Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nano-Tera Poster 2014 Third Prize MIXSEL
Nano-Tera Poster 2014 Third Prize MIXSEL
Uploaded by
nanoteraCHCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nano-Tera Poster 2014 Third Prize MIXSEL
Nano-Tera Poster 2014 Third Prize MIXSEL
Uploaded by
nanoteraCHCopyright:
Available Formats
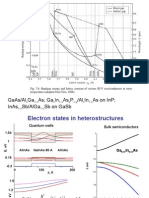
OpticaI
Frequency
Microwave Output
Frequency comb:
AIIows connection
between opticaI and
microwave frequencies
1 mW
10 mW
100 mW
1 W
10 W
a
v
e
r
a
g
e
o
u
t
p
u
t
p
o
w
e
r
100 fs 1 ps 10 ps 100 ps
pulse duration
QW-VECSEL with SESAM
QD-VECSEL with SESAM
MIXSEL
Ultrafast vertical external cavity surface-emitting laser (VECSEL)
A. S. Mayer, M. Mangold, C. A. Zaugg, S. M. Link, M. Golling,
B. W. Tilma, and U. Keller
ETH Zurich, Institute for Quantum Electronics, Ultrafast Laser Physics
MIXSEL2
RTD 2012
VECSEL: potential compact
frequency comb source with
gigahertz repetition rate
Phase shift by saturation
(Kramers-Kronig)
saturation + positive GDD
! quasi-solitons [1]
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-20 p
h
a
s
e
c
h
a
n
g
e
(
m
r
a
d
)
-4 -2 0 2 4
time (ps)
pulse power (a.u.)
gain = 3
sesam = 2
total
experimentally veried in
picosecond regime [2]
[1] R. Paschotta, R Hring, A Garnache, S Hoogland, A.C Tropper, U Keller, Appl. Phys. B 75 (2002), 445
[2] M. Hoffmann, O.D. Sieber, D.J.H.C. Maas, V.J. Wittwer, M.Golling, T. Sdmeyer and U.Keller, Opt Express 18 (2010), 10143
Ultrafast VECSELs
Motivation
distributed Bragg reflectors
for lasing/pump wavelength
active region
QWs or QDs
AR
section
laser
pump
h
e
a
t
s
p
r
e
a
d
e
r
h
e
a
t
s
p
r
e
a
d
e
r
pump
output
coupler
SESAM
g
a
i
n
c
h
i
p
Pulse Formation Mechanism
frequency
high frep
low
frep
!easier to access to
individual lines
!higher power per
mode
!increased S/N ratio
Requirements
Broad spectrum
Fast measurement speed
Spectral stability
Mechanical compactness
SESAM:
passive loss-modulation
100.0
99.8
99.6
99.4
99.2
99.0
r
e
f
le
c
t
iv
it
y
(
%
)
1 10 100 1'000 10'000
pulse fluence (!J/cm2)
!Rns
!R
3.2
3.0
2.8
2.6
2.4
2.2
2.0
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
gain
loss
pulse
Current Status Conclusion & Outlook
compact self-referenceable
frequency comb from a
VECSEL
low noise Sub-200-fs pulses combined with high average power
Requirements
Compact system
Gigahertz repetition
rates
Multiphoton microscopy:
!high penetration depth
!high sensitivity
!exibility
(uorescence plus
second harmonic or
third harmonic image) Requirements
Pulsed IR-source
Cheap (compared to currently used Ti:Sapphire systems)
Spectroscopy Metrology Applications
Frequency Combs
Biomedical Imaging
Optical clock
Precise frequency
calibration
Gas spectroscopy
Process monitoring
and control
Requirements for self-
referenceable frequency comb
Low noise
Sub-200-fs pulses combined with
high average power
Sub-300 femtosecond QW-VECSEL
! 273-fs-pulses at 605 mW of average
output power in a 1.8 GHz-cavity
wavelength
filter
saturation noise
losses gain SESAM gain GDD
output coupler
[5] O. D. Sieber, V. J. Wittwer, M. Mangold, M. Hoffmann, M. Golling, T. Sdmeyer, U. Keller, Optics
Express 19 (2011), 3538, 2011
Chip Design Goals Experimental Results
First Watt-level femtosecond QD-VECSEL
[3]
! 784-fs-pulses with >1 W output power in a
5.4 GHz V-cavity
First CEO-frequency detection of a
SESAM-modelocked VECSEL
[4]
! amplied and recompressed 240-fs
pulses from a 100-mW VECSEL
[3] M. Hoffmann et. al., Optics Express (2011) vol. 19, 8108-8116
[4] C.A. Zaugg et. al., submitted to 6th EPS-QEOD Europhoton Conference
Theoretical Investigations & Simulations
Iterative application of
cavity elements on the
pulse
Macroscopic
measurable parameters
as input parameters
correct prediction of output
power and pulse duration
+
design guidelines
high gain saturation
fluences for short pulse
generation and high
output power
high small
signal gain for
high power
operation
low saturation
uences of SESAM for
short pulse generation
low and slightly
positive GDD for
femtosecond
pulses
saturation uence gain GDD saturation uence
MIXSEL
Modelocked Integrated
External-Cavity Surface
Emitting Laser
VECSEL Chip Structure
Cavity Design
Distributed Bragg reector (AlAs/GaAs)-pairs
grown on GaAs for laser reection
Active region: Laser light amplication in
quantum wells (QW) or quantum dots (QD)
Antireection-coating: Minimizing losses and
tuning group delay dispersion (GDD)
V- or Z-shape cavity
Pumping under 45
SESAM: SEmiconductor Saturable Absorber
Mirror to obtain self-starting pulsed operation
1:1 mode-locking
(spot size on SESAM
= spot size on
VECSEL)
VECSEL: compact & cheap
pulsed laser source in the IR
spectral range
Dynamic gain
saturation
Losses decrease
faster than gain
!net gain window
VECSEL SESAM
optical frequencies
RF beat note
Integration of
the absorber
SESAM
VECSEL
Cavity Design Goals
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
i
n
t
.
(
d
B
c
)
1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0
frequency (GHz)
RBW 100 kHz
f
CEO 2
f
CEO 1
f
rep
=1.75 GHz
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
i
n
t
.
(
d
B
c
)
1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600
wavelength (nm)
6
8
0
n
m
1
3
6
0
n
m
signal
background
RBW 5 nm
You might also like
- Discovery MR750w 3.0T GEMDocument52 pagesDiscovery MR750w 3.0T GEMJasmina Cabukovska100% (1)
- SMi Radar - MiniDocument29 pagesSMi Radar - MinimfahimehaNo ratings yet
- Ultralow Noise Miniature External Cavity Semiconductor LaserDocument19 pagesUltralow Noise Miniature External Cavity Semiconductor LaserVEENA K THOMAS VLSI20-22No ratings yet
- Smart Surveillance System: Learn - Grow - ExcelDocument18 pagesSmart Surveillance System: Learn - Grow - ExcelVEENA K THOMAS VLSI20-22No ratings yet
- MIT X-Ray Laser ProjectDocument47 pagesMIT X-Ray Laser ProjectWiji AstutiNo ratings yet
- Quantum Cascade LasersDocument36 pagesQuantum Cascade LaserssatyaseshadriNo ratings yet
- Wagner SingleDocument8 pagesWagner SingleanandareddynittNo ratings yet
- Gamma Spectroscopy PrinciplesDocument35 pagesGamma Spectroscopy PrinciplesSara AlSaadiNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Munoz - OpticsExpressDocument15 pages2020 - Munoz - OpticsExpressFDNo ratings yet
- S. Golwala Et Al - A WIMP Dark Matter Detector Using MKIDsDocument7 pagesS. Golwala Et Al - A WIMP Dark Matter Detector Using MKIDsUmav24No ratings yet
- David E. Moncton - An X-Ray Laser at The Transform Limit: Technical Challenges and Scientific PayoffDocument35 pagesDavid E. Moncton - An X-Ray Laser at The Transform Limit: Technical Challenges and Scientific PayoffDublin000No ratings yet
- PGEW Series of Single and Multi Epi 905nm Pulsed Semiconductor Lasers DatasheetDocument6 pagesPGEW Series of Single and Multi Epi 905nm Pulsed Semiconductor Lasers DatasheetVideogamer555No ratings yet
- Multi-Color Cavity MetrologyDocument14 pagesMulti-Color Cavity MetrologyflavioferiNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Investigation of RF Signal Energy HarvestingDocument7 pagesResearch Article: Investigation of RF Signal Energy HarvestingrameshsophidarlaNo ratings yet
- Carr 2001 0449Document9 pagesCarr 2001 0449Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- Quanta-Ray Pulsed YAG LaserDocument5 pagesQuanta-Ray Pulsed YAG LaserKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Sol Xe Doc s88 Exs020 High 1Document2 pagesSol Xe Doc s88 Exs020 High 1Hafid Papeda SaguNo ratings yet
- ECEN689: Special Topics in High-Speed Links Circuits and Systems Spring 2011Document28 pagesECEN689: Special Topics in High-Speed Links Circuits and Systems Spring 2011api-127299018No ratings yet
- Millimetre-Wave Gunn Diode Technology and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesMillimetre-Wave Gunn Diode Technology and ApplicationsJeong-geun KimNo ratings yet
- Rectifier For RF Energy HarvestingDocument15 pagesRectifier For RF Energy HarvestingMd Ahsan HalimiNo ratings yet
- Caracteristicas CombaDocument2 pagesCaracteristicas CombaPnumbraNo ratings yet
- GM6VHSDocument12 pagesGM6VHSFernando Jose CarrasqueroNo ratings yet
- Xr-100T-Cdte: AmptekDocument4 pagesXr-100T-Cdte: AmptekPrashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Design and VLSI Implementation of Low Power Voltage Controlled Ring Oscillator For Wireless LAN SystemsDocument22 pagesDesign and VLSI Implementation of Low Power Voltage Controlled Ring Oscillator For Wireless LAN SystemsDavid Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Imaging The Heart With Ultrasound: Zili YuDocument28 pagesImaging The Heart With Ultrasound: Zili YuAshwin BhatNo ratings yet
- SE Institute of Microdevices STC "Institute For Single Crystals", National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, UkraineDocument5 pagesSE Institute of Microdevices STC "Institute For Single Crystals", National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, UkraineboisolivierNo ratings yet
- Delay-Based Spread Spectrum Clock GeneratorDocument11 pagesDelay-Based Spread Spectrum Clock GeneratorHamad JamilNo ratings yet
- 33ssc07 VaucherDocument12 pages33ssc07 VaucherAlooomNo ratings yet
- Wave Guide LimitsDocument20 pagesWave Guide LimitsJAYESHTRIVNo ratings yet
- Microwave Devices: Irineo P. QuintoDocument14 pagesMicrowave Devices: Irineo P. QuintojephtahNo ratings yet
- Super High-Power AlGaInN-based Laser DiodesDocument4 pagesSuper High-Power AlGaInN-based Laser DiodesPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- RFIC Group: Advanced VLSI Design Lab IIT KharagpurDocument7 pagesRFIC Group: Advanced VLSI Design Lab IIT Kharagpurg.ven18No ratings yet
- CMOS Integrated Circuits For Millimeter-Wave Applications Millimeter-Wave ApplicationsDocument45 pagesCMOS Integrated Circuits For Millimeter-Wave Applications Millimeter-Wave ApplicationswalkmemberNo ratings yet
- W-Band Optoelectronic OscillatorDocument4 pagesW-Band Optoelectronic OscillatorHari EnthiranNo ratings yet
- High Performance Inertial Navigation Grade Sigma-Delta MEMS AccelerometerDocument24 pagesHigh Performance Inertial Navigation Grade Sigma-Delta MEMS AccelerometerRaul RosaNo ratings yet
- 3 Gamma Ray Spectroscopy Using Nai TLDocument20 pages3 Gamma Ray Spectroscopy Using Nai TLMaw MawNo ratings yet
- 665 SRR Fall08Document27 pages665 SRR Fall08freiwildNo ratings yet
- Pulse-Resolved Measurement of Quadrature Phase Amplitudes of Squeezed Pulse Trains at A Repetition Rate of 76 MHZDocument3 pagesPulse-Resolved Measurement of Quadrature Phase Amplitudes of Squeezed Pulse Trains at A Repetition Rate of 76 MHZ張贇No ratings yet
- Presentacion YAODocument29 pagesPresentacion YAOVanessa MorenoNo ratings yet
- A Miniature 25-Ghz 9-Db Cmos Cascaded Single-Stage Distributed AmplifierDocument3 pagesA Miniature 25-Ghz 9-Db Cmos Cascaded Single-Stage Distributed AmplifierLe Nguyen MinhNo ratings yet
- Satellite Antenna TestingDocument47 pagesSatellite Antenna Testingsailee_gharatNo ratings yet
- DC-to-DC Converter Combats EMIDocument4 pagesDC-to-DC Converter Combats EMIJonathan JaegerNo ratings yet
- Continuous-Time Delta-Sigma Modulators For High-Speed AD ConversionDocument271 pagesContinuous-Time Delta-Sigma Modulators For High-Speed AD ConversionEnrique Tejada GameroNo ratings yet
- Photonics: Engineering Multi-Section Quantum Cascade Lasers For Broadband TuningDocument6 pagesPhotonics: Engineering Multi-Section Quantum Cascade Lasers For Broadband TuningJorge Ernesto Ojeda ChavezNo ratings yet
- TT - Ultrashort Laser PulsesDocument19 pagesTT - Ultrashort Laser Pulsesbiomed41No ratings yet
- Needed Works Ss ADocument7 pagesNeeded Works Ss AdalvirphotonNo ratings yet
- BrukerDocument33 pagesBrukeridhem1110No ratings yet
- Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing-BLUESTARDocument93 pagesPhased Array Ultrasonic Testing-BLUESTARLương Hồ Vũ100% (3)
- Design and Test of Fast Laser Driver Circuits: White PaperDocument10 pagesDesign and Test of Fast Laser Driver Circuits: White PaperdemononesNo ratings yet
- PreamplifiersDocument2 pagesPreamplifiersTintu ViswamNo ratings yet
- Scan Speak 12m Revelator - SpecsDocument2 pagesScan Speak 12m Revelator - SpecsVlad GrigoreNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Beam Fromation 2009Document13 pagesUltrasound Beam Fromation 2009scuby660No ratings yet
- Compact 20 W Femtosecond Laser System Based On Fiber Laser Seeder, Yb:YAG Rod Amplifier and Chirped Volume Bragg Grating CompressorDocument7 pagesCompact 20 W Femtosecond Laser System Based On Fiber Laser Seeder, Yb:YAG Rod Amplifier and Chirped Volume Bragg Grating CompressorLaurynas VeselisNo ratings yet
- 7 6ESAdsDocument12 pages7 6ESAdsSandro Omar Lizano GuzmanNo ratings yet
- High Power Antenna Design For Lower Hybrid Current Drive in MSTDocument1 pageHigh Power Antenna Design For Lower Hybrid Current Drive in MSTIon PusculitaNo ratings yet
- Application of LIGO Technology To Biomedical OpticsDocument17 pagesApplication of LIGO Technology To Biomedical OpticsOh NaniNo ratings yet
- Chip-Scale Absolute Scalar Magnetometer For Space ApplicationsDocument2 pagesChip-Scale Absolute Scalar Magnetometer For Space ApplicationsDoceigenNo ratings yet
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignFrom EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignNo ratings yet
- EnvirobotDocument17 pagesEnvirobotnanoteraCH100% (1)
- OpenSense IIDocument27 pagesOpenSense IInanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Flusi TexDocument24 pagesFlusi TexnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- ShineDocument18 pagesShinenanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Heat ReservesDocument15 pagesHeat ReservesnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- The Future of Computing Robotizing The World!: MontreuxDocument41 pagesThe Future of Computing Robotizing The World!: MontreuxnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound To GoDocument16 pagesUltrasound To GonanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Optimization: Is A Keyword in CPS DesignDocument7 pagesOptimization: Is A Keyword in CPS DesignnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Panel On Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) : Prof. David Atienza, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne (EPFL)Document5 pagesPanel On Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) : Prof. David Atienza, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne (EPFL)nanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Emerging Computing Paradigms: The Case of Neuromorphic PlatformsDocument21 pagesEmerging Computing Paradigms: The Case of Neuromorphic PlatformsnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Carbon Nanotube Computing: Subhasish Mitra Collaborator: H.-S. Philip WongDocument50 pagesCarbon Nanotube Computing: Subhasish Mitra Collaborator: H.-S. Philip WongnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Panel QuestionsDocument14 pagesPanel QuestionsnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Panel On Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) : Prof. David Atienza, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne (EPFL)Document5 pagesPanel On Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) : Prof. David Atienza, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne (EPFL)nanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Deploying Iot To Enable Cyberphysical SystemsDocument9 pagesDeploying Iot To Enable Cyberphysical SystemsnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Pla Orms For CPS - Adap9ve, Predictable and e CientDocument10 pagesPla Orms For CPS - Adap9ve, Predictable and e CientnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Local Learning Capabili - Es Will Lead To A Breakthrough of Brain - Inspired Compu - NGDocument11 pagesLocal Learning Capabili - Es Will Lead To A Breakthrough of Brain - Inspired Compu - NGnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Nothing Is More Practical Than Hardware Based Security: Securing Physical SystemsDocument7 pagesNothing Is More Practical Than Hardware Based Security: Securing Physical SystemsnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Universityx: Data Driven Science in Education and ResearchDocument7 pagesUniversityx: Data Driven Science in Education and ResearchnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Neuromorphic Technologies: Next-Generation Cognitive ComputingDocument13 pagesNeuromorphic Technologies: Next-Generation Cognitive ComputingnanoteraCHNo ratings yet
- Pricelist Hicell Ongrid & HybridDocument2 pagesPricelist Hicell Ongrid & HybridauliaNo ratings yet
- Best Research Cell Efficiencies.20200925Document1 pageBest Research Cell Efficiencies.20200925عبدالرحمن سعدNo ratings yet
- Future Scope of Dual Axis Solar Tracking SystemDocument1 pageFuture Scope of Dual Axis Solar Tracking SystemArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dataseet Resun - Rsm100p - 100wDocument2 pagesDataseet Resun - Rsm100p - 100wzitrofjNo ratings yet
- TUV SUD Certificate Double Glass New Standard 488a1e03caDocument3 pagesTUV SUD Certificate Double Glass New Standard 488a1e03caStefan BusoiNo ratings yet
- Laser TechnologyDocument10 pagesLaser TechnologyPratik RaneNo ratings yet
- Arduino Solar TrackerDocument20 pagesArduino Solar TrackerANJALINo ratings yet
- Design of A Solar PV SystemDocument46 pagesDesign of A Solar PV SystemGokulNo ratings yet
- DigitalDocument3 pagesDigitalSoumyajyoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Land Use Services Department: Building & Safety DivisionDocument1 pageLand Use Services Department: Building & Safety DivisionJesusSQANo ratings yet
- M.E Ped - R2017 - X86077 (PS5092)Document2 pagesM.E Ped - R2017 - X86077 (PS5092)MR.R. JEBA RAJNo ratings yet
- Application of SPVDocument8 pagesApplication of SPVTushar SanwareyNo ratings yet
- Why Is Solar Cell Efficiency Low - GreentumbleDocument15 pagesWhy Is Solar Cell Efficiency Low - Greentumblevihan shahNo ratings yet
- Simulation PvsystDocument6 pagesSimulation PvsystSafae Ait madanNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of MPPT Control of Grid Connected Inverter For PV SystemDocument15 pagesModelling and Simulation of MPPT Control of Grid Connected Inverter For PV SystemRam Kumar GogadaNo ratings yet
- Solar ShinglesDocument17 pagesSolar ShinglesBiyenta ElijahNo ratings yet
- SLD PDFDocument1 pageSLD PDFelectromec technologyNo ratings yet
- Chitendai LTD Iradiance Vs Silicon Solar PanelDocument4 pagesChitendai LTD Iradiance Vs Silicon Solar PanelRamon CuevasNo ratings yet
- Approved Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter ListDocument12 pagesApproved Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Listibrahim AdıbelliNo ratings yet
- IQ Field Wireable Connectors E486079 UL CERT EN USDocument1 pageIQ Field Wireable Connectors E486079 UL CERT EN USEric WilsonNo ratings yet
- Active Creation Long An - 3d&pvsyst - 22.12.23Document19 pagesActive Creation Long An - 3d&pvsyst - 22.12.23Ngân Diệp NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Laser by Orazio SveltoDocument16 pagesLaser by Orazio SveltoArkayan Laha100% (1)
- Distributed Feedback Lasers: Mike Huang EE 290F February 17, 2004 (Tuesday)Document29 pagesDistributed Feedback Lasers: Mike Huang EE 290F February 17, 2004 (Tuesday)urimNo ratings yet
- Maysun Solar CatalogueDocument3 pagesMaysun Solar CatalogueHaiducul DelteiNo ratings yet
- Solar PV Lecture Note 1upDocument4 pagesSolar PV Lecture Note 1upsrnwsdbNo ratings yet
- Cebu Solar Panels PricesDocument3 pagesCebu Solar Panels PricesCarlo Ibrahim MaderazoNo ratings yet
- Details of Solar Power Project, April-2021Document1 pageDetails of Solar Power Project, April-2021Aliyana ShresthaNo ratings yet
- LasersDocument173 pagesLasersCompengtech DeptNo ratings yet
- Garbuzov1996 - High Power Separate Confinement Heterostructure Algaas-Gaas Laser Diodes With Broadened WaveguideDocument7 pagesGarbuzov1996 - High Power Separate Confinement Heterostructure Algaas-Gaas Laser Diodes With Broadened WaveguideJun LimNo ratings yet
- Four-Junction Wafer-Bonded Concentrator Solar CellsDocument7 pagesFour-Junction Wafer-Bonded Concentrator Solar CellsFerdi PratamaNo ratings yet