Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summer 1996 CH1: Element Na MG Al Si P S
Summer 1996 CH1: Element Na MG Al Si P S
Uploaded by
Sumaira AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summer 1996 CH1: Element Na MG Al Si P S
Summer 1996 CH1: Element Na MG Al Si P S
Uploaded by
Sumaira AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Summer 1996 CH1
1.
From the position of radium in the Periodic Table, predict the following:
(a)
the formula of radium carbonate;
....................................................................................................................................
(b)
the equation for the thermal decomposition of solid radium carbonate;
....................................................................................................................................
(c)
how the decomposition temperature required in (d)(ii) would compare with that required
for magnesium carbonate.
....................................................................................................................................
(Total 4 marks)
2.
From the position of radium in the Periodic Table, predict the following:
(a)
the formula of radium carbonate;
................................................................................................................
(b)
the equation for the thermal decomposition of solid radium carbonate;
................................................................................................................
(c)
how the decomposition temperature required in (d)(ii) would compare with that required
for magnesium carbonate.
................................................................................................................
(Total 4 marks)
3.
(a)
In the table below, give the formulae of the chlorides of the elements of Period 3, other
than silicon.
Element
Na
Mg
Al
Formula of
chloride
Si
SiCl 4
(2)
(b)
Calculate the percentage by mass of silicon in silicon tetrachloride.
(2)
(c)
(i)
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the bonding in silicon tetrachloride.
www.XtremePapers.net
www.xtremepapers.net
Summer 1996 CH1
(ii)
Draw the shape of this molecule.
Explain your answer in terms of the Electron Pair Repulsion Theory.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(iii)
State the shape of a molecule of AlCl3 and explain why it is different from
that of SiCl4.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(6)
(d)
(i)
Give an equation of the reaction of SiCl4 with cold water.
..........................................................................................................................
(ii)
How does the behaviour of carbon tetrachloride with cold water compare with this?
Explain any differences.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 14 marks)
4.
In the table below, give the formulae of the chlorides of the elements of Period 3, other
than silicon.
Element
Na
Mg
Al
Formula of
chloride
Si
SiCl 4
(2)
5.
Calculate the percentage by mass of silicon in silicon tetrachloride.
(2)
6.
(a)
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the bonding in silicon tetrachloride.
2
www.XtremePapers.net
www.xtremepapers.net
Summer 1996 CH1
(b)
Draw the shape of this molecule.
Explain your answer in terms of the Electron Pair Repulsion Theory.
................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
(c)
State the shape of a molecule of AlCl3 and explain why it is different from that of SiCl4.
................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
(Total 6 marks)
7.
(a)
Give an equation of the reaction of SiCl4 with cold water.
................................................................................................................
(b)
How does the behaviour of carbon tetrachloride with cold water compare with this?
Explain any differences.
................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
(Total 4 marks)
8.
(a)
Give the electronic configuration of the following ions.
4s
3d
Fe
2+
(Ar)
Fe 3+ (Ar)
(2)
www.XtremePapers.net
www.xtremepapers.net
Summer 1996 CH1
(b)
Give the formula and name of the metal-containing ion formed when iron(II) chloride is
dissolved in water. State the shape of this ion.
Formula: ....................................................................................................................
Name: ........................................................................................................................
Shape: ........................................................................................................................
(3)
(c)
(i)
Describe what you would observe if dilute sodium hydroxide is added to the
solution in (c).
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(ii)
Give an equation for this reaction and state the type of reaction occurring.
Equation: ........................................................................................................
Type of reaction: ............................................................................................
(4)
(d)
(i)
What further change would you observe if the product from (d)(i) was allowed to
stand in air?
..........................................................................................................................
(ii)
What type of reaction is occurring in this change?
..........................................................................................................................
(iii)
Explain briefly, in the light of your answer to (a), why you might expect this
reaction to occur.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 13 marks)
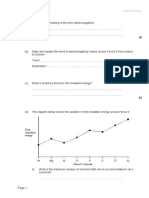
9.
A solution of a week acid H2X was made by dissolving 2.25g of solid H2 X in water to give 500
cm3 of solution. On titration, 25.0cm3 of this solution was completely neutralised by 25.0 cm3
of sodium hydroxide solution containing 0.100 mol dm3.
(a)
Write an equation for the reaction.
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
(i)
Calculate the number of moles of NaOH in 25.0 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm3 solution.
....................................................................................................................................
www.XtremePapers.net
www.xtremepapers.net
Summer 1996 CH1
(ii)
How many moles of H2X would be required to react with this quantity of NaOH?
..........................................................................................................................
(iii)
Calculate the relative molecular mass of H2X.
(iv)
A hydrated form of the acid also exists, H2X.yH2O. A solution containing
6.30 g dm3 of the hydrated acid has the same (molar) concentration as the solution
of the anhydrous acid, H2X, originally used. Using this information and your
answer from (b), calculate the value of y.
(8)
(c)
The presence of sulphur dioxide in the atmosphere is the main cause of acid rain. Outline
a method which could be used to estimate quantitatively the concentration of sulphur
dioxide in a sample of air.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(5)
(Total 14 marks)
www.XtremePapers.net
www.xtremepapers.net
You might also like
- Disc Behavior SurveyDocument5 pagesDisc Behavior Surveynhadsall100% (7)
- Professionalism and Transformative Education: in This Module 1. The 21 Century TeacherDocument38 pagesProfessionalism and Transformative Education: in This Module 1. The 21 Century TeacherNormina Cagunan100% (5)
- NMR Booklet QuestionsDocument21 pagesNMR Booklet QuestionsSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 9701 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2022)Document149 pages9701 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2022)Sumaira AliNo ratings yet
- An International Baccalaureate Education For AllDocument7 pagesAn International Baccalaureate Education For AllLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- UdkdfhvkdhfnfDocument12 pagesUdkdfhvkdhfnfG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - The Alkaline Earth Metals 1 QPDocument8 pagesGroup 2 - The Alkaline Earth Metals 1 QPWilliam TsuiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 U2 Chem RedoxDocument34 pagesAssignment 4 U2 Chem RedoxMoshiurNo ratings yet
- Water and HydrogenDocument7 pagesWater and HydrogenOkumu KevinsNo ratings yet
- 2.4 2.5 2.6 Assessed HomeworkDocument7 pages2.4 2.5 2.6 Assessed HomeworkRabia Rafique100% (1)
- F321 Module 3 Practice 1Document10 pagesF321 Module 3 Practice 1coughsyrup123No ratings yet
- As Chemistry Unit 1 Atomic Structure TestDocument10 pagesAs Chemistry Unit 1 Atomic Structure TestJuilo100% (1)
- AQA C2 Past Paper Q&A Part 1Document184 pagesAQA C2 Past Paper Q&A Part 1Junaid AsgharNo ratings yet
- Shapes of Ions and Molecules AsDocument17 pagesShapes of Ions and Molecules Asalvin2282No ratings yet
- Periodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 1 QPDocument13 pagesPeriodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 1 QPmalakNo ratings yet
- Cons. of Mass, Chemical Measurements - Eqns 2 QPDocument18 pagesCons. of Mass, Chemical Measurements - Eqns 2 QPHusain KamaliNo ratings yet
- 2.4, 2.5, 2.6 TestDocument7 pages2.4, 2.5, 2.6 Testzafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- S6 Aceiteka 2023 Chemistry P1Document16 pagesS6 Aceiteka 2023 Chemistry P1kundukefa25No ratings yet
- Metals - Form 4 Chemistry Topical QuestionsDocument13 pagesMetals - Form 4 Chemistry Topical QuestionsEmmanuel KipyegonNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom and The Periodic Table Chemistry Form 2 Topical Questions and AnswersDocument27 pagesStructure of The Atom and The Periodic Table Chemistry Form 2 Topical Questions and Answersdonaldsonvincent9No ratings yet
- 2 HoursDocument17 pages2 HoursOTTO OLIMANo ratings yet
- Amount of SubstanceDocument13 pagesAmount of Substanceyahvip07No ratings yet
- Quiz - 1 - Matter & StoichiometryDocument4 pagesQuiz - 1 - Matter & StoichiometryDaniel Ngenokesho WandyaNo ratings yet
- Q1. (A) State The Meaning of The Term ElectronegativityDocument97 pagesQ1. (A) State The Meaning of The Term ElectronegativityfaizNo ratings yet
- Test 0902Document4 pagesTest 0902Nav MehrganNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 2 QPDocument7 pagesIonic Bonding 2 QPHuseyn AgazadeNo ratings yet
- As-Level Paper 1 Pp12Document16 pagesAs-Level Paper 1 Pp12faith mNo ratings yet
- Mixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionDocument23 pagesMixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionYaakkwNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 15Document26 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 15Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Metal p4 Ws 4Document10 pagesMetal p4 Ws 4NonnoonoNo ratings yet
- S.3 Chem Test OneDocument2 pagesS.3 Chem Test OneW. Joseph the chemistNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument9 pagesAlkanesyahvip07No ratings yet
- Form 4 Notes v1.0Document45 pagesForm 4 Notes v1.0prospire embeleNo ratings yet
- Compounds Containing The Carbonyl Group QuestionsDocument69 pagesCompounds Containing The Carbonyl Group QuestionsmarvellousadenugaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesChemical BondingnNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 8Document9 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 8Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- As-Level Paper 1 pp9Document15 pagesAs-Level Paper 1 pp9ConorNo ratings yet
- Periodicity Past QuestionsDocument17 pagesPeriodicity Past QuestionsMohammad KhanNo ratings yet
- C2 Structures and Bonding IntermediateDocument13 pagesC2 Structures and Bonding IntermediatedownendscienceNo ratings yet
- January 2022Document12 pagesJanuary 2022Issei SenpaiNo ratings yet
- Gcse Basics 2: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 09-March-2020 Chemsheets AS 1226 1Document4 pagesGcse Basics 2: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 09-March-2020 Chemsheets AS 1226 1Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Group 7Document9 pagesTopic 4 - Group 7Abirame SivakaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsAmanda AnushaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Mid Exam 2019Document12 pagesClass 10 Mid Exam 2019Khalid HassanNo ratings yet
- Types of Reactions WsDocument2 pagesTypes of Reactions WsTomáš Tommy NagyNo ratings yet
- A-Level Paper 3 pp8Document19 pagesA-Level Paper 3 pp822S48 SUNDARAM RAMASUBBU RAKSHANo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 2Document7 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 2Asif ArmanNo ratings yet
- Mytest 1Document8 pagesMytest 1Aditi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 21Document15 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 21Maama PhionaNo ratings yet
- Y10 FF Revision - RecapDocument5 pagesY10 FF Revision - RecaprevansNo ratings yet
- A2 Organic Book 1 2020Document231 pagesA2 Organic Book 1 2020bookworm12045No ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDocument16 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDumpsterFireGamingNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument14 pagesBondingMuizzudin AzaliNo ratings yet
- Chlorine and Its Compounds Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesChlorine and Its Compounds Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and Answersideal writersNo ratings yet
- Science FundamentalsDocument21 pagesScience FundamentalsAlberto MarcusNo ratings yet
- Igcse Acids, Bases and Salts PDFDocument10 pagesIgcse Acids, Bases and Salts PDFbilly ogadaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanisms 3 QPDocument7 pagesReaction Mechanisms 3 QPSiti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- Bonding - Structuce 3 QPDocument14 pagesBonding - Structuce 3 QPtertianerima101No ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Topic 6 - Redox, Group 2 and Group 7 Assessed HomeworkDocument10 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Topic 6 - Redox, Group 2 and Group 7 Assessed HomeworkSumathi GanasenNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 13Document17 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 13Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Chem Pp1 S.6Document17 pagesChem Pp1 S.6Ssendagala Joseph CollineNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2, 4.1.3 Exam QuestionsDocument9 pages4.1.2, 4.1.3 Exam QuestionsHyder OmarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Synthesis of Gold and Zirconia Nanoparticles and their CharacterizationFrom EverandAdvanced Synthesis of Gold and Zirconia Nanoparticles and their CharacterizationNo ratings yet
- Understanding Plastics Engineering Calculations: Hands-on Examples and Case StudiesFrom EverandUnderstanding Plastics Engineering Calculations: Hands-on Examples and Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- 10: Analysis - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument14 pages10: Analysis - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 8: Controlling Reactions 2 - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument11 pages8: Controlling Reactions 2 - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 9: Organic Chemistry 2 - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument9 pages9: Organic Chemistry 2 - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 7: Electricity and Metals - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument12 pages7: Electricity and Metals - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 5: Chemical Trends - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument10 pages5: Chemical Trends - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 3: Controlling Reactions 1 - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument16 pages3: Controlling Reactions 1 - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Crumbs From The Table of JoyDocument72 pagesCrumbs From The Table of JoySumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 2: Bonding and Structure - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument13 pages2: Bonding and Structure - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 9701 U4 Organic TQDocument17 pages9701 U4 Organic TQSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- NMR Booklet AnswersDocument13 pagesNMR Booklet AnswersSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Practice Test: Test 2 - Material From Chapters 5-8Document11 pagesSelf-Assessment Practice Test: Test 2 - Material From Chapters 5-8Sumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Practice Tests: © Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ChemistryDocument1 pageSelf-Assessment Practice Tests: © Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ChemistrySumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1054 AcylationDocument4 pagesChemsheets A2 1054 AcylationSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1055 AcylationDocument18 pagesChemsheets A2 1055 AcylationSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Elements and Compounds: Revision ChecklistDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Elements and Compounds: Revision ChecklistSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Practice Test: Test 1 - Material From Chapters 2-4Document11 pagesSelf-Assessment Practice Test: Test 1 - Material From Chapters 2-4Sumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Practice Test: Test 3 - Material From Chapters 9-12Document12 pagesSelf-Assessment Practice Test: Test 3 - Material From Chapters 9-12Sumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: © Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ChemistryDocument1 pageAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: © Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ChemistrySumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Hala International School: Class Assessment 1 - February 2016 Chemistry - Grade 9Document7 pagesHala International School: Class Assessment 1 - February 2016 Chemistry - Grade 9Sumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Harris1976 PDFDocument7 pagesHarris1976 PDFRoger RamosNo ratings yet
- ALBARRACÍN, Mauricio. Movilización Legal para El Reconocimiento de La Igualdad de Las Parejas Del Mismo Sexo".Document100 pagesALBARRACÍN, Mauricio. Movilización Legal para El Reconocimiento de La Igualdad de Las Parejas Del Mismo Sexo".malbarracin100% (2)
- Development CommunicationDocument11 pagesDevelopment CommunicationNishantNo ratings yet
- The Time of Jacobs TroubleDocument74 pagesThe Time of Jacobs TroubleReinventallnotions ZedNo ratings yet
- Faq PRP CebuDocument2 pagesFaq PRP CebuAllanSalardaAdemNo ratings yet
- ETE 1112 - Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocument27 pagesETE 1112 - Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualSabuj Ahmed100% (1)
- Industrial Training Unit Confidential: Form CDocument3 pagesIndustrial Training Unit Confidential: Form CFortnite College100% (1)
- What Is Breast CancerDocument20 pagesWhat Is Breast CancerKesyaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of A Multi-Link Suspension Mechanism With Compliant JointsDocument6 pagesDynamic Analysis of A Multi-Link Suspension Mechanism With Compliant JointsDhrubajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Faculty Industrial Attachment HandbookDocument15 pagesFaculty Industrial Attachment HandbookKeith Tanyaradzwa MushiningaNo ratings yet
- Labor Law Review Case Digest Duka - Book I To Book IIDocument24 pagesLabor Law Review Case Digest Duka - Book I To Book IINiñoMaurinNo ratings yet
- PDF Pozdravi Na SrpskomDocument42 pagesPDF Pozdravi Na SrpskomTanana97No ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument4 pagesResearch ProposalTom SanchezNo ratings yet
- Resolor 1mg Film-Coated Tablets (SPC) - DrugsDocument8 pagesResolor 1mg Film-Coated Tablets (SPC) - DrugsDhiren PranamiNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Food and Drinks ServiceDocument11 pagesUnit 6: Food and Drinks Servicegab77No ratings yet
- Nick Sand - Journey Into The Realm of IbogaineDocument3 pagesNick Sand - Journey Into The Realm of Ibogaineshenmue12100% (2)
- Capitalization: Mrs. Essediya Siragi Class: 1 BACDocument3 pagesCapitalization: Mrs. Essediya Siragi Class: 1 BACamalineNo ratings yet
- Solar Water Heater BOQDocument69 pagesSolar Water Heater BOQSami Al-aminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 SupplementDocument22 pagesChapter 02 SupplementYoni EscobarNo ratings yet
- Speech TextDocument4 pagesSpeech Textcici clardianNo ratings yet
- My MP ThreadDocument52 pagesMy MP ThreadksathisNo ratings yet
- Daniel James - English A SbaDocument13 pagesDaniel James - English A Sbadanieltjames5092No ratings yet
- Lucifer MeditationDocument7 pagesLucifer MeditationKinguAmdir-Ush100% (2)
- 22 May 2019 Supplementary Examination QUESTIONS AND ANSWERSDocument16 pages22 May 2019 Supplementary Examination QUESTIONS AND ANSWERSLaston MilanziNo ratings yet
- Studies in HistoryDocument5 pagesStudies in HistoryankitNo ratings yet
- Neet ENTDocument391 pagesNeet ENTwilliamsjoseff0No ratings yet
- PFT FormDocument1 pagePFT FormConnie Diaz CarmonaNo ratings yet