Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
Uploaded by
Samantha Dasmariñas Magaan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesThis document discusses several endocrine glands and diseases that can affect them. It describes the pineal gland and its role in producing melatonin to regulate circadian rhythms. It then discusses diseases of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, parathyroid gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and gonads. Common diseases include hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism affecting the thyroid, Cushing's disease impacting the adrenals, and diabetes related to the pancreas. The document provides details on symptoms and treatments for disorders of these important endocrine organs.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several endocrine glands and diseases that can affect them. It describes the pineal gland and its role in producing melatonin to regulate circadian rhythms. It then discusses diseases of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, parathyroid gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and gonads. Common diseases include hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism affecting the thyroid, Cushing's disease impacting the adrenals, and diabetes related to the pancreas. The document provides details on symptoms and treatments for disorders of these important endocrine organs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
Uploaded by
Samantha Dasmariñas MagaanThis document discusses several endocrine glands and diseases that can affect them. It describes the pineal gland and its role in producing melatonin to regulate circadian rhythms. It then discusses diseases of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, parathyroid gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and gonads. Common diseases include hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism affecting the thyroid, Cushing's disease impacting the adrenals, and diabetes related to the pancreas. The document provides details on symptoms and treatments for disorders of these important endocrine organs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Anatomy and Physiology
Magaan, Samantha D. Dr. Sulam
1-2 BSP 8:30-12:30/ TTH
Diseases of Endocrine Glands
Pineal body- The pineal gland, also known as the pineal body, conarium or epiphysis cerebri, is
a small endocrine gland in the vertebratebrain. It produces the serotonin derivative melatonin,
a hormone that affects the modulation of sleep patterns in the circadian rhythms and seasonal
functions. Its shape resembles a tiny pine cone (hence its name), and it is located in
the epithalamus, near the centre of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove
where the two rounded thalamic bodies join.
Hypothalamus- Hypothalamic disease is a disorder presenting primarily in the hypothalamus,
which may be caused by damage resulting from malnutrition,
including anorexia and bulimia eating disorders, genetic disorders, radiation, surgery, head
trauma, lesion, tumour or other physical injury to the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is the
control center for several endocrine functions. Endocrine systems controlled by the
hypothalamus are regulated by anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), corticotropin-releasing
hormone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone, oxytocin, all of
which are secreted by the hypothalamus. Damage to the hypothalamus may impact any of these
hormones and the related endocrine systems. Many of these hypothalamic hormones act on
the pituitary gland. Hypothalamic disease therefore affects the functioning of the pituitary and
the target organs controlled by the pituitary, including the adrenal glands, ovaries and testes, and
the thyroid gland.
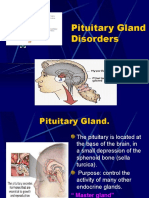
Pituitary Gland - Hypersecretion (Hyperpituitarism, Acromegaly, Gigantism).
The pituitary gl and secretes t oo much of t he growt h
hormone. If t his occurs in children, t he resul t is giantism ( an abnormal skeletal
devel opment ). Excessive production of t he growt h hormone when an individual is
anadul t causes acromegal y (head, face, hands, feet, and internal organs get progre
ssivelylarger). In giantism, t he people are general l y large but usual l y ver y weak. I
nacromegal y, t he bones of t he face, hands, and feet wi den. The j aw protrudes, and
t he forehead bones bul ge
Hyposecretion. The condition occurs when not enough hormones are
secreted by t he anterior lobe of t he pituitary gl and. The resul t is metabolic dysfunct i
on, sexual immaturit y, and growt h retardation when t he probl em takes place in chil
dhood. In an adul t , insufficient amount s of t hese hormones result s in
a condition called
Simmond' s disease. Signs and sympt oms i ncl ude emaciation (ext reme thinness), as
thenia (severe weakness or loss of strength), lowered metabolic rate, l ow
temperature, and l ow blood pressure. The cause of this deficiency in t he production
of hormones is usual l y t rauma, t umor, or hemorrhage.
Parathyroid Gl and-
Hyperparathyroidism. One or more of the parathyroid glands enlarges. Too
much parathyroid hormone is secreted, and the serum calcium level becomes too high.
There is a change in the function of cells of the bone, renal tubules, and gastrointestinal
mucosa. The withdrawal of calcium from bones (osteoporosis) leads to hypercalcemia
(abnormally high concentration of calcium in the blood) and kidney stones. Other signs
and symptoms include muscular weakness, gastrointestinal symptoms such as
anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pains. Treatment depends on the diagnosis
of the cause of the condition. Surgical removal of the parathyroid tissue is often the
treatment.
Thyroi d Gl and- is a common problem that can cause symptoms because of over- or under-
function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is an essential organ for producing thyroid
hormones, which maintain body metabolism. The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck
below the Adam's apple. Thyroid disease can also sometimes lead to enlargement of the thyroid
gland in the neck, which can cause symptoms that are directly related to the increase in size of
the organ (such as difficulty swallowing and discomfort in front of the neck).
Adrenal gland- Adrenal gland disorders (or diseases) are conditions that interfere with the
normal functioning of the adrenal glands. They are characterized by adrenal insufficiencies,
where there are deficiencies in the availability of steroids that are produced by the adrenal
glands. Adrenal Gland disorder is rather prevalent in small animals including rabbits, ferrets &
guinea pigs. They may cause hyperfunction or hypofunction, and it may be congenital or
acquired. Adrenal gland disorders are challenging to diagnose, but if left untreated, they are life
threatening and can be very deadly.
Pancreas- The pancreas is a gland behind your stomach and in front of your spine. It produces
juices that help break down food and hormones that help control blood sugar levels. Problems
with the pancreas can lead to many health problems. These include
Pancreatitis, or inflammation of the pancreas: This happens when digestive enzymes start
digesting the pancreas itself
Pancreatic Cancer
Cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder in which thick, sticky mucus can also block tubes in your
pancreas
Gonads- Gonadal dysgenesis is any congenital developmental disorder of the reproductive system
characterized by a progressive loss of germ cellson the developing gonads of an embryo. This loss
leads to extremely hypoplastic (underdeveloped) and dysfunctioning gonads mainly composed
of fibrous tissue, hence the name streak gonads - i.e., a form of aplasia in which the ovary is replaced
by functionless tissue. The accompanying hormonal failure also prevents the development of secondary
sex characteristics in either sex, resulting in a sexually infantile female appearance and infertility.
You might also like
- Roger A. Mackinnon, Robert Michels, Peter J. Buckley-The Psychiatric Interview in Clinical Practice (2015)Document724 pagesRoger A. Mackinnon, Robert Michels, Peter J. Buckley-The Psychiatric Interview in Clinical Practice (2015)Selma Churukova92% (13)
- AWHONN Advanced Fetal Monitoring CourseDocument51 pagesAWHONN Advanced Fetal Monitoring CourseVanessa FloresNo ratings yet
- MI40-X - Nutrition GuideDocument12 pagesMI40-X - Nutrition GuideJoe Merengues100% (2)
- Reviewer With AnswersDocument11 pagesReviewer With AnswersSing KoNo ratings yet
- Ky 9 KZ OCt YO96 LBRL 0 HH DDocument22 pagesKy 9 KZ OCt YO96 LBRL 0 HH DVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 - The Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesTOPIC 3 - The Endocrine SystemKaren Pearl TagleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument46 pagesEndocrine Systemespinajeff07No ratings yet
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document3 pages11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- ArainDocument71 pagesArainAllah Bux KhosoNo ratings yet
- Alteration in Endocrine Function: Alteration in Hypothalamic Pituitary Functions Empty Sella SyndromeDocument11 pagesAlteration in Endocrine Function: Alteration in Hypothalamic Pituitary Functions Empty Sella SyndromeReneé CamilleNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesDiseases of The Endocrine SystemJerahmeel Sombilon Genilla100% (1)
- Diseases of Endocrine GlandDocument4 pagesDiseases of Endocrine GlandAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- 5 Diseases Affecting Nervous Syste1Document10 pages5 Diseases Affecting Nervous Syste1John Lawrence Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Synthesis On Endocrine Disoder and Repro Cancer, Family PlanningDocument11 pagesSynthesis On Endocrine Disoder and Repro Cancer, Family PlanningEmilio Antang JrNo ratings yet
- DwarfismDocument5 pagesDwarfismjasminemuammilNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Notes - NCERT BasedDocument8 pagesEndocrine System Notes - NCERT Basedpallab mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Tumors (Adenoma, Craniopharyngioma)Document6 pagesPituitary Tumors (Adenoma, Craniopharyngioma)Ram RamNo ratings yet
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocument24 pagesHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostBha nu Sin ghNo ratings yet
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocument24 pagesHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostBha nu Sin ghNo ratings yet
- 40.43.function of Endocrine - Pptx?targetDocument28 pages40.43.function of Endocrine - Pptx?targetAnnemerline RavixNo ratings yet
- Graves DseDocument5 pagesGraves DseHester Marie SimpiaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesThe Endocrine SystemtumisobeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: One of Us, and I'm Not Certain Which, Has A Glandular DisorderDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: One of Us, and I'm Not Certain Which, Has A Glandular Disorderroserem2000No ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland DisordersDocument80 pagesPituitary Gland DisordersNang KhamNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System (Notes)Document4 pagesThe Endocrine System (Notes)Wasim HakimNo ratings yet
- The InternationalDocument73 pagesThe Internationalgem065No ratings yet
- 4th Block Endocrine PowerpointDocument70 pages4th Block Endocrine PowerpointKevinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Function(s) of Hormones (1) Hypothalamus (2) PituitaryDocument5 pagesEndocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Function(s) of Hormones (1) Hypothalamus (2) PituitaryJohn Ericsson RobariosNo ratings yet
- BioSci LO#2Document16 pagesBioSci LO#2AudzkieNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Co OrdinationDocument26 pagesHormonal Co OrdinationkpnotessNo ratings yet
- Enocrine System DisordersDocument14 pagesEnocrine System Disordersanaghau777No ratings yet
- 8 NotesDocument24 pages8 Notesnzcbx5wzt8No ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersDocument78 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disordershenny1620100% (1)
- GenBio EndocrineOutlineDocument12 pagesGenBio EndocrineOutlineJhon AmorNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Endocrine Systemefjddr4z100% (1)
- Subdivisions of HypoparathyroidismDocument7 pagesSubdivisions of HypoparathyroidismBellezzaNo ratings yet
- WorkshopBIO 12 CH. 50Document5 pagesWorkshopBIO 12 CH. 50JISAS CLIMAXNo ratings yet
- Goiter: Prepared By: Felix Kevin M. Villa Iv, RNDocument47 pagesGoiter: Prepared By: Felix Kevin M. Villa Iv, RNFelix Kevin VillaNo ratings yet
- HypopituitarismDocument2 pagesHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNo ratings yet
- Adama KanuDocument41 pagesAdama KanuAlie TholleyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders: Adrenal GlandDocument7 pagesEndocrine Disorders: Adrenal GlandDaniel AcusarNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 10 - Endocrine Glands Revision NotesDocument4 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 10 - Endocrine Glands Revision NoteshkkcreativityNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Group 6Document43 pagesEndocrine System: Group 6Redona Audrey RoseNo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine SystemAishwarya WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism 2011Document30 pagesHyperthyroidism 2011Elyza MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 5Document15 pagesEndocrine System 5Ace Vincent LunaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Calcium in Your Blood To Rise, A Condition Known As Hypercalcemia)Document3 pagesLevels of Calcium in Your Blood To Rise, A Condition Known As Hypercalcemia)Pandesal with EggNo ratings yet
- Levels of Calcium in Your Blood To Rise, A Condition Known As Hypercalcemia)Document3 pagesLevels of Calcium in Your Blood To Rise, A Condition Known As Hypercalcemia)Pandesal with EggNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument38 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationSajeev S Chadayamangalam SajNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System DiseasesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System DiseasesPrincess Xzmae Ramirez100% (1)
- Causes of Endocrine DisordersDocument8 pagesCauses of Endocrine DisordersKrystel Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemAnne Jillian83% (6)
- GoiterDocument48 pagesGoiterRizki NurNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Endocrine System - 230525 - 173127Document17 pagesPathology of Endocrine System - 230525 - 173127gregorydonald315No ratings yet
- Endocrine System 13 معدلDocument11 pagesEndocrine System 13 معدلhanaalhadidi567No ratings yet
- Endocrineglands 140817003157 Phpapp01Document61 pagesEndocrineglands 140817003157 Phpapp01Musfira KhalidNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology Lecture by Mrs M MUTSANGU POLY ND1Document56 pagesEndocrine Physiology Lecture by Mrs M MUTSANGU POLY ND1letwinemwale02No ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine Systemdenebrench23No ratings yet
- The Pituitary GlandDocument2 pagesThe Pituitary GlandGerelNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System UHMMMDocument35 pagesEndocrine System UHMMMletletNo ratings yet
- Activity70 HypopituitarismDocument8 pagesActivity70 HypopituitarismJohanna Recca MarinoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Adrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyFrom EverandAdrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!From EverandThyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!No ratings yet
- My Drummer Boy by Nikkidoo - SOFTDocument708 pagesMy Drummer Boy by Nikkidoo - SOFTSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Select An Equation To Solve For A Different Unknown CircleDocument3 pagesSelect An Equation To Solve For A Different Unknown CircleSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Campus LoveteamDocument592 pagesCampus LoveteamSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Introversion: Reliability Determines How Consistently A Measurement of Skill orDocument1 pageIntroversion: Reliability Determines How Consistently A Measurement of Skill orSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Meet The J.E.R.K. (Oinkoink)Document881 pagesMeet The J.E.R.K. (Oinkoink)Samantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Let Me Be The OneDocument357 pagesLet Me Be The OneYoona JungNo ratings yet
- Arranged MarriageDocument155 pagesArranged MarriageSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Displacement: Distance PositionDocument2 pagesDisplacement: Distance PositionSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Alluringangel - My Husband Is A Multi Millionaire Prince CompletedDocument51 pagesAlluringangel - My Husband Is A Multi Millionaire Prince CompletedSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- I Won't Let You GoDocument229 pagesI Won't Let You GoSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Alluringangel - My Husband Is A Multi Millionaire Prince CompletedDocument51 pagesAlluringangel - My Husband Is A Multi Millionaire Prince CompletedSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Have You Seen This GirlDocument631 pagesHave You Seen This GirlSamantha Dasmariñas Magaan100% (2)
- Animal Diversity - The Kingdom Animalia 1. Phylum Porifera - SpongesDocument6 pagesAnimal Diversity - The Kingdom Animalia 1. Phylum Porifera - SpongesSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Extension of Meaning of Primary Activities. Nothing Is More Striking Than The Difference Between AnDocument2 pagesExtension of Meaning of Primary Activities. Nothing Is More Striking Than The Difference Between AnSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- CampusDocument1 pageCampusSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- A by EcologyDocument1 pageA by EcologySamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Animals Live On Land Animals Live On WaterDocument1 pageAnimals Live On Land Animals Live On WaterSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Ang Kalusugan Ay KayamananDocument3 pagesAng Kalusugan Ay KayamananSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity - The Kingdom Animalia 1. Phylum Porifera - SpongesDocument6 pagesAnimal Diversity - The Kingdom Animalia 1. Phylum Porifera - SpongesSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Only Reminds Me of YouDocument2 pagesOnly Reminds Me of YouSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 The Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 22 The Female Reproductive SystemEllä PabustanNo ratings yet
- 2017JeronimusLaceulle Frustration PDFDocument5 pages2017JeronimusLaceulle Frustration PDFJopher NazarioNo ratings yet
- CT Scanning-Based Phenotypes Vary With ADRB2 Polymorphisms in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument6 pagesCT Scanning-Based Phenotypes Vary With ADRB2 Polymorphisms in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseAtika Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary System Note PDFDocument13 pagesHepatobiliary System Note PDFMohd Syaiful Mohd ArisNo ratings yet
- The Patriots' MonologueDocument2 pagesThe Patriots' MonologuetechctrlNo ratings yet
- Bio 2B03 Essay Retinitis PigmentosaDocument8 pagesBio 2B03 Essay Retinitis PigmentosaitsvaishpNo ratings yet
- Female Genital TractDocument5 pagesFemale Genital Tractsarguss14100% (1)
- Hypothyroidism and Histamine IntoleranceDocument7 pagesHypothyroidism and Histamine IntolerancealbinutaNo ratings yet
- Psych 101 Midterm ExamDocument11 pagesPsych 101 Midterm ExamMarie Dominique LavalleNo ratings yet
- 9700 s10 Ms 21Document6 pages9700 s10 Ms 21ClairDeLune123No ratings yet
- 1 Benign and Malignant Lesions of The CervixDocument46 pages1 Benign and Malignant Lesions of The CervixRohitNo ratings yet
- Final Human Bone Morphogenetic ProteinDocument23 pagesFinal Human Bone Morphogenetic Proteinbiologicscorp100% (1)
- 0970 s18 QP 11 CIE IGCSE BiologyDocument16 pages0970 s18 QP 11 CIE IGCSE BiologySri GanesNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument5 pagesCataractcarls burg a. resurreccionNo ratings yet
- Animal CloningDocument2 pagesAnimal CloningSASDSDNo ratings yet
- Material Transfer Agreement: Klinikum Rechts Der Isar Der Technischen Universität MünchenDocument9 pagesMaterial Transfer Agreement: Klinikum Rechts Der Isar Der Technischen Universität MünchenchristinaNo ratings yet
- Bok:978 1 4614 7119 6Document320 pagesBok:978 1 4614 7119 6gianlucamagagna100% (1)
- Chapter-10 STSDocument4 pagesChapter-10 STSCasimero CabungcalNo ratings yet
- Nutrigenomics in The Modern EraDocument11 pagesNutrigenomics in The Modern EraDiogo JuniorNo ratings yet
- Human Genome ProjectDocument16 pagesHuman Genome ProjectAbhishek GandhiNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. New Criteria For AKI Diagnosis Are Displayed. in Order To Diagnose AKIDocument8 pagesFigure 1. New Criteria For AKI Diagnosis Are Displayed. in Order To Diagnose AKIMayra Alejandra Prada SerranoNo ratings yet
- Metabolic MRCPCHDocument11 pagesMetabolic MRCPCHJawwad Masood AhmadNo ratings yet
- Breast MassDocument3 pagesBreast MassYum CNo ratings yet
- SBA4Document81 pagesSBA4Jenny TaylorNo ratings yet
- Tamilnadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences UniversityDocument46 pagesTamilnadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences UniversityVinod SivadasanNo ratings yet
- Measurment of Health Edited PDFDocument347 pagesMeasurment of Health Edited PDFBekele AberaNo ratings yet