Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth Forms and Life Begins
Earth Forms and Life Begins
Uploaded by
homamunfatOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth Forms and Life Begins
Earth Forms and Life Begins
Uploaded by
homamunfatCopyright:
Available Formats
B
i
o
l
o
g
y
D
i
s
c
l
a
i
m
e
r
:
t
h
i
s
s
t
u
d
y
g
u
i
d
e
w
a
s
n
o
t
c
r
e
a
t
e
d
t
o
r
e
p
l
a
c
e
y
o
u
r
t
e
x
t
b
o
o
k
a
n
d
i
s
f
o
r
c
l
a
s
s
r
o
o
m
o
r
i
n
d
i
v
i
d
u
a
l
u
s
e
o
n
l
y
.
Study Guides
Page 1 of 2
v1.1.11.2012
This guide was created by Danielle Phan and Jin Yu. To learn more about the
student authors, visit http://www.ck12.org/about/about-us/team/interns.
RNA World Hypothesis: RNA was the frst genetic material to appear on earth.
Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA): A prokaryotic cell that paved the way for all life on Earth to form.
Oxygen Catastrophe: As some early cells began making their own food via photosynthesis, cells that could not
tolerate living in an oxygen environment (because oxygen is a waste product of photosynthesis) died, but there
were also cells that evolved to use the oxygen for things like cellular respiration.
Endosymbiosis: Formed when an organism lives within another organism.
Fossil: Whats left of an organism after it has died, usually the bones or teeth. Even though the soft parts of the body
often decompose soon after an animals death, the hard parts of the body can leave an imprint on rock or dirt,
which means that the imprinted rock can be found millions of years later, after everything else has decomposed.
Relative Dating: If the fossil is lower in the rock, then the fossil is older. This does not give an exact age to the fossil.
Absolute Dating: By understanding a half-life of carbon-14, scientists can measure the amount of carbon-14 left in
an organism to fgure out how old it is.
Half-Life: Time it takes for 50% of atoms to decay.
Humans and other organisms did not suddenly appear on Earth; instead, they evolved from earlier organisms. The
frst life forms appeared about 4 billion years ago and were microscopic, single-celled organisms. Earth started out as
a jumble of gases and inorganic materials that later reacted together and formed organic materials, which made way
for prokaryotic cells and later eukaryotic cells to form. We know this by looking at the fossil record, and we measure
the age of the fossil through absolute and relative dating
Key Terms
Timeline of Earths History
Big Picture
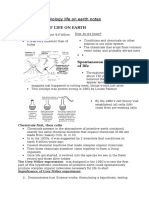
Image Credit: Hardwigg, Public Domain
Here is a fgure depicting the
history of the Earth, displaying
each milestone.
Earth formed about 4.6
billion years ago
Life frst appeared about 4
billion years ago
Notice how relatively recent
humans' appearance onto Earth
was, and how much time passed
by before photosynthesis began
on Earth.
Ma = million years ago
Ga = billion years ago
Earth Forms & LiFE BEgins
Page 2 of 2
B
i
o
l
o
g
y
Living things are made up of organic molecules. The frst
organic molecules were thought to have formed from
lightning passing through Earths early atmosphere.
In the Miller and Ulrich experiment, these two
scientists took all the materials (inorganic chemicals)
that they believed were in Earths early atmosphere
and passed sparks through the gases. They found
that amino acids and other organic molecules were
created, showing that inorganic chemicals can
indeed form organic molecules.
Since the exact composition of Earths atmosphere
is uncertain, we dont know the process that created
the frst organic molecules.
According to the RNA world hypothesis, RNA was the
frst organic molecule to evolve.
RNA can act like DNA by forming proteins and can
act like proteins by carrying out chemical reactions.
Of the different early cells and molecules, scientists
think that all life today evolved from one cell called the
Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA).
Would not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound
organelles
Probably existed about 3.5 billion years ago
About 2.5 billion years ago, the oxygen catastrophe
took place.
Oxygen produced from photosynthesis had been
accumulating in the atmosphere. This accumulation
of oxygen killed many early cells.
The few cells that survived evolved in a way to use
oxygen (via cellular respiration)
Eukaryotic cells probably evolved about 2 billion
years ago by forming endosymbioses (plural of
endosymbiosis).
The theory is that a small cell was eaten by a large
cell but was not entirely digested.
These two cells lived together and benefted as a
result.
Because this arrangement was advantageous, this
cell went on and eventually evolved to become the
modern eukaryote with organelles.
Figure: This picture shows how two cells can come together,
how the smaller cell becomes engulfed by the larger cell, and
how both cells eventually become one cell with organelles.
Origin of Life
Carbon Dating
Fossils are used to piece together the history of life on Earth. There are two ways to determine how old the fossil is:
Relative dating: can determine the relative age if one fossil is older than another by looking at the fossils position
in the rock
Absolute dating: can determine the age based on carbon dating
When an organism is alive, it has a certain percentage of carbon-14 atoms. Once the organism has died, the number
of carbon-14 atoms decays over time.
We can determine how long ago the organism died if we know the half-life of carbon-14. The half-life of carbon-14 is
about 5,730 years. Taking the fossil remains, we could fgure how much carbon-14 is in the remains and compare that
amount with how much carbon-14 is in a living organism.
We can then fgure out how many half-lives the remains went through. When we have that information, we can
multiply the number of half-lives with how many years are in a half-life to determine the approximate time of when
the organism died.
Carbon dating is important to fguring out the age of the fossil. However, after a certain point, the amount of carbon-14
remaining is so small that it is undetectable, or not enough to predict how many half lives an organism has gone
through. Therefore, carbon dating is only useful for dating back 60,000 years.
Notes
Earth Forms & LiFE BEgins cont.
Image Credit: Franciscosp2, CC-BY 3.0
You might also like
- AWS Module 3 - AWS Global InfrastructureDocument36 pagesAWS Module 3 - AWS Global Infrastructuredsadasdasdas0% (1)
- AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Document16 pagesAP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Shiv Ganesh100% (1)
- 29.00.00004 28-JUN-2019 21-JAN-2021 Open A318, A319, A320, A321 29-00 UpdateDocument26 pages29.00.00004 28-JUN-2019 21-JAN-2021 Open A318, A319, A320, A321 29-00 Updatesaid PalaoNo ratings yet
- Socratic Questions:: Questions and General Answers Created and Compiled byDocument5 pagesSocratic Questions:: Questions and General Answers Created and Compiled byVeronique Plaatjies100% (1)
- Biology Life On Earth NotesDocument10 pagesBiology Life On Earth NotesEmmanuel Onyebuchi ObinwanorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Lesson 8.2-Biological Evidence For EvolutionDocument15 pagesChapter 8-Lesson 8.2-Biological Evidence For Evolutionrojelbartolome23No ratings yet
- Q2 PPT ELSDocument80 pagesQ2 PPT ELSnheill718No ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument6 pagesOrigin of LifeBillal JohnNo ratings yet
- KISS Notes Life On EarthDocument24 pagesKISS Notes Life On EarthJenniferBackhus100% (2)
- 2) Origin of LifeDocument28 pages2) Origin of LifeAnthony RiveraNo ratings yet
- Origin of de VitaDocument12 pagesOrigin of de VitaJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemoDocument3 pagesWeek 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemogladiatornthabiNo ratings yet
- Theories of OriginDocument7 pagesTheories of OriginAbby VillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: The History of Life On EarthDocument6 pagesChapter 25: The History of Life On EarthErrol KingNo ratings yet
- Gbio2-Week 12Document31 pagesGbio2-Week 12Kai SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 21 SummaryJamesBlackmanNo ratings yet
- Lec01-Origin of Life IDocument18 pagesLec01-Origin of Life IAndy PikiNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument73 pagesOrigin of Lifeianespecial0830No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 9Document16 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 9benes salamancaNo ratings yet
- Pre Final Module Earth and Life ScienceDocument22 pagesPre Final Module Earth and Life ScienceMarjorie Rose TeodosioNo ratings yet
- Astrobiology: Published by The Association Pro ISSI No 16, July 2006Document20 pagesAstrobiology: Published by The Association Pro ISSI No 16, July 2006Jtari MinterNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Week 1 - 2Document18 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Week 1 - 2Einjhel Gaverielle Reyes100% (2)
- EARTH and LIFE SCIENCE NOTESDocument1 pageEARTH and LIFE SCIENCE NOTESFrances Vale BasanNo ratings yet
- Origin of Life in The Early Universe12Document7 pagesOrigin of Life in The Early Universe12induwaraanushkaNo ratings yet
- A Narrative of Human Evolution (Draft)Document4 pagesA Narrative of Human Evolution (Draft)Aniuś TaluwīsNo ratings yet
- Early Life On Earth: Principles of BiologyDocument15 pagesEarly Life On Earth: Principles of Biologyron abrahamNo ratings yet
- Life Might Be More Common in The Universe Than We ThoughtDocument6 pagesLife Might Be More Common in The Universe Than We ThoughtаяиNo ratings yet
- Science ReportDocument11 pagesScience ReportangelaNo ratings yet
- Evolusi - Asal Usul & Evolusi Awal Kehidupan BDocument50 pagesEvolusi - Asal Usul & Evolusi Awal Kehidupan BtommerraasanneNo ratings yet
- History of LifeDocument25 pagesHistory of LifeMalik Ammar KhawarNo ratings yet
- Big Bang TheoryDocument9 pagesBig Bang Theoryrucha kNo ratings yet
- What Is Life?Document19 pagesWhat Is Life?anon_846194098No ratings yet
- Human Origin and EvolutionDocument15 pagesHuman Origin and EvolutionBala PrasannaNo ratings yet
- History of Life On EarthDocument9 pagesHistory of Life On EarthblablaNo ratings yet
- History Life Earth: of OnDocument28 pagesHistory Life Earth: of OnTamer Hesham AhmedNo ratings yet
- Daily Science Original 2003Document17 pagesDaily Science Original 2003Sabeen khalidiNo ratings yet
- Life's OriginDocument11 pagesLife's OriginGd Rajib DasNo ratings yet
- Taxa Protista - Origin and DevelopmentDocument36 pagesTaxa Protista - Origin and DevelopmentsenjicsNo ratings yet
- Science Mock QuizDocument4 pagesScience Mock QuizEm ClaroNo ratings yet
- Earthlife Science q2 Week 1 EditedDocument17 pagesEarthlife Science q2 Week 1 EditedRhea RegaladoNo ratings yet
- 2nd-qrt. Week-12 ELSDocument26 pages2nd-qrt. Week-12 ELSMickaela MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Module Q.2 ElsDocument4 pagesModule Q.2 Elsaltheaveniceholanda02No ratings yet
- Life OriginDocument2 pagesLife OriginMuhammad Imran FazalNo ratings yet
- Origin of Life On EarthDocument8 pagesOrigin of Life On Earthharpal_abhNo ratings yet
- Cosmos 02Document3 pagesCosmos 02Shahid AnsariNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Q2 ReviewerDocument25 pagesEarth Life Science Q2 ReviewerAsejo LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Theory of LifeDocument18 pagesTheory of Liferyan valerio100% (1)
- UNIT 2 - The Origin and Chemistry of LifeDocument10 pagesUNIT 2 - The Origin and Chemistry of LifeRachel Ae Ra JangNo ratings yet
- 2 The Origin of LifeDocument39 pages2 The Origin of LifeRydel GreyNo ratings yet
- Astro Biolog I ADocument64 pagesAstro Biolog I AAlexei Ochoa100% (1)
- Earth S History: Spread of LifeDocument13 pagesEarth S History: Spread of LifeMed Mark Mansit PaitNo ratings yet
- Script-The Origin of LifeDocument3 pagesScript-The Origin of LifeMubarrach MatabalaoNo ratings yet
- Abiogenic Origin of LfeDocument17 pagesAbiogenic Origin of LfeMary Angelica YatongNo ratings yet
- Eals Lesson 1Document41 pagesEals Lesson 1eugene medinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Life Science Objective: Organic Molecules. Some Form of Energy FromDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Life Science Objective: Organic Molecules. Some Form of Energy FromBuzz manzhjanaNo ratings yet
- Eals LessonDocument41 pagesEals Lessonred carbinNo ratings yet
- Life's Engines: How Microbes Made Earth HabitableFrom EverandLife's Engines: How Microbes Made Earth HabitableRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Origin of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument10 pagesOrigin of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellssrisankaraglobalacademy7No ratings yet
- Cellular BiologyDocument132 pagesCellular BiologyunigeNo ratings yet
- Evolutionxii 180730153121 PDFDocument45 pagesEvolutionxii 180730153121 PDFrajaprasad2No ratings yet
- 2nd-Quarter ELSDocument39 pages2nd-Quarter ELSAshley Joy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- GCSE ELIT REVISED Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard MayJune Series 2011 9983Document16 pagesGCSE ELIT REVISED Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard MayJune Series 2011 9983homamunfatNo ratings yet
- Every Child Matters: Change For Children: in Social CareDocument16 pagesEvery Child Matters: Change For Children: in Social CarehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- 16.1 Questioning John ProctorDocument2 pages16.1 Questioning John ProctorhomamunfatNo ratings yet
- 18 Yatcb Lesson Plans Complete Book FINALDocument146 pages18 Yatcb Lesson Plans Complete Book FINALhomamunfatNo ratings yet
- 50 Word Story TellingDocument1 page50 Word Story TellinghomamunfatNo ratings yet
- B. Red, Yellow, and Blue Can Be Mixed Together To Make Secondary ColorsDocument1 pageB. Red, Yellow, and Blue Can Be Mixed Together To Make Secondary ColorshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Colors: Lesson Ten: The Three Primary Colors Are Red, Yellow, and Blue. They CanDocument1 pageColors: Lesson Ten: The Three Primary Colors Are Red, Yellow, and Blue. They CanhomamunfatNo ratings yet
- 13.05.15 Prepostions of PlaceDocument1 page13.05.15 Prepostions of PlacehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- 15.1 Speaking and Listening Assessment - Role PlayingDocument2 pages15.1 Speaking and Listening Assessment - Role PlayinghomamunfatNo ratings yet
- B. Write The Following Information On The Calendar On Page 10. Write SmallDocument1 pageB. Write The Following Information On The Calendar On Page 10. Write SmallhomamunfatNo ratings yet
- St. Benedict's College - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSt. Benedict's College - Lesson PlanhomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Thinking Skills & Discussion SkillsDocument6 pagesThinking Skills & Discussion SkillshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- 6 HATS - What Are They SayingDocument1 page6 HATS - What Are They SayinghomamunfatNo ratings yet
- To Be or Not To Be Haben and SeinDocument1 pageTo Be or Not To Be Haben and SeinhomamunfatNo ratings yet
- 6 Areas Mindmap - OurselvesDocument1 page6 Areas Mindmap - OurselveshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Fida Ur Rehman SP19-BBA-022 Section - A Assignment #1Document4 pagesFida Ur Rehman SP19-BBA-022 Section - A Assignment #1N ZaibNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument15 pagesProposalCourage JuwawoNo ratings yet
- Good Homes - June 2015 IN PDFDocument90 pagesGood Homes - June 2015 IN PDFElena ElenaNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Technique 2: Ysmael O. Alip, RRTDocument81 pagesRadiographic Technique 2: Ysmael O. Alip, RRTMarts Rivera100% (1)
- Grove 890Document50 pagesGrove 890cristian faundesNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 - Garden Design (Pages-32)Document25 pagesUnit-3 - Garden Design (Pages-32)siva ramanNo ratings yet
- 0068 NehaDocument1 page0068 Nehang.neha8990No ratings yet
- Abdellatif Kashkoush SMDocument5 pagesAbdellatif Kashkoush SMRacha BadrNo ratings yet
- Kingfisher CalendarDocument54 pagesKingfisher CalendarMalay K GhoshNo ratings yet
- The Golden Fish Keeps A Promise StoryDocument2 pagesThe Golden Fish Keeps A Promise StoryDe Guzman Diane Marie B.No ratings yet
- Astm d5453Document9 pagesAstm d5453aqmar aqeemNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Gizi BurukDocument80 pagesTatalaksana Gizi BurukIntania FadillaNo ratings yet
- 360 Degree Peer Evaluation FormDocument4 pages360 Degree Peer Evaluation FormAjisafe Jerry T-money100% (1)
- Cisco Cloud DefinitionDocument72 pagesCisco Cloud DefinitionmienmobkNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answer Key Unit 8 AcbeuDocument1 pageWorkbook Answer Key Unit 8 AcbeuLuisa Mari AlvamoreNo ratings yet
- 7-Step Ultimate Guide To Legal TranslationsDocument3 pages7-Step Ultimate Guide To Legal TranslationsDomenic TorNo ratings yet
- Torque Spiral Wound GSKT TableDocument2 pagesTorque Spiral Wound GSKT TableCarlos Roberto Tamariz100% (1)
- Chap 1 RevisedDocument5 pagesChap 1 RevisedCess AquinoNo ratings yet
- DD RhinosinusitisDocument9 pagesDD RhinosinusitisZuhal Darwis100% (1)
- To Study The Impact of Technology On RecruitmentDocument9 pagesTo Study The Impact of Technology On RecruitmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Airbus Family Figures BookletDocument17 pagesAirbus Family Figures BookletCoffardNo ratings yet
- 22 Passage 2 - Western Immigration of Canada Q14-26Document6 pages22 Passage 2 - Western Immigration of Canada Q14-26Cương Nguyễn DuyNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar D6Document3 pagesCaterpillar D6RasoolKhadibi100% (1)
- The Measures of Central TendencyDocument40 pagesThe Measures of Central TendencyMark Lester Brosas TorreonNo ratings yet
- Fruits and Veg SCMDocument11 pagesFruits and Veg SCMamoldhawanNo ratings yet
- Labour Law - GuidelinesDocument21 pagesLabour Law - GuidelinesJames AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Timothy StainbrookDocument1 pageTimothy Stainbrookapi-548131304No ratings yet
- Beg Unit5 RevisionDocument2 pagesBeg Unit5 RevisionSimina EnăchescuNo ratings yet