Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such
Blood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such
Uploaded by
Michelle E. CapacioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such
Blood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such
Uploaded by
Michelle E. CapacioCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood is a bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such
as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from
those same cells.
In vertebrates, it is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which
constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume),
[1]
and contains
dissipated proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the
main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells
themselves. Albuminis the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the
colloidalosmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells(also called
RBCs or erythrocytes) and white blood cells, including leukocytes and platelets. The
most abundant cells in vertebrate blood are red blood cells. These contain hemoglobin,
an iron-containing protein, which facilitates transportation of oxygen by reversibly
binding to this respiratory gas and greatly increasing its solubility in blood. In contrast,
carbon dioxide is almost entirely transported extracellularly dissolved in plasma
asbicarbonate ion.
Vertebrate blood is bright red when its hemoglobin is oxygenated. Some animals, such
as crustaceans and mollusks, use hemocyanin to carry oxygen, instead of
hemoglobin. Insects and some mollusks use a fluid called hemolymph instead of blood,
the difference being that hemolymph is not contained in a closed circulatory system. In
most insects, this "blood" does not contain oxygen-carrying molecules such as
hemoglobin because their bodies are small enough for their tracheal systemto suffice for
supplying oxygen.
Jawed vertebrates have an adaptive immune system, based largely on white blood cells.
White blood cells help to resist infections and parasites. Platelets are important in
the clotting of blood. Arthropods, using hemolymph, have hemocytes as part of
their immune system.
Blood is circulated around the body through blood vessels by the pumping action of
the heart. In animals with lungs, arterial blood carries oxygen from inhaled air to the
tissues of the body, and venous blood carries carbon dioxide, a waste product
ofmetabolism produced by cells, from the tissues to the lungs to be exhaled.
Medical terms related to blood often begin with hemo- or hemato- (also spelledhaemo-
and haemato-) from the Greek word (haima) for "blood". In terms
ofanatomy and histology, blood is considered a specialized form of connective tissue,
given its origin in the bones and the presence of potential molecular fibers in the form
of fibrinogen.
What are the different components of blood and what do
they do?
Red cells -give blood its colour and account for 40-50% of its volume.
Their main function is to carry oxygen from the lungs to all the cells of the body and remove
waste products such as carbon dioxide.
Transfusions are used to treat people with severe anaemia, those whose red blood cells do not
function adequately and people experiencing severe bleeding such as accident victims and
patients undergoing surgery.
Red cells are stored in a refrigerator and have a shelf life of up to 42 days.
Platelets -are components of blood that assist in the blood clotting process.
They are literally tiny plates that wedge together covering tears in the blood vessels and
preventing blood from leaking into surrounding tissue.
The primary use of platelets is in the treatment of people with various cancers and other
diseases such as leukaemia where the bone marrow is unable to produce adequate numbers of
platelets, as well as for people receiving medical treatments like chemotherapy which can
decrease a person's platelet count. Platelets are also used to treat people suffering severe blood
loss.
Platelets are stored at room temperature and have a shelf life of only 5 days. This is why it is
vital to have a constant flow of blood donations coming in.
Plasma- is the straw coloured fluid in which the red cells, white cells and platelets are suspended.
Plasma is the most versatile component of blood as it can be processed into a variety of products
and each product can be used to treat a number of potentially life-threatening conditions.
Plasma is stored frozen and has a shelf life of up to 12 months
You might also like
- Biology SS2 3RD Term e NotesDocument45 pagesBiology SS2 3RD Term e NotesAdio Babatunde Abiodun Cabax100% (2)
- AP Psych Prep 3 - Biological Psychology (Part II)Document36 pagesAP Psych Prep 3 - Biological Psychology (Part II)dms727No ratings yet
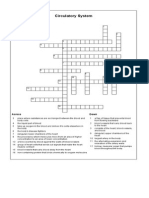
- Circulatory System Crossword PuzzleDocument1 pageCirculatory System Crossword PuzzleJames ChuaNo ratings yet
- Blood@Wikipedia Org enDocument18 pagesBlood@Wikipedia Org enHelmiNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A: Haima) For "Blood". in Terms ofDocument2 pagesBlood Is A: Haima) For "Blood". in Terms ofMica SaeronNo ratings yet
- Definisi BloodDocument4 pagesDefinisi BloodFriska Asita DewiNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument1 pageBloodKurt HillNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument1 pageBloodAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument5 pagesBody Fluids and CirculationSheehan MathurNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument4 pagesBlood ComponentsVishweshPatel100% (1)
- Blood: Blood Is A SpecializedDocument1 pageBlood: Blood Is A Specializedhai haiNo ratings yet
- Blood - WikipediaDocument106 pagesBlood - WikipediaZoha AliNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document8 pagesModule 6mezieldunlao1997No ratings yet
- Blood BasicsDocument24 pagesBlood BasicsMusallam M. AbukhalilNo ratings yet
- Blood and Clotting FactorsDocument34 pagesBlood and Clotting FactorsAnand KasiNo ratings yet
- Año de La Lucha Contra La Corrupción y La ImpunidadDocument5 pagesAño de La Lucha Contra La Corrupción y La ImpunidadHelen Salazar SagasteguiNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument7 pagesBloodNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesBlood Anatomy and PhysiologyRao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterm Notes (The Blood Summary)Document4 pagesAnaphy Midterm Notes (The Blood Summary)Zosia Sage100% (1)
- Blood: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesBlood: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchProfesi NersNo ratings yet
- Online Assignment: Submitted byDocument11 pagesOnline Assignment: Submitted byPrasant NatarajanNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument5 pagesBLOODSora TensaiNo ratings yet
- Lab Lesson # 1Document2 pagesLab Lesson # 1AsharAnisNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument2 pagesHematologyMohammed Al-RahmaweeNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument18 pagesCardio Vascular SystemjeniferNo ratings yet
- Blood 141004022507 Conversion Gate01Document39 pagesBlood 141004022507 Conversion Gate01Rajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Written OutputDocument19 pagesWritten Outputbvietine009No ratings yet
- Blood: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To:, For Other Uses, SeeDocument26 pagesBlood: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To:, For Other Uses, Seestev_brown89No ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument10 pagesComponents of BloodDJ GAMARINo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of BloodDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Bloodaoi_rachelle100% (1)
- Bone Marrow Is The Soft, Flexible, Vascular Tissue Found in The Hollow InteriorDocument6 pagesBone Marrow Is The Soft, Flexible, Vascular Tissue Found in The Hollow InteriorIanne Sandra SorrosaNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsDocument24 pagesBlood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsPaulo DanielNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument34 pagesHuman PhysiologyMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Blood Is ADocument2 pagesBlood Is ATala GinezNo ratings yet
- Flowing of Blood in HeartDocument5 pagesFlowing of Blood in HeartAkshay BahetyNo ratings yet
- HO Sistem Peredaran DarahDocument8 pagesHO Sistem Peredaran DarahhayrachzaNo ratings yet
- 1 HaematologyDocument6 pages1 HaematologyEma FröhlichováNo ratings yet
- (Abastecimiento) (Tejidos) : Removal of Waste Such As Carbon Dioxide, Urea, and Lactic AcidDocument3 pages(Abastecimiento) (Tejidos) : Removal of Waste Such As Carbon Dioxide, Urea, and Lactic AcidMelissa TorresNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument16 pagesBloodMohsin Bhat100% (1)
- Blood Is A SpecializedDocument15 pagesBlood Is A SpecializedParthiv DaveNo ratings yet
- Blood and Its Components: Fluid Oxygen Cells Carbon Dioxide Heart Tissue PlasmaDocument5 pagesBlood and Its Components: Fluid Oxygen Cells Carbon Dioxide Heart Tissue PlasmaTvijaya simha murthyNo ratings yet
- Blood and CompDocument21 pagesBlood and Compdivyakai143No ratings yet
- Tugas Anatomi IntegumenDocument26 pagesTugas Anatomi IntegumenLailia nur rachmaNo ratings yet
- Heart: Right Heart Left Heart. Fish in Contrast Have Two Chambers, An Atrium and A Ventricle, WhileDocument5 pagesHeart: Right Heart Left Heart. Fish in Contrast Have Two Chambers, An Atrium and A Ventricle, WhileMiguel PatrickNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System2Document9 pagesCirculatory System2Wajeeha AsifNo ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument11 pagesBody FluidsAnkit PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Constitutes The Circulatory System and Performs The Following FunctionsDocument1 pageCardiovascular System Constitutes The Circulatory System and Performs The Following FunctionsAhmad WardimanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Constitutes The Circulatory System and Performs The Following FunctionsDocument1 pageCardiovascular System Constitutes The Circulatory System and Performs The Following FunctionsAhmad WardimanNo ratings yet
- Transport. Blood Provides A Pickup and DeliveryDocument1 pageTransport. Blood Provides A Pickup and DeliveryAhmad WardimanNo ratings yet
- Blood and Blood Vessels Module 3Document16 pagesBlood and Blood Vessels Module 3Jenevieve Tungcul SimanganNo ratings yet
- What Is BloodDocument1 pageWhat Is BloodAygül HaciyevaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDocument5 pagesAnatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Suchjeoffrey_castroNo ratings yet
- Erythrocytes: The erythrocyte is a biconcave disk between 5 and 7.5 μm inDocument7 pagesErythrocytes: The erythrocyte is a biconcave disk between 5 and 7.5 μm inJoselyn Vilcherrez CruzNo ratings yet
- Blood PDFDocument9 pagesBlood PDFsanafarheen93No ratings yet
- BloodDocument9 pagesBloodCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- The Blood's Composition of Domestic Animals - CAYLANDocument13 pagesThe Blood's Composition of Domestic Animals - CAYLANMariel CaylanNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cells: The Human Heart Is About The Size of A Clenched FistDocument5 pagesRed Blood Cells: The Human Heart Is About The Size of A Clenched FistPrince JenovaNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology 1Document78 pagesBlood Physiology 1Jude ChinecheremNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesCirculatory SystemccparangueNo ratings yet
- Blood ReportDocument15 pagesBlood ReportSaadNo ratings yet
- Week 2 TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS 2021Document40 pagesWeek 2 TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS 2021DJ GAMARINo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy Physiology HandoutsDocument6 pagesBlood Anatomy Physiology HandoutsKids JangNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument77 pagesLevels of OrganizationHyu Dum FakNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.5 (Jan Ray)Document4 pagesActivity 1.5 (Jan Ray)JAN RAY CUISON VISPERASNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Parts PacketDocument2 pagesDigestive System Parts PacketRusherNo ratings yet
- PWSAT Syllabus and Marking Scheme 2024Document11 pagesPWSAT Syllabus and Marking Scheme 2024aayushmishra4546No ratings yet
- The Anatomy of VertebratesDocument698 pagesThe Anatomy of VertebratesJhenys Maiker100% (1)
- Annelida LabDocument4 pagesAnnelida Labapi-297841438No ratings yet
- Animal DevelopmentDocument43 pagesAnimal DevelopmentZach ThorpeNo ratings yet
- DENT3002-Oral Histology and Embryology FDocument146 pagesDENT3002-Oral Histology and Embryology FLorenzini GrantNo ratings yet
- WS B. Invertebrates On Land - AgsaldaDocument11 pagesWS B. Invertebrates On Land - AgsaldaEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Class IX Practicals TISSUESDocument6 pagesClass IX Practicals TISSUESDhruv BhagatNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology PDFDocument22 pagesAnatomical Terminology PDFProdosh Chatterjee100% (1)
- Photo SkinDocument13 pagesPhoto SkinChan JianweiNo ratings yet
- English Yr 4 Comprehension The Duckbill PlatypusDocument2 pagesEnglish Yr 4 Comprehension The Duckbill PlatypusNiceman Natiqi100% (2)
- Anatomy/physiology BookDocument428 pagesAnatomy/physiology BookTushant100% (4)
- Activity 3.1 The Male Reproductive System - 084332Document1 pageActivity 3.1 The Male Reproductive System - 084332Megan WolvesNo ratings yet
- Animal Communication: by Shahid Mahmood University of GujratDocument29 pagesAnimal Communication: by Shahid Mahmood University of Gujratmaha Ch100% (1)
- Biltong 1Document10 pagesBiltong 1MakunguNo ratings yet
- Abala Lab Ex 5Document6 pagesAbala Lab Ex 5a19-1-00227No ratings yet
- Saksham Singh Viii B 8228: Name:-Class: - Roll No.Document31 pagesSaksham Singh Viii B 8228: Name:-Class: - Roll No.sakshamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Organization and General Plan of TheDocument64 pagesChapter 1 Organization and General Plan of TheLoverna Abella0% (1)
- WWF - WiW - 2017 - Factsheet - Tiger FINALDocument2 pagesWWF - WiW - 2017 - Factsheet - Tiger FINALDebraj DattaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Animal CellsDocument3 pagesLab 2 Animal CellsCherryNo ratings yet
- Birds (Nutrition and Digestion) .Docx (Mudassir)Document5 pagesBirds (Nutrition and Digestion) .Docx (Mudassir)AliNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimliaDocument20 pagesKingdom AnimliaALISHBA TANOLINo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 2 All Topics QuestionsDocument160 pagesBio Unit 2 All Topics Questionsareyouthere92100% (2)
- Reading Comprehension ExerciseDocument3 pagesReading Comprehension ExerciseBiji YouthNo ratings yet
- Waec 2021 Biology Practical: BOTH HAVE: I. Large Neural Canal Ii. Transverse Process Iii. Neural SpinesDocument8 pagesWaec 2021 Biology Practical: BOTH HAVE: I. Large Neural Canal Ii. Transverse Process Iii. Neural SpinesJacob Spiritual100% (2)