Professional Documents
Culture Documents
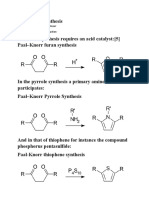
Geranyl Pyrophosphate Linaloyl
Geranyl Pyrophosphate Linaloyl
Uploaded by
Salis Iqbal MazariCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hagerman, 2002Document116 pagesHagerman, 2002Dini Iga PutriNo ratings yet
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 6 PhenylpropanoidsDocument15 pages6 Phenylpropanoidskusum AkkiNo ratings yet
- Terpenoids Lower PDFDocument7 pagesTerpenoids Lower PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Tannin ChemistryDocument116 pagesTannin ChemistryExaudi EbennezerNo ratings yet
- Aryl GroupDocument18 pagesAryl GroupDaniel BakerNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument24 pagesChemical ReactionTommy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Terpineol From Hydration of Crude Sulfate Turpentine OilDocument6 pagesTerpineol From Hydration of Crude Sulfate Turpentine OilDertySulistyowatiNo ratings yet
- Natural Products: Dr. Tukiran, M.SiDocument18 pagesNatural Products: Dr. Tukiran, M.SiSangeetha PrakashNo ratings yet
- What Are AlkaloidsDocument29 pagesWhat Are AlkaloidsmhadhiehNo ratings yet
- Phenolic Compound IIDocument24 pagesPhenolic Compound IIMuhammad Irfan AmiruddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture Structure Of-A TerpineolDocument12 pagesLecture Structure Of-A TerpineolRk ShituNo ratings yet
- Alcaloides A 2023Document76 pagesAlcaloides A 2023Alex osorioNo ratings yet
- 080 Shikimates Phenyl PropanoidsDocument60 pages080 Shikimates Phenyl PropanoidsRaatuu Suud HanumNo ratings yet
- My AssignmentDocument13 pagesMy AssignmentAmos JamesNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument18 pagesOrganic ChemistryLucky SinghNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of AlcoholDocument5 pagesDerivatives of AlcoholEcho MoralesNo ratings yet
- Pfitzinger Synthesis: Department of Chemistry, College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, PhilippinesDocument6 pagesPfitzinger Synthesis: Department of Chemistry, College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, PhilippinesNoir SalifoNo ratings yet
- Org - Unit 4Document29 pagesOrg - Unit 4lijyohannesmekonnen7No ratings yet
- Food ColourantDocument61 pagesFood ColourantLebohang Mofokeng DavidNo ratings yet
- Phenol SDocument9 pagesPhenol SAnonymous 8rsxG4No ratings yet
- Alpha Ternipeol From Hydration of Crude Sulfate Turpentine OilDocument5 pagesAlpha Ternipeol From Hydration of Crude Sulfate Turpentine OilPhạm NgânNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in The Chemistry of Oripavine & DerivativesABB - 2014072111275178Document15 pagesRecent Advances in The Chemistry of Oripavine & DerivativesABB - 2014072111275178Ji ChemNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Comparative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulation of ParacetamolDocument12 pagesSynthesis and Comparative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulation of ParacetamolHello oNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Plant Secondary MetabolitesDocument34 pagesBiosynthesis of Plant Secondary MetabolitesPuvaneswary LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Purine AlkaloidsDocument10 pagesPurine Alkaloidsharishkumar kakrani100% (1)
- PhenolDocument20 pagesPhenolUmar TahirNo ratings yet
- CompoundsDocument2 pagesCompoundsapi-427955664No ratings yet
- 2 Shikimic Acid Pathway 1Document10 pages2 Shikimic Acid Pathway 1Akshay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Alkaloidal AminesDocument31 pagesAlkaloidal AminesphkakraniNo ratings yet
- Plant Secondary MetabolitesDocument36 pagesPlant Secondary MetabolitesvishnuNo ratings yet
- Index: Sr. No. Topics Page NoDocument69 pagesIndex: Sr. No. Topics Page NoRoshan Rohit100% (3)
- AlkaloidsDocument28 pagesAlkaloidsKamala Badalova100% (2)
- Secondary Metabolites: Are Derived From Primary MetabolitesDocument38 pagesSecondary Metabolites: Are Derived From Primary MetabolitesPutre Cellalu CahyangNo ratings yet
- TANNIN - Resin - FlavanoidDocument44 pagesTANNIN - Resin - FlavanoidParajapati SanjivNo ratings yet
- AnilinDocument18 pagesAnilinM Septian PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument24 pagesBenzeneElla ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Group 03 (2A) 2Document8 pagesGroup 03 (2A) 2-No ratings yet
- 'The Flavor and Fragrance High Production Volume ConsortiaDocument55 pages'The Flavor and Fragrance High Production Volume ConsortiaIndah SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Template Formal ReportDocument6 pagesTemplate Formal ReportMarian Alisangco100% (1)
- Ijcb 53B (10) 1255-1262Document8 pagesIjcb 53B (10) 1255-1262Alex WasabiNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument4 pagesPhenolAbeer AbdelganeNo ratings yet
- Aniline Project 1234Document6 pagesAniline Project 1234kareem100% (1)
- Isoquinoline - Lec6 PDFDocument16 pagesIsoquinoline - Lec6 PDFHassan mohamad Al-bayateNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Comparative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulation of Paracetamol905Document11 pagesSynthesis and Comparative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulation of Paracetamol905johnpatrickecoduNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Benzene Carbon Chemical Formula H Coal Tar Distillation Petroleum Water Moth Sulfonic Acid DyestuffDocument2 pagesHydrocarbon Benzene Carbon Chemical Formula H Coal Tar Distillation Petroleum Water Moth Sulfonic Acid Dyestuffvikas aggarwalNo ratings yet
- OC-V p5Document14 pagesOC-V p5Derek Ross0% (1)
- Alkaloids 1Document85 pagesAlkaloids 1drprambabu2011No ratings yet
- Quinones: Prof. Dr. Ali Hikmet MeriçliDocument55 pagesQuinones: Prof. Dr. Ali Hikmet MeriçliEduard NiñoNo ratings yet
- ANTHONY CRASTO - Flavors and FragrancesDocument81 pagesANTHONY CRASTO - Flavors and FragrancesShishir Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Hess 1975Document16 pagesHess 1975Aarti RajanikantNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Aromatic Amino Acids.Document6 pagesBiosynthesis of Aromatic Amino Acids.Karime Flores BarreraNo ratings yet
- 8 - TerpenoidDocument95 pages8 - TerpenoidTim IrmaNo ratings yet
- Phenol - Amino Antipyrine InteractionDocument7 pagesPhenol - Amino Antipyrine InteractionAbdulwasim KhanNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (19) : Inventors: Hyman L. Schulman, Fort LeeDocument4 pagesUnited States Patent (19) : Inventors: Hyman L. Schulman, Fort Leemajji100% (1)
- ALKALOIDSDocument27 pagesALKALOIDSamit jainNo ratings yet
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- Mother's Remedies Over One Thousand Tried and Tested Remedies from Mothers of the United States and CanadaFrom EverandMother's Remedies Over One Thousand Tried and Tested Remedies from Mothers of the United States and CanadaNo ratings yet
- Ch17 Answer KeyDocument17 pagesCh17 Answer KeySalis Iqbal Mazari100% (1)
- Spring 2014 - CS101 - 1Document2 pagesSpring 2014 - CS101 - 1Salis Iqbal MazariNo ratings yet
- Starch 2006Document41 pagesStarch 2006mynym100% (2)
- Amjid QDocument2 pagesAmjid QSalis Iqbal MazariNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry DK024Document19 pagesOrganic Chemistry DK024RosdianaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Ozone Micro-And Nanobubble Technologies in Water and Wastewater Treatment: ReviewDocument11 pagesApplications of Ozone Micro-And Nanobubble Technologies in Water and Wastewater Treatment: ReviewZaqiaNo ratings yet
- O RingsDocument105 pagesO Ringsrafaellos19No ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Thushara Kandaramath Hari, Zahira Yaakob, Narayanan N. BinithaDocument11 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Thushara Kandaramath Hari, Zahira Yaakob, Narayanan N. BinithaCostelCosNo ratings yet
- Softcopy of CHEMISTRY-F5 PDFDocument188 pagesSoftcopy of CHEMISTRY-F5 PDFainihasshim79% (282)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 2Document7 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 2Atie SuriNo ratings yet
- Trial STPM Chemistry Sem 1 PDFDocument7 pagesTrial STPM Chemistry Sem 1 PDFsuhaidah47No ratings yet
- Anthocyanidins and Anthocyanins: Colored Pigments As Food, Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and The Potential Health BenefitsDocument21 pagesAnthocyanidins and Anthocyanins: Colored Pigments As Food, Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and The Potential Health BenefitsSherlyn Joy Panlilio IsipNo ratings yet
- Chem All in One Final AnsweredDocument334 pagesChem All in One Final AnsweredAbhishek GunjalNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214714418300990 Main PDFDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S2214714418300990 Main PDFLinda Girlessa Imbago RojasNo ratings yet
- Ps02epch01 Natural Product IIDocument2 pagesPs02epch01 Natural Product IIArunabh MishraNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument100 pagesSyllabusAlok chauhanNo ratings yet
- Iodometric Assay-AntibioticsDocument2 pagesIodometric Assay-AntibioticsZahra AdiyatiNo ratings yet
- Valve Lubrication Pumps LubriAlloys PDFDocument16 pagesValve Lubrication Pumps LubriAlloys PDFPEDRONo ratings yet
- SAC 451 - Designer Fertilizer Production (Optional Course)Document110 pagesSAC 451 - Designer Fertilizer Production (Optional Course)rajap02No ratings yet
- Scale Problem Oil and GasDocument11 pagesScale Problem Oil and GasMas ChopinNo ratings yet
- TQ G10 POST TEST CompleteDocument2 pagesTQ G10 POST TEST CompleteLorenz Gallo VillaseranNo ratings yet
- Tannin Estimation PDFDocument5 pagesTannin Estimation PDFTanyaradzwa ChimwendoNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument20 pagesRecombinant DNAUmme rubabNo ratings yet
- Selective Extraction of Benzene From Benzene-Cyclohexane Mixture Using 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Ionic LiquidDocument8 pagesSelective Extraction of Benzene From Benzene-Cyclohexane Mixture Using 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Ionic LiquidBüşraNo ratings yet
- Forest Paper1 - 2023Document13 pagesForest Paper1 - 2023Amit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in PDFDocument21 pagesCorrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in PDFNsubektiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21: PolymerDocument4 pagesChapter 21: PolymerRoshan SupurmaniamNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2Document8 pages10 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- PPE and Its UseDocument38 pagesPPE and Its UseManash HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocument54 pagesDeep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applicationspepe verazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Part 1 Introduction Classification of Edible OilDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - Part 1 Introduction Classification of Edible OilFirdaus ZubbirNo ratings yet
- Iso 14896 2009Document9 pagesIso 14896 2009Fairmont Ind Quality DivisionNo ratings yet
- Waste-To-Energy Power PlantsDocument9 pagesWaste-To-Energy Power Plantshamidniky100% (1)
- Alkyd ResinDocument6 pagesAlkyd ResinMahazabin MimNo ratings yet
Geranyl Pyrophosphate Linaloyl
Geranyl Pyrophosphate Linaloyl
Uploaded by
Salis Iqbal MazariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geranyl Pyrophosphate Linaloyl
Geranyl Pyrophosphate Linaloyl
Uploaded by
Salis Iqbal MazariCopyright:
Available Formats
Pinene (C
10
H
16
) is a bicyclic monoterpene chemical compound.
There are two structural isomers of pinene found in nature: -pinene and -
pinene. As the name suggests, both forms are important constituents of pine
resin; they are also found in the resins of many other conifers, as well as in non-
coniferous plants such as big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata). Both isomers are
used by many insects in their chemical
-Pinene and -pinene are both produced from geranyl pyrophosphate,
via cyclisation of linaloyl pyrophosphate followed by loss of a proton from the
carbocation equivalent.
-Pinene is an organic compound of the terpene class, one of two isomers of
pinene
.
It is an alkene and it contains a reactive four-membered ring. It is found in
the oils of many species of many coniferous trees, notably the pine. It is also
found in the essential oil of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis). Both enantiomers
are known in nature; (1S,5S)- or ()--pinene is more common in European pines,
whereas the (1R,5R)- or (+)--isomer is more common in North America. The
racemic mixture is present in some oils such as eucalyptus oil and orange peel oil.
Chemical Formula: C
10
H
16
Apearance: liquid with a turpentine odour
Melting Point: -55 C
Boiling Point: 156 C
Flash Point: 33 C
Water Solubility: insoluble
Stability: Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
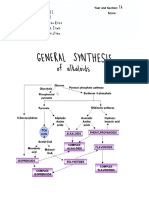
The four-membered ring in -pinene 1 makes it a reactive
hydrocarbon, prone to skeletal rearrangements such as the Wagner-
Meerwein rearrangement. For example, attempts to perform hydration
or hydrogen halide addition with the alkene functionality typically lead
to rearranged products. With concentrated sulfuric acid and ethanol
the major products are terpineol 2 and its ethyl ether 3, while glacial
acetic acid gives the corresponding acetate ester 4. With dilute acids,
terpin hydrate 5 becomes the major product.
With one molar equivalent of anhydrous HCl, the simple addition
product 6a can be formed at low temperature in the presence of ether,
but it is very unstable. At normal temperatures, or if no ether is
present, the major product is bornyl chloride 6b, along with a small
amount of fenchyl chloride 6c.
[3]
For many years 6b (also called
"artificial camphor") was referred to as "pinene hydrochloride", until it
was confirmed as identical with bornyl chloride made from camphene.
If more HCl is used, achiral 7 (dipentene hydrochloride) is the major
product along with some 6b. Nitrosyl chloride followed by base leads to
the oxime 8 which can be reduced to "pinylamine" 9. Both 8 and 9 are
stable compounds containing an intact four-membered ring, and these
compounds helped greatly in identifying this important component of
the pinene skeleton.
[4]
A variety of reagents such as iodine or PCl
3
cause aromatisation, leading
to p-cymene 10.
Under aerobic oxidation conditions, the main oxidation products are
pinene oxide, verbenyl hydroperoxide, verbenol and verbenone.
Bicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene, 2,6,6-trimethyl-;2-
Pinene;Pinene;2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene;PINENE,
alpha;2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo(3.1.1)-2-hept-2-ene;2,6,6-
Trimethylbicyclo(3.1.1)-2-heptene;Acintene A;4,6,6-
Trimethylbicyklo(3,1,1)hept-3-en;UN 2368;alpha-(+)-Pinene;a-
Pinene;Pc 500;Terpene hydrocarbon;c 500;,6,6-Trimethyl-
bicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene;Alpha pinene;2,6,6-trimethylbicyclo[3,1,1]-2-
heptene (alpha&ra
Monoterpenes, of which -pinene is one of the
principal species, are emitted in substantial amounts by vegetation, and
these emissions are affected by temperature and light intensity. In the
atmosphere alpha-pinene undergoes reactions with ozone, the OH
radical or the NO
3
radical, leading to low-volatility species which partly
condense on existing aerosols, thereby generating secondary organic
aerosols. This has been shown in numerous laboratory experiments for
the mono- and sesquiterpenes. Products of -pinene which have been
identified explicitly are pinonaldehyde, norpinonaldehyde, pinic acid,
pinonic acid and pinalic acid.
At low exposure levels, -Pinene is a bronchodilator in
humans, and is highly bioavailable with 60% human pulmonary uptake
with rapid metabolism or redistribution. Alpha-Pinene is an anti-
inflammatory via PGE1, and seems to be a broad-spectrum antibiotic. It
exhibits activity as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, aiding memory.
Alpha-Pinene forms the biosynthetic base for CB2 ligands, such as HU-
308.
You might also like
- Hagerman, 2002Document116 pagesHagerman, 2002Dini Iga PutriNo ratings yet
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 6 PhenylpropanoidsDocument15 pages6 Phenylpropanoidskusum AkkiNo ratings yet
- Terpenoids Lower PDFDocument7 pagesTerpenoids Lower PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Tannin ChemistryDocument116 pagesTannin ChemistryExaudi EbennezerNo ratings yet
- Aryl GroupDocument18 pagesAryl GroupDaniel BakerNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument24 pagesChemical ReactionTommy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Terpineol From Hydration of Crude Sulfate Turpentine OilDocument6 pagesTerpineol From Hydration of Crude Sulfate Turpentine OilDertySulistyowatiNo ratings yet
- Natural Products: Dr. Tukiran, M.SiDocument18 pagesNatural Products: Dr. Tukiran, M.SiSangeetha PrakashNo ratings yet
- What Are AlkaloidsDocument29 pagesWhat Are AlkaloidsmhadhiehNo ratings yet
- Phenolic Compound IIDocument24 pagesPhenolic Compound IIMuhammad Irfan AmiruddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture Structure Of-A TerpineolDocument12 pagesLecture Structure Of-A TerpineolRk ShituNo ratings yet
- Alcaloides A 2023Document76 pagesAlcaloides A 2023Alex osorioNo ratings yet
- 080 Shikimates Phenyl PropanoidsDocument60 pages080 Shikimates Phenyl PropanoidsRaatuu Suud HanumNo ratings yet
- My AssignmentDocument13 pagesMy AssignmentAmos JamesNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument18 pagesOrganic ChemistryLucky SinghNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of AlcoholDocument5 pagesDerivatives of AlcoholEcho MoralesNo ratings yet
- Pfitzinger Synthesis: Department of Chemistry, College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, PhilippinesDocument6 pagesPfitzinger Synthesis: Department of Chemistry, College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, PhilippinesNoir SalifoNo ratings yet
- Org - Unit 4Document29 pagesOrg - Unit 4lijyohannesmekonnen7No ratings yet
- Food ColourantDocument61 pagesFood ColourantLebohang Mofokeng DavidNo ratings yet
- Phenol SDocument9 pagesPhenol SAnonymous 8rsxG4No ratings yet
- Alpha Ternipeol From Hydration of Crude Sulfate Turpentine OilDocument5 pagesAlpha Ternipeol From Hydration of Crude Sulfate Turpentine OilPhạm NgânNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in The Chemistry of Oripavine & DerivativesABB - 2014072111275178Document15 pagesRecent Advances in The Chemistry of Oripavine & DerivativesABB - 2014072111275178Ji ChemNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Comparative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulation of ParacetamolDocument12 pagesSynthesis and Comparative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulation of ParacetamolHello oNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Plant Secondary MetabolitesDocument34 pagesBiosynthesis of Plant Secondary MetabolitesPuvaneswary LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Purine AlkaloidsDocument10 pagesPurine Alkaloidsharishkumar kakrani100% (1)
- PhenolDocument20 pagesPhenolUmar TahirNo ratings yet
- CompoundsDocument2 pagesCompoundsapi-427955664No ratings yet
- 2 Shikimic Acid Pathway 1Document10 pages2 Shikimic Acid Pathway 1Akshay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Alkaloidal AminesDocument31 pagesAlkaloidal AminesphkakraniNo ratings yet
- Plant Secondary MetabolitesDocument36 pagesPlant Secondary MetabolitesvishnuNo ratings yet
- Index: Sr. No. Topics Page NoDocument69 pagesIndex: Sr. No. Topics Page NoRoshan Rohit100% (3)
- AlkaloidsDocument28 pagesAlkaloidsKamala Badalova100% (2)
- Secondary Metabolites: Are Derived From Primary MetabolitesDocument38 pagesSecondary Metabolites: Are Derived From Primary MetabolitesPutre Cellalu CahyangNo ratings yet
- TANNIN - Resin - FlavanoidDocument44 pagesTANNIN - Resin - FlavanoidParajapati SanjivNo ratings yet
- AnilinDocument18 pagesAnilinM Septian PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument24 pagesBenzeneElla ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Group 03 (2A) 2Document8 pagesGroup 03 (2A) 2-No ratings yet
- 'The Flavor and Fragrance High Production Volume ConsortiaDocument55 pages'The Flavor and Fragrance High Production Volume ConsortiaIndah SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Template Formal ReportDocument6 pagesTemplate Formal ReportMarian Alisangco100% (1)
- Ijcb 53B (10) 1255-1262Document8 pagesIjcb 53B (10) 1255-1262Alex WasabiNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument4 pagesPhenolAbeer AbdelganeNo ratings yet
- Aniline Project 1234Document6 pagesAniline Project 1234kareem100% (1)
- Isoquinoline - Lec6 PDFDocument16 pagesIsoquinoline - Lec6 PDFHassan mohamad Al-bayateNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Comparative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulation of Paracetamol905Document11 pagesSynthesis and Comparative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulation of Paracetamol905johnpatrickecoduNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Benzene Carbon Chemical Formula H Coal Tar Distillation Petroleum Water Moth Sulfonic Acid DyestuffDocument2 pagesHydrocarbon Benzene Carbon Chemical Formula H Coal Tar Distillation Petroleum Water Moth Sulfonic Acid Dyestuffvikas aggarwalNo ratings yet
- OC-V p5Document14 pagesOC-V p5Derek Ross0% (1)
- Alkaloids 1Document85 pagesAlkaloids 1drprambabu2011No ratings yet
- Quinones: Prof. Dr. Ali Hikmet MeriçliDocument55 pagesQuinones: Prof. Dr. Ali Hikmet MeriçliEduard NiñoNo ratings yet
- ANTHONY CRASTO - Flavors and FragrancesDocument81 pagesANTHONY CRASTO - Flavors and FragrancesShishir Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Hess 1975Document16 pagesHess 1975Aarti RajanikantNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Aromatic Amino Acids.Document6 pagesBiosynthesis of Aromatic Amino Acids.Karime Flores BarreraNo ratings yet
- 8 - TerpenoidDocument95 pages8 - TerpenoidTim IrmaNo ratings yet
- Phenol - Amino Antipyrine InteractionDocument7 pagesPhenol - Amino Antipyrine InteractionAbdulwasim KhanNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (19) : Inventors: Hyman L. Schulman, Fort LeeDocument4 pagesUnited States Patent (19) : Inventors: Hyman L. Schulman, Fort Leemajji100% (1)
- ALKALOIDSDocument27 pagesALKALOIDSamit jainNo ratings yet
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- Mother's Remedies Over One Thousand Tried and Tested Remedies from Mothers of the United States and CanadaFrom EverandMother's Remedies Over One Thousand Tried and Tested Remedies from Mothers of the United States and CanadaNo ratings yet
- Ch17 Answer KeyDocument17 pagesCh17 Answer KeySalis Iqbal Mazari100% (1)
- Spring 2014 - CS101 - 1Document2 pagesSpring 2014 - CS101 - 1Salis Iqbal MazariNo ratings yet
- Starch 2006Document41 pagesStarch 2006mynym100% (2)
- Amjid QDocument2 pagesAmjid QSalis Iqbal MazariNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry DK024Document19 pagesOrganic Chemistry DK024RosdianaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Ozone Micro-And Nanobubble Technologies in Water and Wastewater Treatment: ReviewDocument11 pagesApplications of Ozone Micro-And Nanobubble Technologies in Water and Wastewater Treatment: ReviewZaqiaNo ratings yet
- O RingsDocument105 pagesO Ringsrafaellos19No ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Thushara Kandaramath Hari, Zahira Yaakob, Narayanan N. BinithaDocument11 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Thushara Kandaramath Hari, Zahira Yaakob, Narayanan N. BinithaCostelCosNo ratings yet
- Softcopy of CHEMISTRY-F5 PDFDocument188 pagesSoftcopy of CHEMISTRY-F5 PDFainihasshim79% (282)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 2Document7 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 2Atie SuriNo ratings yet
- Trial STPM Chemistry Sem 1 PDFDocument7 pagesTrial STPM Chemistry Sem 1 PDFsuhaidah47No ratings yet
- Anthocyanidins and Anthocyanins: Colored Pigments As Food, Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and The Potential Health BenefitsDocument21 pagesAnthocyanidins and Anthocyanins: Colored Pigments As Food, Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and The Potential Health BenefitsSherlyn Joy Panlilio IsipNo ratings yet
- Chem All in One Final AnsweredDocument334 pagesChem All in One Final AnsweredAbhishek GunjalNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214714418300990 Main PDFDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S2214714418300990 Main PDFLinda Girlessa Imbago RojasNo ratings yet
- Ps02epch01 Natural Product IIDocument2 pagesPs02epch01 Natural Product IIArunabh MishraNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument100 pagesSyllabusAlok chauhanNo ratings yet
- Iodometric Assay-AntibioticsDocument2 pagesIodometric Assay-AntibioticsZahra AdiyatiNo ratings yet
- Valve Lubrication Pumps LubriAlloys PDFDocument16 pagesValve Lubrication Pumps LubriAlloys PDFPEDRONo ratings yet
- SAC 451 - Designer Fertilizer Production (Optional Course)Document110 pagesSAC 451 - Designer Fertilizer Production (Optional Course)rajap02No ratings yet
- Scale Problem Oil and GasDocument11 pagesScale Problem Oil and GasMas ChopinNo ratings yet
- TQ G10 POST TEST CompleteDocument2 pagesTQ G10 POST TEST CompleteLorenz Gallo VillaseranNo ratings yet
- Tannin Estimation PDFDocument5 pagesTannin Estimation PDFTanyaradzwa ChimwendoNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument20 pagesRecombinant DNAUmme rubabNo ratings yet
- Selective Extraction of Benzene From Benzene-Cyclohexane Mixture Using 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Ionic LiquidDocument8 pagesSelective Extraction of Benzene From Benzene-Cyclohexane Mixture Using 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Ionic LiquidBüşraNo ratings yet
- Forest Paper1 - 2023Document13 pagesForest Paper1 - 2023Amit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in PDFDocument21 pagesCorrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in PDFNsubektiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21: PolymerDocument4 pagesChapter 21: PolymerRoshan SupurmaniamNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2Document8 pages10 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- PPE and Its UseDocument38 pagesPPE and Its UseManash HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocument54 pagesDeep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applicationspepe verazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Part 1 Introduction Classification of Edible OilDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - Part 1 Introduction Classification of Edible OilFirdaus ZubbirNo ratings yet
- Iso 14896 2009Document9 pagesIso 14896 2009Fairmont Ind Quality DivisionNo ratings yet
- Waste-To-Energy Power PlantsDocument9 pagesWaste-To-Energy Power Plantshamidniky100% (1)
- Alkyd ResinDocument6 pagesAlkyd ResinMahazabin MimNo ratings yet