Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacology: Identify The 3 Natural Steroids That Are Secreted by The Adrenal Cortex
Pharmacology: Identify The 3 Natural Steroids That Are Secreted by The Adrenal Cortex
Uploaded by
Tyisha CharlesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology: Identify The 3 Natural Steroids That Are Secreted by The Adrenal Cortex
Pharmacology: Identify The 3 Natural Steroids That Are Secreted by The Adrenal Cortex
Uploaded by
Tyisha CharlesCopyright:
Available Formats
CH3058354
Tyisha Charles
Pharmacology
Identify the 3 natural steroids that are secreted by the adrenal cortex.
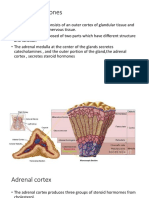
The adrenal glands are paired endocrine organs situated on top of the kidneys. The adrenal gland
is divided into an inner medulla which produced epinephrine and norepinephrine, and an outer
cortex which produced steroid hormones. The cortex has three zones, the zona glomerulosa, zona
fasciculata, and zona reticularis.
The zona glomerulosa produces aldosterone, which acts on the kidneys to conserve salt and
water. The inner two zones of the adrenal cortexthe zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis
function as a physiological unit to produce cortisol and adrenal androgens (male hormones), with
dehydroepiandrosterone, a weak androgen, being the major product.
1. Glucocorticoids: Hydrocortisone (cortisol), Corticosterone
Glucosortocoids affect mainly metabolism in diverse ways, decrease inflammation and
increase resistance to stress. Glucocorticoids also reduce the function and action of the
immune system, making them useful for protecting against transplant rejection and
ameliorating autoimmune and allergic diseases.
Hydrocortisone has two primary actions: (1) stimulation of gluconeogenesisi.e., the
breakdown of protein and fat in muscle and their conversion to glucose in the liverand
(2) anti-inflammatory actions.
Hydrocortisone helps control the bodys use of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Hydrocortisone is a potent metabolic regulatory hormone, increasing plasma glucose
level and promoting use of alternate metabolic substrates form energy. Cortisol stimulates
appetite and leads to removal of fat in some central adipose tissue despite the use of fat
from peripheral tissues. Metabolic changes in cortisol assist the transition to non-glucose
support of metabolism in starvation. Cortisol has significant anti-inflammatory effects,
retarding the development and enhancing the resolution of the inflammatory response.
Therefore glucocorticoids are used as inflammatory agents.
Corticosterone, together with hydrocortisone, supresses inflammatory reactions in the
body and also affects the immune system.
CH3058354
2. Mineralocorticoids: Aldosterone
The mineralocorticoids get their name from their effect on mineral metabolism
Aldosterone regulates the level of sodium and potassium in the body and helps maintain
blood volume and blood pressure. Aldosterone is regulated by complex feedback
mechanisms involving sodium and potassium levels as well as blood volume to maintain
salt and water balance. The biological action of aldosterone is to increase the retention of
sodium and water and to increase the excretion of potassium by the kidneys (and to a
lesser extent by the skin and intestines). It acts by binding to and activating a receptor in
the cytoplasm of renal tubular cells. The activated receptor then stimulates the production
of ion channels in the renal tubular cells, thereby increasing sodium reabsorption into the
blood and increasing potassium excretion into the urine.
3. Androgens: testosterone, androsterone
Androgens originate in the adrenal cortex and gonads and primarily affect maturation and
function of secondary sex organs (male sexual determination). Androgens are hormones
that primarily influence the growth and development of the male reproductive system.
Androgens also are necessary for the formation of sperm cells and for the maintenance of
sexual interest and behaviour. The growth of pubic hair and of facial and chest hair and
the regression of scalp hair, or baldness, are influenced by androgens. During
adolescence, androgens lengthen and thicken the male vocal cords, causing voice
deepening; they also enhance bone growth and increase the number and thickness of
muscle fibres in the male body. Other growth patterns that androgens stimulate are
kidney weight and size, the increase of protein in bone tissue, the regeneration of red
blood cells (erythrocytes), the presence of pigments in the skin, and the increased activity
of sweat and sebaceous (oil-producing) glands.
Testosterone and androsterone give the male its sex characteristics during puberty and for
promoting tissue and muscle growth. In sexually-mature males, this source of
testosterone is so much lower than that of the testes that it is probably of little
physiological significance. However, excessive production of adrenal androgens can
cause premature puberty in young boys.
Bibliography
- Encyclopaedia Britannica (2013). Androgen. Retrieved November 8
th
, 2013, from
http://www.britannica.com
- The Johns Hopkins University, The Johns Hopkins Hospital, and Johns Hopkins Health System
(2013). The Adrenal Glands. Retrieves November 8
th
, 2013, from http:// www.hopkinsmedicine.org
- St. Edwards University (2013). Steroid Hormones. Retrieves November 8
th
, from,
http://www.cs.stedwards.edu
- RCN Telecom Services (2013). The Adrenal Cortex. Retrieved November 8
th
2013 from
http://www.users.rcn.com
You might also like
- Addison's DiseaseDocument15 pagesAddison's DiseaseRonald A. Ogania50% (4)
- Chakra Lesson PDFDocument14 pagesChakra Lesson PDFDoc LymanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Review NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System Review Notesjeshema100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandsDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Adrenal Glandsxxxcamzxxx100% (3)
- Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesStructure and FunctionsErnesto RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Glandula SuprarenalisDocument6 pagesGlandula SuprarenalisYohanes BongNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Cortex: Functions & Disorders: By: Post Graduate Student Dept. of Oral Medicine, Diagnosis & RadiologyDocument80 pagesAdrenal Cortex: Functions & Disorders: By: Post Graduate Student Dept. of Oral Medicine, Diagnosis & Radiologyvihang146No ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Function(s) of Hormones (1) Hypothalamus (2) PituitaryDocument5 pagesEndocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Function(s) of Hormones (1) Hypothalamus (2) PituitaryJohn Ericsson RobariosNo ratings yet
- Steroids AND TerpenesDocument88 pagesSteroids AND Terpenesbuttercuplady_18763No ratings yet
- Influence of Steroid Hormones On The PeriodontiumDocument69 pagesInfluence of Steroid Hormones On The PeriodontiumSamra NausheenNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingDocument58 pagesPharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingRaveenmayiNo ratings yet
- Endonotes 2Document75 pagesEndonotes 2Libi FarrellNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument36 pagesAdrenal Glandpranutan739No ratings yet
- Assignment of Adrenal CortexDocument12 pagesAssignment of Adrenal CortexWania AliNo ratings yet
- Steroids HormonesDocument15 pagesSteroids HormonesZain Ul Abdin Mughal100% (1)
- BioSci LO#2Document16 pagesBioSci LO#2AudzkieNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System and Excretion WordDocument10 pagesEndocrine System and Excretion WordJoachim “Jayrz” MwambireNo ratings yet
- Adrenocortical HormonesDocument77 pagesAdrenocortical HormonesMaxamed Faarax XaashiNo ratings yet
- SteroidsDocument12 pagesSteroidsSwapnil DabholkarNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument16 pagesAdrenal GlandTanya SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnshNo ratings yet
- Progesterone in Orthomolecular MedicineDocument68 pagesProgesterone in Orthomolecular Medicineederbernadino92No ratings yet
- Steroids Discussion Points: 1. Examine The Diagram Below. Dicuss About SteroidsDocument7 pagesSteroids Discussion Points: 1. Examine The Diagram Below. Dicuss About SteroidsDinu YTBNo ratings yet
- ICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)Document14 pagesICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)TAHMEENA ZAFARNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 CommunicationIII 1Document30 pagesLecture10 CommunicationIII 1Liana Rose MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 2Document50 pagesEndocrine System 2park jongseongNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland1Document27 pagesAdrenal Gland1Rasel IslamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFDocument12 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration PDFSanjana SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Assessment of Endocrine System Key PointsDocument3 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Assessment of Endocrine System Key PointsDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Uni 5 SteroidsDocument20 pagesUni 5 Steroidsmuazmohammed1443No ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument7 pagesAdrenal GlandSamaj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Organ Functioning by Steroid Hormones. Tissue HormonesDocument47 pagesCoordination of Organ Functioning by Steroid Hormones. Tissue HormonesPurwa RaneNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Cortex HormonesDocument21 pagesAdrenal Cortex HormonesAaa JjjjNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument124 pagesHormonesMr T KillworthNo ratings yet
- Wiki Human HomeostasisDocument5 pagesWiki Human HomeostasisMagdy Ali ELsherbenyNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument50 pagesAdrenal GlandAnita YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 9 The Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesModule 9 The Endocrine SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- How Estrogen Protects BonesDocument7 pagesHow Estrogen Protects BonesAndreas Pratama NugrahaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFDocument8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFSaurav SoniNo ratings yet
- Depart. Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik: Universitas Sumatera Utara-MedanDocument19 pagesDepart. Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik: Universitas Sumatera Utara-MedanMasyithah TetaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Endocrine System Questions 5 - 7Document35 pagesGroup 2 Endocrine System Questions 5 - 7Marcus KaglNo ratings yet
- Ky 9 KZ OCt YO96 LBRL 0 HH DDocument22 pagesKy 9 KZ OCt YO96 LBRL 0 HH DVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument38 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationSajeev S Chadayamangalam SajNo ratings yet
- Cortisol: Alternative Names For Cortisol What Is Cortisol?Document7 pagesCortisol: Alternative Names For Cortisol What Is Cortisol?Ifeoluwa AdeniyiNo ratings yet
- Development of Topical Corticosteroids and Consideration of Their Formulation For The Treatment of Inflammatory ConditionsDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Topical Corticosteroids and Consideration of Their Formulation For The Treatment of Inflammatory ConditionsKamal HassanNo ratings yet
- 13 Lipids SteroidsDocument17 pages13 Lipids Steroidssubhan ali subhan aliNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemLen Len Ochinang OchinangNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 10 - Endocrine Glands Revision NotesDocument4 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 10 - Endocrine Glands Revision NoteshkkcreativityNo ratings yet
- 3010 Adrenal and Parathyroid HormonesDocument21 pages3010 Adrenal and Parathyroid HormonesDenesha KaurNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemMarmie Babaran GallibuNo ratings yet
- 3-Adrenal Glands and Its Hormones-MWDocument103 pages3-Adrenal Glands and Its Hormones-MWAbditsion DhiisaniiNo ratings yet
- Ana, Patho UroDocument5 pagesAna, Patho UroDan Ataniel EnsaladaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Endocrine Systemefjddr4z100% (1)
- Endocrine GlandsDocument10 pagesEndocrine Glandsعلي منذر عبدالصمد خلفNo ratings yet
- Addison Ds 9Document3 pagesAddison Ds 9Eden Jay Calija AgoyNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Excerpts: Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal AxisDocument9 pagesEndocrinology Excerpts: Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal AxisKiana TehraniNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandsDocument18 pagesAdrenal GlandsNitesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Steroid Hormones / Steriodgenesis Steroid HormoneDocument10 pagesBiosynthesis of Steroid Hormones / Steriodgenesis Steroid Hormoneajay004004No ratings yet
- Lecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMDocument17 pagesLecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMabdulsaboor30No ratings yet
- Presented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarDocument34 pagesPresented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarSohaib NasirNo ratings yet
- Anabolic SteroidsDocument8 pagesAnabolic SteroidsSunilNo ratings yet
- British J Pharmacology - 2009 - Kicman - Pharmacology of Anabolic SteroidsDocument20 pagesBritish J Pharmacology - 2009 - Kicman - Pharmacology of Anabolic Steroidsdouglas 87No ratings yet
- Adrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyFrom EverandAdrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyNo ratings yet
- Cis-Retinal Changes Shape and Becomes Another Isomer, All-Trans-Retinal, Transforming TheDocument3 pagesCis-Retinal Changes Shape and Becomes Another Isomer, All-Trans-Retinal, Transforming TheTyisha CharlesNo ratings yet
- Cis-Retinal Changes Shape and Becomes Another Isomer, All-Trans-Retinal, Transforming TheDocument3 pagesCis-Retinal Changes Shape and Becomes Another Isomer, All-Trans-Retinal, Transforming TheTyisha CharlesNo ratings yet
- WolpeDocument1 pageWolpeTyisha CharlesNo ratings yet
- Name of Organism Type of Organism Special Characteristics Diseases Caused TreatmentDocument4 pagesName of Organism Type of Organism Special Characteristics Diseases Caused TreatmentTyisha CharlesNo ratings yet
- Jesus Messiah Lyrics - Chris TomlinDocument2 pagesJesus Messiah Lyrics - Chris TomlinTyisha CharlesNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityTyisha CharlesNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument3 pagesAcute PainTyisha CharlesNo ratings yet
- Stress and Physiological ResponseDocument11 pagesStress and Physiological ResponseCampbell BellNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument13 pagesEarth and Life ScienceShareah Faith BalanguiNo ratings yet
- PPP Embryo N Histo Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesPPP Embryo N Histo Endocrine SystemMarisol AcostaNo ratings yet
- Invisible Minerals Part II by DR Carolyn DeanDocument46 pagesInvisible Minerals Part II by DR Carolyn Deanlihu74100% (1)
- GT134 DamsDocument119 pagesGT134 Damsসোমনাথ মহাপাত্র0% (1)
- Adrenal Gland OSCEDocument14 pagesAdrenal Gland OSCEOmar AttaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Emergencies (After Discharge) : Robert Englert, M.D. Dept Neonatology Bethesda Naval HospitalDocument43 pagesNeonatal Emergencies (After Discharge) : Robert Englert, M.D. Dept Neonatology Bethesda Naval HospitalTresno JoyoNo ratings yet
- Qigong For Strengthening The KidneysDocument15 pagesQigong For Strengthening The Kidneysdan20050505100% (1)
- Tutorial 4.5Document4 pagesTutorial 4.5Rosa FinizioNo ratings yet
- Course Objectives 3313Document11 pagesCourse Objectives 3313Hugh JacobsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument27 pagesEndocrine Disordersasdfgrttt100% (4)
- Krok1 2017 Explanation Ewlm PDFDocument96 pagesKrok1 2017 Explanation Ewlm PDFHimanshu Rana0% (1)
- A Study of The Students Perception of Academic Stress Due To Their Parents About Their Studies.Document7 pagesA Study of The Students Perception of Academic Stress Due To Their Parents About Their Studies.Anonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 The Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesChapter 34 The Endocrine Systemtheia28No ratings yet
- Chap 5 Hormonal Response To ExerciseDocument53 pagesChap 5 Hormonal Response To ExerciseAnnie KhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemKimberly Anne SP Padilla100% (2)
- Mix Questions PDFDocument40 pagesMix Questions PDFZazo RawashdehNo ratings yet
- Notes-Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFDocument19 pagesNotes-Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- Blok 4 Skenario 1Document14 pagesBlok 4 Skenario 1Dots FfastNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Endocrine SystemDocument38 pagesChapter 10 Endocrine SystemMacthalas QuiazonNo ratings yet
- Alopecia Androgenetica review50-297-2-PBDocument11 pagesAlopecia Androgenetica review50-297-2-PBAnderson FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Adrenal InsufficiencyDocument15 pagesAdrenal InsufficiencyJuvial DavidNo ratings yet
- Patologi AnatomiDocument3 pagesPatologi Anatomidika anggrainniNo ratings yet
- EE MOCK TEST 1 Jan 2017 Q& Answers62 PDFDocument92 pagesEE MOCK TEST 1 Jan 2017 Q& Answers62 PDFMohit Koladia100% (2)
- Astro Diagnosis Libra Part ADocument26 pagesAstro Diagnosis Libra Part AOvn MurthyNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit: What Is A Lymphocyte?Document8 pagesCell Unit: What Is A Lymphocyte?Kokushishikiku CabrerosNo ratings yet
- Slow Burn SumaryDocument10 pagesSlow Burn SumarySharizan GhaniNo ratings yet