Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment - 2 Object:-Study and Obtain Waveforms of 3-Ø Half Controlled Bridge Converter With R and RL
Experiment - 2 Object:-Study and Obtain Waveforms of 3-Ø Half Controlled Bridge Converter With R and RL
Uploaded by
sahumanish9240Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment - 2 Object:-Study and Obtain Waveforms of 3-Ø Half Controlled Bridge Converter With R and RL
Experiment - 2 Object:-Study and Obtain Waveforms of 3-Ø Half Controlled Bridge Converter With R and RL
Uploaded by
sahumanish9240Copyright:
Available Formats
Marudhar Engineering College, Bikaner Electrical Drives & Control Lab Manual
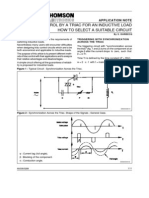
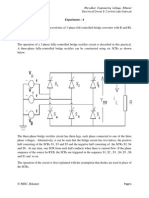
Experiment 2 Object:- Study and obtain waveforms of 3- half controlled bridge converter with R and RL loads. Theory:To control the load voltage, the half wave rectifier uses three, common-cathode thyristor arrangement. the most common circuit is the three-phase bridge shown in Fig. Neglecting commutation effects for the moment, this circuit has a control range of 180 from full positive output voltage to full negative output voltage, although the circuit requires a load such as an inductor that is capable of sinking positive current while sourcing negative voltage. The bridge circuit allows power flow in either direction for these types of loads, and it is capable of supplying regenerative braking for DC motors with field reversal. Figure 1 below shows the R/C snubbers as well as protective MOV devices on the power line.
1. SCR three-phase bridge converter The set of figures that follows show the control characteristics of the SCR converter. The gate circuits are set to gate each SCR at 30 after the line-to-line zero crossings. Figure 2 shows the line-to neutral voltages and the line currents with an inductive load, Fig. 3 shows the positive and negative bus voltages, Fig. 4 shows the line-to-line voltage of phase A, and Fig. 5 shows the DC output waveform. When an SCR is fired, the incoming and outgoing phases are shorted, and the output bus voltage drops to the average of the two phase voltages. The process is identical to that with diodes, except the beginning of commutation is determined by the timing of the gate delay. The positive bus always assumes the most positive gated voltage in the system, and the negative bus follows the most negative gated voltage once commutation is completed. The DC output voltage will continue to decrease as the firing angle is phased back farther. At 90 phase back, the average output voltage will be zero with an inductive load. The converter supplies the
MEC, Bikaner
Page 1
Marudhar Engineering College, Bikaner Electrical Drives & Control Lab Manual
positive portions of the voltage, and the load induces a mirror-image voltage to form the negative portions.
2. Converter L-N voltages and line currents (inductive load)
3. Converter bus voltages
MEC, Bikaner
Page 2
Marudhar Engineering College, Bikaner Electrical Drives & Control Lab Manual
4. Converter line-to-line voltage
5. Converter DC output voltage Figure 6 shows waveforms at = 120, a region of negative output voltage where operation is possible with an inductive load already be completed, and the full load current will return to the original phase as the voltage swings from positive to negative. This is termed a commutation failure, and it leaves the full load current in only one of the SCR pairs with possible over current damage. Furthermore, a large AC voltage is impressed on the load, and this may be undesirable. To avoid commutation failure, a margin angle must be observed between the maximum phase back angle and the angle at which the commutating voltage changes polarity. A phase back limit of 165 with a 15margin angle is often used in relatively low-reactance systems where commutation angles are low. In special applications such as high reactance pulsed power systems, the margin angle is load compensated so that the angle can be increased as load current decreases. This allows a maximum sustained negative voltage and rapid energy recovery.
MEC, Bikaner
Page 3
Marudhar Engineering College, Bikaner Electrical Drives & Control Lab Manual
While the bridge is the most popular circuit, several other arrangements are in use. The semi converter substitutes diodes for three of the SCRs. This circuit was popular in the early days of SCRs, when they were quite expensive, but it is used less often now. One major objection to the circuit is that it draws DC from the source. The same is true of a simple half-wave circuit that has found occasional use in the rotating rectifiers of brushless exciters for synchronous motors and generators. It not only draws DC but also requires a source with a power neutral.
6. Converter DC inversion at 150 phaseback
Result :The Circuit and Characteristics Waveform of the 3- half controlled bridge converter with R and RL loads have been studied successfully.
MEC, Bikaner
Page 4
You might also like
- Ups 3Document32 pagesUps 3abdulkadhir100% (1)
- Experiment - 1 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converter. TheoryDocument6 pagesExperiment - 1 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converter. Theorysahumanish9240No ratings yet
- Single Phase Three Leg Ac/ac ConverterDocument8 pagesSingle Phase Three Leg Ac/ac ConvertermycatalystsNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter: Four Switches V V 2, Capacitive Turn-Off Snubbing, ZV Turn-OnDocument10 pagesDC-DC Converter: Four Switches V V 2, Capacitive Turn-Off Snubbing, ZV Turn-OnRomitan AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Single Stage Inverter Topology For Renewable Resources: Jeena Mary Abraham, M.S.P. Subathra, Senraj. RDocument5 pagesSingle Stage Inverter Topology For Renewable Resources: Jeena Mary Abraham, M.S.P. Subathra, Senraj. RskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Zero-Voltage Switching For Three-Level Capacitor Clamping InverterDocument11 pagesZero-Voltage Switching For Three-Level Capacitor Clamping InverterTiền Hoàng VănNo ratings yet
- A Novel ZVS Bidirectional DC-DC Converter For Fuel Cell ApplicationsDocument4 pagesA Novel ZVS Bidirectional DC-DC Converter For Fuel Cell ApplicationsS B RajNo ratings yet
- Single Phase To Three Phase ConverterDocument5 pagesSingle Phase To Three Phase ConverterGabriel MejiaNo ratings yet
- Bi-Directional DC-to-DC Converter For Solar Applications With Battery BackupDocument5 pagesBi-Directional DC-to-DC Converter For Solar Applications With Battery BackupPaulius BruneikaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solve of Indutrial Electronics FinalDocument9 pagesProblem Solve of Indutrial Electronics FinalMd Raton AliNo ratings yet
- EE 410 Lab1 Fall10-1305411901Document27 pagesEE 410 Lab1 Fall10-1305411901Mohamad SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Application in DC Motor Drives - Case Study - ss03595 - Sarwan Shah PDFDocument6 pagesPower Electronics Application in DC Motor Drives - Case Study - ss03595 - Sarwan Shah PDFMehdi Raza KhorasaniNo ratings yet
- Carga Inductiva Con TriacDocument11 pagesCarga Inductiva Con Triacanon_274509247No ratings yet
- Ac Link Buck Boost ConverterDocument6 pagesAc Link Buck Boost ConverterrigowNo ratings yet
- DC To AC Converters PDFDocument4 pagesDC To AC Converters PDFrizwanNo ratings yet
- PLC Based Load Sharing On Slide ShareDocument28 pagesPLC Based Load Sharing On Slide ShareHemu Bhai PatelNo ratings yet
- Basic of ElectricalDocument10 pagesBasic of ElectricalAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - NewDocument61 pagesUnit 2 - NewMonster AmanNo ratings yet
- Q 7) Explain The Basic Principle of Control in HVDCTDocument12 pagesQ 7) Explain The Basic Principle of Control in HVDCTrasashpujNo ratings yet
- Ed Lab ManualDocument27 pagesEd Lab ManualBonnieNo ratings yet
- Ecce 2018 8558336Document6 pagesEcce 2018 8558336mosiurrahmanjony16No ratings yet
- Tugas 6 Kendali Mesin Listrik Industri - Aulia Silfani - 20130072Document8 pagesTugas 6 Kendali Mesin Listrik Industri - Aulia Silfani - 20130072Aulia SilfaniNo ratings yet
- Flyback Converter - WikipediaDocument3 pagesFlyback Converter - WikipediaRobert MasipNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsDocument5 pagesComparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Effect of Source InductanceDocument25 pagesEffect of Source InductanceSriram Anil Kumar Gandham100% (1)
- Study of AC and-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesStudy of AC and-WPS OfficeBeena PalNo ratings yet
- Resonant DC Link InvertersDocument6 pagesResonant DC Link InvertersSanchit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Design and Application For PV Generation System Using A Soft-Switching Boost Converter With SARCDocument13 pagesDesign and Application For PV Generation System Using A Soft-Switching Boost Converter With SARCIJERDNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Fyp EdittdDocument20 pagesDC Motor Fyp EdittdRabia BilalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalNo ratings yet
- Non Isolated Bidirectional DC DC ConverterDocument6 pagesNon Isolated Bidirectional DC DC ConverterAnuja VargheseNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost Converter ReportDocument5 pagesBuck Boost Converter ReportMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Heavy Load Light Load Conversion ReportDocument41 pagesHeavy Load Light Load Conversion ReportSanjivee SachinNo ratings yet
- An Application of Matlab/Simulink For Speed Control of DC Series Motor Using Buck ConverterDocument5 pagesAn Application of Matlab/Simulink For Speed Control of DC Series Motor Using Buck ConverterArghya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Digital Current Limiting Techniques For Switching Power Supplies PDFDocument9 pagesDigital Current Limiting Techniques For Switching Power Supplies PDFAdolfo A HerreraNo ratings yet
- Beng BenggsssDocument11 pagesBeng BenggsssBeth PartozaNo ratings yet
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDocument9 pagesFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- Transformer Based Resonant DC Inverter For Brushless DC Motor Drive SystemDocument7 pagesTransformer Based Resonant DC Inverter For Brushless DC Motor Drive SystemStudents Xerox ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault DetectorDocument25 pagesCable Fault DetectorHarshalNo ratings yet
- Single Phase To Three Phase SystemDocument57 pagesSingle Phase To Three Phase SystemASK projects100% (1)
- L4-Controlled RectifiersDocument36 pagesL4-Controlled Rectifiershamza malikNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report REVISEDDocument21 pagesSeminar Report REVISEDayash mohantyNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering & Technology LahoreDocument43 pagesUniversity of Engineering & Technology LahoreKantesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Relay Setting (Directional) : Leakage FluxDocument8 pagesRelay Setting (Directional) : Leakage Fluxjyoti kachareNo ratings yet
- UtcDocument8 pagesUtcمحمدضيأ الدينNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter SimulationDocument3 pagesDC-DC Converter SimulationMThe StrokesNo ratings yet
- Wenzel ISH09Document6 pagesWenzel ISH09Long LeoNo ratings yet
- A Novel Three-Level DC-DC Converter With Load Adaptive ZVS Auxiliary CircuitDocument6 pagesA Novel Three-Level DC-DC Converter With Load Adaptive ZVS Auxiliary Circuitdsshin_psNo ratings yet
- Generation of Energy Usig MagnetsDocument26 pagesGeneration of Energy Usig MagnetsSridhar PatilNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-13 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-13 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- SCAP - Power InverterDocument14 pagesSCAP - Power InverterFolorunso AbiodunNo ratings yet
- EE6503-Power ElectronicsDocument41 pagesEE6503-Power Electronicscwizard60No ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Drive Lab: Exp1: Single Phase Rectifier Instructor: Eng.: Nazmi Abu AshourDocument11 pagesPower Electronics and Drive Lab: Exp1: Single Phase Rectifier Instructor: Eng.: Nazmi Abu AshourBaha DaoudNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of A 6-Pulse Converter and A 12-Pulse Converter For HVDC Station.Document6 pagesA Comparative Study of A 6-Pulse Converter and A 12-Pulse Converter For HVDC Station.Naveen JainNo ratings yet
- Emergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractDocument20 pagesEmergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractAakash SheelvantNo ratings yet
- Zero-Voltage Switching Technique in DC/DC Converters: Abstruct-ADocument12 pagesZero-Voltage Switching Technique in DC/DC Converters: Abstruct-ARushikeshKatkarNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Lab ReportDocument13 pagesPower Transmission: Lab ReportMohibur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Experiment - 4: © MEC, BikanerDocument5 pagesExperiment - 4: © MEC, Bikanersahumanish9240No ratings yet
- Experiment - 3 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of 3-Phase Full Controlled Bridge Converter. TheoryDocument3 pagesExperiment - 3 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of 3-Phase Full Controlled Bridge Converter. Theorysahumanish9240100% (1)
- Experiment - 1 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converter. TheoryDocument6 pagesExperiment - 1 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converter. Theorysahumanish9240No ratings yet
- Marudhar Engg. College, Bikaner: AbstractDocument1 pageMarudhar Engg. College, Bikaner: Abstractsahumanish9240No ratings yet
- Moc3041 and Moc3021Document1 pageMoc3041 and Moc3021ahm_adNo ratings yet
- Pi044g 06 TD en Rev ADocument9 pagesPi044g 06 TD en Rev AVladimirGuerreroNo ratings yet
- Zig-Zag Connection of TransformerDocument3 pagesZig-Zag Connection of TransformerNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- 2SA2099 / 2SC5888: High-Current Switching ApplicationsDocument5 pages2SA2099 / 2SC5888: High-Current Switching ApplicationsnguyenhieuproNo ratings yet
- Valve & Amplifier Design, Mullard Maintenance Manual (1961)Document112 pagesValve & Amplifier Design, Mullard Maintenance Manual (1961)Valve Data83% (6)
- Reverse EngineeringDocument18 pagesReverse Engineeringkanha ddNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Ac Machines - IDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Ac Machines - IVARAPRASADNo ratings yet
- Liebert Exl s1Document243 pagesLiebert Exl s1Jose MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Fooling The Projector PDFDocument13 pagesFooling The Projector PDFVictor D'souzaNo ratings yet
- 30 LED Projects Book PDFDocument46 pages30 LED Projects Book PDFBien Morfe100% (2)
- Module 3Document71 pagesModule 3Blesson RoyNo ratings yet
- DC SwitchgearDocument10 pagesDC SwitchgearpjchauhanNo ratings yet
- SG2K-S SG2K5-S SG3KS - Datasheet - ENDocument2 pagesSG2K-S SG2K5-S SG3KS - Datasheet - ENThắng CòiNo ratings yet
- g9sr Instruction Sheet enDocument2 pagesg9sr Instruction Sheet enSamer ChahroukNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mechatronics: Mechanical Actuators, Electrical Actuators, Hydraulic and Pneumatic ActuatorsDocument39 pagesFundamentals of Mechatronics: Mechanical Actuators, Electrical Actuators, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Actuatorsanuhas wanigasekaraNo ratings yet
- DC Motor StartersDocument6 pagesDC Motor StartersAreeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Euroflat Series Types Cm11/O Cm31/O CE11/O CE31/ODocument6 pagesEuroflat Series Types Cm11/O Cm31/O CE11/O CE31/ORier LabNo ratings yet
- El Operation Concept Extract ExampleDocument1 pageEl Operation Concept Extract ExampleAdetunji TaiwoNo ratings yet
- RIT Models For LTSPICEDocument3 pagesRIT Models For LTSPICEDavid Villamarin RiveraNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics EngineeringsushilNo ratings yet
- Maxon Motor - Online Shop PDFDocument5 pagesMaxon Motor - Online Shop PDFFrank GNo ratings yet
- Smart Street Light Project 2 1Document14 pagesSmart Street Light Project 2 1Rohan TiwariNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Based Brushless DC Motor Closed Loop Drive For Electric VehicleDocument7 pagesPhotovoltaic Based Brushless DC Motor Closed Loop Drive For Electric VehicleMani KandanNo ratings yet
- AT9932 Automotive Boost Buck LED Lamp Driver IC Data Sheet 20005789ADocument18 pagesAT9932 Automotive Boost Buck LED Lamp Driver IC Data Sheet 20005789AJohnNo ratings yet
- HDW6 2000acbDocument19 pagesHDW6 2000acbRoxanneNo ratings yet
- SCR Phase Control Dimmer SchematicDocument9 pagesSCR Phase Control Dimmer SchematicCris DucusinNo ratings yet
- UT582Document1 pageUT582qaqcmepteamNo ratings yet
- Mep Spa Reana Del Rojale Mini Syntax 16Document127 pagesMep Spa Reana Del Rojale Mini Syntax 16Anca PîrvanNo ratings yet
- TLE MAJOR TEST SET 010 Basic Electricity 1Document9 pagesTLE MAJOR TEST SET 010 Basic Electricity 1edsonlligananNo ratings yet
- A626S21 INT69-DMY Diagnose 71000445 0-EbookDocument2 pagesA626S21 INT69-DMY Diagnose 71000445 0-EbookSergeyNo ratings yet