Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
Uploaded by
biotech_vidhyaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Juicing VegetablesDocument5 pagesJuicing Vegetablestenbears m.No ratings yet
- Maca Lepidium Meyenii Materia Medica HerbsDocument9 pagesMaca Lepidium Meyenii Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Expectorant and Demulcent HerbsDocument3 pagesExpectorant and Demulcent HerbsqueencelNo ratings yet
- Hpylorisolution PDFDocument66 pagesHpylorisolution PDFAndrej OfakNo ratings yet
- Offers 2012 S MHDocument24 pagesOffers 2012 S MHwlfhjoreihfloergjbNo ratings yet
- Coconut Success StoriesDocument23 pagesCoconut Success StoriescheniahmNo ratings yet
- The Many Benefits of Coconut Water KefirDocument3 pagesThe Many Benefits of Coconut Water KefirMa Geobelyn LopezNo ratings yet
- Blocked Fallopian TubesDocument2 pagesBlocked Fallopian TubesPreethi JoseNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide: The Body EcologyDocument15 pagesQuick Start Guide: The Body EcologymNo ratings yet
- DoctrineDocument1 pageDoctrinevinay44No ratings yet
- 2023 - George Felfoldi (eBook-Herbal) - Healing Properties of Thistles, 113 PagesDocument113 pages2023 - George Felfoldi (eBook-Herbal) - Healing Properties of Thistles, 113 PagesGeorge FelfoldiNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle An Ayurvedic ProspectiveDocument9 pagesMenstrual Cycle An Ayurvedic ProspectiveRGuti13No ratings yet
- Natural Cleanising TechniquesDocument88 pagesNatural Cleanising TechniquesPetra JobovaNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Blocked Fallopian TubesDocument80 pagesCh06 Blocked Fallopian TubesAasia Najaf SoomroNo ratings yet
- HERBAL TEA RECIPES: Aromatic Delights: Herbal Tea Recipes for Health and WellnessFrom EverandHERBAL TEA RECIPES: Aromatic Delights: Herbal Tea Recipes for Health and WellnessNo ratings yet
- Fenugreek Benefits PDFDocument10 pagesFenugreek Benefits PDFrecianzubyNo ratings yet
- Fenugreek SeedsDocument6 pagesFenugreek SeedsAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Drugs From Marine OriginatesDocument10 pagesAyurvedic Drugs From Marine Originateskunalprabhu148No ratings yet
- Reversing Clogged Arteries: Super Herbal Remedies for Heart HealthFrom EverandReversing Clogged Arteries: Super Herbal Remedies for Heart HealthNo ratings yet
- Growing HerbsDocument19 pagesGrowing HerbsspicerjlNo ratings yet
- For Herbal Medicines": Scientific Editors Data ManagerDocument1 pageFor Herbal Medicines": Scientific Editors Data ManagerSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Herbal Med.Document14 pagesHerbal Med.Jerry V. CaraecleNo ratings yet
- 6 Health Benefits CoffeeDocument5 pages6 Health Benefits CoffeeJaime GarciaNo ratings yet
- Best Ayurvedic Medicine For Diabetes - Comparison & ReviewsDocument13 pagesBest Ayurvedic Medicine For Diabetes - Comparison & ReviewsSomanshu BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Restorative Efficiency of Bursera Simarubaisolated Phytonutrients For The Therapy of Various DiseasesDocument15 pagesRestorative Efficiency of Bursera Simarubaisolated Phytonutrients For The Therapy of Various DiseasesleonardoNo ratings yet
- American IndiansDocument14 pagesAmerican IndiansYunita D. SetyoriniNo ratings yet
- French OPC Grape Seed For Diabetes, Heart, Cancer and MoreDocument4 pagesFrench OPC Grape Seed For Diabetes, Heart, Cancer and MoreTheVitaminStore.comNo ratings yet
- 2015 - George Felfoldi - (Ebook - Cooking) Good Food and Art Cookbook, 407 Pages PDFDocument407 pages2015 - George Felfoldi - (Ebook - Cooking) Good Food and Art Cookbook, 407 Pages PDFGeorge FelfoldiNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Macrobiotic PrinciplesDocument23 pagesA Guide To The Macrobiotic PrinciplesMus Oub100% (1)
- Bioactives and Traditionalmedicines For Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument177 pagesBioactives and Traditionalmedicines For Cardiovascular DiseasesSocioCamp MediaNo ratings yet
- Herbs and Spices For The Home GardenDocument8 pagesHerbs and Spices For The Home GardenSharad BhutoriaNo ratings yet
- 2023 - George Felfoldi - (Ebook - Health) - Another Look at Seaweed and Algae, 136 PagesDocument136 pages2023 - George Felfoldi - (Ebook - Health) - Another Look at Seaweed and Algae, 136 PagesGeorge FelfoldiNo ratings yet
- Human Body Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesHuman Body Parts and Their FunctionsCarlos Bladimir Estrada MontecinosNo ratings yet
- 10 Lavender Oil Benefits For Major Diseases & Minor Ailments - Dr. AxeDocument10 pages10 Lavender Oil Benefits For Major Diseases & Minor Ailments - Dr. AxeJoseph TupasNo ratings yet
- 5 Benefits of BoswelliaDocument6 pages5 Benefits of BoswelliaPaulNo ratings yet
- E Cookbooks Library Mexican RecipesDocument22 pagesE Cookbooks Library Mexican RecipesMarkella KoufNo ratings yet
- Apatani HerbsDocument0 pagesApatani HerbsLuvjoy ChokerNo ratings yet
- Herbal PharmacologyDocument11 pagesHerbal Pharmacologywingrace688No ratings yet
- The 29 Healthiest Foods On The WorldDocument9 pagesThe 29 Healthiest Foods On The WorldlittlenemzNo ratings yet
- Corn SilkDocument1 pageCorn Silkwillyagung4557No ratings yet
- Spice List 20121Document2 pagesSpice List 20121ravivarmahyd8173No ratings yet
- Food Revolution Summit: Program & ScheduleDocument13 pagesFood Revolution Summit: Program & ScheduleDNo ratings yet
- Periodontitis and Systemic Disease: FeatureDocument4 pagesPeriodontitis and Systemic Disease: Featurewendyjemmy8gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Herbal Plants and Its Uses: 1. Akapulko (Cassia Alata)Document5 pagesHerbal Plants and Its Uses: 1. Akapulko (Cassia Alata)Luz Sumaylo MiñozaNo ratings yet
- HERBAL TEA FOR BEGINNERS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Make Some of the Best Herbal Teas and Prevent Diseases with the Natural Healing Power of HerbsFrom EverandHERBAL TEA FOR BEGINNERS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Make Some of the Best Herbal Teas and Prevent Diseases with the Natural Healing Power of HerbsNo ratings yet
- Hippocrates - The Father of MedicineDocument1 pageHippocrates - The Father of Medicine123121No ratings yet
- Caffeine and Theobromine Content of Selected Hershey's ChocolateDocument2 pagesCaffeine and Theobromine Content of Selected Hershey's ChocolateJude PaxmrosyNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plant Diversity in Kulathupuzha Locality, Kollam DistrictDocument18 pagesMedicinal Plant Diversity in Kulathupuzha Locality, Kollam DistrictSandeepamol P SNo ratings yet
- Super FoodsDocument70 pagesSuper FoodsThe Health Therapist AcademyNo ratings yet
- My Herbs Issue 22 November 2022Document84 pagesMy Herbs Issue 22 November 2022Andrea JozsaNo ratings yet
- Ancient WondersDocument13 pagesAncient WondersK. ZinNo ratings yet
- Cow Ayurvedic PANACEASDocument57 pagesCow Ayurvedic PANACEASmpidoh100% (1)
- 30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutDocument38 pages30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutMaria BarbaliaNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Diet FOR DISEASE PREVENTION: The Ultimate Guide to Eat Healthy, Fight Inflammation, Lose Weight and Fight Cronic DiseaseFrom EverandAlkaline Diet FOR DISEASE PREVENTION: The Ultimate Guide to Eat Healthy, Fight Inflammation, Lose Weight and Fight Cronic DiseaseNo ratings yet
- The Many Health Benefits of Aloe VeraDocument3 pagesThe Many Health Benefits of Aloe VeraTanvir MirzaNo ratings yet
- Neem TreeDocument2 pagesNeem Treeyuvi087No ratings yet
- Natural Remedies Encyclopedia (PDFDrive) - 2Document30 pagesNatural Remedies Encyclopedia (PDFDrive) - 2angelobuffaloNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential Nutrients PDFDocument15 pages6 Essential Nutrients PDFJuan Rodriguez Jr100% (1)
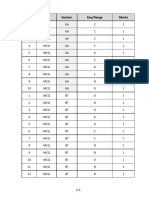
- Q.No. Type Section Key/Range MarksDocument3 pagesQ.No. Type Section Key/Range Marksbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Buffer Preparation PDFDocument6 pagesBuffer Preparation PDFbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- BT 2019Document13 pagesBT 2019biotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting SDS-PAGE 1Document3 pagesTroubleshooting SDS-PAGE 1biotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document3 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)biotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Whole Cell ExtractDocument1 pageWhole Cell Extractbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Buffer Preparation PDFDocument6 pagesBuffer Preparation PDFbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ExtractsDocument2 pagesNuclear Extractsbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Group 1 Prelim Book List PDFDocument2 pagesTNPSC Group 1 Prelim Book List PDFbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Code No. 14: Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2010Document20 pagesMechanical Engineering Code No. 14: Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2010biotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Ies 17 Set A Me Q ADocument67 pagesIes 17 Set A Me Q Abiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- 1 TolerancesDocument1 page1 Tolerancesbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Befcv List PDFDocument22 pagesBefcv List PDFbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Teachers Recruitment Board: 1. Important DatesDocument13 pagesTeachers Recruitment Board: 1. Important Datesbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Lec09 Three PhaseDocument84 pagesLec09 Three Phasebiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Isa BusDocument30 pagesIsa Busbiotech_vidhya100% (1)
- Olsen MethodDocument18 pagesOlsen MethodMark CarpesoNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- C100 Eng Bulletin Sulfuric Acid 0910Document24 pagesC100 Eng Bulletin Sulfuric Acid 0910wacsii ccasullaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Disorders in Fruit CropsDocument8 pagesPhysiological Disorders in Fruit CropsMohamed BahgatNo ratings yet
- Product Analysis Certificate: Propanol-2 (Iso-Propanol) A.RDocument1 pageProduct Analysis Certificate: Propanol-2 (Iso-Propanol) A.RAMMARNo ratings yet
- LigniteDocument23 pagesLigniteMayra Sánchez CabanillasNo ratings yet
- Solved 2024 Specimen Paper ICSE Class 10 ChemistryDocument11 pagesSolved 2024 Specimen Paper ICSE Class 10 ChemistrymmroyalethegreatNo ratings yet
- 2014 Test Paper DR Homi BhabhaDocument9 pages2014 Test Paper DR Homi BhabhaDr Mohan Savade100% (1)
- Herbal Drugs ReportDocument288 pagesHerbal Drugs Reportparakhurd0% (1)
- Soil Science 2019 LEADocument10 pagesSoil Science 2019 LEAElsa De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 5070 w16 QP CompleteDocument120 pages5070 w16 QP CompleteAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- Physiological Disorders and Corrective Measures For Greenhouse TomatoesDocument5 pagesPhysiological Disorders and Corrective Measures For Greenhouse Tomatoesstand backNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 2)Document2 pagesEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 2)Alexandrea ModillasNo ratings yet
- Optimisation de L'utilisation de Lait de Chaux Image MEB de Ineich2017Document9 pagesOptimisation de L'utilisation de Lait de Chaux Image MEB de Ineich2017Yassine GouzzaliNo ratings yet
- Usp31nf26s1 - m11430, USP Monographs - Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageUsp31nf26s1 - m11430, USP Monographs - Calcium CarbonateEfsha KhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaDocument6 pages2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaTheodora HamletNo ratings yet
- Rishab Soya MilkDocument8 pagesRishab Soya MilkRishabJaiswal100% (1)
- 03 Lewabrane Manual System Design 03Document13 pages03 Lewabrane Manual System Design 03zamijakaNo ratings yet
- Sample Persuasi-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesSample Persuasi-WPS OfficeLeilla Mae PataNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-26 at 7.29.30 PMDocument103 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-26 at 7.29.30 PMfahad212qwNo ratings yet
- Causes of Distress and Deterioration of Concrete, EM 1110-2-2002 1995-06-30Document14 pagesCauses of Distress and Deterioration of Concrete, EM 1110-2-2002 1995-06-30RONALD MUELLERNo ratings yet
- Korean Construction SpecificationDocument14 pagesKorean Construction SpecificationOnnuri WonNo ratings yet
- PROCESS FLOW OF APPLICATION OF PNP LICENSES AND PERMITS - UPLB Oct 5 2016Document33 pagesPROCESS FLOW OF APPLICATION OF PNP LICENSES AND PERMITS - UPLB Oct 5 2016Trish AustriaNo ratings yet
- BergaFat: A Fat Powder With Value AddedDocument2 pagesBergaFat: A Fat Powder With Value AddedMilling and Grain magazineNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY BOOK 2 ObjDocument44 pagesCHEMISTRY BOOK 2 ObjHaris AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 20-Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument4 pages20-Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistrythucinorNo ratings yet
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet I PDFDocument3 pagesNaming Ionic Compounds Worksheet I PDFgowrimanohar1975No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School,: VijayawadaDocument8 pagesDelhi Public School,: VijayawadaBild Andhra PradeshNo ratings yet
- Journal of African Earth Sciences: M. Meck, J. Atlhopheng, W.R.L. MasambaDocument5 pagesJournal of African Earth Sciences: M. Meck, J. Atlhopheng, W.R.L. MasambaMuhammad Imam WahyuddinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision NotesDocument7 pagesChemistry Revision NotesFarhan RahmanNo ratings yet
Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
Uploaded by
biotech_vidhyaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
Uploaded by
biotech_vidhyaCopyright:
Available Formats
3/25/2014 Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
http://www.healthaliciousness.com/articles/foods-high-in-calcium.php 1/6
Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
Calcium is necessary for the growth and maintenance of strong teeth and bones, nerve signaling, muscle contraction, and secretion of certain hormones
and enzymes. A deficiency in calcium can lead to numbness in fingers and toes, muscle cramps, convulsions, lethargy, loss of appetite, and abnormal
heart rhythms. Conversely, excess calcium (particularly from supplements) can lead to kidney stones, calcification of soft tissue, and increased risk of
vascular diseases like stroke and heart attack. Most calcium is found in dark leafy greens and dairy. While there is some evidence that oxalates in greens
can hinder calcium absorption, they are still a good source of calcium, and the calculated percent daily value (%DV) already takes into account
absorption and bio-availability. For more, see the section on calcium absorption. The %DV for calcium is 1000mg. Below is a list of high calcium
foods by common serving size, for more, see the extended lists of high calcium foods by nutrient density, and calcium rich foods.
#1: Dark Leafy Greens (Watercress)
Calcium in 100g (Raw) 1 Cup Chopped (34g) 10 Sprigs (25g)
120mg (12% DV) 41mg (8% DV) 30mg (3% DV)
Other Greens High in Calcium (%DV per cup, chopped, raw): Curly Kale (14%), Dandelion Greens (10%), Turnip Greens (10%),
Arugula (6%), and Collards (5%). Click to see complete nutrition facts.
#2: Low Fat Cheese (Mozzarella Nonfat)
Calcium in 100g 1 Cup Shredded (113g) 1 Ounce (28g)
961mg (95% DV) 1086mg (109% DV) 269mg (27% DV)
Other Cheeses High in Calcium (%DV per ounce): Low Fat Swiss (27%), Reduced Fat Parmesan (31%) and Cottage Cheese 2%
Fat (2%). Click to see complete nutrition facts.
#3: Low Fat Milk & Yogurt (Nonfat Milk)
Calcium in 100g 1 Cup (245g) Per Fluid Ounce (31g)
125mg (13% DV) 306mg (31% DV) 39mg (4% DV)
Other Dairy High in Calcium (%DV per cup): Nonfat yogurt (49%) and Low Fat Yogurt (45%). Click to see complete nutrition facts.
#4: Chinese Cabbage (Pak Choi, Bok Choy)
Calcium in 100g (Raw) 1 Cup Shredded (70g) 1 Head (840g)
105mg (11% DV) 74mg (7% DV) 882mg (88% DV)
Other Cabbage (%DV per cup cooked): Green Cabbage Cooked (4% DV), Red Leaf Cabbage Cooked (3% DV). Click to see complete
nutrition facts.
#5: Fortified Soy Products (Tofu)
Calcium in 100g (Raw) 1/2 Cup Raw (124g) 1/2 Cup Fried (124g)
350mg (35% DV) 434mg (43% DV) 1192mg (119% DV)
Other Soy Products High in Calcium (%DV per 1/2 cup): Nonfat Soy Milk with added calcium and vitamins A and D (13%) and
Unsweetened Soy Milk with added calcium and vitamins (13%). Click to see complete nutrition facts.
3/25/2014 Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
http://www.healthaliciousness.com/articles/foods-high-in-calcium.php 2/6
#6: Okra (Cooked)
Calcium in 100g 1 Cup Sliced (160g) 8 Pods (85g)
77mg (8% DV) 124mg (12% DV) 65mg (7% DV)
Click to see complete nutrition facts.
#7: Broccoli
Calcium in 100g 1 Cup Chopped (91g) 1 Cup Cooked (156g)
47mg (5% DV) 43mg (4% DV) 62mg (6% DV)
One cup of cooked broccoli, boiled in water contains just 54 calories. Click to see complete nutrition facts.
#8: Green Snap Beans
Calcium in 100g (Raw) 1 Cup Raw (110g) Per Cup Cooked (125g)
37mg (4% DV) 41mg (4% DV) 55mg (6% DV)
One cup of cooked green snap beans, boiled in water contains just 44 calories. Click to see complete nutrition facts.
#9: Almonds
Calcium in 100g 1 Cup Whole (143g) 1 Ounce (28g)
264mg (26% DV) 378mg (38% DV) 74mg (7% DV)
A one ounce (28g) serving of almonds, which is about 23 kernels, contains 161 calories. Click to see complete nutrition facts.
#10: Fish Canned (Sardines, in Oil, with Bones)
Calcium in 100g 1 Cup Drained (149g) 1 Ounce (28g)
383mg (38% DV) 569mg (57% DV) 107mg (11% DV)
Other Canned Fish High in Calcium (%DV per ounce serving): Pink Salmon (8%), Anchovies (6%) and Shrimp (4%). Click to see
complete nutrition facts.
The Top 10 High Calcium Foods by Nutrient Density (Calcium per Gram)
#1: Dried Herbs (Dried Basil, Thyme, Marjoram,
Rosemary, Dill)
2113mg (211% DV) per
100 grams
106mg (11% DV) per ground
tablespoon (5 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Dried Herbs
#2: Cheese (Parmesan, Romano, Gruyere,
Goats, Swiss)
1376mg (138% DV) per
100 grams
385mg (39% DV) per ounce
(28 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Cheese
#3: Sesame Seeds
975mg (98% DV) per
100 grams
88mg (9% DV) per tablespoon
(9 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Sesame Seeds
#4: Tofu (Fried)
372mg (37% DV) per
100 grams
48mg (5% DV) per piece (13
grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Tofu
#5: Almonds
264mg (26% DV) per
100 grams
74mg (7% DV) per ounce (23
kernels, 28 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Almonds
#6: Flaxseeds
255mg (26% DV) per
100 grams
26mg (3% DV) per tablespoon
(10 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Flaxseeds
3/25/2014 Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
http://www.healthaliciousness.com/articles/foods-high-in-calcium.php 3/6
#7: Dark Green Leafy Vegetables (Spinach,
Swiss Chard, Beet Greens, Kale)
99mg (10% DV) per
100 grams Raw
245mg (24% DV) per cup
cooked (180 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Dark Green Vegetables
#8: Milk and Yogurt (Whole Milk and Whole Milk
Yogurt)
113mg (11% DV) per
100 grams
276mg (28% DV) per cup (244
grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Milk and Yogurt
#9: Brazil Nuts
160mg (16% DV) per
100 grams
45mg (4% DV) per ounce or 6
kernels (28 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Brazil Nuts
#10: Fish (Herring, Pike, Bass, Perch, Rainbow
Trout, Pollock)
74mg (7% DV) per 100
grams cooked
106mg (11% DV) per cooked
fillet (143 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts for
Fish
Other Calcium Rich Foods
Whey Powder
796mg (80% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
1154mg (115% DV) per
(cup) (227 grams)
64mg (6% DV) per
tablespoon
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Sweet Dried Whey
Whole Milk
113mg (11% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
276mg (28% DV) per cup
(244 grams)
35mg (4% DV) in a fluid
ounce (31 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Whole Milk
Low-Fat Buttermilk
116mg (12% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
284mg (28% DV) per cup
(245 grams)
36mg (4% DV) in a fluid
ounce (31 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Low-fat Buttermilk
Whole Wheat Bread
107mg (11% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
60mg (6% DV) in two
slices (56 grams)
30mg (3% DV) per slice
(28 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Whole Wheat Bread
Rhubarb
86mg (9% DV) per
100 gram serving
105mg (10% DV) per cup
diced (122 grams)
44mg (4% DV) per stalk
(51 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Rhubarb
Fresh Thyme
405mg (41% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
4mg (0% DV) per
teaspoon (1 gram)
2mg (0% DV) in 1/2
teaspoon (0.5 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Fresh Thyme
Parsley
138mg (14% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
83mg (8% DV) per cup
(60 grams)
6mg (1% DV) per
tablespoon (4 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Fresh Parsley
Endive
52mg (5% DV) per
100 gram serving
26mg (2% DV) per cup
chopped (50 grams)
267mg (27% DV) per
head (513 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Endive
Capers (Canned)
40mg (4% DV) per
100 gram serving
4mg (0% DV) per
tablespoon (9 grams)
8mg (1% DV) in two
tablespoons (18 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Capers
Tahini (Sesame Seed Paste)
426mg (43% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
64mg (6% DV) per
tablespoon (15 grams)
119mg (12% DV) per
ounce (28 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Tahini
Molasses
205mg (21% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
691mg (69% DV) per cup
(337 grams)
41mg (4% DV) per
tablespoon (20 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Molasses
Garlic
181mg (18% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
246mg (25% DV) per cup
(136 grams)
16mg (2% DV) in three
cloves (9 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Garlic
Basil
177mg (18% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
11mg (1% DV) per cup of
whole leaves (6 grams)
9mg (1% DV) in 2
chopped tablespoons (5
grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Basil
Lettuce (Greenleaf)
36mg (4% DV) per
100 gram serving
13mg (1% DV) per cup
shredded (36 grams)
9mg (1% DV) per large
outer leaf (24 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Basil
Grape Leaves (Canned)
289mg (29% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
81mg (7% DV) per ounce
(7 leaves)(28 grams)
12mg (1% DV) per leaf (4
grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Canned Grape Leaves
Amaranth Greens (Chinese Spinach, Hinn
Choy, Yin Tsoi, Rajgira, Bayam, Kulitis,
Callaloo)
215mg (22% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
60mg (6% DV) per cup
(28 grams)
30mg (3% DV) per leaf
(14 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Raw Amaranth Leaves
47mg (5% DV) per Click to see complete nutrition facts
3/25/2014 Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
http://www.healthaliciousness.com/articles/foods-high-in-calcium.php 4/6
Amaranth (Grain)
100 gram serving 116mg (12% DV) per cup cooked (246 grams) for Amaranth Grain (Cooked)
Jute (Meloukhia)
211mg (21% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
184mg (18% DV) per cup
(87 grams)
92mg (9% DV) in a half-
cup (44 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Cooked Jute (Meloukhia)
Fireweed Leaves
429mg (43% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
99mg (10% DV) per cup
(23 grams)
94mg (9% DV) per plant
(22 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Raw Fireweed Leaves
Kelp (Seaweed)
168mg (17% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
134mg (13% DV) per cup
(80 grams)
17mg (2% DV) in 2
tablespoons (10 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Raw Kelp (Seaweed)
Nopales
164mg (16% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
244mg (24% DV) per cup
(149 grams)
48mg (5% DV) per pad or
leaf (29 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Nopales
Canned Sardines
382mg (38% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
351mg (35% DV) per can
(3.75 oz) (92 grams)
92mg (9% DV) in two
average sardines (24
grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Canned Sardines with Bones
Chili Powder
278mg (28% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
22mg (2% DV) per
tablespoon (8 grams)
8mg (1% DV) per
teaspoon (3 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Chili Powder
Chia Seeds (Dried)
631mg (63% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
177mg (18% DV) per ounce (28 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Dried Chia Seeds
Lotus Seeds
163mg (16% DV)
per 100 gram
serving
52mg (5% DV) per cup
(32 grams)
46mg (5% DV) per ounce
(42 seeds) (28 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Dried Lotus Seeds
Cooked Mustard Greens
74mg (7% DV) per
100 gram serving
104mg (10% DV) per cup
(140 grams)
52mg (5% DV) in a half
cup (70 grams)
Click to see complete nutrition facts
for Cooked Mustard Greens
Health Benefits of Calcium
Bone Health and Osteoporosis (*Controversial) - Adequate intake of calcium during childhood, adolescence, and early adulthood up to age
30 is essential to increase bone mass. The higher the bone mass at this age, the lower the risk of osteoporosis.
2
Many factors lead to
osteoporosis and affect its severity.
3
There is mixed evidence if a diet higher in calcium benefits those with osteoporosis, however, the U.S. Food
and Drug Administration still suggests that a diet high in calcium in addition with vitamin D and regular exercise may reduce risk of osteoporosis.
4
Lower Blood Pressure (*Controversial) - There is mixed evidence if increased intake of calcium will lower or raise blood pressure.
5-7
Several
studies report that those who obtain calcium from plant sources are likely to have lower blood pressure and reduced risk of heart
disease.
8-12
Conversely, those who predominantly consume their calcium from salty cheeses are more likely to have higher blood
pressure and increased risk of heart disease.
Reduced Risk of Colon Cancer (*Controversial) - Several observational studies link a higher intake of calcium with reduced colon cancer
risk.
13-16
However, various other studies report the results to be inconclusive when compared to a placebo group.
16-18
Factors which Affect Calcium Absorption
Amount of Calcium Consumed - The more calcium you consume, the less you absorb. Though consuming more calcium will increase your total
level.
2
Age - Children absorb about 60% of the calcium from foods, while adults absorb only 20%. Calcium absorption decreases with age and people
over 50 should eat more calcium.
2
Pregnancy - Pregnant women absorb more calcium.
2
Vitamin D Intake - Vitamin D enhances calcium absorption. It can be found in foods or created by exposing skin to sunshine.
2
Phytic and Oxalic Acid - Even though some studies suggest phytic and oxalic acid affect calcium absorption, people eating a balanced diet will
not be affected, further, the percent daily value already accounts for this absorption factor. High amounts of oxalic acid is found in plant foods like
spinach, collard greens, sweet potatoes, rhubarb, and beans. Phytic acid is found in whole bread, and wheat bran.
2
Sodium, Protein, Alcohol, Caffeine (Coffee and Tea) - A diet high in sodium, protein, alcohol, and caffeine (coffee and tea) can harm
absorption and retention of calcium by causing more calcium to be excreted. Alcohol also interferes with the metabolism of vitamin D.
2
3/25/2014 Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
http://www.healthaliciousness.com/articles/foods-high-in-calcium.php 5/6
Health Risks of Excessive Calcium Intake
Kidney Stones (*Controversial) - At least one clinical trial has shown that 7 years of vitamin D and calcium supplementation is associated with
increased risk of kidney stones.
30
However, several other studies report lower risk of kidney stones with increased calcium intake,
31-33
which
suggests that consumption of oxalates and lower intake of fluids are more likely to play a role in increasing kidney stone risk.
34
Impairment of the Kidneys - Extremely high levels of calcium, often associated with hyperparathyroidism, as opposed to food or supplement
intake, can impair functioning of the kidneys, and lead to reduced absorption of other essential minerals, such as iron, zinc, magnesium, and
phosphorus.
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease (*Controversial) - Some studies show that taking calcium supplements in excess of 500mg daily
can increase risk of cardiovascular diseases.
44,45
Increased Risk of Prostate Cancer (*Controversial) - Several studies have found a link between increased calcium intake, or 2.5 servings of
dairy foods, and increased risk of prostate cancer. It is inconclusive whether the dairy products or the calcium increases the risk.
19-25
However,
several other studies have found no association between prostate cancer and calcium,
26-29
suggesting that calcium from plant foods is better
than from dairy products.
Decreased Absorption of Certain Medications - Excessive intake of calcium can decrease the absorption of the following:
35-37
Biphosphonates (for osteoporosis)
Antibiotics (fluoroquinolone and tetracycline)
Levothyroxine (for hypothyroidism)
Phenytoin (an anticonvulsant)
Tiludronate disodium (for Paget's disease)
People at Risk of a Calcium Deficiency
Postmenopausal women - Due to a reduced level of the hormone estrogen, calcium absorption decreases in menopausal women.
38
Unfortunately, an increased intake of calcium during this time may not help.
39,40
Women who miss their menstrual period (Amenorrhea) - Amenorrhea is a condition that typically occurs in anorexic women, or women who
are athletes. This is again due to a reduced level of estrogren. Increased intake of calcium foods is recommended.
41
Individuals with lactose intolerance - People with lactose intolerance consume fewer dairy products, which in turn, can reduce the amount of
calcium consumed.
Vegetarians and Vegans (*Controversial) - Oxalic and phytic acids found primarily in plant products are thought to reduce absorption of
calcium.
42
However, consumption of meats has also been shown to increase the excretion of calcium.
43
As such vegetarians and vegans might
not be any worse off than omnivores, but should still be sure to eat plenty of plant foods high in calcium.
People taking Certain Medications
Aluminum and magnesium containing antacids.
Mineral oil and stimulant laxatives.
Glucocorticoids, such as prednisone.
Recipes High in Calcium
Wine Steamed Kale
Vegetarian Gumbo with Okra
Lightly Cooked Napa Cabbage
Blackberry Salad
Spicey Lentil Cabbage
Warnings
Cheese and Whole Milk are high cholesterol foods which should be eaten in moderate amounts and avoided by people at risk of heart disease or
stroke.
Sesame Seeds, Flax Seeds, Almonds, Molasses, and Brazil Nuts are high calorie foods and should be eaten in moderate amounts by people with
a high body mass index.
3/25/2014 Top 10 Foods Highest in Calcium
http://www.healthaliciousness.com/articles/foods-high-in-calcium.php 6/6
Buy Calcium Foods
Dried Herbs, Parmesan cheese, Sesame Seeds, Almonds, Flax Seeds, Molasses, Brazil Nuts, Herring.
You might also like
- Juicing VegetablesDocument5 pagesJuicing Vegetablestenbears m.No ratings yet
- Maca Lepidium Meyenii Materia Medica HerbsDocument9 pagesMaca Lepidium Meyenii Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Expectorant and Demulcent HerbsDocument3 pagesExpectorant and Demulcent HerbsqueencelNo ratings yet
- Hpylorisolution PDFDocument66 pagesHpylorisolution PDFAndrej OfakNo ratings yet
- Offers 2012 S MHDocument24 pagesOffers 2012 S MHwlfhjoreihfloergjbNo ratings yet
- Coconut Success StoriesDocument23 pagesCoconut Success StoriescheniahmNo ratings yet
- The Many Benefits of Coconut Water KefirDocument3 pagesThe Many Benefits of Coconut Water KefirMa Geobelyn LopezNo ratings yet
- Blocked Fallopian TubesDocument2 pagesBlocked Fallopian TubesPreethi JoseNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide: The Body EcologyDocument15 pagesQuick Start Guide: The Body EcologymNo ratings yet
- DoctrineDocument1 pageDoctrinevinay44No ratings yet
- 2023 - George Felfoldi (eBook-Herbal) - Healing Properties of Thistles, 113 PagesDocument113 pages2023 - George Felfoldi (eBook-Herbal) - Healing Properties of Thistles, 113 PagesGeorge FelfoldiNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle An Ayurvedic ProspectiveDocument9 pagesMenstrual Cycle An Ayurvedic ProspectiveRGuti13No ratings yet
- Natural Cleanising TechniquesDocument88 pagesNatural Cleanising TechniquesPetra JobovaNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Blocked Fallopian TubesDocument80 pagesCh06 Blocked Fallopian TubesAasia Najaf SoomroNo ratings yet
- HERBAL TEA RECIPES: Aromatic Delights: Herbal Tea Recipes for Health and WellnessFrom EverandHERBAL TEA RECIPES: Aromatic Delights: Herbal Tea Recipes for Health and WellnessNo ratings yet
- Fenugreek Benefits PDFDocument10 pagesFenugreek Benefits PDFrecianzubyNo ratings yet
- Fenugreek SeedsDocument6 pagesFenugreek SeedsAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Drugs From Marine OriginatesDocument10 pagesAyurvedic Drugs From Marine Originateskunalprabhu148No ratings yet
- Reversing Clogged Arteries: Super Herbal Remedies for Heart HealthFrom EverandReversing Clogged Arteries: Super Herbal Remedies for Heart HealthNo ratings yet
- Growing HerbsDocument19 pagesGrowing HerbsspicerjlNo ratings yet
- For Herbal Medicines": Scientific Editors Data ManagerDocument1 pageFor Herbal Medicines": Scientific Editors Data ManagerSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Herbal Med.Document14 pagesHerbal Med.Jerry V. CaraecleNo ratings yet
- 6 Health Benefits CoffeeDocument5 pages6 Health Benefits CoffeeJaime GarciaNo ratings yet
- Best Ayurvedic Medicine For Diabetes - Comparison & ReviewsDocument13 pagesBest Ayurvedic Medicine For Diabetes - Comparison & ReviewsSomanshu BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Restorative Efficiency of Bursera Simarubaisolated Phytonutrients For The Therapy of Various DiseasesDocument15 pagesRestorative Efficiency of Bursera Simarubaisolated Phytonutrients For The Therapy of Various DiseasesleonardoNo ratings yet
- American IndiansDocument14 pagesAmerican IndiansYunita D. SetyoriniNo ratings yet
- French OPC Grape Seed For Diabetes, Heart, Cancer and MoreDocument4 pagesFrench OPC Grape Seed For Diabetes, Heart, Cancer and MoreTheVitaminStore.comNo ratings yet
- 2015 - George Felfoldi - (Ebook - Cooking) Good Food and Art Cookbook, 407 Pages PDFDocument407 pages2015 - George Felfoldi - (Ebook - Cooking) Good Food and Art Cookbook, 407 Pages PDFGeorge FelfoldiNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Macrobiotic PrinciplesDocument23 pagesA Guide To The Macrobiotic PrinciplesMus Oub100% (1)
- Bioactives and Traditionalmedicines For Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument177 pagesBioactives and Traditionalmedicines For Cardiovascular DiseasesSocioCamp MediaNo ratings yet
- Herbs and Spices For The Home GardenDocument8 pagesHerbs and Spices For The Home GardenSharad BhutoriaNo ratings yet
- 2023 - George Felfoldi - (Ebook - Health) - Another Look at Seaweed and Algae, 136 PagesDocument136 pages2023 - George Felfoldi - (Ebook - Health) - Another Look at Seaweed and Algae, 136 PagesGeorge FelfoldiNo ratings yet
- Human Body Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesHuman Body Parts and Their FunctionsCarlos Bladimir Estrada MontecinosNo ratings yet
- 10 Lavender Oil Benefits For Major Diseases & Minor Ailments - Dr. AxeDocument10 pages10 Lavender Oil Benefits For Major Diseases & Minor Ailments - Dr. AxeJoseph TupasNo ratings yet
- 5 Benefits of BoswelliaDocument6 pages5 Benefits of BoswelliaPaulNo ratings yet
- E Cookbooks Library Mexican RecipesDocument22 pagesE Cookbooks Library Mexican RecipesMarkella KoufNo ratings yet
- Apatani HerbsDocument0 pagesApatani HerbsLuvjoy ChokerNo ratings yet
- Herbal PharmacologyDocument11 pagesHerbal Pharmacologywingrace688No ratings yet
- The 29 Healthiest Foods On The WorldDocument9 pagesThe 29 Healthiest Foods On The WorldlittlenemzNo ratings yet
- Corn SilkDocument1 pageCorn Silkwillyagung4557No ratings yet
- Spice List 20121Document2 pagesSpice List 20121ravivarmahyd8173No ratings yet
- Food Revolution Summit: Program & ScheduleDocument13 pagesFood Revolution Summit: Program & ScheduleDNo ratings yet
- Periodontitis and Systemic Disease: FeatureDocument4 pagesPeriodontitis and Systemic Disease: Featurewendyjemmy8gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Herbal Plants and Its Uses: 1. Akapulko (Cassia Alata)Document5 pagesHerbal Plants and Its Uses: 1. Akapulko (Cassia Alata)Luz Sumaylo MiñozaNo ratings yet
- HERBAL TEA FOR BEGINNERS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Make Some of the Best Herbal Teas and Prevent Diseases with the Natural Healing Power of HerbsFrom EverandHERBAL TEA FOR BEGINNERS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Make Some of the Best Herbal Teas and Prevent Diseases with the Natural Healing Power of HerbsNo ratings yet
- Hippocrates - The Father of MedicineDocument1 pageHippocrates - The Father of Medicine123121No ratings yet
- Caffeine and Theobromine Content of Selected Hershey's ChocolateDocument2 pagesCaffeine and Theobromine Content of Selected Hershey's ChocolateJude PaxmrosyNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plant Diversity in Kulathupuzha Locality, Kollam DistrictDocument18 pagesMedicinal Plant Diversity in Kulathupuzha Locality, Kollam DistrictSandeepamol P SNo ratings yet
- Super FoodsDocument70 pagesSuper FoodsThe Health Therapist AcademyNo ratings yet
- My Herbs Issue 22 November 2022Document84 pagesMy Herbs Issue 22 November 2022Andrea JozsaNo ratings yet
- Ancient WondersDocument13 pagesAncient WondersK. ZinNo ratings yet
- Cow Ayurvedic PANACEASDocument57 pagesCow Ayurvedic PANACEASmpidoh100% (1)
- 30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutDocument38 pages30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutMaria BarbaliaNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Diet FOR DISEASE PREVENTION: The Ultimate Guide to Eat Healthy, Fight Inflammation, Lose Weight and Fight Cronic DiseaseFrom EverandAlkaline Diet FOR DISEASE PREVENTION: The Ultimate Guide to Eat Healthy, Fight Inflammation, Lose Weight and Fight Cronic DiseaseNo ratings yet
- The Many Health Benefits of Aloe VeraDocument3 pagesThe Many Health Benefits of Aloe VeraTanvir MirzaNo ratings yet
- Neem TreeDocument2 pagesNeem Treeyuvi087No ratings yet
- Natural Remedies Encyclopedia (PDFDrive) - 2Document30 pagesNatural Remedies Encyclopedia (PDFDrive) - 2angelobuffaloNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential Nutrients PDFDocument15 pages6 Essential Nutrients PDFJuan Rodriguez Jr100% (1)
- Q.No. Type Section Key/Range MarksDocument3 pagesQ.No. Type Section Key/Range Marksbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Buffer Preparation PDFDocument6 pagesBuffer Preparation PDFbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- BT 2019Document13 pagesBT 2019biotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting SDS-PAGE 1Document3 pagesTroubleshooting SDS-PAGE 1biotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document3 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)biotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Whole Cell ExtractDocument1 pageWhole Cell Extractbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Buffer Preparation PDFDocument6 pagesBuffer Preparation PDFbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ExtractsDocument2 pagesNuclear Extractsbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Group 1 Prelim Book List PDFDocument2 pagesTNPSC Group 1 Prelim Book List PDFbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Code No. 14: Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2010Document20 pagesMechanical Engineering Code No. 14: Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2010biotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Ies 17 Set A Me Q ADocument67 pagesIes 17 Set A Me Q Abiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- 1 TolerancesDocument1 page1 Tolerancesbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Befcv List PDFDocument22 pagesBefcv List PDFbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Teachers Recruitment Board: 1. Important DatesDocument13 pagesTeachers Recruitment Board: 1. Important Datesbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Lec09 Three PhaseDocument84 pagesLec09 Three Phasebiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Isa BusDocument30 pagesIsa Busbiotech_vidhya100% (1)
- Olsen MethodDocument18 pagesOlsen MethodMark CarpesoNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- C100 Eng Bulletin Sulfuric Acid 0910Document24 pagesC100 Eng Bulletin Sulfuric Acid 0910wacsii ccasullaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Disorders in Fruit CropsDocument8 pagesPhysiological Disorders in Fruit CropsMohamed BahgatNo ratings yet
- Product Analysis Certificate: Propanol-2 (Iso-Propanol) A.RDocument1 pageProduct Analysis Certificate: Propanol-2 (Iso-Propanol) A.RAMMARNo ratings yet
- LigniteDocument23 pagesLigniteMayra Sánchez CabanillasNo ratings yet
- Solved 2024 Specimen Paper ICSE Class 10 ChemistryDocument11 pagesSolved 2024 Specimen Paper ICSE Class 10 ChemistrymmroyalethegreatNo ratings yet
- 2014 Test Paper DR Homi BhabhaDocument9 pages2014 Test Paper DR Homi BhabhaDr Mohan Savade100% (1)
- Herbal Drugs ReportDocument288 pagesHerbal Drugs Reportparakhurd0% (1)
- Soil Science 2019 LEADocument10 pagesSoil Science 2019 LEAElsa De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 5070 w16 QP CompleteDocument120 pages5070 w16 QP CompleteAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- Physiological Disorders and Corrective Measures For Greenhouse TomatoesDocument5 pagesPhysiological Disorders and Corrective Measures For Greenhouse Tomatoesstand backNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 2)Document2 pagesEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 2)Alexandrea ModillasNo ratings yet
- Optimisation de L'utilisation de Lait de Chaux Image MEB de Ineich2017Document9 pagesOptimisation de L'utilisation de Lait de Chaux Image MEB de Ineich2017Yassine GouzzaliNo ratings yet
- Usp31nf26s1 - m11430, USP Monographs - Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageUsp31nf26s1 - m11430, USP Monographs - Calcium CarbonateEfsha KhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaDocument6 pages2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaTheodora HamletNo ratings yet
- Rishab Soya MilkDocument8 pagesRishab Soya MilkRishabJaiswal100% (1)
- 03 Lewabrane Manual System Design 03Document13 pages03 Lewabrane Manual System Design 03zamijakaNo ratings yet
- Sample Persuasi-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesSample Persuasi-WPS OfficeLeilla Mae PataNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-26 at 7.29.30 PMDocument103 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-26 at 7.29.30 PMfahad212qwNo ratings yet
- Causes of Distress and Deterioration of Concrete, EM 1110-2-2002 1995-06-30Document14 pagesCauses of Distress and Deterioration of Concrete, EM 1110-2-2002 1995-06-30RONALD MUELLERNo ratings yet
- Korean Construction SpecificationDocument14 pagesKorean Construction SpecificationOnnuri WonNo ratings yet
- PROCESS FLOW OF APPLICATION OF PNP LICENSES AND PERMITS - UPLB Oct 5 2016Document33 pagesPROCESS FLOW OF APPLICATION OF PNP LICENSES AND PERMITS - UPLB Oct 5 2016Trish AustriaNo ratings yet
- BergaFat: A Fat Powder With Value AddedDocument2 pagesBergaFat: A Fat Powder With Value AddedMilling and Grain magazineNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY BOOK 2 ObjDocument44 pagesCHEMISTRY BOOK 2 ObjHaris AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 20-Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument4 pages20-Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistrythucinorNo ratings yet
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet I PDFDocument3 pagesNaming Ionic Compounds Worksheet I PDFgowrimanohar1975No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School,: VijayawadaDocument8 pagesDelhi Public School,: VijayawadaBild Andhra PradeshNo ratings yet
- Journal of African Earth Sciences: M. Meck, J. Atlhopheng, W.R.L. MasambaDocument5 pagesJournal of African Earth Sciences: M. Meck, J. Atlhopheng, W.R.L. MasambaMuhammad Imam WahyuddinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision NotesDocument7 pagesChemistry Revision NotesFarhan RahmanNo ratings yet