3)2 + B(x + 3)2 + Cx2(x + 3) + Dx2 x 2 = A(x3 + 6x2 + 9x) + B(x2 + 6x + 9) + C(x3 + 3x2) + Dx2 x3: 0 = A + C x2: 0 = 6A + B + 3C + D x: 1 = 9A + 6B c: -2 = 9B 7 2 7 5 A = 27 , B = 9 , C = 27 , D = 9
2 5+z ^ 21 = 5 ln 2 2
25 - z
1 *yung 2 i-move mo sa harap
2 1 (5 + z)(5 + z) = 5 2 ln (5 + z)(5 - z)
1 *change the limits. To do that, substitute x sa z = tan2 x
7 2 7 5 = 27 lnx 9 x 27 ln(x + 3) 9(x + 3) + c C. Quadratic, Distinct Factors 1. +2 A(2x + 4) + B x +x 4x + 5 dx = x + 4x + 5 dx
2 2
1 5+z = 5 ln 5 - z III. Partial Fractions
1 0
1 3 = 5 ln 2
*(2x + 4) came from the derivative of x2 + 4x + 5
A. Linear, Distinct Factors 1. + 11)dx (2x + 11)dx (2x x + x - 6 = (x + 3)(x - 2) A B = x + 3 + x - 2 dx
2
2x + 4 dx = A x2 + 4x + 5 dx + B x2 + 4x + 5 du *dun sa A, u .
*multiply the whole equation
with the denominator of the original fraction
(2x + 11)dx = (A(x - 2) + B(x + 3)) dx = A(x - 2)dx + B(x + 3)dx
= Aln(x 2) + Bln(x + 3) + lnc
*lnc yung ginamit para lang maging mas pretty/simplified yung kalabasang equation later hihi when x = 2: when x = -3: 2(2) + 11 = A(0) + B(2 + 3) 2(-3) + 11 = A(-3 2) + B(0) 15 = 5B 5 = -5A B=3 A = -1
dx = Aln(x + 4x + 5) + B(x + 2) + (1)
2 2 2 -1
dx 2 = Aln(x + 4x + 5) + B x2 + 4x + 4 + (5 - 4)
2
u2 + a2
du
= Aln(x + 4x + 5) + B Tan (x + 2) + c
Equating Coefficients: x + 2 = A(2x + 4) + B 1 x: 1 = 2A A = 2 1 c: 2 =4(2 ) + B B = 0
c(x - 2) = ln(x + 3) + 3ln(x 2)+ lnc = ln (x + 3)
1 2 = 2 ln(x + 4x + 5) + c
*remember yung exponent pwede itanspose transpose. Well do it sa 3ln(x 2) to magiging ln(x 2)3
C. Quadratic, Distinct Factors 1.
B. Horizontal Element A=
x (x(x+- 3)dx 4x + 5) A B C(2x + 4) + D E(2x + 4) + F = x + x + x + 4x + 5 + (x + 4x + 5) dx
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
(xR xL)dy y(xR xL)dy (xR2 xL2)dy
Ay = Ax =
dx (2x + 4)dx dx = A x + B x-2dx + C x2 + 4x + 5 + D x2 + 4x + 4 + (5 - 4) + (2x + 4)dx dx E (x2 + 4x + 5)2 + F (x2 + 4x + 5)2
ANALYSIS OF POLAR CURVES I. Symmetry ox: F(r,) = F(r , -) F(-r, - ) F(r , - ) F(-r , - ) F(-r , ) F(r, + )
B 2 -1 = Alnx + x + Cln(x + 4x + 5) + DTan (x + 2) + E dx 2 2 2 x + 4x + 5 + F [(x + 4x + 4) + (5 - 4)]
dx *Now lets focus on F [(x + 2)2 + (1)]2 .
oxy: F(r,) = ox: F(r,) =
u=x+2 u = asin x + 2 = tan
a=1 dx = sec d
x+2 tan = 1 *draw this
Bianca
II. Intersection w/ the pole set r = 0 and solve for i III. Intersection with axes 0 90 180 270 360
d F = Fsec = F cos d = 2 (1 + cos2)d
sec d sec d sec d 2 2 2 2 4 =F (tan + 1) = F (sec ) = F sec
2 2
r IV. Critical Points dr set d = 0 and solve for C V. Divisions use i & C VI. Additional Points SOME COMMON POLAR POLES A. Limacons : r = a bsin or r = a bcos a 0<|b|<1 a 0<|b|=1 a 1<|b|<2 a |b |2 B. Rose Curves r = asin(n) r = acos(n) with a loop cardioid with a dent convex
F 1 = 2 * + 2 sin2]
1 *recall that 2 sin2 = sincos. According to the drawing of the triangle, sin = x+2
2
x + 4x + 5 x + 4x + 5 x+2 1 multiply them to get x2 + 4x + 5 . So yun yung value ng 2 sin2. *as for , recall that x + 2 = tan. So = Tan-1(x + 2). *so the final equation is:
and cos =
1
2
. So
B 2 -1 = Alnx + x + Cln(x + 4x + 5) + DTan (x + 2) + E F x+2 -1 2 2 x + 4x + 5 + 2 Tan (x + 2) + x + 4x + 5 + G
*just solve for the values of A, B, C, D, E and F and youll get the final answer
AREAS & CENTROIDS OF PLANE AREAS A. Vertical Element A=
(ya yb)dx x(ya yb)dx (ya
2 2 yb )dx
Ax = Ay =
1.
r = 2 2sin (cardioid) Intersection with the pole: r = 2 2sin 0 = 2 2sin 2sin = 2 -1 = sin (1) =2
5. r = 2 at 360 or back to 0 ulit Then TA-DAAA!
Intersection with the axes: Compute for the Area: r 0 2 90 0 180 2 270 4 360 2 1 A=2
r2d
Critical Points: dr d = -2cos 0 = -2cos = cos (0) 3 =2, 2 Plot the points on the graph and draw the heart: 1. r = 2 when the angles nasa 0. So plot the first point sa (2,0)
-1
*isang half lang yung area na kukunin mo. Eh since sobrang carbon copy yung other half of the heart, multiply the Area by 2.
1 A=22
/2 -/2
(2 2sin) d
2
A = (4 + 8sin + 4sin )d A = 4 (1+ 2sin + sin )d
2
1 1 A = 4 2cos + 2 - 2 sin2
3 1 A = 42 - 2cos - 4 sin2
] -/2 = 6
/2
2.
2. r = 0 at 90. As you plot it, gawa ka na ng curve
3. r = 2 at 180. Ilagay mo yung point 2 units TOWARDS 180. Kumbaga sa side ng 180 yung 2.
4. r = 4 at 270. Like 180, plot 4 sa side ng 270.
r = 3sin2 Intersection with the pole: r = 3sin2 0 = 3sin2 0 = sin2 -1 2 = sin (0) 2 = 0, , 2, 3, etc. 3 = 0, 2 , , 2 , etc. Critical Points: dr d = 6sin2 = 0 0 = sin2 -1 2 = sin (0) 3 5 7 2 = 2 , 2 , 2 , 2 3 5 7 =4, 4 , 4 , 4 Intersection with axes & Critical Points:
r 0 0 45 3 90 0 135 -3 180 0 225 3 270 0 315 -3 360 0
VOLUMES & CENTROIDS OF PLANE AREAS A. Method of Circular Disk
b
2.
Find the volume of y = x and y = x about x + 1 = 0.
Points of Intersection: (x2)2 = x x4 = x x4 x = 0 x(x3 1) = 0 x = 0, y = 0 and x = 1, y = 1
V=
r dh
Vx = XCdv Vy = YCdv CONDITIONS: 1. element must be parallel to the axis 2. r must be parallel to the axis 3. the axis should be a boundary
XRIGHT: y = x x = y
XLEFT: y = x x = y r=y +1
2
R = y + 1 (kasi about x = -1)
1
V=
(R r )dh
2 2 2
V = (( y + 1) (y + 1) 1. Find V, x, y of the solid generated by rendering the 3 region bounded by y = 1 x , ox and oy about ox. V = r dx
2
) dx
2
V = (y + 2y
2
1/2
+ 1 y 2y 1)dx y 2y - 5 - 3 - y
5 3
y 4y V = 2 + 3
2
3/2
1 0
29 = 30
V = (ya yb) dx V = (1 x 0) dx
3 2
C. Method of Cylindrical Shell
b
V = 2
xydx
V= x x V = (x - 2 + 7 ) B. Method of Circular Ring
b
2 7
(1 2x + x )d
(when using a vertical element)
b
1 0
9 = 14
V = 2
xydy
(when using a horizontal element)
3
V=
(R r )dh 1. Find V if the area bounded by y = 1 x , ox and oy is revolved about ox. y=1x x =1yx=
1
3 3 3
1.
Find V if the axes bounded 2 3 by y = x and y = 2x is revolved about ox.
*substitute y = 2x sa y = x to get the points of intersection
2 3
1-y
V = 2
xydy V = 2 (xL xR)ydy
1/3
(2x) = x 4x x = 0 x (4 x) = 0 x =0 x = 0, then y = 0
4
2 2
V = 2 (1 - y) ydy
*use algebraic substitution & change limits u = (1 y)1/3 y = 1 u3 dy = 3u2du
0
4x=0 x = 4, then y = 8
u3 = 1 y
*change the limits. To do that, substitute y sa u = (1 y)1/3 V = 2
1
V=
(R r )dh
2 3/2 2
u(1 u ) 3u du
*you may interchange the limits by turning the equation to negative
1
V = [(2x) (x ) ]dx V = (4x x )dx
2 3
V = 6
u (1 u ) du
3 6
4x x V= 3 - 4
4 0
64 = 3
V = 6 (u u ) du u u V = 6 4 7
4 7
1 0
9 = 14
LENGTH OF ARC
1 + ( ) y in terms of x dx S = 1 + (dy ) x in terms of y dx dy S = (dt ) + ( dt ) parametric dr S = r + (d ) r in terms of
S=
dy 2 dx
2 2 2 2 2
S = 2a 2 + 2cos d S = 2 2 a 1 + cos d *lets focus on 1 + cos. Recall that: 1 2 cos = 2 (1 + cos2) 2cos = 1 + cos2
2 2cos 2 = 1 + cos 2
1.
Find the length of the curve y = lncosx from x = 0 to x = 4 .
y = lncosx dy sinx dx = cosx S=
S = 2 2 a
2 2cos 2 d
S = 2 2 2 acos2 d
1 + cosx
2
sinx
)
]
dx =
1 +tan x dx
S = 4a(2)sin2 SA = 2ydS
= 8aError! Bookmark not defined.
S = sec x dx = = secxdx
/4 0
AREA OF A SURFACE OF REVOLUTION about ox about oy 2)
3/2 2
S = ln(secx + tanx) 2.
= ln(1 +
SA = 2xdS 1.
Find the length of the curve x = 2(2t + 3) , y = 3(t + 1) from t = 0 to t = 1. dx 1/2 3 dt = 22 (2t + 3) (2) = 6 2t + 3 dy dt = 6(t + 1) S= (6 2t + 3 ) + (6(t + 1)) dt
2 2 2
Find the area of the surface of revolution generated by 3 revolving y = x between x = 0 and x = a about ox. SA = 2ydS SA = 2x SA = 2x
3
1 + dx
4
( )
dy
dx
n
1 + 9x dx u du
4
S = 36(2t + 3) + 36(t + 1) dt S = 6 2t + 3 + t + 2t + 1 dt
2
u = 1 + 9x
du = 36x du
1 2 4 3/2 SA = 2 36 3 (1 + 9x ) 3/2 SA = 27 [ (1 + 9x) + 1]
a 0
S = 6 (t + 1) dt
2
S = 6 (t + 1)dt S = 3(t + 1) 3.
2
1 0
= 15
Find the total arc length of the cardioid r = a(1 + cos). dr d = a(sin) S = 2 (a(1 + cos)) + (asin)
2 2
*minultply sa 2 kasi 2 parts yung cardioid
S =2
a (1 + cos) + a sin
2 2
S = 2a 1 + 2cos + cos + sin d *recall cos + sin = 1
2 2
SECOND THEOREM OF PAPPUS V = 2Ad where:
A = area d = perpendicular distance of the centroid from the axis of revolution
1.
Find the volume if area bounded by y = x and y = x is revolved about x = -1. A = (ya yb)dx A = (x
1/2
x )dx
3
2 3/2 x A=3x 3
1 0
1 =3
Ax = Ax = Ax =
x(ya yb)dx x(x1/2 x2)dx (x3/2 x3)dx
4
2 5/2 x Ax =5x 4 1 3 x = 20 3 9 x = 20
1 0
1 9 29 V = 2Ad = 23 20 + 1 = 30
* may + 1 kasi yung yung axis nasa x = -1.
You might also like
- Clever Keeping Maths SimpleDocument104 pagesClever Keeping Maths SimpleNuurani60% (5)
- 1st Module - Numerical Solutions To CE Problems - Physical Meaning of Derivatives and IntegralsDocument12 pages1st Module - Numerical Solutions To CE Problems - Physical Meaning of Derivatives and IntegralsELSA M. ARCIBAL100% (1)
- Differential Equations:: Cagayan State University-Carig CampusDocument3 pagesDifferential Equations:: Cagayan State University-Carig Campusjohn dave rivasNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Problems With SolutionsDocument8 pagesAnalytic Geometry Problems With SolutionsMercedita Ginoo100% (1)
- Solutions To Selected Exercises in Elementary Differential Equations-Rainville Bedient (Chua)Document87 pagesSolutions To Selected Exercises in Elementary Differential Equations-Rainville Bedient (Chua)Charles Warren GoNo ratings yet
- Differential and Integral Calculus by Feliciano and UyDocument2 pagesDifferential and Integral Calculus by Feliciano and UyJohn Mark Huros0% (3)
- Integral Calculus Module 1 PDFDocument12 pagesIntegral Calculus Module 1 PDFRara JaveeeNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument26 pagesAnalytic GeometryJohn Rey Blasco33% (3)
- Differential EquationDocument134 pagesDifferential EquationHalzinashein Abella100% (1)
- Problem Set of Differential Equation PDFDocument72 pagesProblem Set of Differential Equation PDFIbnu Rafi100% (1)
- D.E 3rd EditionDocument33 pagesD.E 3rd Editionken100% (2)
- Analytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)Document9 pagesAnalytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)James Lindo100% (1)
- Integral CalculusDocument120 pagesIntegral CalculusBernadette Boncolmo100% (3)
- Chapter 10 Differential EquationsDocument22 pagesChapter 10 Differential EquationsAloysius Raj67% (3)
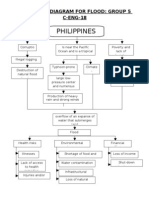
- Philippines: Schematic Diagram For Flood: Group 5 C-ENG-18Document1 pagePhilippines: Schematic Diagram For Flood: Group 5 C-ENG-18Jaimee NavarroNo ratings yet
- Elementary Differential Equation: MATH 2103 Engr. Ernesto P. PucyutanDocument72 pagesElementary Differential Equation: MATH 2103 Engr. Ernesto P. PucyutanSevy100% (1)
- Differential CalculusDocument5 pagesDifferential Calculusnico aspraNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus: Engr. Kenneth Rene Ian M. Talag Aeronautical Eng. Board Exams 2012 ReviewDocument73 pagesIntegral Calculus: Engr. Kenneth Rene Ian M. Talag Aeronautical Eng. Board Exams 2012 ReviewDustin Remegio CasillanNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations:: Cagayan State University-Carig CampusDocument5 pagesDifferential Equations:: Cagayan State University-Carig CampusJulia Macugay100% (1)
- Differential EquationDocument4 pagesDifferential EquationGreg Cabillete0% (1)
- Lesson 1 Derivative of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Derivative of Trigonometric FunctionsrickiegasparNo ratings yet
- MATH 160A - Calculus 2 Lecture 3: Integration of Trigonometric FunctionDocument2 pagesMATH 160A - Calculus 2 Lecture 3: Integration of Trigonometric FunctionVape DrugNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Reviewer PDFDocument64 pagesDifferential Calculus Reviewer PDFうおみ 勇気100% (2)
- Intergal CalculusDocument20 pagesIntergal CalculusElizabeth ErwanNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Maxima and Minima (Diffirential Calculus)Document12 pagesSolved Problems in Maxima and Minima (Diffirential Calculus)Aurum Chantal50% (2)
- Some Solved Differential Equations Problems PDFDocument123 pagesSome Solved Differential Equations Problems PDFRafael Bermudez100% (1)
- Module 6 Plane GeometryDocument2 pagesModule 6 Plane GeometryGlenn Frey LayugNo ratings yet
- Elementary Differential EquationsDocument43 pagesElementary Differential EquationsAngelo Lirio InsigneNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 A Simplified Text in Differential Calcu PDFDocument150 pagesCalculus 1 A Simplified Text in Differential Calcu PDFRichard Serquina100% (2)
- Standard Integration FormulasDocument5 pagesStandard Integration FormulasMika Vernadeth SingNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus Part 1Document124 pagesIntegral Calculus Part 1Jeric IsraelNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Differential CalculusDocument2 pagesReviewer in Differential CalculusEdith Alarcon CastilloNo ratings yet
- MATHENG4 Differential EquationsDocument66 pagesMATHENG4 Differential EquationsJed Guzarem YbañezNo ratings yet
- (For Dummies) Earl Boysen, Nancy C. Muir - Electronics Projects For Dummies (2006, Wiley)Document6 pages(For Dummies) Earl Boysen, Nancy C. Muir - Electronics Projects For Dummies (2006, Wiley)Sharukh KhanNo ratings yet
- 3.homogeneous Differential EquationsDocument18 pages3.homogeneous Differential EquationsSourabhThakurNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument21 pagesDifferential Equationssreekantha100% (1)
- Advance Engineering Mathematics WorkbookDocument130 pagesAdvance Engineering Mathematics WorkbookLorraine Sta. Clara100% (1)
- Module 6. Differentiation of Transcendental FuntionsDocument23 pagesModule 6. Differentiation of Transcendental FuntionsMark Daniel RamiterreNo ratings yet
- Differential and Integral CalculusDocument10 pagesDifferential and Integral CalculusCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations ModuleDocument172 pagesDifferential Equations ModuleTrina CastañoNo ratings yet
- Algebra ReviewerDocument83 pagesAlgebra ReviewerKaye BatacanNo ratings yet
- Integration by Partial FractionDocument23 pagesIntegration by Partial FractionMisa KurobaneNo ratings yet
- Exponential Shift and Inverse Differential OperatorsDocument20 pagesExponential Shift and Inverse Differential OperatorsMark MercadoNo ratings yet
- Math111 Limits and ContinuityDocument23 pagesMath111 Limits and ContinuityAbdul Halil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry ReviewDocument73 pagesAnalytic Geometry ReviewIrah Mae Escaro Custodio100% (1)
- Differential and Integral CalculusDocument71 pagesDifferential and Integral Calculusjucar fernandezNo ratings yet
- LP-1-Differential EquationDocument25 pagesLP-1-Differential EquationHaya BusaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Midterm 1 v1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesDifferential Equations Midterm 1 v1 SolutionsRodney HughesNo ratings yet
- Problems in CalculusDocument8 pagesProblems in CalculusJefrey Gamban100% (1)
- Limits of FunctionsDocument11 pagesLimits of Functionsnormasulasa100% (1)
- Differential Equation 2Document6 pagesDifferential Equation 2Cinderella WhiteNo ratings yet
- Ln2 Sync Elimination of Arbitrary Constants and Families of Curves g079 A g097 ADocument23 pagesLn2 Sync Elimination of Arbitrary Constants and Families of Curves g079 A g097 ARicci De JesusNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Definite IntegralsDocument9 pagesEvaluating Definite IntegralsbillyNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET (Differential & Integral Calculus and De)Document3 pagesPROBLEM SET (Differential & Integral Calculus and De)Irvin ReyNo ratings yet
- Limits and ContinuityDocument32 pagesLimits and ContinuityAnik100% (2)
- EcuacionesDocument3 pagesEcuacionesYessica Garcia HernandezNo ratings yet
- Math 8Document60 pagesMath 8Glaiza MotasNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument27 pagesIntegralesKevin DgoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Calculo IntegralDocument3 pagesEjercicios Calculo IntegralJohana AmpudiaNo ratings yet
- Tugas KalkulusDocument2 pagesTugas KalkulusJefin PaputNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Labview Training: Jaimee C. Navarro, I-Stone Systems Pte. LTDDocument16 pagesLabview Training: Jaimee C. Navarro, I-Stone Systems Pte. LTDJaimee NavarroNo ratings yet
- Gastritis Grocery ListDocument1 pageGastritis Grocery ListJaimee NavarroNo ratings yet
- Task List: Wise Innovators For Responsible Empowered DesignsDocument1 pageTask List: Wise Innovators For Responsible Empowered DesignsJaimee NavarroNo ratings yet
- Five Examples of Assembly/ Exploded Drawings:: Name: Jaimee Navarro Section 1-1 SN: 31Document6 pagesFive Examples of Assembly/ Exploded Drawings:: Name: Jaimee Navarro Section 1-1 SN: 31Jaimee NavarroNo ratings yet
- UST NSTP e-READ Chapter4Document53 pagesUST NSTP e-READ Chapter4Jaimee NavarroNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structural Analysis Prof. Devdas Menon Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument34 pagesAdvanced Structural Analysis Prof. Devdas Menon Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasGirish ReddyNo ratings yet
- Eulerian GraphsDocument47 pagesEulerian GraphsLekshmi NairNo ratings yet
- A33 Final Winter 2014Document12 pagesA33 Final Winter 2014Krish AhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation - Examples of Substitution Suggested by The EquationDocument2 pagesDifferential Equation - Examples of Substitution Suggested by The EquationAimi Najwa Zailan100% (1)
- Infinite DimensionsDocument5 pagesInfinite DimensionsIdkNo ratings yet
- Math 252 - Exam 2 Review - FA20Document2 pagesMath 252 - Exam 2 Review - FA20Tony RocheNo ratings yet
- Low-Degree Phase Transitions For Detecting A Planted Clique in Sublinear TimeDocument23 pagesLow-Degree Phase Transitions For Detecting A Planted Clique in Sublinear TimeJohn PeterNo ratings yet
- Function: Q-Series: Mathematics For BS/MS.C QM Khan Wazir 14Document10 pagesFunction: Q-Series: Mathematics For BS/MS.C QM Khan Wazir 14Kamran JalilNo ratings yet
- CalcI TangentsRates SolutionsDocument10 pagesCalcI TangentsRates SolutionsLeophil RascoNo ratings yet
- 02 - Relationships Between PixelsDocument31 pages02 - Relationships Between PixelsDr. M. Muntasir RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lyapunov Stability AnalysisDocument17 pagesLyapunov Stability AnalysisumeshgangwarNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus 01Document16 pagesIntegral Calculus 01shlokpandey0202No ratings yet
- EDUC 107 Ppt2 Fractions Geometrymodel Drawing LessonDocument19 pagesEDUC 107 Ppt2 Fractions Geometrymodel Drawing LessonNeriza Pis-oNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument90 pagesUntitledDema IhabNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Pre O'LevelDocument18 pagesMathematics Pre O'LevelGuestNo ratings yet
- Solutions Assign 1 2022 AutumnDocument5 pagesSolutions Assign 1 2022 AutumnVijayasimha rao RavooriNo ratings yet
- Markov Analysis FT C 2021Document28 pagesMarkov Analysis FT C 2021Ivar the bonelessNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 System StabilityDocument32 pagesChapter 6 System StabilityIzzat AiresNo ratings yet
- 9A05403 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument4 pages9A05403 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- MHF4U Unit3 LogFuncSEDocument9 pagesMHF4U Unit3 LogFuncSEJulia ZhouNo ratings yet
- InequalitiesDocument9 pagesInequalitiesewjuhewauwajuawhukawhdwajhdwajwadhjadwhNo ratings yet
- Applied Math - 1Document25 pagesApplied Math - 1Miley Girmay100% (2)
- A First Course in Elementary Differential Equations: Problems and SolutionsDocument8 pagesA First Course in Elementary Differential Equations: Problems and SolutionsjuanNo ratings yet
- EMT by Jakson PDFDocument145 pagesEMT by Jakson PDFSafi Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- AddmathDocument162 pagesAddmathMuhammad Amirul AdlieNo ratings yet
- 2nd QUARTERLY EXAM MATH 9Document1 page2nd QUARTERLY EXAM MATH 9Leslie Vine DelosoNo ratings yet
- 12b) Power Series in XDocument6 pages12b) Power Series in XAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Graphing Linear EquationDocument6 pagesGraphing Linear EquationNursupriatna AmadNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: (Part-1)Document50 pagesDigital Signal Processing: (Part-1)meseret sisayNo ratings yet