Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learn Before Lecture (LBL) 1 Worksheet: Nucleus and Ribosomes ( 20 Min)
Learn Before Lecture (LBL) 1 Worksheet: Nucleus and Ribosomes ( 20 Min)
Uploaded by
Manmeet Bhullar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pagelbl
Original Title
LBL1Lec5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlbl
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageLearn Before Lecture (LBL) 1 Worksheet: Nucleus and Ribosomes ( 20 Min)
Learn Before Lecture (LBL) 1 Worksheet: Nucleus and Ribosomes ( 20 Min)
Uploaded by
Manmeet Bhullarlbl
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Learn Before Lecture (LBL) 1 Worksheet:
Nucleus and Ribosomes (~20 min)
Type your answers in the boxes provided. Upload your assignment as a word or pdf to your EEE Dropbox
before 9 am on Mon. Take the Lecture 4 online quiz (this material will be on the quiz!). Bring a copy of
assignment with you to class.
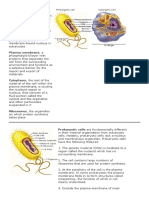
The nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the genetic library in all eukaryotic cells. Read pages
102-103, examine Figure 6.9 and answer the following questions.
1. What is chromatin?
2. What specific process takes place in the
nucleolus, a specialized region within the nucleus?
3. What structure allows proteins and other large
macromolecules to move into and out of the nucleus?
Ribosomes are the organelles involved in the synthesis of all proteins. Ribosomes are made of two subunits, one
large and one small (see fig. 6.10). These are found separately in the cytoplasm and they only combine when
mRNA binds to the small subunit. After mRNA binds, the large subunit binds and protein synthesis begins. Read
the short section on ribosomes, pg 102-103, to find out where ribosomes go to finish protein synthesis, and
answer the following questions.
4. Synthesis of all proteins begins first on free ribosomes
(True or False).
5. If synthesis of a protein is completed by a free ribosome,
where in the cell will the protein function?
6. If a protein is going to be secreted where will protein
synthesis be completed?
7. To understand how secreted proteins are synthesized look
carefully at Figure 17.22 in your text. In your own words, write 6
statements that describe each step shown in the process of a
ribosome that is making a secreted protein.
The complex of DNA and proteins making up chromosomes.
In the nucleolus a type of RNA called ribosomal RNA is
synthesized from instructions in the DNA. Also, proteins
imported from the cytoplasm are assembled with rRNA
into large and small subunits of ribosomes.
An intricate protein structure called a pore complex lines each pore of the nuclear
envelope and plays an important part in the cell by regulating the entry and exit of
proteins and RNAs, as well as large complexes of macromolecules.
False
Most of the proteins function within the
cytosol.
It will be completed by a bound protein.
1. To begin, polypeptide synthesis begins in the cytosol as the free ribosome receives an mRNA molecule and
begins to translate it.
2. The polypeptides are all marked by a signal peptide with allows to be carried to the ER membrane by a
signal-recognition particle.
3. The signal-recognition particle then binds to a receptor protein on the ER membrane.
4. After carrying it to the receptor the signal-recognition particle leaves and the polypeptide is allowed to go
through the receptor pore, where it will make its way to the ER lumen.
5. The signal peptide that bonded with the signal-recognition particle is now cut off.
6. The peptide is allowed to go into the ER lumen, where it will become a protein.
You might also like
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11Th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11Th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmagdalavicemanocgp100% (13)
- Biotech8 q3 Mod1 Toolsusedingeneticengineering v3Document28 pagesBiotech8 q3 Mod1 Toolsusedingeneticengineering v3Gabriel Martin Olea81% (16)
- Animal Cells IDocument3 pagesAnimal Cells Irandomscribduser2012No ratings yet
- 04 Structure To FunctionDocument5 pages04 Structure To Function897291868100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Cell Review AssignmentDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Cell Review Assignmentsarahmohammed801No ratings yet
- Functions of The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Synthesis of Proteins On Membrane-Bound Versus Free RibosomesDocument7 pagesFunctions of The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Synthesis of Proteins On Membrane-Bound Versus Free RibosomesDanie MorenoNo ratings yet
- q3l3 - 3ndquarter Science 10Document12 pagesq3l3 - 3ndquarter Science 10Billy Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Tema 3 - Ribosome - Gavrila Lucian-IonutDocument3 pagesTema 3 - Ribosome - Gavrila Lucian-IonutIonut ManolescuNo ratings yet
- Question1: (3 Points) : Assignment 2 Name: IDDocument4 pagesQuestion1: (3 Points) : Assignment 2 Name: IDDental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Protein TargetingDocument7 pagesProtein TargetingRaven JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Topic 7.3 Review Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesTopic 7.3 Review Practice QuestionsGlen JojiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Tour of The CellDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Tour of The CellAstrii LyNo ratings yet
- Protein SortingDocument10 pagesProtein SortingRasika RathnayakaNo ratings yet
- MasteringBiology - The Endomembrane SystemDocument11 pagesMasteringBiology - The Endomembrane Systemshiyi33% (3)
- NucleusDocument20 pagesNucleusmadhavi vemulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Tour of The CellDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Tour of The CellAstrii LyNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2 Review AnswersDocument35 pagesMidterm 2 Review AnswershamoudyelmouallemNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 &2 Biology IUDocument5 pagesHomework 1 &2 Biology IUVanessa NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ibd A09-Ppt Individu Topik 1-Robi KholiqDocument29 pagesIbd A09-Ppt Individu Topik 1-Robi KholiqDiniSylvanaNo ratings yet
- DNA, The Genetic MaterialDocument6 pagesDNA, The Genetic MaterialMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting2Document6 pagesMechanism of Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting2ahmeddiab2022No ratings yet
- Types of Cellular CompartmentsDocument26 pagesTypes of Cellular CompartmentsAsim Bin ArshadNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell's Genetic Instruction Are Haused in The Nucleus and Carried Out by The RibosomesDocument3 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell's Genetic Instruction Are Haused in The Nucleus and Carried Out by The Ribosomesvin caNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Composition of CellDocument84 pagesBiochemical Composition of Cellmuskaankhan27No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis in CellDocument7 pagesProtein Synthesis in Cellkvpyqegld100% (2)
- A-Endoplasmic Reticulum - Wrapping It Up: Rough and SmoothDocument9 pagesA-Endoplasmic Reticulum - Wrapping It Up: Rough and SmoothRahul PurwarNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Inventory COMPLETEDocument18 pagesCell Biology Inventory COMPLETEmariam miladNo ratings yet
- Bio 110 Study GuideDocument8 pagesBio 110 Study Guidecptran0No ratings yet
- 6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Document7 pages6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Sadasivarao GaddeNo ratings yet
- Flujo de Información GenéticaDocument23 pagesFlujo de Información GenéticaKennyDeLosReyesNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Topic 2 Hand OutDocument14 pagesCytogenetics Topic 2 Hand OutJean Carmelette BalalloNo ratings yet
- BMB Test 3 Study GuidesDocument8 pagesBMB Test 3 Study GuidesNate LisbinNo ratings yet
- How The Ribosome Works American ScientistDocument6 pagesHow The Ribosome Works American ScientistDr Carlos Estrada VázquezNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manualantheagian4p4y4100% (34)
- Lesson 2: Molecular Organization of CellsDocument12 pagesLesson 2: Molecular Organization of CellsremshopNo ratings yet
- The Nucleus: Genome (Genetic Information) in Eukaryotic Cells, So It Is ResponsibleDocument9 pagesThe Nucleus: Genome (Genetic Information) in Eukaryotic Cells, So It Is ResponsibleAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- Weel 4 SurveyDocument29 pagesWeel 4 SurveyAaron MostNo ratings yet
- f215 Spec NotesDocument25 pagesf215 Spec NoteswbaturleyNo ratings yet
- MODULE of Genetic MaterialDocument11 pagesMODULE of Genetic MaterialFadila AftrianiNo ratings yet
- Unit: 07: Mechanism of Cellular Differentiation / Differential Gene ExpressionDocument76 pagesUnit: 07: Mechanism of Cellular Differentiation / Differential Gene ExpressionMuhammad SibtainNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisAbigailNo ratings yet
- Cell Lect 2Document16 pagesCell Lect 2sadaffardoosNo ratings yet
- Frym 11 1034112Document11 pagesFrym 11 10341124143No ratings yet
- 05 - Kompart Sorting Protein 1Document33 pages05 - Kompart Sorting Protein 1Haddhi WhibowoNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Essentials of The Living World 5th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument28 pagesInstant Download PDF Essentials of The Living World 5th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manual Full Chapternoudafimke100% (6)
- Test 5 Study Guide Biology 1107Document6 pagesTest 5 Study Guide Biology 1107Brandon 'CuddleMuffins StuartNo ratings yet
- Full Download Genetics A Conceptual Approach 5th Edition Pierce Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesFull Download Genetics A Conceptual Approach 5th Edition Pierce Solutions Manualdopemorpheanwlzyv100% (29)
- The Nucleus and RibosomesDocument9 pagesThe Nucleus and RibosomestadiwaospencioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Plant CellsDocument13 pagesLecture 2 Plant Cellsmichael328wanjiruNo ratings yet
- Thedumpedgangxthaothongep ScienceprojectDocument8 pagesThedumpedgangxthaothongep Scienceprojectapi-353155625No ratings yet
- Module 4-From Gene To Protein Basic Molecular Genetic MechanismsDocument43 pagesModule 4-From Gene To Protein Basic Molecular Genetic MechanismsBelinda GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Kanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesKanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Biology Answer KeyDocument5 pagesCentral Dogma of Biology Answer KeyMusah Lamusah AlaleNo ratings yet
- Fronda - CMB - PPT - Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument45 pagesFronda - CMB - PPT - Endoplasmic ReticulumJericho D. FrondaNo ratings yet
- NRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANDocument14 pagesNRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANEllen Mynelle MabulacNo ratings yet
- Cellbiologyreview AnswersDocument8 pagesCellbiologyreview AnswersCARLISABEL GALLARDONo ratings yet
- Biosyntesis Modification, and Cell Secretion 1Document63 pagesBiosyntesis Modification, and Cell Secretion 1Sri HayuniNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function: Structure of The Nuclear EnvelopeDocument40 pagesCell Structure and Function: Structure of The Nuclear EnvelopeKitkat AlorroNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes - What Are The Similarities, Differences, and Examples - RS' ScienceDocument1 pageEukaryotes and Prokaryotes - What Are The Similarities, Differences, and Examples - RS' ScienceCandela Sierra ThomasaNo ratings yet
- Jeopardy - Dna Rna and MitosisDocument27 pagesJeopardy - Dna Rna and Mitosisapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Batobalani MagazineDocument6 pagesBatobalani MagazineJUSTINE MAE AGRAVANTENo ratings yet
- Full Download Understanding Pathophysiology 6th Edition Huether Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Understanding Pathophysiology 6th Edition Huether Test Bankkuhsegrady100% (28)
- Transcribed Ultraconserved Region in Human CancersDocument8 pagesTranscribed Ultraconserved Region in Human CancersmartarmarcosNo ratings yet
- Current Issues in Molecular Virology - Viral Genetics and Biotechnological Applications 2013Document286 pagesCurrent Issues in Molecular Virology - Viral Genetics and Biotechnological Applications 2013Daoud IssaNo ratings yet
- Libro Yason BiotechnologyDocument62 pagesLibro Yason BiotechnologyAGRAIZNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: Mrs. Mary Vienne M. PascualDocument73 pagesBiological Molecules: Mrs. Mary Vienne M. PascualVienne Monroid100% (1)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument27 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentRafika SyedNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesGene Expression Literature Reviewafdtyaxfv100% (1)
- Chapter - 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance - WatermarkDocument31 pagesChapter - 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Watermarktejeshnaik026No ratings yet
- Aspergillus Brasiliensis: (Atcc 16404™)Document2 pagesAspergillus Brasiliensis: (Atcc 16404™)arsa1aNo ratings yet
- BIO201 FIF Final Exam Practice QuestionsDocument13 pagesBIO201 FIF Final Exam Practice QuestionswillpawnNo ratings yet
- RBalderas - CBE3 Pre Test Answer KeyDocument39 pagesRBalderas - CBE3 Pre Test Answer KeyMikyle NatorNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids - DNA and RNADocument53 pagesNucleic Acids - DNA and RNATom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Biomolecules ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience 10 Biomolecules ReviewerTasha Heart QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument18 pagesOrigin of LifeJoana Pearl FranciscoNo ratings yet
- B.SC Biotechnology (Honors) : B-Biofertilizers and BiopesticidesDocument46 pagesB.SC Biotechnology (Honors) : B-Biofertilizers and BiopesticidesVishwajeet AryaNo ratings yet
- Stootsd UnitplanreflectionDocument3 pagesStootsd Unitplanreflectionapi-317044149No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Techniques in Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Techniques in Cell and Molecular BiologyZorin RealceNo ratings yet
- 10.06 Prokaryotic TranslationDocument4 pages10.06 Prokaryotic TranslationWidya NingsiNo ratings yet
- How The Genes Are Regulated & Expressed?: AssignmentDocument17 pagesHow The Genes Are Regulated & Expressed?: AssignmentSuraiya Siraj NehaNo ratings yet
- Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 3rd Edition Starr Test BankDocument12 pagesBiology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 3rd Edition Starr Test Bankjoanneesparzagwjxmyqont100% (31)
- Cell Biology: Course Code: LSE-01 Assignment Code: LSE-01/TMA/2020 Maximum Marks: 100Document26 pagesCell Biology: Course Code: LSE-01 Assignment Code: LSE-01/TMA/2020 Maximum Marks: 100Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Genetics in OrthoDocument58 pagesGenetics in OrthoAthira JithendranathNo ratings yet
- siRNA ReviewDocument26 pagessiRNA ReviewSara AlrubaiiNo ratings yet
- Say It With DNADocument14 pagesSay It With DNAJoanna SeproNo ratings yet
- Research in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Document27 pagesResearch in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Kim GoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 What Is Biochemistry-1Document19 pagesLecture 1 What Is Biochemistry-1Carina JLNo ratings yet