Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Low Level Return or Exhaust Air Grilles Are Usually Preferred
Low Level Return or Exhaust Air Grilles Are Usually Preferred
Uploaded by
Nadya Putri Dwi Yanari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views3 pagesThe document discusses heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for clean rooms and pharmaceutical facilities. It describes different options for return air locations and airflow schematics. Recirculation of air is acceptable if HEPA filters are used to prevent cross-contamination. Systems using 100% fresh air are recommended when toxic products are involved to avoid recirculating air with contaminants. Energy recovery wheels should generally not be used in multi-product facilities due to contamination risks.
Original Description:
Low Level Return or Exhaust Air Grilles Are Usually Preferred
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for clean rooms and pharmaceutical facilities. It describes different options for return air locations and airflow schematics. Recirculation of air is acceptable if HEPA filters are used to prevent cross-contamination. Systems using 100% fresh air are recommended when toxic products are involved to avoid recirculating air with contaminants. Energy recovery wheels should generally not be used in multi-product facilities due to contamination risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views3 pagesLow Level Return or Exhaust Air Grilles Are Usually Preferred
Low Level Return or Exhaust Air Grilles Are Usually Preferred
Uploaded by
Nadya Putri Dwi YanariThe document discusses heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for clean rooms and pharmaceutical facilities. It describes different options for return air locations and airflow schematics. Recirculation of air is acceptable if HEPA filters are used to prevent cross-contamination. Systems using 100% fresh air are recommended when toxic products are involved to avoid recirculating air with contaminants. Energy recovery wheels should generally not be used in multi-product facilities due to contamination risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
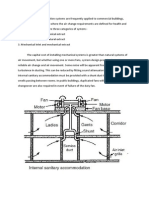
low level return or exhaust air grilles are usually preferred.
however, where this is not possible, a higher
air change rate may be needed to achieve a specified clean area classification, e.g where ceiling return
air grilles are used.
there may be alternative locations for return air. for example, referring to Fig 4, room D (low-level
return air) and room E (ceiling return air).
The airflow schematics of two systems (Fig 4 and 5) indicate air-handling units with return air or
recirculated, having a percentage of fresh air added. Fig 5 is schematic diagram of an air-handling
system serving rooms with horizontal unidirectional flow, vertical unidirectional flow and turbulent flow,
for rooms A, B and C, respectively.
The airflow diagram in Fig 4 is an example of a typical system with a lower clean area classification.
Recirculation system
There should be no risk of contamination or cross-contamination (including by fumes and volatiles) due
to recirculation of air.
Depending on the airbone contaminants in the return-air system it may be acceptable to use
recirculated air, provided that HEPA filters are installed in the supply air stream to remove contaminants
and thus prevent cross-contamination. The HEPA filters for this application should have an EN1822
classification of H13. HEPA filters may not be required where the air-handling system is serving a single
product facility and there is evidence that cross-contamination would not be possible.
Recirculation of air from areas where pharmaceutical dust is not generated such as secondary packing,
may not require HEPA filters in the system
HEPA filters may be located in the air-handling unit or placed terminally.
Air containing dust from highly toxic processes should never be recirculated to the HVAC system.
Tingkat pengembalian udara yang rendah biasanya paling disukai . Namun, di mana hal ini tidak
mungkin ,karena mungkin tingkat pertukaran udara yang lebih tinggi diperlukan untuk mencapai
klasifikasi area bersih spesifik.
mungkin ada lokasi alternatif untuk pengembalian udara . misalnya , mengacu pada Gambar 4 , ruang
D ( tingkat rendah pengambilan udara) dan ruang E ( langit-langit pengembalian udara) .
skema aliran udara dari dua sistem ( Gambar 4 dan 5 ) menunjukkan unit penanganan udara dengan
udara kembali atau diresirkulasi , memiliki persentase udara segar ditambahkan . Gambar 5 adalah
diagram skematik dari sistem penanganan udara yang melayani kamar dengan aliran horizontal
searah , arus searah vertikal dan aliran turbulen , untuk kamar A , B dan C , masing-masing.
Diagram aliran udara pada Gambar 4 adalah contoh dari sistem yang khas dengan klasifikasi daerah
bersih yang lebih rendah.
sistem resirkulasi
Seharusnya tidak ada resiko kontaminasi atau kontaminasi silang ( termasuk oleh asap dan volatil )
karena resirkulasi udara .
Tergantung pada kontaminan airbone dalam sistem return- udara mungkin dapat diterima untuk
menggunakan udara disirkulasikan, asalkan filter HEPA dipasang dalam aliran pasokan udara untuk
menghilangkan kontaminan dan dengan demikian mencegah kontaminasi silang . The filter HEPA
untuk aplikasi ini harus memiliki klasifikasi EN1822 dari H13 .
Filter HEPA mungkin tidak diperlukan dimana sistem penanganan udara melayani fasilitas produk
tunggal dan ada bukti bahwa kontaminasi silang tidak akan mungkin.
Resirkulasi udara dari daerah di mana debu produk farmasi tidak dihasilkan seperti pengemasan
sekunder, mungkin tidak memerlukan filter HEPA dalam sistem
Filter HEPA mungkin berlokasi di unit penanganan udara atau ditempat beresiko
Air yang mengandung debu dari proses yang sangat beracun tidak boleh diedarkan kembali ke sistem
HVAC.
Full fresh-air systems
Fig 6 indicates a system operating on 100% fresh air and would normally be used in a facility dealing
with toxic products, where recirculation of air with contaminants should be avoided.
The required degree of filtration of the exhaust air contaminants and local environmental regulations.
Energy recovery wheels should normally not be used in multiproduct facilities. When such wheels are
used they should not become a source of possible contamination (see Fig 7).
NOTE: alternatives to the the energy-recovery wheels, such as cross over plate heat exchangers, may be
used in multi product facilities.
The potential for air leakage between the supply air and exhaust air as it passes through the wheel
should be prevented. The relative pressures between supply and exhaust air systems should be such
that the exhaust air system operates at a lower pressure than the supply system.
Sistem udara segar penuh
Gambar 6 menunjukkan sistem operasi pada 100% udara segar dan biasanya akan digunakan di
fasilitas berurusan dengan produk-produk beracun, di mana resirkulasi udara dengan kontaminan
harus dihindari.
Tingkat penyaringan yang digunakan tergantung pembuangan kontaminan udara dan peraturan
lingkungan setempat.
Roda pemulihan energi harus biasanya tidak digunakan dalam fasilitas multiproduct. Ketika roda
tersebut digunakan mereka tidak seharusnya menjadi sumber kemungkinan kontaminasi (lihat
Gambar 7).
CATATAN: alternatif untuk roda energi-recovery, seperti cross over heat exchanger piring, dapat
digunakan dalam fasilitas multi produk.
Potensi kebocoran udara antara udara pasokan dan pembuangan udara saat melewati roda harus
dicegah. Tekanan relatif antara pasokan dan sistem pembuangan udara harus sedemikian rupa
sehingga sistem pembuangan udara beroperasi pada tekanan rendah dari sistem pasokan.
You might also like
- TexPro Service ManualDocument128 pagesTexPro Service ManualJuan Pablo GómezNo ratings yet
- Aeration PaperDocument11 pagesAeration PapersehonoNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE HVAC-HospitalBook Room DesignDocument4 pagesASHRAE HVAC-HospitalBook Room DesignAbdallah Abu Irmaileh100% (1)
- Partes GT40Document70 pagesPartes GT40JHONNATTAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Clean RoomDocument9 pagesClean Roomxyzscribd1988No ratings yet
- A33 Si - Kitchen VentilationDocument1 pageA33 Si - Kitchen VentilationAhmed NabilNo ratings yet
- 5.1. Air Preparation: Chapter 5: Pneumatic SystemsDocument36 pages5.1. Air Preparation: Chapter 5: Pneumatic SystemsSiraj BusseNo ratings yet
- Engineering Letter: FansandblowersforcombustionprocessDocument4 pagesEngineering Letter: Fansandblowersforcombustionprocessnedduc20No ratings yet
- Pneumatic Conveying - GJ74, HauckDocument6 pagesPneumatic Conveying - GJ74, Hauckjfejfe100% (1)
- Reasons Engineers Are Choosing Dedicated OA SystemsDocument3 pagesReasons Engineers Are Choosing Dedicated OA SystemsADsupermanNo ratings yet
- Hvac TermsDocument65 pagesHvac Termszebidians100% (1)
- An Air Handling UnitDocument4 pagesAn Air Handling UnitDono WayNo ratings yet
- Airflow Design For Clean Rooms and Its Economic ImplicationsDocument7 pagesAirflow Design For Clean Rooms and Its Economic ImplicationsDanny D.No ratings yet
- Course Number: Me 433 Fluidics: Pneumatic System & CircuitDocument16 pagesCourse Number: Me 433 Fluidics: Pneumatic System & CircuitM RazzaqueNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic ConveyingDocument6 pagesPneumatic Conveyingsudhirm16100% (1)
- Optimization of Recirculating Laminar Air FlowDocument6 pagesOptimization of Recirculating Laminar Air FlowreiferNo ratings yet
- Cleanroom Energy EfficiencyDocument6 pagesCleanroom Energy EfficiencysdvitkoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Guide Price Critical Environments: Hospital Operating RoomsDocument6 pagesEngineering Guide Price Critical Environments: Hospital Operating RoomsHenry SuarezNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Systems Are Frequently Applied To Commercial BuildingsDocument9 pagesMechanical Ventilation Systems Are Frequently Applied To Commercial BuildingsIbn Shaffee IVNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About FansDocument10 pagesAll You Need To Know About FansgertibajNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Cleanrooms and Air Quality - A Risk-Based ApproachDocument13 pages2.4 Cleanrooms and Air Quality - A Risk-Based ApproachJorge Humberto HerreraNo ratings yet
- BP Recovery 508Document8 pagesBP Recovery 508Gustavo ChavesNo ratings yet
- L 2 1 C: B P: e R V A LDocument8 pagesL 2 1 C: B P: e R V A LChesa LumaguiNo ratings yet
- How Buildings Are Cooled Using AHUDocument4 pagesHow Buildings Are Cooled Using AHUrgopinath.gctNo ratings yet
- Blower Selection For Wastewater AerationDocument10 pagesBlower Selection For Wastewater AerationRobert MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Double Blower SystemDocument1 pageDouble Blower SystemdelaykingNo ratings yet
- Lec No 17Document32 pagesLec No 17zohaibali30No ratings yet
- ASHRAE - HVAC-HospitalBook - Room Design PDFDocument4 pagesASHRAE - HVAC-HospitalBook - Room Design PDFalialavi2No ratings yet
- % Outdoor Air CalculationDocument6 pages% Outdoor Air Calculationamirin_kingNo ratings yet
- By Douglas C. Hittle, PH.D., Fellow ASHRAEDocument5 pagesBy Douglas C. Hittle, PH.D., Fellow ASHRAENiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Air SystemDocument22 pagesAir Systemabhi_mohit2005100% (1)
- Testing, Adjusting & Balancing - ASHRAEDocument7 pagesTesting, Adjusting & Balancing - ASHRAEZainul Abedin Sayed100% (1)
- LEV - CalculationDocument15 pagesLEV - CalculationkarvadNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Ventilation Flow RateDocument3 pagesBasic Concept of Ventilation Flow RateiwansantosoNo ratings yet
- VAV Systems and Outdoor Air: H H H H HDocument7 pagesVAV Systems and Outdoor Air: H H H H HdimchienNo ratings yet
- Uktra Clean OTsDocument8 pagesUktra Clean OTshadianatyaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation-GuidelineDocument8 pagesVentilation-GuidelineCử NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Modeling Guidelines Using ASHRAE 90.1-1999: October 2005Document16 pagesLaboratory Modeling Guidelines Using ASHRAE 90.1-1999: October 2005hassani yahiaNo ratings yet
- Hood Types: Enclosing Hoods Are Those in Which The Source Is Either Partially or Totally Enclosed To Provide TheDocument11 pagesHood Types: Enclosing Hoods Are Those in Which The Source Is Either Partially or Totally Enclosed To Provide TheSudhakar KarnanNo ratings yet
- Air Ejector Cheaper Than SteamDocument5 pagesAir Ejector Cheaper Than SteamjungmukNo ratings yet
- Air Handler: (HvacDocument9 pagesAir Handler: (Hvacدنيا قيس كاظمNo ratings yet
- Detailed Drawing Drawings (Air Handling Unit) : Dijlah University CollegeDocument10 pagesDetailed Drawing Drawings (Air Handling Unit) : Dijlah University Collegeدنيا قيس كاظمNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Generation & Distribution SystemDocument6 pagesCompressed Air Generation & Distribution SystemSnehalkumar GhaytadkarNo ratings yet
- Instructions Purging High Purity Delivery SystemsDocument8 pagesInstructions Purging High Purity Delivery Systemssharklasers sharklasersNo ratings yet
- Industrial Pneumatics: Introduction: Chapter 4 Pneumatics and ElectropneumaticsDocument2 pagesIndustrial Pneumatics: Introduction: Chapter 4 Pneumatics and ElectropneumaticsRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Amt 1201 - Midterm - Module 2 - DelgadoDocument7 pagesAmt 1201 - Midterm - Module 2 - DelgadoBrendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Skema Soalan Final v.2 - BFC315332603Document15 pagesSkema Soalan Final v.2 - BFC315332603Johnson KenNo ratings yet
- HVAC in Hospital PDFDocument7 pagesHVAC in Hospital PDFMohammed Toema100% (1)
- Documento - Teste de Estanquidade em DutosDocument5 pagesDocumento - Teste de Estanquidade em DutosRogerio OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Saving Energy in Lab Exhaust SystemsDocument11 pagesSaving Energy in Lab Exhaust Systemspal_stephenNo ratings yet
- Air HandlerDocument15 pagesAir HandlerShashank BijweNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument3 pagesAir ConditioningBoJassim100% (1)
- EC Motor FansDocument4 pagesEC Motor Fansrgopinath.gctNo ratings yet
- Special Departmental HVAC Issues: Operating RoomsDocument6 pagesSpecial Departmental HVAC Issues: Operating RoomshadianatyaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Fan Pressure OptimizationDocument11 pagesVentilation Fan Pressure OptimizationchoibeNo ratings yet
- Cleanrooms & Air Quality - A Risk-Based Approach - Tim SandleDocument13 pagesCleanrooms & Air Quality - A Risk-Based Approach - Tim SandleHubert BonamisNo ratings yet
- YORK EconomizerPressurization AHUDocument8 pagesYORK EconomizerPressurization AHUAhmed TahaNo ratings yet
- Estimating Air LeakageDocument5 pagesEstimating Air Leakagenasirmuzaffar100% (1)
- VAV System Air BalancingDocument3 pagesVAV System Air BalancingShoukat Ali ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationFrom EverandThe Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Lung Function in Health and Disease Basic Concepts of Respiratory Physiology and PathophysiologyFrom EverandLung Function in Health and Disease Basic Concepts of Respiratory Physiology and PathophysiologyNo ratings yet
- PDS Guide - PDF FormatDocument28 pagesPDS Guide - PDF FormatCynna EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Removal Organic Compound of Domestic Waste Waters Containing Heavy Metals Using Mendong, Fimbrystilis GlobulosaDocument2 pagesRemoval Organic Compound of Domestic Waste Waters Containing Heavy Metals Using Mendong, Fimbrystilis Globulosaapi-3736766No ratings yet
- Advisor Webcast - Customizing The Workflows in Oracle EBS ProcurementDocument53 pagesAdvisor Webcast - Customizing The Workflows in Oracle EBS ProcurementhgopalanNo ratings yet
- Supreme UPVC PipeDocument6 pagesSupreme UPVC PipeRamesh HadiyaNo ratings yet
- Practical Microwave Filter DesignDocument5 pagesPractical Microwave Filter Designbongoloid100% (1)
- CV Ahmed MechanicalDocument2 pagesCV Ahmed MechanicalAhmed PathanNo ratings yet
- LM 8102Document2 pagesLM 8102Rico PratamaNo ratings yet
- Implementation and Monitoring:: Assessing Performance in Contract RelationshipsDocument49 pagesImplementation and Monitoring:: Assessing Performance in Contract RelationshipsReddy SumanthNo ratings yet
- Hi-Kal Stock 18-06-17Document5 pagesHi-Kal Stock 18-06-17Игорь Ширенин100% (1)
- Pioneer cdj350 Service ManualDocument97 pagesPioneer cdj350 Service Manualstefano bluNo ratings yet
- 2012-14 Revised Improvement PlanDocument7 pages2012-14 Revised Improvement Planapi-250619894No ratings yet
- EngineersSkillDevelopment22.8.2016 SurajSinghDocument29 pagesEngineersSkillDevelopment22.8.2016 SurajSinghP Eng Suraj Singh100% (1)
- First Certificate 5 Practise Tests PDFDocument162 pagesFirst Certificate 5 Practise Tests PDFAlicia HG100% (2)
- L10-Casting DesignDocument42 pagesL10-Casting DesignKhayrulIslam100% (2)
- 80096503-001-E ID TECH SecureMag OPOS User's ManualDocument34 pages80096503-001-E ID TECH SecureMag OPOS User's ManualEvangelista Francisco LacombaNo ratings yet
- ATD Tutorial 3Document2 pagesATD Tutorial 3Dheeraj PatelNo ratings yet
- OOP Basics - Java Programming TutorialDocument27 pagesOOP Basics - Java Programming TutorialchitranshpandeyNo ratings yet
- Cummins Efc Troubleshooting Guide 2Document2 pagesCummins Efc Troubleshooting Guide 2andrew100% (62)
- Operating Manual Photoflex WTWDocument109 pagesOperating Manual Photoflex WTWmcycloneNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard - Industrial Plant Layout-Code of Safe PracticeDocument29 pagesIndian Standard - Industrial Plant Layout-Code of Safe PracticeDineshKumarNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Range Meter ReportDocument75 pagesUltrasonic Range Meter Reportkopiko100% (1)
- DC 2022 0553 and PhilHealth Policy StatementsDocument27 pagesDC 2022 0553 and PhilHealth Policy StatementsJay-ar RicoNo ratings yet
- Liebherr L514-790 Wheel Loader Service Repair Manual SN 14000 PDFDocument40 pagesLiebherr L514-790 Wheel Loader Service Repair Manual SN 14000 PDFjfjksekdmeikNo ratings yet
- Masonry Stove Claimed To Be Most Efficient FARM S HOW Magazine: 1980 - Volume 4 Issue 5 Page 31Document2 pagesMasonry Stove Claimed To Be Most Efficient FARM S HOW Magazine: 1980 - Volume 4 Issue 5 Page 31VajranathaNo ratings yet
- Data ONTAP 81 Cluster Peering Express Guide ForDocument29 pagesData ONTAP 81 Cluster Peering Express Guide ForKamlesh SinghNo ratings yet
- SPGPrints Pre-Print Textile Brochure A4 2019 DigitalDocument12 pagesSPGPrints Pre-Print Textile Brochure A4 2019 DigitalkkkkrolikNo ratings yet
- Document Feeder: (Machine Code: A662)Document32 pagesDocument Feeder: (Machine Code: A662)servicerNo ratings yet