Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handout 9 NA - For Merge
Handout 9 NA - For Merge
Uploaded by
Muddasar YaminCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 2018 Australian Mathematics Competition AMC Middle Primary Years 3 and 4 - SolutionsDocument8 pages2018 Australian Mathematics Competition AMC Middle Primary Years 3 and 4 - SolutionsJeni100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Total Evaporable Moisture Content of Aggregate by Drying: Standard Test Method ForDocument3 pagesTotal Evaporable Moisture Content of Aggregate by Drying: Standard Test Method ForYarisel Shosha MuñozNo ratings yet
- Difficult Task ForceDocument17 pagesDifficult Task ForceMuddasar Yamin100% (3)
- Handout 8 NADocument3 pagesHandout 8 NAMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Euler's Method: Mohsin Raza/Handout 10 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Document2 pagesEuler's Method: Mohsin Raza/Handout 10 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Muddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Handout 6 NADocument5 pagesHandout 6 NAMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Interpolation and Polynomial Approximation Motivation:: Mohsin Raza/Handout 5 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Document6 pagesInterpolation and Polynomial Approximation Motivation:: Mohsin Raza/Handout 5 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Muddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Handout 4 NADocument10 pagesHandout 4 NAMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 NADocument6 pagesHandout 1 NAMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Handout 3 N.ADocument6 pagesHandout 3 N.AMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Arif PresentationDocument14 pagesArif PresentationMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Equation in One Variable Motivation: Mohsin Raza/Handout 2 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Document4 pagesSolutions of Equation in One Variable Motivation: Mohsin Raza/Handout 2 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Muddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Barani Institute of Information and Technology: Psychology PresentationDocument17 pagesBarani Institute of Information and Technology: Psychology PresentationMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Lab Programs Numerical Analysis: BS (CS) - 6Document81 pagesLab Programs Numerical Analysis: BS (CS) - 6Muddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Need Based Perspectives On MotivationDocument11 pagesNeed Based Perspectives On MotivationMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction: Replica of The Toyota Model AA, The First Production Model of Toyota in 1936Document52 pagesCustomer Satisfaction: Replica of The Toyota Model AA, The First Production Model of Toyota in 1936John100% (3)
- Operating System Proposal ReportDocument3 pagesOperating System Proposal ReportMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
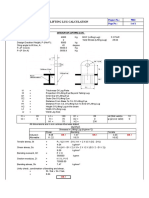
- Third Floor Beam Design CalculationDocument3 pagesThird Floor Beam Design CalculationArnold VercelesNo ratings yet
- M1 June 2009Document7 pagesM1 June 2009markodeanoNo ratings yet
- Akarshan Sood Graduate Marine Engineer Main Engine Bearing: Inserting Type Removable Shell BearingDocument7 pagesAkarshan Sood Graduate Marine Engineer Main Engine Bearing: Inserting Type Removable Shell Bearingakarshansood100% (4)
- Technical Notes: Short Tendon ElongationsDocument4 pagesTechnical Notes: Short Tendon ElongationsUdom RithNo ratings yet
- Determining Visible Abrasion Resistance of Glazed Ceramic TileDocument6 pagesDetermining Visible Abrasion Resistance of Glazed Ceramic TileBetsy WiedenfeldNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Termodinamica - FinalDocument72 pagesEjercicios Termodinamica - FinalGEOVANI ESCAJADILLO LUQUENo ratings yet
- The Alcoholysis Reaction of Isocyanates Giving Urethanes: Evidence For A Multimolecular MechanismDocument8 pagesThe Alcoholysis Reaction of Isocyanates Giving Urethanes: Evidence For A Multimolecular MechanismViviana TorresNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ManualDocument48 pagesPhysics Lab ManualHimanshu UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Aspen HYSYSDocument23 pagesBest Practices For Aspen HYSYSfdddddd100% (2)
- General Pre Stress and ElasticDocument28 pagesGeneral Pre Stress and ElasticJorge Nickolai NavalesNo ratings yet
- ESD Audit Check Sheet r1Document20 pagesESD Audit Check Sheet r1ecpuneetsharma01100% (1)
- Project Heat and Mass TransferDocument14 pagesProject Heat and Mass TransferAreen Emilia Faizlukman Jerry100% (1)
- Erosion Wear Rate in Copper Slurry PipelineDocument13 pagesErosion Wear Rate in Copper Slurry PipelinepankhadingtidingNo ratings yet
- Brochure Mikrocad 3d ScannerDocument2 pagesBrochure Mikrocad 3d ScannerbehipiluwuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7-Induction MotorsDocument1 pageAssignment 7-Induction MotorsAli HarisNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Lab Syeed HasanDocument8 pagesProjectile Motion Lab Syeed Hasanapi-130453141No ratings yet
- Cooling Loads Calculation: Cooling Load Temperature Difference (CLTD) MethodDocument8 pagesCooling Loads Calculation: Cooling Load Temperature Difference (CLTD) MethodChristopher LloydNo ratings yet
- AE Question PDFDocument12 pagesAE Question PDFAkhil SureshNo ratings yet
- LagrangeDocument32 pagesLagrangepuiteraNo ratings yet
- Experimental Analysis of Fin Tube and Bare Tube Type Tube-In-Tube Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesExperimental Analysis of Fin Tube and Bare Tube Type Tube-In-Tube Heat ExchangerMohammed Abdul Hai CHE VI ANo ratings yet
- Praktikum Bab Karakteristik LED Dan Laser DiodeDocument4 pagesPraktikum Bab Karakteristik LED Dan Laser DiodeErvina IkkeNo ratings yet
- Metrologic Colombia S.A.S. Medellín Medellín Colombia: Oferta Economica CO20233Document3 pagesMetrologic Colombia S.A.S. Medellín Medellín Colombia: Oferta Economica CO20233Julian MoraNo ratings yet
- SCIT - SampleTest Pattern For 2015Document8 pagesSCIT - SampleTest Pattern For 2015heeNo ratings yet
- A Dielectric Lens Antenna With Enhanced Aperture Efficiency For Industrial Radar ApplicationsDocument3 pagesA Dielectric Lens Antenna With Enhanced Aperture Efficiency For Industrial Radar ApplicationsacademicosNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three (3) Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesNewton's Three (3) Laws of MotionCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- 11 Math - Test Maker @Document2 pages11 Math - Test Maker @ashfaq4985No ratings yet
- Lifting Lug - Skid - 2018.07.16Document4 pagesLifting Lug - Skid - 2018.07.16RaghNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) Solutionsrsarthak227No ratings yet
Handout 9 NA - For Merge
Handout 9 NA - For Merge
Uploaded by
Muddasar YaminCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handout 9 NA - For Merge
Handout 9 NA - For Merge
Uploaded by
Muddasar YaminCopyright:
Available Formats
Mohsin Raza/Handout 9 -1- Numerical Analysis CS-572
Lecture 15 &16
Initial-Value Problemsfor Ordinary Differential Equations
The motion of a swinging pendulum under certain simplifying assumptions is described by
the second-order differential equation
Well-Posed Problems
Now that we have, to some extent, taken care of the question of when initial-value problems
have unique solutions, we can move to the second important consideration when
approximating the solution to an initial-value problem. Initial-value problems obtained by
observing physical phenomena generally only approximate the true situation, so we need to
know whether small changes in the statement of the problem introduce correspondingly small
changes in the solution. This is also important because of the introduction of round-off error
when numerical methods are used. That is,
Mohsin Raza/Handout 9 -2- Numerical Analysis CS-572
Question: How do we determine whether a particular problem has the property that small
changes, or perturbations, in the statement of the problem introduce correspondingly
small changes in the solution?
The basic method involved in approximating
( )
b
a
f x dx
}
is called numerical quadrature.
let us consider formulas produced by using first and second Lagrange polynomials with
equally-spaced nodes. This gives the Trapezoidal rule and Simpsons rule,
Recall (handout 1 lecture 2)
Theorem 1.13 (Weighted mean value theorem for integrals)
Suppose
| |
, , f C a b e the Riemann integral of g exists on
| |
a , b , and
( )
g x does not
change sign on
| |
, , a b then there exists a number c in
( )
a , b , with
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
b b
a a
f x g x dx f c g x dx =
} }
The Trapezoidal Rule
When we use the term trapezoid we mean a four-sided figure that has at least two of its sides
parallel. The European term for this figure is trapezium. To further confuse the issue, the
European word trapezoidal refers to a four-sided figure with no sides equal, and the
American word for this type of figure is trapezium.
Derivation of Trapezoidal Formula
To derive the Trapezoidal rule for approximating
( )
b
a
f x dx
}
,let
0
, x a =
1
, x b h b a = =
and use the linear Lagrange polynomial:
Mohsin Raza/Handout 9 -3- Numerical Analysis CS-572
Note
The error term for the Trapezoidal rule involves ( )
f x '' , so the rule gives the exact result
when applied to any function whose second derivative is identically zero, that is, any
polynomial of degree one or less.
Mohsin Raza/Handout 9 -4- Numerical Analysis CS-572
Class Task
Compare the Trapezoidal rule and Simpsons rule approximations to
( )
2
0
f x dx
}
when
( )
f x is
Solution
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This lesson is identical to the lecture which is presented in the Class and
this lesson is not intended as a complete set of lecture for the course: there
are many things explained in the lecture that arent in these notes.
Important for the Readers
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 2018 Australian Mathematics Competition AMC Middle Primary Years 3 and 4 - SolutionsDocument8 pages2018 Australian Mathematics Competition AMC Middle Primary Years 3 and 4 - SolutionsJeni100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Total Evaporable Moisture Content of Aggregate by Drying: Standard Test Method ForDocument3 pagesTotal Evaporable Moisture Content of Aggregate by Drying: Standard Test Method ForYarisel Shosha MuñozNo ratings yet
- Difficult Task ForceDocument17 pagesDifficult Task ForceMuddasar Yamin100% (3)
- Handout 8 NADocument3 pagesHandout 8 NAMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Euler's Method: Mohsin Raza/Handout 10 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Document2 pagesEuler's Method: Mohsin Raza/Handout 10 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Muddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Handout 6 NADocument5 pagesHandout 6 NAMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Interpolation and Polynomial Approximation Motivation:: Mohsin Raza/Handout 5 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Document6 pagesInterpolation and Polynomial Approximation Motivation:: Mohsin Raza/Handout 5 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Muddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Handout 4 NADocument10 pagesHandout 4 NAMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 NADocument6 pagesHandout 1 NAMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Handout 3 N.ADocument6 pagesHandout 3 N.AMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Arif PresentationDocument14 pagesArif PresentationMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Equation in One Variable Motivation: Mohsin Raza/Handout 2 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Document4 pagesSolutions of Equation in One Variable Motivation: Mohsin Raza/Handout 2 - 1-Numerical Analysis CS-572Muddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Barani Institute of Information and Technology: Psychology PresentationDocument17 pagesBarani Institute of Information and Technology: Psychology PresentationMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Lab Programs Numerical Analysis: BS (CS) - 6Document81 pagesLab Programs Numerical Analysis: BS (CS) - 6Muddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Need Based Perspectives On MotivationDocument11 pagesNeed Based Perspectives On MotivationMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction: Replica of The Toyota Model AA, The First Production Model of Toyota in 1936Document52 pagesCustomer Satisfaction: Replica of The Toyota Model AA, The First Production Model of Toyota in 1936John100% (3)
- Operating System Proposal ReportDocument3 pagesOperating System Proposal ReportMuddasar YaminNo ratings yet
- Third Floor Beam Design CalculationDocument3 pagesThird Floor Beam Design CalculationArnold VercelesNo ratings yet
- M1 June 2009Document7 pagesM1 June 2009markodeanoNo ratings yet
- Akarshan Sood Graduate Marine Engineer Main Engine Bearing: Inserting Type Removable Shell BearingDocument7 pagesAkarshan Sood Graduate Marine Engineer Main Engine Bearing: Inserting Type Removable Shell Bearingakarshansood100% (4)
- Technical Notes: Short Tendon ElongationsDocument4 pagesTechnical Notes: Short Tendon ElongationsUdom RithNo ratings yet
- Determining Visible Abrasion Resistance of Glazed Ceramic TileDocument6 pagesDetermining Visible Abrasion Resistance of Glazed Ceramic TileBetsy WiedenfeldNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Termodinamica - FinalDocument72 pagesEjercicios Termodinamica - FinalGEOVANI ESCAJADILLO LUQUENo ratings yet
- The Alcoholysis Reaction of Isocyanates Giving Urethanes: Evidence For A Multimolecular MechanismDocument8 pagesThe Alcoholysis Reaction of Isocyanates Giving Urethanes: Evidence For A Multimolecular MechanismViviana TorresNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ManualDocument48 pagesPhysics Lab ManualHimanshu UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Aspen HYSYSDocument23 pagesBest Practices For Aspen HYSYSfdddddd100% (2)
- General Pre Stress and ElasticDocument28 pagesGeneral Pre Stress and ElasticJorge Nickolai NavalesNo ratings yet
- ESD Audit Check Sheet r1Document20 pagesESD Audit Check Sheet r1ecpuneetsharma01100% (1)
- Project Heat and Mass TransferDocument14 pagesProject Heat and Mass TransferAreen Emilia Faizlukman Jerry100% (1)
- Erosion Wear Rate in Copper Slurry PipelineDocument13 pagesErosion Wear Rate in Copper Slurry PipelinepankhadingtidingNo ratings yet
- Brochure Mikrocad 3d ScannerDocument2 pagesBrochure Mikrocad 3d ScannerbehipiluwuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7-Induction MotorsDocument1 pageAssignment 7-Induction MotorsAli HarisNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Lab Syeed HasanDocument8 pagesProjectile Motion Lab Syeed Hasanapi-130453141No ratings yet
- Cooling Loads Calculation: Cooling Load Temperature Difference (CLTD) MethodDocument8 pagesCooling Loads Calculation: Cooling Load Temperature Difference (CLTD) MethodChristopher LloydNo ratings yet
- AE Question PDFDocument12 pagesAE Question PDFAkhil SureshNo ratings yet
- LagrangeDocument32 pagesLagrangepuiteraNo ratings yet
- Experimental Analysis of Fin Tube and Bare Tube Type Tube-In-Tube Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesExperimental Analysis of Fin Tube and Bare Tube Type Tube-In-Tube Heat ExchangerMohammed Abdul Hai CHE VI ANo ratings yet
- Praktikum Bab Karakteristik LED Dan Laser DiodeDocument4 pagesPraktikum Bab Karakteristik LED Dan Laser DiodeErvina IkkeNo ratings yet
- Metrologic Colombia S.A.S. Medellín Medellín Colombia: Oferta Economica CO20233Document3 pagesMetrologic Colombia S.A.S. Medellín Medellín Colombia: Oferta Economica CO20233Julian MoraNo ratings yet
- SCIT - SampleTest Pattern For 2015Document8 pagesSCIT - SampleTest Pattern For 2015heeNo ratings yet
- A Dielectric Lens Antenna With Enhanced Aperture Efficiency For Industrial Radar ApplicationsDocument3 pagesA Dielectric Lens Antenna With Enhanced Aperture Efficiency For Industrial Radar ApplicationsacademicosNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three (3) Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesNewton's Three (3) Laws of MotionCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- 11 Math - Test Maker @Document2 pages11 Math - Test Maker @ashfaq4985No ratings yet
- Lifting Lug - Skid - 2018.07.16Document4 pagesLifting Lug - Skid - 2018.07.16RaghNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) Solutionsrsarthak227No ratings yet