Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Blood: Name: Nuryuhainis Shazreen Class: 3 Jujur Teacher: PN Linda Gomez
Human Blood: Name: Nuryuhainis Shazreen Class: 3 Jujur Teacher: PN Linda Gomez
Uploaded by
Rosdan JadidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Blood: Name: Nuryuhainis Shazreen Class: 3 Jujur Teacher: PN Linda Gomez
Human Blood: Name: Nuryuhainis Shazreen Class: 3 Jujur Teacher: PN Linda Gomez
Uploaded by
Rosdan JadidCopyright:
Available Formats
humanbloodhumanbloodhuman
bloodhumanbloodhumanbloodh
umanbloodhumanbloodhumanbl
oodhumanbloodhumanbloodhu
manbloodhumanbloodhumanblo
odhumanbloodhumanbloodhuma
nbloodhumanbloodhumanblood
humanbloodhumanbloodhuman
bloodhumanbloodhumanbloodh
umanbloodhumanbloodhumanbl
oodhumanbloodhumanbloodhu
manbloodhumanbloodhumanblo
odhumanbloodhumanbloodhuma
nbloodhumanbloodhumanblood
humanbloodhumanbloodhuman
bloodhumanbloodhumanbloodh
umanbloodqwertyuiopasdfghjklz
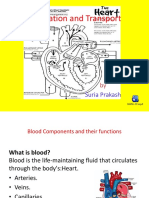
Human Blood
Name: Nuryuhainis Shazreen
Class: 3 Jujur
Teacher: Pn Linda Gomez
Blood components & functions
Blood is made up of blood cells&platelets suspended in a
liquid.
The yellow part is called plasma.
And forms about 55% of the volume of blood.
It carries dissolved substances.
The blood cells & platelets form 45% of blood.
Blood consists of:
a) Plasma
b) Red blood cells
c) White blood cells
d) Platelets (blood clotting cells)
Plasma
Pale yellowish liquid
It is made up of 90% water
10% is soluble substances like nutrients, mineral salts, blood proteins, &
hormones.
Red blood & White blood cells & platelets float in plasma.
Composition of plasma
Components Percentage
Water 92
Protein 6
Mineral salts 0.8
Lipid 0.6
Glucose (blood sugar) 0.1
Others 0.5
Functions of plasma
a) To transport digested food to the cells
b) To transport waste products like urea from the body tissues to the
excretory organs
c) To controls the body temperature at 37`C by spreadingheat to all parts
of the body
d) To carry hormones to tissues to regulate body processes
Red blood cells have a
biconcave shape.
Red blood cells do not have a nucleus.
Function of the red blood cells:
a) transport oxygen to body cells.
Red blood cells contain haemoglobin (a red
pigment) which combines with oxygen to form
oxyhaemoglobin.
Oxyhaemoglobinreleases oxygen when it reaches
the body cells.
Red blood cells are
produced in the bone
marrow.
White blood cells are larger size
thanred blood cells.
White blood cells have nucleus.
White blood cells do not have a
definite shape.
Functions of white blood cells:
a) protect the body form being attacked by
microoraganisms like bacteria & viruses.
White blood cells form a part of the bodys
defence system.
Some white blood cells can:
a) Kill bacteria in the blood.
b) Produce antibodies to neutralize poisonus
substances (toxins) produced by microorganisms
in the blood.
White blood cells are produced in the bone
marrow & lymph glands.
Platelets are small
pieces in the blood
that have no definite shape.
Platelets do not have nucleus.
The size of platelets is very small.
Functions of platelets:
a) clot blood in a wound to prevent the loss of an
excessive amount of blood.
Platelets are produced
in the bone marrow.
The lifespan of
platelets is very short,
i.e. from a few hours to
nine days.
Blood Groups
Human blood is classified into four groups:
a) A
b) B
c) AB
d) O
A person who donates his blood to another is
called blood donor.
A person who receives blood from another is
called recipient.
Blood transfusion is the transfer of blood from a
donor to a recipient.
People with blood group O can donate blood to
people having blood groups O, A, AB, Bbecause of
this, people with blood group O are called
universal donors.
Donors blood/
Recipients
blood group
A B AB O
A
yes
yes
B
yes yes
AB
yes
O
yes yes yes yes
Blood Donation
The loss if a lot of blood as a result of an accident
or an operation needs to be replaced with blood
transfused from another person. This is because
massive blood loss will damage bodily functions &
cause death.
People are encouraged to donate blood to save
lives of others.
Blood transfusion must be carried out with care
to avoid blood clotting from occurring.
The type of blood transfused to a recipient must
be suitable & compatible.
There are to types of blood transfusion:
a) Through blood kept in the blood bank.
b) Through direct channeling from the donor to the
recipient.
Storage & Handling of Blood
Each blood donor must be tested before hand in
to know his or her blood group. He or she must
also be examined by a doctor to ensure that his
or her body is healthy enough for donations.
Before blood is transfused into a patient, it
must be tested to ensure that it is free from
diseases like hepatitis B & C , HIV & venereal
diseases like syphilis
Blood obtained from a donor should be stored
in a clod place before use.
You might also like
- Blood BankingDocument10 pagesBlood BankingSheen AmboyNo ratings yet
- Transport System 2Document17 pagesTransport System 2Akiela JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Bloodbanking 220327155325Document42 pagesBloodbanking 220327155325goesvidhiNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument13 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportLadangGadekNo ratings yet
- Blood Basics: The Need Is Constant. The Gratification Is Instant. Give BloodDocument54 pagesBlood Basics: The Need Is Constant. The Gratification Is Instant. Give BloodSAlNo ratings yet
- Transfusi DarahDocument29 pagesTransfusi Darahanggie pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation ProgramDocument11 pagesBlood Donation Programmeroy28No ratings yet
- Form 3: Blood: Components (B6D3E1)Document10 pagesForm 3: Blood: Components (B6D3E1)Yuslina YusoffNo ratings yet
- 1.soal Praktika Uas BHS Inggris IiDocument3 pages1.soal Praktika Uas BHS Inggris IiMaysaNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation: By: Nila Wahyu Saputri NPM: 2006598345 English For Nursing - B Faculty of Nursing 2021/2022Document15 pagesBlood Donation: By: Nila Wahyu Saputri NPM: 2006598345 English For Nursing - B Faculty of Nursing 2021/2022NilawsNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 Revision Notes PDFDocument8 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 7 Revision Notes PDFNayla Masroor 9BNo ratings yet
- Human Blood - English - 1561800335 - English - 1579005206Document9 pagesHuman Blood - English - 1561800335 - English - 1579005206Rahul Dev PNo ratings yet
- Scrapbook ScienceDocument29 pagesScrapbook ScienceKhairil AzriNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation: SMJK Kwang Hua, Klang Project Base Learning 2Document8 pagesBlood Donation: SMJK Kwang Hua, Klang Project Base Learning 2LOOK YU QI MoeNo ratings yet
- BLOOD TRANSFUSION FinalDocument64 pagesBLOOD TRANSFUSION Finalxaalam easyNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionVikraman ThamotharanNo ratings yet
- Blood: Raeesa Sattar Faculty of Allied Health SciencesDocument25 pagesBlood: Raeesa Sattar Faculty of Allied Health SciencesNAMRA RASHEEDNo ratings yet
- Give Blood.: Donating Blood Is A Simple Thing To Do, But It Can Make A Big Difference in The Lives of OthersDocument17 pagesGive Blood.: Donating Blood Is A Simple Thing To Do, But It Can Make A Big Difference in The Lives of Othersgtrin15No ratings yet
- Blood Basics: The Need Is Constant. The Gratification Is Instant. Give BloodDocument25 pagesBlood Basics: The Need Is Constant. The Gratification Is Instant. Give Bloodsatyvan2003No ratings yet
- BloodDocument40 pagesBloodShaina Charmaine Quirol100% (1)
- Welcome: by DR - Mrs. Grace Helina Prof - and Head Dept - of Exercise Physiology and Nutrition Tnpesu Chennai - 06Document18 pagesWelcome: by DR - Mrs. Grace Helina Prof - and Head Dept - of Exercise Physiology and Nutrition Tnpesu Chennai - 06Ajay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Human BloodDocument4 pagesHuman BloodAiney QureshiNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument4 pagesBlood ComponentsVishweshPatel100% (1)
- Bloodbasics 1Document10 pagesBloodbasics 1api-203306348No ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument31 pagesBlood TransfusionMilagros Florita100% (1)
- BLOODDocument5 pagesBLOODSora TensaiNo ratings yet
- Blood Trasfusion Atalel FinalDocument54 pagesBlood Trasfusion Atalel Finalstilahun651No ratings yet
- The Transport System in HumansDocument8 pagesThe Transport System in HumansazuraNo ratings yet
- Blood: Starter: Create Your Own Mind Map - Add Anything You Know About BloodDocument23 pagesBlood: Starter: Create Your Own Mind Map - Add Anything You Know About BloodsarahfdrakeNo ratings yet
- Physiology of BloodDocument59 pagesPhysiology of BloodFarah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Blood - A Fluid Tissue That Circulates Throughout The Body, Via The Arteries and Veins, Providing A VehicleDocument7 pagesBlood - A Fluid Tissue That Circulates Throughout The Body, Via The Arteries and Veins, Providing A VehicleArnie Jude CaridoNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument24 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemHanirutha.M 7BNo ratings yet
- Blood BasicsDocument24 pagesBlood BasicsMusallam M. AbukhalilNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Topic-1Body Fluidsquick ReviewDocument13 pagesCirculatory System: Topic-1Body Fluidsquick ReviewAppyNo ratings yet
- HaematologyDocument11 pagesHaematologyjess waldenNo ratings yet
- What Is So Wonderful About BloodDocument5 pagesWhat Is So Wonderful About BloodrasiragaNo ratings yet
- PS44 Blood Transfusion 2020finalDocument28 pagesPS44 Blood Transfusion 2020finalchandanisoni4759No ratings yet
- Blood and Lymp SysDocument13 pagesBlood and Lymp SysBRAIMA JOHNNo ratings yet
- Wong Chun SamDocument7 pagesWong Chun SamYuslina YusoffNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion SeminarDocument20 pagesBlood Transfusion SeminarJeezreel100% (1)
- Blood Basics - Unit 5Document10 pagesBlood Basics - Unit 5api-292042538No ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument28 pagesBlood Anatomy and PhysiologyPORTRAIT OF A NURSENo ratings yet
- Title:Human Blood: Name:Kua Choon Hoong CLASS:3A12Document12 pagesTitle:Human Blood: Name:Kua Choon Hoong CLASS:3A12Yuslina YusoffNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank 2 PDFDocument5 pagesBlood Bank 2 PDFRajkumar RoderickNo ratings yet
- Blood Group MLDDocument5 pagesBlood Group MLDHarsheen KaurNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Blood TissueDocument10 pagesGR 10 Blood TissueMelanie TrevelyanNo ratings yet
- Bio CirculationDocument7 pagesBio CirculationPriya MalpaniNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation: "A Gift of Life From Us To Other People"Document22 pagesBlood Donation: "A Gift of Life From Us To Other People"Devesh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Blood Products & Plasma SubstitutesDocument15 pagesBlood Products & Plasma Substitutesahmadslayman1No ratings yet
- BloodDocument20 pagesBloodkorbet korbetNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation NotesDocument8 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation Notessatyam6449No ratings yet
- Blood Type MatchingDocument5 pagesBlood Type MatchingAsveene LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology II: Topic: Anatomy of The Blood Sub Topic: Introduction To Blood and Its CompositionsDocument28 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology II: Topic: Anatomy of The Blood Sub Topic: Introduction To Blood and Its Compositionsngong ngong ametNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Blood and Blood Typing: The Circulatory System: Blood, Pages 679-712 (Saladin, 4Document4 pagesLab 1 - Blood and Blood Typing: The Circulatory System: Blood, Pages 679-712 (Saladin, 4math_mallikarjun_sapNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument7 pagesBloodpravinambadeNo ratings yet
- 550 ICSE ClassX Biology TheCirculatorySystem RNDocument14 pages550 ICSE ClassX Biology TheCirculatorySystem RNHarshitNo ratings yet
- Biology (Neet)Document2 pagesBiology (Neet)YashwanthNo ratings yet
- 4 G 8 J FRQ Nvgotg 8 VL Bs OJDocument8 pages4 G 8 J FRQ Nvgotg 8 VL Bs OJvashisthchandra65No ratings yet
- Lab Lesson # 1Document2 pagesLab Lesson # 1AsharAnisNo ratings yet
- I Can Do Hard Things: My Journey Toward Reconciliation, Recovery, and HealingFrom EverandI Can Do Hard Things: My Journey Toward Reconciliation, Recovery, and HealingNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Transfusion MedicineDocument50 pagesCompendium of Transfusion MedicineLudmilla MartinsNo ratings yet
- What Is Blood BankDocument3 pagesWhat Is Blood Banksams haqNo ratings yet
- Blood Groups PPT by TKR&SRDocument24 pagesBlood Groups PPT by TKR&SRseshagiriNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Voluntary Blood DonationDocument2 pagesAdvantages of Voluntary Blood DonationSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Trima Accel The Art of Blood CollectionDocument7 pagesTrima Accel The Art of Blood CollectionMohamed ElmasryNo ratings yet
- Package Insert - Procleix Ultrio Elite Assay PDFDocument50 pagesPackage Insert - Procleix Ultrio Elite Assay PDFmooooooooodyNo ratings yet
- 43 Shravan ParmarDocument30 pages43 Shravan Parmarsai projectNo ratings yet
- Baseline SurveyDocument1 pageBaseline SurveyRhoda DalugdogNo ratings yet
- Region 4ADocument11 pagesRegion 4AAlyssa Alexis RamosNo ratings yet
- Chaudhari 2018Document7 pagesChaudhari 2018Reshma SindhuNo ratings yet
- 08 31 16Document26 pages08 31 16WoodsNo ratings yet
- RBC AliquotsDocument1 pageRBC AliquotsARIF AHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Chapter 7 - Ethical Considerations On Community Health NursingDocument45 pages0.1 Chapter 7 - Ethical Considerations On Community Health NursingyounggirldavidNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank Management System Research PaperDocument7 pagesBlood Bank Management System Research PapercalciummNo ratings yet
- Immuno HematologyDocument35 pagesImmuno HematologyAlan McLeanNo ratings yet
- NSTP CogieDocument14 pagesNSTP CogieCogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Notice: English XII (Core)Document46 pagesNotice: English XII (Core)Alisha GoelNo ratings yet
- Pamflet Donor DarahDocument3 pagesPamflet Donor DarahAlifianti Balinda PramatasariNo ratings yet
- Waiver For Blood DonationDocument4 pagesWaiver For Blood Donationeleazar_magsino08No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentMuhaimin ShahNo ratings yet
- Beltran V. Secretary of HealthDocument1 pageBeltran V. Secretary of HealthjaninnahuangNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 Hemoglobin Estimation (CuSo4 Preparation)Document3 pages1.3.1 Hemoglobin Estimation (CuSo4 Preparation)Ross Navarro SupeñaNo ratings yet
- Initial Management of Moderate To Severe Hemorrhage in The Adult Trauma Patient - UpToDateDocument28 pagesInitial Management of Moderate To Severe Hemorrhage in The Adult Trauma Patient - UpToDatePerla RuizNo ratings yet
- ABO Grouping BB LabDocument5 pagesABO Grouping BB LabBless MarieNo ratings yet
- Newsletter E2 June 2011 Final PressDocument16 pagesNewsletter E2 June 2011 Final PressDustin ChinNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation Quotes - Blood Donors Slogans With ImagesDocument19 pagesBlood Donation Quotes - Blood Donors Slogans With Imagesrao talhaNo ratings yet
- Who TRS 924 A4Document75 pagesWho TRS 924 A4Andres AbrilNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument2 pagesBlood TransfusionsenyorakathNo ratings yet
- Publications: CatalogDocument36 pagesPublications: CatalogNeerja ChauhanNo ratings yet