Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharm 2 Test
Pharm 2 Test
Uploaded by
Jaime Hayes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views7 pages1) CNS stimulants like Ritalin and Daytrana are used to treat ADHD and related conditions. They can cause insomnia, restlessness, weight loss, and cardiovascular or psychotic symptoms as side effects.
2) Strattera is a norepinephrine selective reuptake inhibitor used to treat ADHD with fewer side effects than stimulants. It can cause appetite suppression, weight loss, GI issues, and suicidal ideation in children and adolescents.
3) Risperdal is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat psychotic disorders and related conditions. It can cause weight gain, metabolic changes, and movement or cardiovascular side effects.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) CNS stimulants like Ritalin and Daytrana are used to treat ADHD and related conditions. They can cause insomnia, restlessness, weight loss, and cardiovascular or psychotic symptoms as side effects.
2) Strattera is a norepinephrine selective reuptake inhibitor used to treat ADHD with fewer side effects than stimulants. It can cause appetite suppression, weight loss, GI issues, and suicidal ideation in children and adolescents.
3) Risperdal is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat psychotic disorders and related conditions. It can cause weight gain, metabolic changes, and movement or cardiovascular side effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views7 pagesPharm 2 Test
Pharm 2 Test
Uploaded by
Jaime Hayes1) CNS stimulants like Ritalin and Daytrana are used to treat ADHD and related conditions. They can cause insomnia, restlessness, weight loss, and cardiovascular or psychotic symptoms as side effects.
2) Strattera is a norepinephrine selective reuptake inhibitor used to treat ADHD with fewer side effects than stimulants. It can cause appetite suppression, weight loss, GI issues, and suicidal ideation in children and adolescents.
3) Risperdal is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat psychotic disorders and related conditions. It can cause weight gain, metabolic changes, and movement or cardiovascular side effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
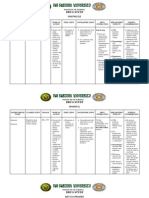
CNS Stimulants
Ritalin: Short acting
Daytrana: (transdermal) Long acting
PURPOSE: ADHD
Conduct Disorder
SE: CNS Stimulation (Insomnia, Restlessness)
Weight Loss
Cardiovascular Effect
Development of psychotic symptoms such as hallucination and paranoid.
Withdrawal reaction
Hypersensitivity skin
CONTRAINDICATED: History of drug abuse, cardiovascular disease
severe anxiety and psychosis
INTERACTIONS: MAOI can cause hypertensive crisis, OTC cold and decongestant
can increase
CNS.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Do not crush or chew take whole tablet.
Take daily
Place patch on hip daily in morning and don't leave
longer than 9 hours, alternate hip.
Controlled by Federal law, refill require handwritten
RX
High potential for abuse.
Norepinephrine Selective Reuptake Inhibiter
Strattera:
PURPOSE: ADHD (tolerated well with minimal SE)
SE: Appetite suppression, weight loss, growth suppression
GI effects Nausea and vomiting
Suicidal ideation (children and Adolescent)
Hepatotoxicity
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Cautiously with cardiovascular disorders
INTERACTIONS: MAOI can cause hypertensive crisis
Paxil, Prozac, and quinidine can increase levels of atomoxetine
NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Takes about 1 week to full develop.
Antipsychotics- Atypical
Risperal
PURPOSE: PDD pervasive development disorders
decrease autistic disorder
conduct disorders
PTSD
Relief of psychotic symptoms
SE: Onset of diabetes or loss of glucose control in clients with diabetes
weight gain hypercholesterolemia ( risk for hypertension and other cardiovascular
disease
Orthostatic
Anticholinergic
Agitation, dizziness, sedation, sleep disruption
Mild EPY such as tremors
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Avoid alcohol
Cautiously used with cardiovascular disease, seizures or DM
(obtain baseline on fasting glucose for diabetic
patients)
INTERACTIONS: Alcohol, opoids, and antihistamine cause CNS depression
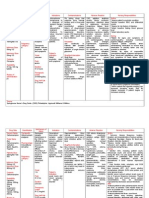
BARBITURATES (dilatin)
Diflucan
NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Give low dose and then gradually increase
Medications to support
Withdrawal/Abstienence from Alcohol
detox: Benzodiazepine: Librium
PURPOSE: Client vital sign within expected reference range
decrease in the risk of seizure and delirium tremors
decrease in the intensity of symptoms
Adjunct medication
following Detox:
Tegretol
PURPOSE: Decrease in seizures
Abstinenece Maintenance
Antabuse:
PURPOSE: Oral type of aversion (behavioral therapy)
if use with alcohol will cause Acetaldehyde Syndrome
N/V weakness, sweating, palpitations and hyportnesion
Acetaldehyde syndrome can progress to respiratory depression,
cardiovascular suppression, seizure and death.
reVial
PURPOSE: Pure opioid antagonist that suppresses the craving and pleasurable
effects of alcohol
(also used for opioid withdrawal)
Campral
PURPOSE: decrease unpleasant effects resulting from abstinence (anxiety and
restlessness)
Medications to support withdrawal
Abstinence from Opoids
Catapress and Narcan
PURPOSE Opioid overdose
Assist with withdrawal of symptoms related to autonomic
hyperactivity (diarrhea, N/V)
Does not reduce the craving for opioids.
Mdications to support withdrawal
Abstinence from Nicotine
Wellbutrin
PURPOSE decrease nicotine craving with symptom withdrawal
Cholinsesterase inhibitors
Prostigmin
PURPOSE: treatment of maysthenia gravis (abnormal weakness of certain muscle)
Reversal of non depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents
SE: increase GI secretion
Bradycardia excessive muscarinic stimulation which cause
cholinergic
Urinary Urgency crisis
CONTRAINDICATION: with obstruction of GI & GU (genitourinary)
peptic ulcer, asthma and coronary insuffiency
INTERACTION: Atropine
Succinylcholine increase neuromuscular blockade
NURSING INTERVENTION: PO, IM, IV and Subcutaneously
Start low does and titrated until desired muscle
function is achieve Recognize signs of inadequate dosing
such as difficulty swallowing
or signs of overmedicated such as urinary
urgency
Advise clients to wear medical bracelet
Anti-parkinson medication
dopaminergics: levodopa or carbidopa (sinemet)
PURPOSE: Parkinson (usually dose dependent)
1st line of PD treatment
SE: N/V
dyskinesia (head tremors)
orthostatic
cardiovascular
psychosis (hallucinations, nightmares)
discoloration of sweat & urine
Activation of malignant melanoma
CARBIDOPA
SE: Abnormal movements of psychiatric disorders
heart disease
psychiatric disorder in older clients
INTERACTION: proteins interefere
conventional antipsychotic (haldol)
pyridoxine (vit B)
MAOI (Hypertensive crisis)
Carbidopa, dopamine &anticholinergics increase levels of rx
Dopamine agonists: Pramipede (mirapex)
PURPOSE: Parkinson disease
SE: sudden inability to stay awake
daytime sleepiness
orthostatic
psychosis
Dyskinesias (head throbbing)
Nausea
CONTRAINDICATIONS: In clients with liver and kidney impairment
INTERACTIONS: Used with levodopa can decrease motor control fluctuation and
allow lower dosage of levodopa
NURSING INTERVENTIONS: effects may not be noticeable for several weeks to
several months
Instruct patient that a medication"holiday" may be
prescribed but
will take place in a inpatient setting
Antiepileptic (AEDS)
Pheytoin (dilantin)
PURPOSE: control seizure
use for all form of epilepsy except absence seizure
use IV route
use dysrhythmias with QT prolong action
CONTRAINDICATIONS: With sinus bradycardia SA blocks 2nd & 3rd AV block or
stocks adam syndrome
SE: CNS effects (nystagmsu, sedation, ataxia, cognitive impairment, double vision
Gingival hyperplasia
Skin rash
Teratogenic
Endocrine (causing of facial features, hirsutism & interfere with Vit D.
INTERACTIONS: decrease coumadin and glucorticoids
Alcohol, Valium, tagament & depakote decrease phenytoin levels
carbamazepin (tegretol)
PURPOSE: Use for treatment of partial (simple & complex seizures) tonic clonic
seizure bipolar
disorder and trigeminal and glosspharngeal neuralgias
SE: cognitive function is minimal affected but CNS effect can occur
Blood dyscrasias );eukopenia, anemia, throbocytopenia)
Hypo-osmolarity (promotes secretion of ADH which inhibits water excretion by
kidneys and places clients who have heart failure at risk for fluid overload
skin disorders
CONTRAINDICATIONS: With Bone marrow or bleeding disorders
INTERACTIONS: decrease effects of oral contraceptives and coumadin because of
stimulation of hepatic drug metabolize enzyme
grapefruit
pheyntoin and phenobarbital decrease tegretol
ethosuximide (zarontin)
PURPOSE: Use only for absence seizure
SE: GI effects (N/V)
Valproic acid (depakote)
PURPOSE: use for partial generalized and absentce seizure, bipolar disorder and
migraine headaches
SE: GI effects
hepatoxixity (anorexia, abdominal pain, jaundice)
pancreatitis (N/V and abdominal pain)
throbocytopenia
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Patients with liver disorder and children less than 3yrs of age
INTERACTIONS: Concurrent use with valproic acid increase the levels of phenytoin
and phenobarbital.
Non- selective Beta-adrenergic Blockers
Timolol
PURPOSE: Decrease IOP
treatment of POAG
SE: Temporary stinging and discomfort
Occasinal conjuctivitits, blurred vision photophobia, and dry eyes
Systmeic effects of Beta blockade on heart and lungs may occur
CONTRAINDICATION: Bradycardia
heart block
Cautiously in clients who have heart failure
INTERACTION: Calcium channel blockers can increase cardiovascular and
respiratory effects
interfere with some insulin
NURSING: Hold gentle pressure on nasolacrimal duct for 30 to 60 seconds
immediately after i nstilling any expected systemic effect
monitor pulse rate
Second line topical for glaucoma
Carbonic anhydrage inhibitor
dorzolamide (trust Both increase effects works better
Timolol (Cosopt)
SE: Allergic reaction in 15% of clients
Blurred vision
Dryness
Photophobia
osmotic agents
Mannitol (osmitrol IV)
Purpose: treat rapid progression of angle-closure glaucoma to prevent blindness
You might also like
- ATI FinalPharmacologyDocument7 pagesATI FinalPharmacologyClaudia Manning100% (17)
- Pharmacology ChartDocument6 pagesPharmacology ChartPaula67% (3)
- Cardiac Med ChartsDocument6 pagesCardiac Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (15)
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaNo ratings yet
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureDocument31 pagesOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420No ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument1 pageAnalgesicsPaul AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Analgesics: (Vistaril, Atarax), Promethazine (Phenergan, Etc)Document5 pagesAnalgesics: (Vistaril, Atarax), Promethazine (Phenergan, Etc)jhjNo ratings yet
- Medications For The ElderlyDocument8 pagesMedications For The ElderlyShawn TaylorNo ratings yet
- HaldolDocument6 pagesHaldolJon ChuaNo ratings yet
- Anticonvulsants NotesDocument19 pagesAnticonvulsants NotesPIRENANo ratings yet
- Drug ListDocument30 pagesDrug ListKristineNo ratings yet
- Pharma Nervous Day 2Document76 pagesPharma Nervous Day 2Nhelia Santos BañagaNo ratings yet
- NociceptionDocument8 pagesNociceptionfootballjeinNo ratings yet
- Pharm Review For Hesi From JanaDocument8 pagesPharm Review For Hesi From Janacheyenne.black5205100% (1)
- Psychotropic Medication ReviewDocument7 pagesPsychotropic Medication ReviewAakash Shah100% (1)
- Neurological Pharmacology PresentationDocument49 pagesNeurological Pharmacology PresentationAmit MartinNo ratings yet
- Alpha 1 Blocker: Obstruction and Relieving Effects of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHDocument21 pagesAlpha 1 Blocker: Obstruction and Relieving Effects of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHKaylee LengNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument13 pagesDrugsChristine UdhayNo ratings yet
- CardiotonicsDocument21 pagesCardiotonicsmohsen mirdamadiNo ratings yet
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Drug Cards 2Document6 pagesDrug Cards 2p_dawgNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument84 pagesPsychopharmacologyKhyra Ysabelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- ICU Pharmacology: Sean Forsythe M.D. Assistant Professor of MedicineDocument52 pagesICU Pharmacology: Sean Forsythe M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicinecoolboy1990No ratings yet
- Generic Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse and Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse and Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationsimthebossNo ratings yet
- Medications NHBDocument40 pagesMedications NHBAnonymous 7hJgATNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic Drugs: Pam Pam LamDocument7 pagesPsychotherapeutic Drugs: Pam Pam Lamchubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Pain Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- High Ceiling Loop Diuretics Thiazides and Realted DiureticsDocument3 pagesHigh Ceiling Loop Diuretics Thiazides and Realted DiureticsDaphne GoreNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneDocument28 pagesAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoeNo ratings yet
- Therabloc DrugDocument2 pagesTherabloc DrugMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- RUSS Emergency DrugDocument6 pagesRUSS Emergency DrugKat BausaNo ratings yet
- ICU Pharmacology: Sedatives Analgesics Paralytics PressorsDocument51 pagesICU Pharmacology: Sedatives Analgesics Paralytics Pressorsdevi trismiaNo ratings yet
- 5 MG Iv BidDocument17 pages5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: POTASSIUM CHLORIDE Brand Name: MICRO K: Apo-Alpraz - XANAXDocument17 pagesGeneric Name: POTASSIUM CHLORIDE Brand Name: MICRO K: Apo-Alpraz - XANAXJoane LacapNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- DrugQuiz 1bDocument4 pagesDrugQuiz 1bDorothy ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Pain Medications: Dr. Ave Olivia Rahman, Msc. Bagian Farmakologi Fkik UnjaDocument49 pagesPain Medications: Dr. Ave Olivia Rahman, Msc. Bagian Farmakologi Fkik UnjaHawa Ambarwati100% (1)
- Sympatholytic DrugsDocument20 pagesSympatholytic DrugsAudrey Beatrice Reyes100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument70 pagesDrug Studyjahmaicao50% (2)
- Drugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument7 pagesDrugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationPrincess Jenelly CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug General Action Specific Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageName of Drug General Action Specific Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesNicole SooNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Blocking, Cholinergic, Sedatives and Hypnotic WORDDocument5 pagesAdrenergic Blocking, Cholinergic, Sedatives and Hypnotic WORDKeon RicoNo ratings yet
- Ing GrisDocument9 pagesIng GrisKaerud ZamanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudySuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- Pharm Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesPharm Exam ReviewAshleyNo ratings yet
- Neuro3: Study Online atDocument3 pagesNeuro3: Study Online atcharitoaveNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: CardiacDocument36 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: CardiacHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- 1ST Drug StudyDocument10 pages1ST Drug Study황춘히No ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument7 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsFatima Asim 922-FSS/BSPSY/F17No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Resurrection University Medication CardDocument2 pagesResurrection University Medication CardBohung ConNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocument36 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studytamtam_antonioNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: Complications of Diabetes: The most important information you need to improve your healthFrom EverandDiabetes: Complications of Diabetes: The most important information you need to improve your healthNo ratings yet
- DNRS 6630 Final Exam Week 11 February.Document20 pagesDNRS 6630 Final Exam Week 11 February.Sandra JeffersonNo ratings yet
- Facultad de Psicología: Universidad Anáhuac México Campus NorteDocument4 pagesFacultad de Psicología: Universidad Anáhuac México Campus NorteJaneth GmNo ratings yet
- Atomoxetine Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesAtomoxetine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Uncrc AdhdDocument20 pagesUncrc AdhdKelley Dobson-SmithNo ratings yet
- Halter: Varcarolis' Foundations of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing: A Clinical Approach, 8th EditionDocument5 pagesHalter: Varcarolis' Foundations of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing: A Clinical Approach, 8th EditionKristinelou Marie N. ReynaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia-NPRA List of Comparator Products For Bioequivalence Studies December 2015Document47 pagesMalaysia-NPRA List of Comparator Products For Bioequivalence Studies December 2015Noples RozaliaNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesQuick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFAaron ShokarNo ratings yet
- Neuropharmacology: Jay S. Schneider, Sandhya KortagereDocument11 pagesNeuropharmacology: Jay S. Schneider, Sandhya KortageregustavoNo ratings yet
- Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in Adhd Neurodevelopment and Pharmacological Implications 505Document14 pagesGlutamatergic Neurotransmission in Adhd Neurodevelopment and Pharmacological Implications 505Petrut BiligaNo ratings yet
- 2022 FL FormularyDocument174 pages2022 FL FormularyJay SteeleNo ratings yet
- Adult ADHD - What Do When Your First Drug Fails - Dr.-James-LazowskiDocument77 pagesAdult ADHD - What Do When Your First Drug Fails - Dr.-James-LazowskiJason WongNo ratings yet
- Attention Deficit Hyper-Activity Disorders (ADHD) : Prepare By: Jumana AlmomaniDocument30 pagesAttention Deficit Hyper-Activity Disorders (ADHD) : Prepare By: Jumana AlmomaniJanuaryNo ratings yet
- ADHD PresentationDocument21 pagesADHD PresentationZainab Ali HassanNo ratings yet
- Medication - Chart ADHD PDFDocument2 pagesMedication - Chart ADHD PDFaayceeNo ratings yet
- Amphetamine Positive Urine Toxicology Screen SecoDocument1 pageAmphetamine Positive Urine Toxicology Screen SecoJonathan FishbeckNo ratings yet
- 191thmeeting (R I)Document20 pages191thmeeting (R I)Syed Ayaz Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderDocument42 pagesAttention Deficit Hyperactivity DisordermengakuNo ratings yet
- Atomoxetine in ADHD in Children With and Without Comorbid Mood DisordersDocument10 pagesAtomoxetine in ADHD in Children With and Without Comorbid Mood DisordersNeuro GYMNo ratings yet
- PG19Document22 pagesPG19Nabila ChakourNo ratings yet
- AdhdDocument2 pagesAdhdAlexander SaladinNo ratings yet
- DCC 233 MinutesDocument35 pagesDCC 233 Minutesproduction.avaroxpharmabdNo ratings yet
- Atomoxetine - STRATTERA® (Monography)Document22 pagesAtomoxetine - STRATTERA® (Monography)Max PowellsNo ratings yet
- ADHD in MalaysiaDocument67 pagesADHD in MalaysiaHaz100% (1)
- Mechler - 2022 - Evidence-Based Pharmacological Treatment Options For ADHD in Children and AdolescentsDocument11 pagesMechler - 2022 - Evidence-Based Pharmacological Treatment Options For ADHD in Children and AdolescentsRene LutherNo ratings yet
- DBD Chapter 23 PsychiaDocument29 pagesDBD Chapter 23 PsychiaTrixie Myr AndoyNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Final Exam NURS 6630N ..Document17 pagesWeek 11 Final Exam NURS 6630N ..troillerdrippyNo ratings yet
- Medication Information For Parents and Teachers: Atomoxetine-StratteraDocument8 pagesMedication Information For Parents and Teachers: Atomoxetine-StratteraMonique WrightNo ratings yet
- 1a2fb7bf1049ac79371db6838638e95dDocument8 pages1a2fb7bf1049ac79371db6838638e95dLavinia DragalauNo ratings yet
- Everything You Wanted To Know About ADHD But Forgot You Wanted To AskDocument76 pagesEverything You Wanted To Know About ADHD But Forgot You Wanted To AskPola PremNo ratings yet
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of AdhdDocument116 pagesThe Diagnosis and Treatment of AdhdrajvolgaNo ratings yet