Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nodal and Mesh Analysis: Galgotias University
Nodal and Mesh Analysis: Galgotias University
Uploaded by
Agnivesh SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Exhibit 5A - Search Fund Formation - Initial LLC Operating AgreementDocument5 pagesExhibit 5A - Search Fund Formation - Initial LLC Operating AgreementLiorNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualDocument86 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualKenneth Vogt100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Mesh & Nodal Full SolutionsDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Mesh & Nodal Full SolutionsLeszekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Homework SolutionDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Homework SolutionözlemArtuk100% (5)
- Circuit Theory Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2008Document28 pagesCircuit Theory Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2008Muhammad Umair100% (3)
- Lesson 6 Nodal AnalysisDocument22 pagesLesson 6 Nodal AnalysisjunaidalighouriNo ratings yet
- Chap 3.1Document27 pagesChap 3.1Muhd RzwanNo ratings yet
- L-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document11 pagesL-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)nvnmnitNo ratings yet
- Node-Voltage Analysis of Resistive Circuit in The Context of DC Voltages and CurrentsDocument10 pagesNode-Voltage Analysis of Resistive Circuit in The Context of DC Voltages and Currentsanand agarwalNo ratings yet
- DC-Lab Report 05Document9 pagesDC-Lab Report 05Shahriar Ahsan JohaNo ratings yet
- Nodal AnalysisDocument25 pagesNodal AnalysisFreezing FlamesNo ratings yet
- DC CIRCUITS - Methods of AnalysisDocument22 pagesDC CIRCUITS - Methods of AnalysisLuthfan TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- Nodal AnalysisDocument33 pagesNodal AnalysisJamiza shenningNo ratings yet
- Softlab 1Document9 pagesSoftlab 1Mission DeyNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis: Branch Node Loop Mesh Short CircuitDocument13 pagesNetwork Analysis: Branch Node Loop Mesh Short CircuitMathew ClewlowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic Laws: Ohm'S LawDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - Basic Laws: Ohm'S LawDenver Gabitan0% (1)
- Solutions of Homework Problems HardDocument21 pagesSolutions of Homework Problems HardJagadeesh Kumar TentuNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three TutorialsDocument13 pagesChapter Three TutorialsSaif HassanNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 - Circuit AnalysisDocument22 pagesChap 2 - Circuit AnalysisYang Yew RenNo ratings yet
- E104 - Superposition Theorem and LinearityDocument19 pagesE104 - Superposition Theorem and LinearityRick AlvientoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nodal and Mesh Equations - Circuit Theorems 3.14 ExercisesDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Nodal and Mesh Equations - Circuit Theorems 3.14 ExercisesRitchie Quinto DE TorresNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory For ECEDocument14 pagesCircuit Theory For ECESIVARAJAN SANKARAPANDIANNo ratings yet
- Nodal & Loop AnalysisDocument28 pagesNodal & Loop AnalysisSohail NaveedNo ratings yet
- Mesh Nodal Analysis 1Document20 pagesMesh Nodal Analysis 1subasriramiahNo ratings yet
- EE 201 - HW 1 Solutions W2007Document11 pagesEE 201 - HW 1 Solutions W2007mrm3zaNo ratings yet
- BENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaDocument39 pagesBENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaWan MamatkNo ratings yet
- Lec2 BranchCurrentDocument71 pagesLec2 BranchCurrentKuro ShiroNo ratings yet
- EECE210 Spring2021 Chap+4Document55 pagesEECE210 Spring2021 Chap+4starboyNo ratings yet
- Review For Exam #1: DCGN 381: Introduction To Electrical Circuits, Electronics, and PowerDocument6 pagesReview For Exam #1: DCGN 381: Introduction To Electrical Circuits, Electronics, and PowerNeha GuptaNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument33 pagesDiodesReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Lecture Voltage DividerDocument37 pagesLecture Voltage DividerGaurav SinghalNo ratings yet
- Theory: To Familiarize Students With The Pspice Circuit Simulation Tool and Be Able ToDocument4 pagesTheory: To Familiarize Students With The Pspice Circuit Simulation Tool and Be Able Toعصير نفيشNo ratings yet
- Module I Lecture 3Document19 pagesModule I Lecture 3Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument181 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringPrakash Chandran CNo ratings yet
- Circuits and ElektroniksDocument415 pagesCircuits and ElektroniksjftheoretNo ratings yet
- Power Flow Analysis PDFDocument33 pagesPower Flow Analysis PDFAwal SaktiNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 04 Thevenin B WDocument7 pagesElec1111 04 Thevenin B WuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- First LE: Mar 6 12-2PMDocument22 pagesFirst LE: Mar 6 12-2PMByron BanzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 SolutionsDocument102 pagesChapter - 5 SolutionsForrest LingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 DiodesDocument52 pagesLecture 1 DiodesfaradeyisaheroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Operational AmplifierDocument0 pagesChapter 5 - Operational AmplifierManiranjan RoutNo ratings yet
- ECE4762007 Lect12Document42 pagesECE4762007 Lect12Salvador JovenNo ratings yet
- NodalDocument21 pagesNodalStrife Ci-ZeusNo ratings yet
- M1L2 DC Network TheoremsDocument57 pagesM1L2 DC Network TheoremsChandan Pandey super cricket gamesNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 1 To Study Superposition TheoremDocument4 pagesExperiment: 1 To Study Superposition TheoremhetalsolankiNo ratings yet
- Mosfet DC AnalysisDocument13 pagesMosfet DC AnalysiswaqarNo ratings yet
- M1L2 DC Network TheoremsDocument64 pagesM1L2 DC Network TheoremsUDhayNo ratings yet
- Kirchoffs Law With Cramers RuleDocument14 pagesKirchoffs Law With Cramers RuleRoy BernardNo ratings yet
- Eeen Lab 6 FinalDocument16 pagesEeen Lab 6 FinalTSHEGOFATSO GOTSILENGNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Movia Metro DelhiDocument4 pagesMovia Metro DelhiAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ajay Kumar New CV FormatDocument2 pagesAjay Kumar New CV FormatAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Contact SellerDocument1 pageContact SellerAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Warning ReportDocument5 pagesWarning ReportAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sr. MIS Executive - Fix Sat Sun - Off - Pune Male Candidates OnlyDocument2 pagesSr. MIS Executive - Fix Sat Sun - Off - Pune Male Candidates OnlyAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Taufiq Iqbal ShaikhDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Taufiq Iqbal ShaikhAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- New CCIM Third Year Syllabus BAMS 281014Document25 pagesNew CCIM Third Year Syllabus BAMS 281014Agnivesh Sharma100% (1)
- Data Entry Operator JobDocument7 pagesData Entry Operator JobAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Report MarketDocument8 pagesReport MarketAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Guideliines For Round 1Document9 pagesGuideliines For Round 1Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25Document3 pagesLecture 25Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Galgotias University: Laboratory ManualDocument52 pagesGalgotias University: Laboratory ManualAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Summer TRG 2015 Final BHELDocument2 pagesSummer TRG 2015 Final BHELAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Galgotias University: Course Topics: (Syllabus)Document1 pageGalgotias University: Course Topics: (Syllabus)Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Please Affix Recent Passport Size Photo (Colour)Document1 pagePlease Affix Recent Passport Size Photo (Colour)Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- BIM 2015-16 Recorded NotesDocument19 pagesBIM 2015-16 Recorded NotesAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Drilling Boring Reaming and TappingDocument24 pagesDrilling Boring Reaming and TappingAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Logical Reasoning SetsDocument4 pagesLogical Reasoning SetsJason WestNo ratings yet
- Binary Logic QuestionsDocument3 pagesBinary Logic QuestionsAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Indexing MachineDocument6 pagesIndexing MachineAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4-Iii Me-Mee214-FmpDocument5 pages4-Iii Me-Mee214-FmpAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tapping and ThreadingDocument15 pagesTapping and Threadingsomapala88100% (2)
- Cutting FluidsDocument3 pagesCutting FluidsAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chip Thickness RatioDocument2 pagesChip Thickness RatioAgnivesh Sharma67% (3)
- Factors Affecting Tool LifeDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Tool LifeAgnivesh Sharma75% (4)
- Shaper PlanerDocument1 pageShaper PlanerAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fuels Liq Manufacture of Metallurgical Coke: Beehive Oven Otto Hoffmann OvenDocument51 pagesFuels Liq Manufacture of Metallurgical Coke: Beehive Oven Otto Hoffmann OvenAgnivesh Sharma0% (3)
- UserManual X7Document14 pagesUserManual X7wagneraguiarNo ratings yet
- Practice Manager Job Description - Oct 2019Document3 pagesPractice Manager Job Description - Oct 2019M LubisNo ratings yet
- Brittany Lossow CVDocument3 pagesBrittany Lossow CVapi-449997488No ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals For The Tenth CircuitDocument11 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals For The Tenth Circuitdillon-richardsNo ratings yet
- WaterGEMS For ArcMap Sesion1Document38 pagesWaterGEMS For ArcMap Sesion1franklin2891100% (1)
- Tought Leadership - Ridwan KamilDocument19 pagesTought Leadership - Ridwan KamilKevin McleanNo ratings yet
- Indistractable - How To Control Your Attention and Choose Your Life - Z-LibraryDocument5 pagesIndistractable - How To Control Your Attention and Choose Your Life - Z-LibraryAmjada YasminNo ratings yet
- Lab#3A: Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterDocument6 pagesLab#3A: Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterSadil BatafNo ratings yet
- Ariens Sno Thro 924 Series Snow Blower Parts ManualDocument28 pagesAriens Sno Thro 924 Series Snow Blower Parts ManualBradCommander409100% (1)
- Maria Mikhaylova PDFDocument6 pagesMaria Mikhaylova PDFPaolo FurlanNo ratings yet
- Serra VS CaDocument4 pagesSerra VS CaLeonardo LawasNo ratings yet
- Application For Probation - RA 9262Document2 pagesApplication For Probation - RA 9262Boom ManuelNo ratings yet
- Emi Stories 476-570 PDFDocument53 pagesEmi Stories 476-570 PDFRishabh BuddhdevNo ratings yet
- Easily Process Your Prints From 135 Film With The SP500Document2 pagesEasily Process Your Prints From 135 Film With The SP500Bosko HerorNo ratings yet
- Safety Induction Format: Job Procedure No: Project HDD & Associated Works For Chandragiri River For KKBMPL, Phase-IIDocument2 pagesSafety Induction Format: Job Procedure No: Project HDD & Associated Works For Chandragiri River For KKBMPL, Phase-IIIsrael Raja AbhilashNo ratings yet
- Application Form 2020Document7 pagesApplication Form 2020sop kakiNo ratings yet
- Garcia Vs Executive SecretaryDocument5 pagesGarcia Vs Executive SecretaryRachelle DomingoNo ratings yet
- Trance 1.5 LTD 2017 ENGDocument1 pageTrance 1.5 LTD 2017 ENGbmirjan2529No ratings yet
- Tea in SLDocument6 pagesTea in SLManaf RazackNo ratings yet
- Gelatin - Black Particle - Tuppguide2015-1539615522Document11 pagesGelatin - Black Particle - Tuppguide2015-1539615522GaneshNo ratings yet
- Email Apology SolutionDocument5 pagesEmail Apology SolutionlinhntmNo ratings yet
- JeffFurman Resume18Document3 pagesJeffFurman Resume18Prashant PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Handover - DE-CIX - 2022 04 15 - Professional Service - LD019348 - Rev PDFDocument8 pagesHandover - DE-CIX - 2022 04 15 - Professional Service - LD019348 - Rev PDFFitra NandesNo ratings yet
- Workplace Safety and Labour Rights in Bangladesh An Analysis of Laws Regarding RMG Sector PDFDocument24 pagesWorkplace Safety and Labour Rights in Bangladesh An Analysis of Laws Regarding RMG Sector PDFA FCNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Application Letter Kelas XiiDocument3 pagesLatihan Soal Application Letter Kelas XiinilassupriyantiNo ratings yet
- Ac Auxiliary Power Supply Scheme 125aDocument13 pagesAc Auxiliary Power Supply Scheme 125aAbhishek RajputNo ratings yet
- RSPDocument24 pagesRSPMassrNo ratings yet
- PROMASEAL-A Spray - PB - EngDocument8 pagesPROMASEAL-A Spray - PB - EngTony StarkNo ratings yet
- Skippers United Pacific Vs Doza DIGESTDocument2 pagesSkippers United Pacific Vs Doza DIGESTHarold ApostolNo ratings yet
Nodal and Mesh Analysis: Galgotias University
Nodal and Mesh Analysis: Galgotias University
Uploaded by
Agnivesh SharmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nodal and Mesh Analysis: Galgotias University
Nodal and Mesh Analysis: Galgotias University
Uploaded by
Agnivesh SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
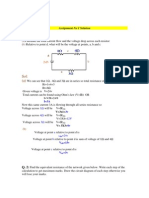
NODAL AND MESH ANALYSIS
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: The Concept.
Every circuit has n nodes with one of the nodes being
designated as a reference node.
We designate the remaining n 1 nodes as voltage nodes
and give each node a unique name, v
i
.
At each node we write Kirchhoffs current law in terms
of the node voltages.
1
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: The Concept.
We form n-1 linear equations at the n-1 nodes
in terms of the node voltages.
We solve the n-1 equations for the n-1 node voltages.
From the node voltages we can calculate any branch
current or any voltage across any element.
2
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Concept Illustration:
reference node
v
1
v
2
v
3
R
2
R
1
R
3
R
4
I
- -
Figure 1: Partial circuit used to illustrate nodal analysis.
I
R
V V
R
V
R
V
R
V V
=
+ + +
4
3 1
3
1
1
1
2
2 1
Eq 1
3
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Concept Illustration:
Clearing the previous equation gives,
I V
R
V
R
V
R R R R
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ + +
3
4
2
2
1
4 3 2 1
1 1 1 1 1 1
Eq 2
We would need two additional equations, from the
remaining circuit, in order to solve for V
1
, V
2
, and V
3
4
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 1
Given the following circuit. Set-up the equations
to solve for V
1
and V
2
. Also solve for the voltage V
6
.
R
2 R
3
R
1
R
4
R
5
R
6
I
1
v
1
v
2
+
_
v
6
- -
Figure 2: Circuit for Example 1.
5
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 1, the nodal equations.
R
2 R
3
R
1
R
4
R
5
R
6
I
1
v
1
v
2
+
_
v
6
- -
0
6 5
2
4
2
3
1 2
1
3
2 1
2 1
1
=
+
+ +
+
+
R R
V
R
V
R
V V
I
R
V V
R R
V
Eq 3
Eq 4
6
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 1: Set up for solution.
0
6 5
2
4
2
3
1 2
1
3
2 1
2 1
1
=
+
+ +
+
+
R R
V
R
V
R
V V
I
R
V V
R R
V
0
1 1 1 1
1 1 1
2
6 5 4 3
1
3
1 2
3
1
3 2 1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+ + +
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
V
R R R R
V
R
I V
R
V
R R R
Eq 3
Eq 4
Eq 5
Eq 6
7
Galgotias University
Nodal Analysis: Example 2, using circuit values.
v
1
v
2
10 O
5 O
20 O
4 A
2 A
- -
Figure 3: Circuit for
Example 2.
Find V
1
and V
2.
At v
1
:
2
5 10
2 1 1
=
+
V V V
At v
2
:
6
20 5
2 1 2
= +
V V V
Eq 7
Eq 8
Basic Circuits
8
Galgotias University
Nodal Analysis: Example 2: Clearing Equations;
From Eq 6.7:
V
1
+ 2V
1
2V
2
= 20
or
3V
1
2V
2
= 20
From Eq 6.8:
4V
2
4V
1
+ V
2
= -120
or
-4V
1
+ 5V
2
= -120
Eq 9
Eq 10
Solution: V
1
= -20 V, V
2
= -40 V
Basic Circuits
9
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 3: With voltage source.
R
1
R
3
I
v
2
v
1
+
_
R
2
R
4
E
Figure 4: Circuit for
Example 3.
At V
1
:
I
R
V V
R
V
R
E V
=
+ +
3
2 1
2
1
1
1
At V
2
:
I
R
V V
R
V
=
+
3
1
2
4
2
Eq 11
Eq 12
10
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 3: Continued.
Collecting terms in Equations (11) and (12) gives
1
2
3
1
1
3
1
2
1
1
1
R
E
I V
R
V
R R R
+ =
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
I
V
R R
V
R
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
4
1
3
1
1
2
1
Eq 13
Eq 14
11
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 4: Numerical example with voltage
source.
v
2
v
1
6 O
4 O
10 O
5 A
+
_
10 V
- -
Figure 5: Circuit for Example 4.
What do we do first?
12
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 4: Continued
v
2
v
1
6 O
4 O
10 O
5 A
+
_
10 V
- -
At v
1
:
5
4
2
10
1
10
1
=
+
+
V V V
At v
2
:
0
4
1
10
2
6
2
=
+
V V V
Eq 15
Eq 16
13
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 4: Continued
Clearing Eq 6.15
4V
1
+ 10V
1
+ 100 10V
2
= -200
or
14V
1
10V
2
= -300
Clearing Eq 6.16
4V
2
+ 6V
2
60 6V
1
= 0
or
-6V
1
+ 10V
2
= 60
Eq 17
Eq 18
V
1
= -30 V, V
2
= -12 V, I
1
= -2 A
14
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 5: Voltage super node.
Given the following circuit. Solve for the indicated nodal voltages.
+
_
6 A
5 O
4 O
2 O
10 O
v
1
v
2
v
3
10 V
x
x
x
x
Figure 6: Circuit for Example 5.
When a voltage source appears between two nodes, an easy way to
handle this is to form a super node. The super node encircles the
voltage source and the tips of the branches connected to the nodes.
super node
15
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 5: Continued.
+
_
6 A
5 O
4 O
2 O
10 O
v
1
v
2
v
3
10 V
At V
1
6
2
3 1
5
2 1
=
+
V V V V
At super
node
0
2
1 3
10
3
4
2
5
1 2
=
+ + +
V V V V V V
Constraint Equation
V
2
V
3
= -10 Eq 19
Eq 20
Eq 21
16
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 5: Continued.
Clearing Eq 19, 20, and 21:
7V
1
2V
2
5V
3
= 60
-14V
1
+ 9V
2
+ 12V
3
= 0
V
2
V
3
= -10
Eq 22
Eq 23
Eq 24
Solving gives:
V
1
= 30 V, V
2
= 14.29 V, V
3
= 24.29 V
17
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 6: With Dependent Sources.
Consider the circuit below. We desire to solve for the node voltages
V
1
and V
2
.
10 O
2 O
4 O
5 O
2 A
+
_
10 V
5V
x
- -
v
1 v
2
V
x
+
_
Figure 6: Circuit for
Example 6.
In this case we have a dependent source, 5V
x
, that must be reckoned
with. Actually, there is a constraint equation of
0
1 2
= V V V
x
Eq 25
18
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 6: With Dependent Sources.
10 O
2 O
4 O
5 O
2 A
+
_
10 V
5V
x
- -
v
1 v
2
V
x
+
_
At node V
1
2
2 5 10
10
2 1 1 1
=
+ +
V V V V
At node V
2
2
4
5
2
2 1 2
=
x
V V V V
The constraint equation:
2 1
V V V
x
=
19
Galgotias University
Basic Circuits
Nodal Analysis: Example 6: With Dependent Sources.
Clearing the previous equations and substituting
the constraint V
X
= V
1
- V
2
gives,
8 8 7
30 5 8
2 1
2 1
= +
=
V V
V V
Eq 26
Eq 27
which yields,
V V V V 03 . 5 , 9 . 6
2 1
= =
20
Galgotias University
You might also like
- Exhibit 5A - Search Fund Formation - Initial LLC Operating AgreementDocument5 pagesExhibit 5A - Search Fund Formation - Initial LLC Operating AgreementLiorNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualDocument86 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualKenneth Vogt100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Mesh & Nodal Full SolutionsDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Mesh & Nodal Full SolutionsLeszekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Homework SolutionDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Homework SolutionözlemArtuk100% (5)
- Circuit Theory Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2008Document28 pagesCircuit Theory Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2008Muhammad Umair100% (3)
- Lesson 6 Nodal AnalysisDocument22 pagesLesson 6 Nodal AnalysisjunaidalighouriNo ratings yet
- Chap 3.1Document27 pagesChap 3.1Muhd RzwanNo ratings yet
- L-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document11 pagesL-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)nvnmnitNo ratings yet
- Node-Voltage Analysis of Resistive Circuit in The Context of DC Voltages and CurrentsDocument10 pagesNode-Voltage Analysis of Resistive Circuit in The Context of DC Voltages and Currentsanand agarwalNo ratings yet
- DC-Lab Report 05Document9 pagesDC-Lab Report 05Shahriar Ahsan JohaNo ratings yet
- Nodal AnalysisDocument25 pagesNodal AnalysisFreezing FlamesNo ratings yet
- DC CIRCUITS - Methods of AnalysisDocument22 pagesDC CIRCUITS - Methods of AnalysisLuthfan TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- Nodal AnalysisDocument33 pagesNodal AnalysisJamiza shenningNo ratings yet
- Softlab 1Document9 pagesSoftlab 1Mission DeyNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis: Branch Node Loop Mesh Short CircuitDocument13 pagesNetwork Analysis: Branch Node Loop Mesh Short CircuitMathew ClewlowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic Laws: Ohm'S LawDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - Basic Laws: Ohm'S LawDenver Gabitan0% (1)
- Solutions of Homework Problems HardDocument21 pagesSolutions of Homework Problems HardJagadeesh Kumar TentuNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three TutorialsDocument13 pagesChapter Three TutorialsSaif HassanNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 - Circuit AnalysisDocument22 pagesChap 2 - Circuit AnalysisYang Yew RenNo ratings yet
- E104 - Superposition Theorem and LinearityDocument19 pagesE104 - Superposition Theorem and LinearityRick AlvientoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nodal and Mesh Equations - Circuit Theorems 3.14 ExercisesDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Nodal and Mesh Equations - Circuit Theorems 3.14 ExercisesRitchie Quinto DE TorresNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory For ECEDocument14 pagesCircuit Theory For ECESIVARAJAN SANKARAPANDIANNo ratings yet
- Nodal & Loop AnalysisDocument28 pagesNodal & Loop AnalysisSohail NaveedNo ratings yet
- Mesh Nodal Analysis 1Document20 pagesMesh Nodal Analysis 1subasriramiahNo ratings yet
- EE 201 - HW 1 Solutions W2007Document11 pagesEE 201 - HW 1 Solutions W2007mrm3zaNo ratings yet
- BENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaDocument39 pagesBENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaWan MamatkNo ratings yet
- Lec2 BranchCurrentDocument71 pagesLec2 BranchCurrentKuro ShiroNo ratings yet
- EECE210 Spring2021 Chap+4Document55 pagesEECE210 Spring2021 Chap+4starboyNo ratings yet
- Review For Exam #1: DCGN 381: Introduction To Electrical Circuits, Electronics, and PowerDocument6 pagesReview For Exam #1: DCGN 381: Introduction To Electrical Circuits, Electronics, and PowerNeha GuptaNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument33 pagesDiodesReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Lecture Voltage DividerDocument37 pagesLecture Voltage DividerGaurav SinghalNo ratings yet
- Theory: To Familiarize Students With The Pspice Circuit Simulation Tool and Be Able ToDocument4 pagesTheory: To Familiarize Students With The Pspice Circuit Simulation Tool and Be Able Toعصير نفيشNo ratings yet
- Module I Lecture 3Document19 pagesModule I Lecture 3Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument181 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringPrakash Chandran CNo ratings yet
- Circuits and ElektroniksDocument415 pagesCircuits and ElektroniksjftheoretNo ratings yet
- Power Flow Analysis PDFDocument33 pagesPower Flow Analysis PDFAwal SaktiNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 04 Thevenin B WDocument7 pagesElec1111 04 Thevenin B WuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- First LE: Mar 6 12-2PMDocument22 pagesFirst LE: Mar 6 12-2PMByron BanzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 SolutionsDocument102 pagesChapter - 5 SolutionsForrest LingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 DiodesDocument52 pagesLecture 1 DiodesfaradeyisaheroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Operational AmplifierDocument0 pagesChapter 5 - Operational AmplifierManiranjan RoutNo ratings yet
- ECE4762007 Lect12Document42 pagesECE4762007 Lect12Salvador JovenNo ratings yet
- NodalDocument21 pagesNodalStrife Ci-ZeusNo ratings yet
- M1L2 DC Network TheoremsDocument57 pagesM1L2 DC Network TheoremsChandan Pandey super cricket gamesNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 1 To Study Superposition TheoremDocument4 pagesExperiment: 1 To Study Superposition TheoremhetalsolankiNo ratings yet
- Mosfet DC AnalysisDocument13 pagesMosfet DC AnalysiswaqarNo ratings yet
- M1L2 DC Network TheoremsDocument64 pagesM1L2 DC Network TheoremsUDhayNo ratings yet
- Kirchoffs Law With Cramers RuleDocument14 pagesKirchoffs Law With Cramers RuleRoy BernardNo ratings yet
- Eeen Lab 6 FinalDocument16 pagesEeen Lab 6 FinalTSHEGOFATSO GOTSILENGNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Movia Metro DelhiDocument4 pagesMovia Metro DelhiAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ajay Kumar New CV FormatDocument2 pagesAjay Kumar New CV FormatAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Contact SellerDocument1 pageContact SellerAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Warning ReportDocument5 pagesWarning ReportAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sr. MIS Executive - Fix Sat Sun - Off - Pune Male Candidates OnlyDocument2 pagesSr. MIS Executive - Fix Sat Sun - Off - Pune Male Candidates OnlyAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Taufiq Iqbal ShaikhDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Taufiq Iqbal ShaikhAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- New CCIM Third Year Syllabus BAMS 281014Document25 pagesNew CCIM Third Year Syllabus BAMS 281014Agnivesh Sharma100% (1)
- Data Entry Operator JobDocument7 pagesData Entry Operator JobAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Report MarketDocument8 pagesReport MarketAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Guideliines For Round 1Document9 pagesGuideliines For Round 1Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25Document3 pagesLecture 25Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Galgotias University: Laboratory ManualDocument52 pagesGalgotias University: Laboratory ManualAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Summer TRG 2015 Final BHELDocument2 pagesSummer TRG 2015 Final BHELAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Galgotias University: Course Topics: (Syllabus)Document1 pageGalgotias University: Course Topics: (Syllabus)Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Please Affix Recent Passport Size Photo (Colour)Document1 pagePlease Affix Recent Passport Size Photo (Colour)Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- BIM 2015-16 Recorded NotesDocument19 pagesBIM 2015-16 Recorded NotesAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Drilling Boring Reaming and TappingDocument24 pagesDrilling Boring Reaming and TappingAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Logical Reasoning SetsDocument4 pagesLogical Reasoning SetsJason WestNo ratings yet
- Binary Logic QuestionsDocument3 pagesBinary Logic QuestionsAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Indexing MachineDocument6 pagesIndexing MachineAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4-Iii Me-Mee214-FmpDocument5 pages4-Iii Me-Mee214-FmpAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tapping and ThreadingDocument15 pagesTapping and Threadingsomapala88100% (2)
- Cutting FluidsDocument3 pagesCutting FluidsAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chip Thickness RatioDocument2 pagesChip Thickness RatioAgnivesh Sharma67% (3)
- Factors Affecting Tool LifeDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Tool LifeAgnivesh Sharma75% (4)
- Shaper PlanerDocument1 pageShaper PlanerAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fuels Liq Manufacture of Metallurgical Coke: Beehive Oven Otto Hoffmann OvenDocument51 pagesFuels Liq Manufacture of Metallurgical Coke: Beehive Oven Otto Hoffmann OvenAgnivesh Sharma0% (3)
- UserManual X7Document14 pagesUserManual X7wagneraguiarNo ratings yet
- Practice Manager Job Description - Oct 2019Document3 pagesPractice Manager Job Description - Oct 2019M LubisNo ratings yet
- Brittany Lossow CVDocument3 pagesBrittany Lossow CVapi-449997488No ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals For The Tenth CircuitDocument11 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals For The Tenth Circuitdillon-richardsNo ratings yet
- WaterGEMS For ArcMap Sesion1Document38 pagesWaterGEMS For ArcMap Sesion1franklin2891100% (1)
- Tought Leadership - Ridwan KamilDocument19 pagesTought Leadership - Ridwan KamilKevin McleanNo ratings yet
- Indistractable - How To Control Your Attention and Choose Your Life - Z-LibraryDocument5 pagesIndistractable - How To Control Your Attention and Choose Your Life - Z-LibraryAmjada YasminNo ratings yet
- Lab#3A: Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterDocument6 pagesLab#3A: Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterSadil BatafNo ratings yet
- Ariens Sno Thro 924 Series Snow Blower Parts ManualDocument28 pagesAriens Sno Thro 924 Series Snow Blower Parts ManualBradCommander409100% (1)
- Maria Mikhaylova PDFDocument6 pagesMaria Mikhaylova PDFPaolo FurlanNo ratings yet
- Serra VS CaDocument4 pagesSerra VS CaLeonardo LawasNo ratings yet
- Application For Probation - RA 9262Document2 pagesApplication For Probation - RA 9262Boom ManuelNo ratings yet
- Emi Stories 476-570 PDFDocument53 pagesEmi Stories 476-570 PDFRishabh BuddhdevNo ratings yet
- Easily Process Your Prints From 135 Film With The SP500Document2 pagesEasily Process Your Prints From 135 Film With The SP500Bosko HerorNo ratings yet
- Safety Induction Format: Job Procedure No: Project HDD & Associated Works For Chandragiri River For KKBMPL, Phase-IIDocument2 pagesSafety Induction Format: Job Procedure No: Project HDD & Associated Works For Chandragiri River For KKBMPL, Phase-IIIsrael Raja AbhilashNo ratings yet
- Application Form 2020Document7 pagesApplication Form 2020sop kakiNo ratings yet
- Garcia Vs Executive SecretaryDocument5 pagesGarcia Vs Executive SecretaryRachelle DomingoNo ratings yet
- Trance 1.5 LTD 2017 ENGDocument1 pageTrance 1.5 LTD 2017 ENGbmirjan2529No ratings yet
- Tea in SLDocument6 pagesTea in SLManaf RazackNo ratings yet
- Gelatin - Black Particle - Tuppguide2015-1539615522Document11 pagesGelatin - Black Particle - Tuppguide2015-1539615522GaneshNo ratings yet
- Email Apology SolutionDocument5 pagesEmail Apology SolutionlinhntmNo ratings yet
- JeffFurman Resume18Document3 pagesJeffFurman Resume18Prashant PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Handover - DE-CIX - 2022 04 15 - Professional Service - LD019348 - Rev PDFDocument8 pagesHandover - DE-CIX - 2022 04 15 - Professional Service - LD019348 - Rev PDFFitra NandesNo ratings yet
- Workplace Safety and Labour Rights in Bangladesh An Analysis of Laws Regarding RMG Sector PDFDocument24 pagesWorkplace Safety and Labour Rights in Bangladesh An Analysis of Laws Regarding RMG Sector PDFA FCNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Application Letter Kelas XiiDocument3 pagesLatihan Soal Application Letter Kelas XiinilassupriyantiNo ratings yet
- Ac Auxiliary Power Supply Scheme 125aDocument13 pagesAc Auxiliary Power Supply Scheme 125aAbhishek RajputNo ratings yet
- RSPDocument24 pagesRSPMassrNo ratings yet
- PROMASEAL-A Spray - PB - EngDocument8 pagesPROMASEAL-A Spray - PB - EngTony StarkNo ratings yet
- Skippers United Pacific Vs Doza DIGESTDocument2 pagesSkippers United Pacific Vs Doza DIGESTHarold ApostolNo ratings yet