Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 1: Reaction On Beam
Experiment 1: Reaction On Beam
Uploaded by
Säbrinä ShukrìOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 1: Reaction On Beam
Experiment 1: Reaction On Beam
Uploaded by
Säbrinä ShukrìCopyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT 1 : REACTION ON BEAM
a. OBJECTIVE
To test the reaction on simply supported beam under point load
b. INTRODUCTION
The reaction on beam reacted as what Newton Third Law stated. Action and reaction is
the same but opposite. Total reaction component depends on the types of supports.
The structure under reaction is in equilibrium. This situation must occured so that the
structure will not move. For that to happened, this structure must obey the rule of
equilibrium. The load must be equalized by the reaction on the supports. The magnitude of
action can be calculated using static equation. If this structure is externally determinacy,
static equation was enough to solve the calculation.
The steps to calculate the reaction are as below:
1. drew a image of the structure
2. identified the supports
3. Marked the reaction that will occur at all support, such as vertical reaction, horizontal
reaction, and moment reaction. Assume that component react at all directions.
4. Write and solve all static equation which suitable to identify all the reaction
magnitudes.
5. If the answer calculated was negative, this show that the direction pointed was
opposite. If the value show positive value, this show that the direction was correct.
These steps should be followed in order to solve the reaction of structure which have not
more than three reactions.
R
1
R
2
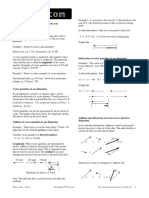
c. APPARATUS
Apparatus is set up as show in the picture below.
W
Diagram 1: One point load
M
1050 mm
x
d. PROCEDURES
Apparatus was set up as shown in Diagram 1 and 2. The beam is to be making sure that it was
flatted by using adjustable screw. The initial reading is on balance spring is jot down
1. Beam was loaded with one point load at different distance (x) from support (A).
Action value on beam was observed and jot down at different weight (M) at different
distance.
2. Two point loads (M
1
and M
2
) was applied as shown in Diagram 2 and the reaction at
difference was jot down carefully.
3. One point load, M
3
was placed at distance y. Reaction on beam by the balance spring
was jot down carefully. Values of M
3
and y are unknown and have to be identifying
from this experiment.
The reaction R1, R2, R3, and R4 id calculated using principle of moment and value have to
be obtained by comparing the reading from balance spring.
m
M1 M2 M3
Diagram 2: Two point load
m
n
y
Balance
spring
e. RESULT
For one point load, M =1 kg
Distance, x (mm) Reaction R
1
on A(N) Reaction R
2
on B(N)
Experiment Calculation Experiment Calculation
375 18 0.64 16 0.36
500 17 0.52 18 0.48
750 15 0.29 20 0.71
1000 12 0.05 22 0.95
Table 1
For two point load, M
1
=1 kg , M
2
=2 kg
Distance,
m
Distance,
n
Reaction R
3
on A(N) Reaction R
4
on B(N)
(mm) (mm) Experiment Calculation Experiment Calculation
125 875 24 1.21 31 2.48
250 750 25 1.33 30 1.67
375 625 27 1.50 28 1.50
Table 2
For point load, M
3
,
Distance, y (mm) Reaction R
5
on
B(N)
Reaction R
6
on
B(N)
M
3
(N)
CALCULATION
F = m x g
Where, F = force created
m = weight of object
g = gravitation force (10ms (
Moment for force on certain point was equal to the total of objects weight multiple with the
distance of the object.
M = Force x Distance
300 2.0 N 0.5 N 2.5 N
Where, M = moment
f. EXAMPLE OF CALCULATION
Table 1
X M
A B
R
1
R
1
1050mm
For one point load, M
1
= 1 KG
Taking moment about B
Clockwise moment = anticlockwise moment
Therefore,
R x 1050 = 1 x 675 Resolving vertically,
R
1
= 675 / 1050 force up = force down
R
1
= 0.64 N R
1
+ R
2
=
1
3.21 + R
2
= 1
R
2
= 1-0.64
R
2
= 0.36 N
Table 2
n
m M
2
M
1
B
A
R
3
R
4
1050 mm
For two point load, M
1
= 1 kg , M
2
= 2 kg
Taking moment about B,
Clockwise = anticlockwise
Therefore,
R
3
x 1050 mm = (1x925) + (2x175)
R
3
= 1275/ 1050
R
3
= 1.21 N
Resolving vertically,
Force up = force down
R
3
+ R
4
= 3
R
4
= 3/1.21
R
4
=2.48N
Taking moment about B
Clockwise = anticlockwise
Therefore,
R
3x
x1050 = 1(800) + 2 (300)
R
3
= 1400/1050
R
3
= 1.33 N
Resolving vertically,
Force up = force down ,
R
3
+ R
4
= 3
1.33 + R
4
= 3
R
4
=1.67N
Taking moment about B, Resolving vertically,
Clockwise = anticlockwise Force up = force down
Therefore,
R
3
+ R
4
= 3
R
3
(1050) = 1 (675) + 2 (452)
R 3= 1.50 N R
4
= 1.50 N
TABLE 3
Taking moment about B Force up = force down
Therefore , clockwise=anticlockwise
R
5
= 2.0 N R
5
+ R
6
= M
3
R
6
= 0.5 N 2.0 + 0.5= 2.5 N
g. DISCUSSION
Explain the reasons of occurring errors and give your conclusion.
In conducting experiment a person encounters one or more errors, systematics error and
random error. In accuracy occurs in the reading due to :
- The imbalance of the equalizer spring.
- Environmental factors such as wind and vibration.
- The flaw of the apparatus.
- Human error (parallax error) when set up experiment misread an instrument or
mistake in calculation.
Facts that causes the error of experiments conclusion.
In accuracy in the experiment can be reduces by taking several precautions method including
:
Taking several readings and taking and average as the final result
Reading and eye level must be perpendicular to reduce parallax error.
The experiment should be done in secure and closed environment to reduce error
caused by the environment surrounding.
h. CONCLUSION
- Beam is equilibrium condition when total force is equal.
- Uncertainly in result can be avoid by taking more than one readings and calculate
the average reading and replace the old apparatus to new one.
You might also like
- Ashrae 15-2022 (Packaged Standard 34-2022)Document5 pagesAshrae 15-2022 (Packaged Standard 34-2022)rpercorNo ratings yet
- Airline Cabin Crew Training IATA Training Course PDFDocument3 pagesAirline Cabin Crew Training IATA Training Course PDFwin computer0% (1)
- CPL Flight Planning ManualDocument94 pagesCPL Flight Planning ManualChina LalaukhadkaNo ratings yet
- Bld323 Tutorial KitDocument14 pagesBld323 Tutorial KitSäbrinä Shukrì100% (1)
- BWT Septron Line 31-61 Rev01!08!05-18 Opm enDocument56 pagesBWT Septron Line 31-61 Rev01!08!05-18 Opm enDavide Grioni100% (1)
- 8 Compound BendingDocument15 pages8 Compound BendingMohammed AltamimiNo ratings yet
- Moments Solutions 4.3aDocument5 pagesMoments Solutions 4.3aHo Lam, Trish LauNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Scalars and VectorsDocument4 pagesModule 1: Scalars and VectorsLaarni Faye SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/04Document26 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/04sinting lim100% (1)
- Module 4 B KineticsDocument42 pagesModule 4 B KineticsKazi Afroz AlamNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper. Prof SolapureDocument3 pagesSample Question Paper. Prof Solapure20CSE1027 Rohan BorseNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2007 SolutionsDocument18 pagesAIEEE 2007 Solutionsapi-19826463No ratings yet
- Phys Grand TestDocument21 pagesPhys Grand TestYogesh BansalNo ratings yet
- 1 Mathematical ToolsDocument41 pages1 Mathematical ToolsHARSHIT GARGNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2007 SolutionsDocument18 pagesAIEEE 2007 SolutionsAditya RamNo ratings yet
- 24 June 2022 Shift I PhysicsDocument6 pages24 June 2022 Shift I PhysicsArav IyerNo ratings yet
- Physics 111 Homework Solution #10Document15 pagesPhysics 111 Homework Solution #10sohail parachaNo ratings yet
- 5 Magnetisms and MatterDocument6 pages5 Magnetisms and MatterSharmaNo ratings yet
- CM Homework 3Document5 pagesCM Homework 3mazhariNo ratings yet
- Ts 3 SolnDocument6 pagesTs 3 SolnKelloggNo ratings yet
- Solution 1366606Document6 pagesSolution 1366606dodo.thetruelegionNo ratings yet
- IntegrationDocument40 pagesIntegrationprateeksuperboy05No ratings yet
- Lecture17 PDFDocument15 pagesLecture17 PDFjayson_09876No ratings yet
- Recit 09 Answers PDFDocument4 pagesRecit 09 Answers PDFMMNo ratings yet
- Handout 15Document26 pagesHandout 15Kudzai MashayaNo ratings yet
- Physics 213-Problem Set 10-Solutions Fall 1997: 1. Reading AssignmentDocument4 pagesPhysics 213-Problem Set 10-Solutions Fall 1997: 1. Reading AssignmentNicolás KozakNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) Motion Vectors: Physics S.ThihaDocument20 pagesChapter (2) Motion Vectors: Physics S.ThihaHan Wai Yan KyawNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Kinetics of Particles), Version 1 Student NameDocument2 pagesAssignment (Kinetics of Particles), Version 1 Student NameFarrina Aziz0% (1)
- Curved Beam Analysis With Energy MethodsDocument10 pagesCurved Beam Analysis With Energy MethodsJohn AlexiouNo ratings yet
- Oscillations Tut - Sol 2022 Q1-3Document24 pagesOscillations Tut - Sol 2022 Q1-3havertz291aNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion NotesDocument7 pagesCircular Motion Notesrifu91No ratings yet
- Sight Distance For Horizontal CurvesDocument89 pagesSight Distance For Horizontal CurvesFirdaus MangawingNo ratings yet
- Problem 3-11 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem 3-11 PDFHarishNo ratings yet
- Solution & Answer For Aieee-2008 Version - A1: (Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics)Document16 pagesSolution & Answer For Aieee-2008 Version - A1: (Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics)rknair92No ratings yet
- Activity 2.1.4 Calculating Force Vectors Answer Key: 5 sin 30 right 2.5 = = װDocument4 pagesActivity 2.1.4 Calculating Force Vectors Answer Key: 5 sin 30 right 2.5 = = װQuentin Andr (CoC)33% (6)
- Dynamics Word ProbDocument7 pagesDynamics Word ProbKelly SisonNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics: By-Miss Rutticka Kedare (New India School Jr. College, Kothrud)Document20 pagesRotational Dynamics: By-Miss Rutticka Kedare (New India School Jr. College, Kothrud)Sangamesh UpsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Azura AhmadNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN 2020 Solved Papers (Crackjee - Xyz) PDFDocument273 pagesJEE MAIN 2020 Solved Papers (Crackjee - Xyz) PDFSavitri Bhandari100% (1)
- Bead and Ring ProblemDocument4 pagesBead and Ring ProblemsayanNo ratings yet
- PHS 105 - B 2cjupj1Document10 pagesPHS 105 - B 2cjupj1olajummy675No ratings yet
- Physics Notes MotionDocument17 pagesPhysics Notes MotionDwomoh Richard AddoNo ratings yet
- 2021 DSE Phy Mock Marking SchemeDocument45 pages2021 DSE Phy Mock Marking SchemeDavid LouNo ratings yet
- Scattering TheoryDocument21 pagesScattering Theorymukesh chawlaNo ratings yet
- Percubaan Negeri Melaka 2020 (K2)Document7 pagesPercubaan Negeri Melaka 2020 (K2)FATIN FARHANAH BINTI HALIDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper2 Quest With SolDocument27 pagesPhysics Paper2 Quest With SolAkanksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Steel Making: Prof. Dr. Mohamed Ahmed Taha Lecture No.06Document20 pagesModern Steel Making: Prof. Dr. Mohamed Ahmed Taha Lecture No.06Jojo HanyNo ratings yet
- Fiz138 w11-ch11Document16 pagesFiz138 w11-ch11mustafadershesabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes PPT 4 PDFDocument17 pagesLecture Notes PPT 4 PDFDrRoja A RNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Angular MomentumDocument5 pagesConservation of Angular MomentumSamir GjoçajNo ratings yet
- N 0 T 0 M I M and Iare Taken With Respect To A CentroidalDocument6 pagesN 0 T 0 M I M and Iare Taken With Respect To A CentroidalRetro GamerNo ratings yet
- Materi Kamis 28 April 2021: Mekanika TeknikDocument27 pagesMateri Kamis 28 April 2021: Mekanika TeknikThoriq SyifaNo ratings yet
- Candidacy Exam Problems With SolutionsDocument6 pagesCandidacy Exam Problems With SolutionsMonica RicoNo ratings yet
- 6 Circular Motion SDocument18 pages6 Circular Motion Sshreyashdarokar89No ratings yet
- Exerciselist6 Eja2022 Physics SolutionsDocument3 pagesExerciselist6 Eja2022 Physics SolutionsfelicioNo ratings yet
- Circ SolnDocument12 pagesCirc SolnAnkit JhaNo ratings yet
- Ai TS 2 (XII) - Q.Paper & SolDocument22 pagesAi TS 2 (XII) - Q.Paper & Solreddit100% (1)
- Devendra K Misra Radio Frequency and Microwave Communication Circuits PDFDocument8 pagesDevendra K Misra Radio Frequency and Microwave Communication Circuits PDFعلي عبدالحسن غضبانNo ratings yet
- This Exam Is Formed of Four Obligatory Exercises in Two Pages Non Programmable Calculators Are AllowedDocument3 pagesThis Exam Is Formed of Four Obligatory Exercises in Two Pages Non Programmable Calculators Are AllowedMJ TarhiniNo ratings yet
- Dispersive Power of PrismDocument6 pagesDispersive Power of PrismGanesh AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- DYNAMICSDocument42 pagesDYNAMICSKazi Afroz AlamNo ratings yet
- Physics RulesDocument17 pagesPhysics Rulesahussein910No ratings yet
- The Many Faces of Gauss-Bonnet TheoremDocument12 pagesThe Many Faces of Gauss-Bonnet TheoremFabian Correa QuinchiaNo ratings yet
- Lect 4 REG 371 2016Document73 pagesLect 4 REG 371 2016Säbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Apprentice VIP Tutor FormDocument3 pagesApprentice VIP Tutor FormSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Intro To IBSDocument41 pagesLecture 3 - Intro To IBSSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Ch01 SolutionsSADocument13 pagesCh01 SolutionsSASäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Donghoon 02 FormworkDocument9 pagesDonghoon 02 FormworkSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Pusat Pengajian Perumahan, Bangunan & Perancangan Jadual Waktu Semester I, Sidang Akademik 2015/2016Document2 pagesPusat Pengajian Perumahan, Bangunan & Perancangan Jadual Waktu Semester I, Sidang Akademik 2015/2016Säbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Tilting Process PanelDocument225 pagesTilting Process PanelSäbrinä Shukrì100% (1)
- Annex I: Methodology For Estimation of Travel TimesDocument6 pagesAnnex I: Methodology For Estimation of Travel TimesSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: Compute The Bearing For LINES BC, CD, DE, and EADocument1 pageAssignment # 3: Compute The Bearing For LINES BC, CD, DE, and EASäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Iphone 6 S (16 GB) : Model Price (Malaysia)Document2 pagesIphone 6 S (16 GB) : Model Price (Malaysia)Säbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Abeysinghe, Chanaka M. Thambiratnam, David P. Perera, Nimal JDocument30 pagesAbeysinghe, Chanaka M. Thambiratnam, David P. Perera, Nimal JSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Design of Lightweight Web Core Sandwich Panels and Application To Residential RoofsDocument30 pagesDesign of Lightweight Web Core Sandwich Panels and Application To Residential RoofsSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Kkibs Brochure - UnlockedDocument20 pagesKkibs Brochure - UnlockedSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: University QP / QBDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank: University QP / QBSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- AssignemDocument1 pageAssignemSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Name: Siti Sabreena Haji Shukri MATRIC: 114787Document1 pageName: Siti Sabreena Haji Shukri MATRIC: 114787Säbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- Outline For Iop5Document1 pageOutline For Iop5Säbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- The Problem: Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDocument94 pagesThe Problem: Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurSäbrinä ShukrìNo ratings yet
- BQ Ibs GroupDocument14 pagesBQ Ibs GroupSäbrinä Shukrì100% (1)
- Audit Non Conformance ReportDocument4 pagesAudit Non Conformance Reportbudi_alamsyah100% (2)
- Introductions To Valuation Methods and Requirements 1672683839Document51 pagesIntroductions To Valuation Methods and Requirements 1672683839v7qksq5bzg100% (1)
- Sep2 Meterview: Energy Measurement and ManagementDocument2 pagesSep2 Meterview: Energy Measurement and ManagementAdil HameedNo ratings yet
- LRS Trading StrategyDocument24 pagesLRS Trading Strategybharatbaba363No ratings yet
- Surya Resume PDFDocument1 pageSurya Resume PDFBEST MOVIES DHAMAKANo ratings yet
- Needle Metal Contamination Control SOP 2Document16 pagesNeedle Metal Contamination Control SOP 2vikkas vermaNo ratings yet
- The Life Eternal Trust Pune: (A Sahaja Yoga Trust Formed by Her Holiness Shree Nirmala Devi)Document20 pagesThe Life Eternal Trust Pune: (A Sahaja Yoga Trust Formed by Her Holiness Shree Nirmala Devi)Shrikant WarkhedkarNo ratings yet
- Transmission - 700R4 General InfoDocument1 pageTransmission - 700R4 General Infotambache69No ratings yet
- IS 15394.2003 Fire Safety in Petroleum RefineriesDocument16 pagesIS 15394.2003 Fire Safety in Petroleum RefineriesnpwalNo ratings yet
- '21 Kona Bicycles Owner's Manual PDFDocument46 pages'21 Kona Bicycles Owner's Manual PDFInsight PeruNo ratings yet
- I) Height of Retaining Wall H: Preliminary DataDocument10 pagesI) Height of Retaining Wall H: Preliminary DataOmPrakashNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Pain ManagementDocument51 pagesWeek 2 Pain Managementعزالدين الطيارNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Presence of Insecticides & Pesticides in FDocument8 pagesChemistry Project On Presence of Insecticides & Pesticides in FShaila BhandaryNo ratings yet
- Projeto Caixa Acustica X-PRO-15Document2 pagesProjeto Caixa Acustica X-PRO-15Denílson SouzaNo ratings yet
- Lamp Ba t302Document16 pagesLamp Ba t302Yeni EkaNo ratings yet
- M1 Activity 1 Plenary GROUP2 BSN3BDocument24 pagesM1 Activity 1 Plenary GROUP2 BSN3BKobe Bryan GermoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects Fluor Albus of Female and Treatment: Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesClinical Aspects Fluor Albus of Female and Treatment: Literature ReviewDafit VdayNo ratings yet
- Website Designing Company in DallasDocument6 pagesWebsite Designing Company in DallasRyan WilsonNo ratings yet
- 5013Document3 pages5013glennfreyolaNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis Capd-1Document15 pagesPeritonitis Capd-1David SenNo ratings yet
- G.O. (MS) No. 92Document10 pagesG.O. (MS) No. 92PAPD NAMAKKALNo ratings yet
- Feedback XI G PRA MID-TERM EP 2Document8 pagesFeedback XI G PRA MID-TERM EP 2Syifa KamilaNo ratings yet
- Himalayan Group of Professional Institutions Kala Amb, Sirmaur, H.PDocument16 pagesHimalayan Group of Professional Institutions Kala Amb, Sirmaur, H.PSanjeevKumarNo ratings yet
- HexWeb HRH10 DataSheet EuDocument6 pagesHexWeb HRH10 DataSheet EuMatijaNo ratings yet
- Facts On Why Homework Is Bad For YouDocument7 pagesFacts On Why Homework Is Bad For Youafmsxohtq100% (1)
- Tepid-Sponge-Bath PRSDocument4 pagesTepid-Sponge-Bath PRSmaryNo ratings yet