Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F4C3 PG 1
F4C3 PG 1
Uploaded by
Woody CysCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pressure Lesson ModuleDocument3 pagesPressure Lesson ModuleCarmela UrsuaNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Pressure NotesDocument22 pagesCIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Pressure Notes9322483% (53)
- 3.1 Force and PressureDocument16 pages3.1 Force and PressureCikgu SyierNo ratings yet
- Force & Pressure PPT-3Document11 pagesForce & Pressure PPT-3ARNAB GHOSH CLASS V100% (1)
- Handout Understanding Pressure Igcse Form 2 Understanding PressureDocument4 pagesHandout Understanding Pressure Igcse Form 2 Understanding PressureMOHAMAD RIZAL BIN MUKHTARNo ratings yet
- Understanding PressureDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Pressurekur8cobain100% (1)
- 3.1 - Understanding PressureDocument5 pages3.1 - Understanding PressureArif KhanNo ratings yet
- F 4 C 3Document19 pagesF 4 C 3jalrizal7No ratings yet
- 3.1 Understanding PressureDocument12 pages3.1 Understanding Pressurenik mohamad solehinNo ratings yet
- Samrat Class 8 ScienceDocument10 pagesSamrat Class 8 ScienceShashwat SumanNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE - Part 1 (Notes)Document1 pagePRESSURE - Part 1 (Notes)ARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Physic Form 4 Chapter 3Document7 pagesPhysic Form 4 Chapter 3Nazhif NazarudinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-Pressure Physics Form 4Document13 pagesCHAPTER 3-Pressure Physics Form 4Matthew Nelson100% (2)
- Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesPressure NotesVaishnavi BannurNo ratings yet
- 1.pressure 2 PDFDocument6 pages1.pressure 2 PDFIshvaryaNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument19 pagesPressureTaufik PamisNo ratings yet
- Density and Pressure: Sheikh Khaliliur RahmanDocument33 pagesDensity and Pressure: Sheikh Khaliliur RahmanKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- 7 Pressure OrigDocument165 pages7 Pressure Origrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Forces and PressureDocument24 pagesChapter 3: Forces and PressureSiah Yih HoongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Forces and PressureDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Forces and PressureYusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- 1.8 PressureDocument48 pages1.8 PressureEbrahimNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Pressure Answer by SidDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank - Pressure Answer by SidAshish GambhirNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 3Document25 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 3Misratul A'la Mahyuddin100% (2)
- 3.1 Pressure 2012Document7 pages3.1 Pressure 2012cikgusuriyati50% (2)
- Pressure RevisedDocument5 pagesPressure ReviseddanielNo ratings yet
- Igcse 51 Density&PressureDocument40 pagesIgcse 51 Density&PressureHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Force & Pressure (Teacher)Document23 pagesChapter 3 Force & Pressure (Teacher)ima_1806No ratings yet
- St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Science Physics Notes PressureDocument3 pagesSt. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Science Physics Notes PressureashokNo ratings yet
- Physics PressureDocument3 pagesPhysics Pressurelajuli.niliNo ratings yet
- 8 - Force and Pressure - NumericalDocument2 pages8 - Force and Pressure - Numericalonlinevidhi.agrawal001No ratings yet
- Force & PressureDocument12 pagesForce & PressureGanesh VNo ratings yet
- Expt 5Document7 pagesExpt 5PARVATHY ANILNo ratings yet
- 3E Sci Phy Chapter 6 Pressure - TRDocument16 pages3E Sci Phy Chapter 6 Pressure - TRXu JianhangNo ratings yet
- Physics CH 1.8 (Pressure)Document4 pagesPhysics CH 1.8 (Pressure)Safiul FaiyazNo ratings yet
- Unit 4,5,6Document11 pagesUnit 4,5,6Adalbert MugambiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document12 pagesUnit 4Adalbert MugambiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HydrostaticsDocument17 pagesUnit 2 HydrostaticsRin MoonNo ratings yet
- 4 Pressure BuoyancyDocument8 pages4 Pressure Buoyancythinkiit100% (1)
- IGCSE 51 Density&PressureDocument45 pagesIGCSE 51 Density&Pressurecharlottekuan0824No ratings yet
- Pressure Synopsis-1Document24 pagesPressure Synopsis-1Rajanikanth100% (1)
- 7 140706224638 Phpapp01Document165 pages7 140706224638 Phpapp01Theodøros D' Spectrøøm0% (1)
- Isolated FootingDocument5 pagesIsolated FootingannNo ratings yet
- Raft Pondasi PDFDocument6 pagesRaft Pondasi PDFIsra HrNo ratings yet
- Science ks3 Lesson Sci Y7 U6 l7 PDFDocument22 pagesScience ks3 Lesson Sci Y7 U6 l7 PDFParth MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Thin and Thick CylindersDocument6 pagesThin and Thick CylindersRamesh Akula80% (5)
- 9L Pressure and MomentsDocument14 pages9L Pressure and MomentsfitrusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Force & Student)Document22 pagesChapter 3 Force & Student)Ah TiNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument20 pagesPressuretrojanfrpNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument12 pagesPressuretrojanfrpNo ratings yet
- Te2 Module 4Document4 pagesTe2 Module 4rmle100% (1)
- Tutorial 3.1Document13 pagesTutorial 3.1cikgusuriyatiNo ratings yet
- 8 Icse Phy SolutionDocument5 pages8 Icse Phy SolutionRAKESH VASANINo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Weather Projects for Young Scientists: Experiments and Science Fair IdeasFrom EverandWeather Projects for Young Scientists: Experiments and Science Fair IdeasRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- PADINI AnnualReport2014Document130 pagesPADINI AnnualReport2014Woody CysNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document10 pagesPhysics Form 4Woody CysNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Form 5Document46 pagesSPM Physics Form 5Woody CysNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Form 5Document46 pagesSPM Physics Form 5Woody CysNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document10 pagesPhysics Form 4Woody CysNo ratings yet
- SPM PhysicsDocument21 pagesSPM PhysicsWoody Cys100% (2)
F4C3 PG 1
F4C3 PG 1
Uploaded by
Woody CysOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F4C3 PG 1
F4C3 PG 1
Uploaded by
Woody CysCopyright:
Available Formats
Foim 4 Chaptei S: Foices anu Piessuie
CYS 1
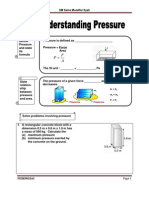
3.1UnderstandingPressure
Pressure
1. Pressureisdefinedasaperpendicularforceactingperunitareaofasurface.
P =
F
A
2. TheSIunitofpressureisPascal(Pa).1Paisequalto1Newtonpermetersquare(N/m
2
)
3. Factorsthataffectthepressureactingonasurface:
a) MagnitudeoftheForce
Thelargertheforce,thehigherthepressure
b) Contactarea
Thelargerthecontactarea,thelowerthepressure
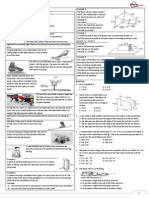
ExamplesofApplicationofHighPressure ExamplesofApplicationofLowPressure
a) SharpKnife
b) IceSkate
c) Soleofshoeswithspike
a) FoundationofBuilding
b) Snowshoes
c) Tyreoftractor
d) FeetofElephant
Examples:
1. Theweightofawoodenblockwithdimensionsasshowninthefigureis12N.Calculatethe
maximumpressurethattheblockexertsonthefloor.
Solution:
Maximumpressurehappenedwhenthecontactareaisthesmallest,
Area=0.2x0.3=0.06m
2
Pressure=
12N
0.06m
2
=200Pa.
3.2UnderstandingPressureinLiquids
PressureinLiquids
1. Pressureinliquidisasaresultoftheweightoftheliquidactingonthesurfaceofanyobjectsin
theliquid.
2. Pressureofaliquidisdirectlyproportionalto:
a) thedepth,h
b) thedensityoftheliquid,("rho")
c) thegravitationalfieldstrength,g
3. Formulae:
a) Pressurecausedbyaliquid
P = hpg
b) Pressureinaliquid
P = hpg +P
atm
P
atm
=Atmosphericpressure,1.01x10
5
You might also like
- Pressure Lesson ModuleDocument3 pagesPressure Lesson ModuleCarmela UrsuaNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Pressure NotesDocument22 pagesCIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Pressure Notes9322483% (53)
- 3.1 Force and PressureDocument16 pages3.1 Force and PressureCikgu SyierNo ratings yet
- Force & Pressure PPT-3Document11 pagesForce & Pressure PPT-3ARNAB GHOSH CLASS V100% (1)
- Handout Understanding Pressure Igcse Form 2 Understanding PressureDocument4 pagesHandout Understanding Pressure Igcse Form 2 Understanding PressureMOHAMAD RIZAL BIN MUKHTARNo ratings yet
- Understanding PressureDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Pressurekur8cobain100% (1)
- 3.1 - Understanding PressureDocument5 pages3.1 - Understanding PressureArif KhanNo ratings yet
- F 4 C 3Document19 pagesF 4 C 3jalrizal7No ratings yet
- 3.1 Understanding PressureDocument12 pages3.1 Understanding Pressurenik mohamad solehinNo ratings yet
- Samrat Class 8 ScienceDocument10 pagesSamrat Class 8 ScienceShashwat SumanNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE - Part 1 (Notes)Document1 pagePRESSURE - Part 1 (Notes)ARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Physic Form 4 Chapter 3Document7 pagesPhysic Form 4 Chapter 3Nazhif NazarudinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-Pressure Physics Form 4Document13 pagesCHAPTER 3-Pressure Physics Form 4Matthew Nelson100% (2)
- Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesPressure NotesVaishnavi BannurNo ratings yet
- 1.pressure 2 PDFDocument6 pages1.pressure 2 PDFIshvaryaNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument19 pagesPressureTaufik PamisNo ratings yet
- Density and Pressure: Sheikh Khaliliur RahmanDocument33 pagesDensity and Pressure: Sheikh Khaliliur RahmanKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- 7 Pressure OrigDocument165 pages7 Pressure Origrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Forces and PressureDocument24 pagesChapter 3: Forces and PressureSiah Yih HoongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Forces and PressureDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Forces and PressureYusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- 1.8 PressureDocument48 pages1.8 PressureEbrahimNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Pressure Answer by SidDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank - Pressure Answer by SidAshish GambhirNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 3Document25 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 3Misratul A'la Mahyuddin100% (2)
- 3.1 Pressure 2012Document7 pages3.1 Pressure 2012cikgusuriyati50% (2)
- Pressure RevisedDocument5 pagesPressure ReviseddanielNo ratings yet
- Igcse 51 Density&PressureDocument40 pagesIgcse 51 Density&PressureHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Force & Pressure (Teacher)Document23 pagesChapter 3 Force & Pressure (Teacher)ima_1806No ratings yet
- St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Science Physics Notes PressureDocument3 pagesSt. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Science Physics Notes PressureashokNo ratings yet
- Physics PressureDocument3 pagesPhysics Pressurelajuli.niliNo ratings yet
- 8 - Force and Pressure - NumericalDocument2 pages8 - Force and Pressure - Numericalonlinevidhi.agrawal001No ratings yet
- Force & PressureDocument12 pagesForce & PressureGanesh VNo ratings yet
- Expt 5Document7 pagesExpt 5PARVATHY ANILNo ratings yet
- 3E Sci Phy Chapter 6 Pressure - TRDocument16 pages3E Sci Phy Chapter 6 Pressure - TRXu JianhangNo ratings yet
- Physics CH 1.8 (Pressure)Document4 pagesPhysics CH 1.8 (Pressure)Safiul FaiyazNo ratings yet
- Unit 4,5,6Document11 pagesUnit 4,5,6Adalbert MugambiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document12 pagesUnit 4Adalbert MugambiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HydrostaticsDocument17 pagesUnit 2 HydrostaticsRin MoonNo ratings yet
- 4 Pressure BuoyancyDocument8 pages4 Pressure Buoyancythinkiit100% (1)
- IGCSE 51 Density&PressureDocument45 pagesIGCSE 51 Density&Pressurecharlottekuan0824No ratings yet
- Pressure Synopsis-1Document24 pagesPressure Synopsis-1Rajanikanth100% (1)
- 7 140706224638 Phpapp01Document165 pages7 140706224638 Phpapp01Theodøros D' Spectrøøm0% (1)
- Isolated FootingDocument5 pagesIsolated FootingannNo ratings yet
- Raft Pondasi PDFDocument6 pagesRaft Pondasi PDFIsra HrNo ratings yet
- Science ks3 Lesson Sci Y7 U6 l7 PDFDocument22 pagesScience ks3 Lesson Sci Y7 U6 l7 PDFParth MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Thin and Thick CylindersDocument6 pagesThin and Thick CylindersRamesh Akula80% (5)
- 9L Pressure and MomentsDocument14 pages9L Pressure and MomentsfitrusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Force & Student)Document22 pagesChapter 3 Force & Student)Ah TiNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument20 pagesPressuretrojanfrpNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument12 pagesPressuretrojanfrpNo ratings yet
- Te2 Module 4Document4 pagesTe2 Module 4rmle100% (1)
- Tutorial 3.1Document13 pagesTutorial 3.1cikgusuriyatiNo ratings yet
- 8 Icse Phy SolutionDocument5 pages8 Icse Phy SolutionRAKESH VASANINo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Weather Projects for Young Scientists: Experiments and Science Fair IdeasFrom EverandWeather Projects for Young Scientists: Experiments and Science Fair IdeasRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- PADINI AnnualReport2014Document130 pagesPADINI AnnualReport2014Woody CysNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document10 pagesPhysics Form 4Woody CysNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Form 5Document46 pagesSPM Physics Form 5Woody CysNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Form 5Document46 pagesSPM Physics Form 5Woody CysNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document10 pagesPhysics Form 4Woody CysNo ratings yet
- SPM PhysicsDocument21 pagesSPM PhysicsWoody Cys100% (2)