Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydraulics & Pneumatics: LECTURE #
Hydraulics & Pneumatics: LECTURE #
Uploaded by
Farah HumaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydraulics & Pneumatics: LECTURE #
Hydraulics & Pneumatics: LECTURE #
Uploaded by
Farah HumaCopyright:
Available Formats
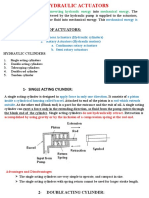
HYDRAULICS
&
PNEUMATICS
LECTURE # -----
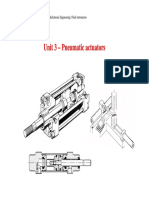
PROBLEM:
A double acting, single
piston cylinder has a
piston of diameter 100
mm and a piston rod of
diameter 25 mm. what
is the ratio of the
extend and return
forces if a pressure of 6
bar is applied as shown
in figure.
DESIGN DEVELOPMENT
Pneumatic cylinders have been developed in the
following directions:
Contact less requirements, hence use of magnet
Stopping heavy loads
Rod less cylinder for limited space
Protective coatings for harsh environment
Increased load carrying capacity
Robotic applications
Hollow piston rods for vacuum suction cups
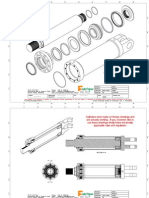
DOUBLE ACTING CYLINDER WITH
END POSITION CUSHIONING
Used to reduce Sudden damage
impacts for heavy loads
To achieve correct deceleration
Regulating screw ,screwed fully
Backed off in order to be adjusted slowly to
the optimum value.
End Cushioning:
TANDEM DOUBLE ACTING CYLINDER
Two double acting cylinders joined to form a
single unit
Suitable for application where high forces
are required but the cylinder diameter is
restricted.
CYLINDERS WITH THROUGH PISTON ROD
Through piston rod open at both sides
Force is same on both sides
Can be hollow to:
Conduct media such as compressed air
Vacuum connection is possible
Multi-position Cylinders:
Consists of two or several
double acting cylinders,
which are interconnected.
In case of two cylinders
with different stroke
lengths, four positions are
obtained.
IMPACT CYLINDERS
Impact cylinders are used for high kinetic
energy.
For high kinetic energy by increasing the
piston speed.
Not suitable for large forming distances.
Semi rotary actuator:
Dual piston type actuator
Vane actuator
DUAL PISTON TYPE ACTUATOR
(Rotary Cylinder):
Gear-tooth profile
Piston rod drives a gear wheel (conversion of linear to
rotary)
Range varies from 45,90,180,270,360.
Torque is dependent on:
Pressure
Piston surface
Gear ratio
VANE ACTUATOR:
Rodless Cylinder:
Shorter in length
Eliminates risk of buckling piston rod
Movement takes place over entire stroke
Extremely large cylinders upto 10m
Load can be directly attached on mounting surface
Principle used for the construction of Rod less
cylinders:
Band or cable cylinder
Sealing band cylinder with slotted cylinder barrel
Cylinder with magnetically coupled slide
Band or cable cylinder
Force is transferred to slide via circulating band
Leaving the piston chamber, the band passes through a seal
Band is reversed via guide rollers
Wipers ensure that no contamination reaches the guide rollers via
the band
Sealing band cylinder with slotted cylinder
barrel
Cylinder barrel is provided with a slot across the entire length
The force is transmitted via a slide
Slide is permanently connected to the piston
Connection is directed outward via the slotted cylinder barrel
Slot is sealed by sealing band
Cylinder with magnetically coupled slide
Consists of
Cylindrical barrel
Piston
2 slides
Angular permanent magnets fitted on piston and slide
Cylinder barrel is hermetically sealed from outer slide
No leakage losses
You might also like
- Pneumatic Reciprocating Powere Hacksaw Machine - Docx FinalDocument11 pagesPneumatic Reciprocating Powere Hacksaw Machine - Docx FinalARVIND DARLING100% (2)
- Chancadores de ConosDocument60 pagesChancadores de Conosvalentina_brune6307100% (8)
- Ga HistoryDocument11 pagesGa HistoryjoshcottNo ratings yet
- Ryanair Magazine January-February 2012Document154 pagesRyanair Magazine January-February 2012Sampaio RodriguesNo ratings yet
- 2020 Dockzilla Loading Dock Buyers GuideDocument11 pages2020 Dockzilla Loading Dock Buyers GuideNadeem RazaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Pneumatic ActuatorsDocument46 pagesLecture 6 Pneumatic ActuatorsKristine DNo ratings yet
- Edusat Presentation On Pneumatics5Document147 pagesEdusat Presentation On Pneumatics5metroroadNo ratings yet
- Welding Machine Project Report FinalDocument44 pagesWelding Machine Project Report FinalJAYAPRABHAKARAN N NNo ratings yet
- Applications of Hydraulics&Pneumatics: Session 6Document12 pagesApplications of Hydraulics&Pneumatics: Session 6Zippygroup ZsgNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Rod Bending Machine Project ReportDocument3 pagesPneumatic Rod Bending Machine Project ReportJeyakumar NNo ratings yet
- L7 - Hydraulic CylindersDocument69 pagesL7 - Hydraulic CylindersMark BeckerNo ratings yet
- SESSION 1-Introduction To Pneumatic ControlsDocument31 pagesSESSION 1-Introduction To Pneumatic Controlsharishme028No ratings yet
- Pumps Course MaterialDocument222 pagesPumps Course Materialarkan1976No ratings yet
- Hydraulic CylindersDocument10 pagesHydraulic CylindersBrandon Ha100% (1)
- Edusat Presentation On Pneumatics5Document147 pagesEdusat Presentation On Pneumatics5metroroadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes HPDocument34 pagesUnit 2 Notes HPVasanth MemoriesNo ratings yet
- 6 - HydrauliccylindersDocument29 pages6 - HydrauliccylindersMohamed ZahranNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder: Guided By:-Dr. Pankaj Sahlot Presented By: - Kishan Savaliya (15Bme149D) Viken Patel (14BME072)Document15 pagesHydraulic Cylinder: Guided By:-Dr. Pankaj Sahlot Presented By: - Kishan Savaliya (15Bme149D) Viken Patel (14BME072)SK MagnetxNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Working Elements: Chapter-4Document56 pagesPneumatic Working Elements: Chapter-4Venkat Preethi ANo ratings yet
- Unit Ii PhiDocument33 pagesUnit Ii PhiAnshul jainNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Actuators: For Power, Motion and ControlDocument162 pagesPneumatic Actuators: For Power, Motion and ControlJulian LajaraNo ratings yet
- 1 Linear ActuatorsDocument34 pages1 Linear ActuatorsSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CylindersDocument36 pagesCylindersNellai Vpr100% (2)
- The Norgren Guide To Specifying Pneumatic ActuatorsDocument34 pagesThe Norgren Guide To Specifying Pneumatic ActuatorssridveiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Hydraulic Actuators L2Document48 pagesChapter 2 Hydraulic Actuators L2kidus tsegayeNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document22 pagesModule 3hansolo7rockzNo ratings yet
- Gas Springs1Document32 pagesGas Springs1GLADWIN PAUL SIM 16-18No ratings yet
- Rotary PumpsDocument34 pagesRotary PumpsMUHAMMAD SOHAIB UR REHMANNo ratings yet
- Mobile Telescopic Cylinders: Selection GuideDocument4 pagesMobile Telescopic Cylinders: Selection Guidehanamant1991100% (1)
- ActuatorsDocument17 pagesActuatorsGururaj GadadNo ratings yet
- Actuators 1Document16 pagesActuators 1DIEGOsemNo ratings yet
- ME080 Section 8 - Other Hydraulic ComponentsDocument101 pagesME080 Section 8 - Other Hydraulic ComponentsAhmed Farag100% (1)
- Linear & Manual - ActuatorDocument20 pagesLinear & Manual - ActuatorsviswaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 3 - WhiteDocument49 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 3 - WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- FLUIDS POWER SLIDES Chapter6Document40 pagesFLUIDS POWER SLIDES Chapter6Kapil KaviNo ratings yet
- Ce 30Document67 pagesCe 30Ravi Shankar JoshiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder by Syed Jaffer PDFDocument39 pagesHydraulic Cylinder by Syed Jaffer PDFSiraj Busse100% (7)
- Clutch Working and PropertiesDocument41 pagesClutch Working and Propertiessarath100% (1)
- Hyd CylDocument41 pagesHyd CylSachin BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Actuators and Output Devices: Chapter B-3Document24 pagesActuators and Output Devices: Chapter B-3stolehaNo ratings yet
- نيوماتيك 4Document18 pagesنيوماتيك 4عمر منيرNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating CompressorsDocument24 pagesReciprocating Compressorsluciano.almeidavieira07No ratings yet
- MD Clutch ResearcDocument4 pagesMD Clutch ResearcJeshua LloreraNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder DesignDocument19 pagesHydraulic Cylinder DesignRumesha Thathsarani100% (4)
- AbstractDocument18 pagesAbstractJohn AjishNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Actuator, Basic Knowledge, by NorgrenDocument162 pagesPneumatic Actuator, Basic Knowledge, by Norgrena_yNo ratings yet
- Fig. 2.1: Bending TerminologyDocument6 pagesFig. 2.1: Bending TerminologyeshwariNo ratings yet
- Different Types of The Pneumatic CylinderDocument10 pagesDifferent Types of The Pneumatic CylinderifyNo ratings yet
- Clutches and BrakesDocument10 pagesClutches and BrakesKhaloud Mahdi Al-JasmiNo ratings yet
- Hydrolic Pipe Bending MachineDocument54 pagesHydrolic Pipe Bending MachineSanketDhande0% (1)
- Hydraulic CylinderDocument6 pagesHydraulic Cylindermichol2014No ratings yet
- PumpsDocument38 pagesPumpsbernabasNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Auto Feed Drilling Machine With Indexing Machine: SynopsisDocument30 pagesPneumatic Auto Feed Drilling Machine With Indexing Machine: SynopsisMaruthi JacsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 37PNEUMATICS ACTUATORSDocument43 pagesLecture 37PNEUMATICS ACTUATORSpratapy234No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Pneumatic Actuators - 2020Document103 pagesChapter 4 - Pneumatic Actuators - 2020tranxuancanh0691No ratings yet
- Hydrolic Pipe Bending MachineDocument59 pagesHydrolic Pipe Bending MachineNilesh Maheshwari67% (3)
- Cement Retainer & Bridge PlugDocument6 pagesCement Retainer & Bridge Plugpetroleumgas100% (2)
- المستند (12)Document11 pagesالمستند (12)a7510378No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinders 22Document42 pagesHydraulic Cylinders 22Mo'taz MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementFrom EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementNo ratings yet
- Pitman's Motorists Library - The Book of the Austin Ten - A Fully Illustrated Instruction Book for All Owners of Models from 1932 to 1939From EverandPitman's Motorists Library - The Book of the Austin Ten - A Fully Illustrated Instruction Book for All Owners of Models from 1932 to 1939No ratings yet
- Hydraulics & Pneumatics: Fourth LectureDocument22 pagesHydraulics & Pneumatics: Fourth LectureFarah HumaNo ratings yet
- 1st LectureDocument17 pages1st LectureFarah HumaNo ratings yet
- Mct-212: Digital Logic DesignDocument17 pagesMct-212: Digital Logic DesignFarah HumaNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Device BasicsDocument13 pagesDigital Logic Device BasicsFarah HumaNo ratings yet
- Shaft DesignDocument37 pagesShaft DesignFarah HumaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Machine Tool LatheDocument19 pagesPresentation Machine Tool LatheFarah HumaNo ratings yet
- Sant Rajinder Singh Ji Maharaj - Visions of The New MilleniumDocument8 pagesSant Rajinder Singh Ji Maharaj - Visions of The New MilleniumjjcalderNo ratings yet
- 102 192 1 SMDocument8 pages102 192 1 SMLinaNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering: V.K SinghDocument32 pagesBasic Civil Engineering: V.K SinghVikash SinghNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument35 pagesBusiness ProposalMJ MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Protein TranslationDocument104 pagesProtein Translationmazahir hussainNo ratings yet
- Question Bank AR VRDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank AR VRarambamranajsingh04No ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects Fluor Albus of Female and Treatment: Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesClinical Aspects Fluor Albus of Female and Treatment: Literature ReviewDafit VdayNo ratings yet
- Report On Seismic CodesDocument2 pagesReport On Seismic CodesLakshmiRaviChanduKolusuNo ratings yet
- Formatted SBI Clerk Mains Previous Year Paper 2021Document78 pagesFormatted SBI Clerk Mains Previous Year Paper 2021shyamveer147No ratings yet
- Rajpura Escorts - ChandigarhnightDocument2 pagesRajpura Escorts - ChandigarhnightChandigarh NightNo ratings yet
- The SNG Blueprint Part 1 PDFDocument26 pagesThe SNG Blueprint Part 1 PDFAdrian PatrikNo ratings yet
- Hoogendoorn Anniversary Magazine - 50 Years - LRDocument20 pagesHoogendoorn Anniversary Magazine - 50 Years - LRtachetNo ratings yet
- 5013Document3 pages5013glennfreyolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Week 2 PerdevDocument15 pagesLesson 10 - Week 2 PerdevChristian OconNo ratings yet
- Resensi Novel B.inggris RikaDocument5 pagesResensi Novel B.inggris RikaRizqi RahmaniaNo ratings yet
- Facts On Why Homework Is Bad For YouDocument7 pagesFacts On Why Homework Is Bad For Youafmsxohtq100% (1)
- MCQ IadDocument23 pagesMCQ Iads soyaNo ratings yet
- NEW Curriculum Vitae Marking Scheme (Jan 2022)Document2 pagesNEW Curriculum Vitae Marking Scheme (Jan 2022)TONo ratings yet
- Chemo Stability Chart - AtoKDocument59 pagesChemo Stability Chart - AtoKAfifah Nur Diana PutriNo ratings yet
- NEW Fees Record 2010-11Document934 pagesNEW Fees Record 2010-11manojchouhan2014No ratings yet
- Tutorial QuiltSquareDocument9 pagesTutorial QuiltSquaremrmenellisNo ratings yet
- Xt2052y2asr GDocument1 pageXt2052y2asr GjoseNo ratings yet
- Hazards and RisksDocument27 pagesHazards and RisksElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- Gopi EnglishDocument31 pagesGopi EnglishGopi ShankarNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3: Talk About Your Weekend or Holiday Plan Using VerbsDocument3 pagesLESSON 3: Talk About Your Weekend or Holiday Plan Using VerbsjoannaNo ratings yet
- A Kick For The GDP: The Effect of Winning The FIFA World CupDocument39 pagesA Kick For The GDP: The Effect of Winning The FIFA World CupBuenos Aires HeraldNo ratings yet
- I) Height of Retaining Wall H: Preliminary DataDocument10 pagesI) Height of Retaining Wall H: Preliminary DataOmPrakashNo ratings yet