Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio
Bio
Uploaded by
Suraj UgraniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio
Bio
Uploaded by
Suraj UgraniCopyright:
Available Formats
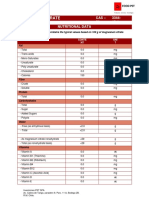
Life: 1)Made of cells. Cells contain DNA(brain of the cell) 2)Cells in a perticular order.
3)Regulate-Cells change to adapt to environment 4)Respond to signals-Plants grow towards the sun. 5)Transfer energy-Humans eat plants to get energy. 6)Grow & develop. 7)Reproduce. 8)Evolve. Acids & Bases:A dissociates in water into H+ and something. B dissociates in water into OH- and something. Carbohydrates(C1 H2 O1):Body breaks them down to get a quick source of energy. Monosaccharides-Sugars with 3-7 Cs. Eg-Glucose Disaccharides-More than 7 Cs. Eg-Sucrose Oligosaccharide-Approx 2-10 monosaccharides Polysaccharide-Long chains of monosaccharides. Eg-Starch Body breaks down carb. into glucose which is used by cells for e nergy. It stores glucose that is not required at the moment in polysaccharides c alled glycogen. Plants store it in starch. Proteins: Amino acids connect to form polypeptide chains which in turn connect to form proteins. Types of protein are collagen(provides support), haemoglobin(car ries oxygen) etc. Nucleic acid: Made up of nucleotides, whick are in turn made up of 1.Nitrogenou base, 2.Sugar with 5 Cs, 3.Phosphate group. Most imp n.a. - DNA- lives in the nucleus of the cell. DNA-contains genes-are the blue print for proteins(how amino acids shoul d combine to form proteins) Lipids(fats): Large hydrophobic molecules which store a lot of energy 3 types-1.Phospholipids-used in cell membrane; 2.Steroids-also found in cell membrane(eg.cholesterol); 3.Triglyceride Cells: Have organelles inside them. Types of cells:1)Prokaryotes(bacteria)-no nucleus and organells;2)Euk aryotes(plants,animals)-have nucleus and organells . Parts of the cell:1)Plasma membrane(skin of the cell).Plants onl y also have cell walls outside it.Phospholipids form a bilayer with proteins & c holesterol(which stabilizes membrane and prevents it from freezing in case of co ld) embeded in them to form membrane.Carbohydrate chains(which determine your bl ood type) are attached on the outside parts of the bilayer. Small molecules like O2 pass through memb. b ut larger ones like food cannot. So proteins create 'channels' else 'carrier pro teins' carry them into the cell. 2 ways(passive-no energy is req from cell) and (active-r eq) by which molecules transport. Passive:Eg.diffusion(O2 diffuses through cellmemb.),osmo sis 2)Cytoplasm(fluid inside cell) 3)Nucleus(brain of the cell)-Nuclear envolope( ~ to celmemb.) protects nucleus. DNA is in nucleus. The messengerRNA(mRNA) carries the DNA code from the nucleus to the ribo some in the cytoplasm which then makes proteins(RNA & ribosome are not ingredien ts of proteins-aminoacids are!) Endoplasmic Reticulum:Series of canals that connects the nucleus to the cytoplasm . 2 types of ER- 1)Rough ER-have ribosomes on it which mak e proteins that end up on the celmem. or other parts of the body as opposed to t hose made by free floating ribosomes which are used in the cell itself 2)Smooth ER-helps in creation of lipids a nd storage of steroids
The proteins and fats(lipids) cr eated are carried by 'transport vescicles' to the Golgi apparatus(an organelle) which packages and labels them, then sends them to appropriate destinations outs ide the cell through channels in the bilayer. Lysosomes(organelle):contain digestive enzymes which break up st uff harmful to the cell. They also break up dead organelles. The pieces are eith er spit out of the cell or used in the cell. Peroxisomes(organelle):contain a different enzyme which break up harmful stuff and also break down lipids Mitochondria(organelle):Takes food & produces energy which is stored in a molecule called ATP. Mito has an outer membrane and a fluid called 'matrix' wh ich also has its own membrane('inner membrane') Enzymes:Act as catalyst. Have active sites to which the substrat e(reacting molecule)attaches,reacts(Eg.breaksdown)and leaves. Lactase breaks dow n lactose, lipase breaks down lipids(fats0 and so on. Anabolic Rxns.:Smaller molecules add to form larger mole cule. Energy is req. Catabolic Rxns.:Larger ones break to give smaller ones. Energy is released. ATP(adenosine triphosphate):Stores energy released from catrxns. Provides energy for anabrxn by decomposing to adenosine diphosphate which takes energy from mitochn and goes back to ATP. Autotrophs:Make own food.[Plants-Photosynthesis] 6H2O+6C O2+sunlight->sugar(C6H12O6)+O2 Heterotrophs:Eat other organisms.[Animals-cellular respi ration] C6H12O6+6O2->6CO2+6H2O+energy Cellular Respiration:Glycolysis(breakdown of glucose molecule-in volves investment of energy)-1)An enzyme(hexokinase)causes ATP to ADP by giving 1 phosphate grp to glucose forming glucose-6-phosphate.2)Another ezym(phosphoglu cose isomerase) isomerizes g6f to fructose-6-phosphate.3)Another enzyme(phosphof ructokinase)uses ATP to add another phosphate to f6p giving fructose-1,6-bisphos phate. 4)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Oxidation of Food ComponentsDocument5 pagesOxidation of Food ComponentsGabriella C VicenteNo ratings yet
- Stability of Cyanocobalamine in Film-Coated TabletsDocument4 pagesStability of Cyanocobalamine in Film-Coated TabletsNoemiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Lecture 11: LipidsDocument34 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Lecture 11: LipidsDương Hà Trúc TâmNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - 2023 - Oligonucleotide SynthesisDocument57 pagesLecture 4 - 2023 - Oligonucleotide SynthesisChen ZhonghaoNo ratings yet
- Data Expired DateDocument8 pagesData Expired DateFARMASI PRIMA HUSADA SUKOREJONo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and Biological Oxidation PDFDocument50 pagesBioenergetics and Biological Oxidation PDFGEROME ABENILLA100% (1)
- Coupling ReagentsDocument5 pagesCoupling Reagentsraamu79No ratings yet
- Chemistry 2nd Year Eamcet Named Reaction Identification of Functional Group-1Document7 pagesChemistry 2nd Year Eamcet Named Reaction Identification of Functional Group-1Surya Charan Reddy100% (1)
- Pharma DermaDocument7 pagesPharma DermaDee SarajanNo ratings yet
- Carbon Preference IndexDocument27 pagesCarbon Preference IndexS S Nanthavarman SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- 3 LipidsDocument42 pages3 LipidsSyifaAnandaNo ratings yet
- Información Nutricional Citrato de Magnesio Food PSTDocument2 pagesInformación Nutricional Citrato de Magnesio Food PSTPamela Urrea AtenasNo ratings yet
- Lipis ReportDocument11 pagesLipis ReportEnnavy YongkolNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga ObatDocument7 pagesDaftar Harga Obatiik abdulkholikNo ratings yet
- 20 Amino AcidsDocument1 page20 Amino AcidsJoseph PaguioNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Oxidation & Ketone BodiesDocument30 pagesFatty Acid Oxidation & Ketone BodiesM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document20 pagesChapter 14J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- Pyrimidines: 1.23), and PyrazineDocument5 pagesPyrimidines: 1.23), and PyrazineMananNo ratings yet
- Mosselm BrochDocument12 pagesMosselm BrochCarlo PizarroNo ratings yet
- 13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsDocument55 pages13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid PDFDocument9 pagesFatty Acid PDFtulasi saladiNo ratings yet
- Named Reactions-1Document79 pagesNamed Reactions-1Pencil Arts -IndiaNo ratings yet
- Protein Purification AND Characterization Techniques: Biochemistry, 7 Ed. Campbell & FarrellDocument14 pagesProtein Purification AND Characterization Techniques: Biochemistry, 7 Ed. Campbell & FarrellJacqueline Rose Alipo-onNo ratings yet
- Beli ObatDocument6 pagesBeli ObatAnggaNo ratings yet
- Ep2670803b1 PDFDocument22 pagesEp2670803b1 PDFEnrique EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chemisstry DPP # 2 (Alkyl Halide+alcDocument7 pagesChemisstry DPP # 2 (Alkyl Halide+alcmohitpatel18032003No ratings yet
- Plastics Compatibility With Sterilization Methods From ISMDocument2 pagesPlastics Compatibility With Sterilization Methods From ISMJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Alcohol-Preparation of Grignard ReagentDocument4 pagesAlcohol-Preparation of Grignard ReagentTida TpNo ratings yet
- Tugas Analisa ABCDocument328 pagesTugas Analisa ABCDon giovNo ratings yet
- Alkene - Alkynes 1Document39 pagesAlkene - Alkynes 1Hajar MuhamadNo ratings yet