Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 viewsDecimal Binary
Decimal Binary
Uploaded by
Jyoti AryaIn a base 10 (or decimal) number, each column in the number stands for a power of 10. Because information in a computer is stored in bits, it's easiest to work in base 2. We will consider two methods for converting between decimal and binary numbers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Практика IctDocument39 pagesПрактика IctNurzat SharipNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Number SystemsDocument30 pagesUnit 1 Number SystemsAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- Conveconvconverting Between Decimal (Base 10) and Binary (Base 2)Document26 pagesConveconvconverting Between Decimal (Base 10) and Binary (Base 2)Himanshu VohraNo ratings yet
- Digital Number SystemDocument44 pagesDigital Number SystemNicholas SaweNo ratings yet
- How To Add Binary NumbersDocument99 pagesHow To Add Binary NumbersRafael Taylor100% (1)
- Number RepresentationDocument25 pagesNumber RepresentationsegdeadeyeytNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Number SystemsDocument70 pagesModule 1 - Number SystemsGrant GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Subnetting?! You Can Do It!: Example 1 (Binary To Decimal) 11001011 203 orDocument2 pagesSubnetting?! You Can Do It!: Example 1 (Binary To Decimal) 11001011 203 orRipunjay MishraNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument35 pagesNumber SystemshasithrNo ratings yet
- CSA Unit 1 NotesDocument46 pagesCSA Unit 1 Notes6747 mohammedjeelaniNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument24 pagesNumber SystemsShishupal SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 and 2. DfaDocument43 pagesUnit 1 and 2. DfaVanchima Devi0% (1)
- Number Systems, Operations, and CodesDocument50 pagesNumber Systems, Operations, and CodesManqoba Muntu MasukuNo ratings yet
- Data Representation Inside Computer SystemDocument32 pagesData Representation Inside Computer SystemOmar KamilNo ratings yet
- Lres 125Document123 pagesLres 125vijay kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming in Java Binary and Hexadecimal Numeration and Logical OperationsDocument12 pagesObject Oriented Programming in Java Binary and Hexadecimal Numeration and Logical Operationsaqil_shamsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Csa SummaryDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Csa Summarycsa94No ratings yet
- 6787 Yhy HHH HHGHDocument10 pages6787 Yhy HHH HHGHmyschoolonthegoNo ratings yet
- CS2Document15 pagesCS2akshat1apsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 NumbersystemDocument13 pagesLecture 4 NumbersystemMuhammad IshaqNo ratings yet
- Electronics-1-Chap 2-17 - 11 - 2021Document5 pagesElectronics-1-Chap 2-17 - 11 - 2021Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- M.C.a. (Sem - I) Discrete MathematicsDocument177 pagesM.C.a. (Sem - I) Discrete MathematicsSomya SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Hand Notes On Number System 1 1Document6 pagesClass 7 Hand Notes On Number System 1 1zannateen nayeemNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument4 pagesNumber Systemdiljithdinesh1501No ratings yet
- A Freshman C++ Programming Course: Dr. Ali H. Al-Saedi Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, IraqDocument86 pagesA Freshman C++ Programming Course: Dr. Ali H. Al-Saedi Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, IraqJibril DefooNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Binary Numbers and ArithmeticDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - Binary Numbers and ArithmeticTraian VladuNo ratings yet
- 01 Ec2106 Unit I-4Document68 pages01 Ec2106 Unit I-4lekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Numsys 2Document13 pagesNumsys 2Abhishek VijayNo ratings yet
- IB - Number Systems and ConversionsDocument30 pagesIB - Number Systems and ConversionsMd Sifat KhanNo ratings yet
- Number System: After Studying Chapter 1, You Should Be Able ToDocument9 pagesNumber System: After Studying Chapter 1, You Should Be Able ToOdrie Audrey NalaunanNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: Kwame Oteng Gyasi Lecture 2: Number SystemDocument28 pagesDigital Electronics: Kwame Oteng Gyasi Lecture 2: Number SystemOperation ResearchNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument7 pagesNumber SystemsAna DshNo ratings yet
- 1.number SystemDocument73 pages1.number SystemOmkar KaleNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMMING 11 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2 PDFDocument13 pagesPROGRAMMING 11 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2 PDFDianne Brucal - MatibagNo ratings yet
- Lab 1.5.9: Converting Numbers Overview: Estimated Time: 25 Minutes ObjectiveDocument5 pagesLab 1.5.9: Converting Numbers Overview: Estimated Time: 25 Minutes ObjectiveHamzaSpahijaNo ratings yet
- C Notes 2 - Number SystemDocument9 pagesC Notes 2 - Number SystemabeetpaulNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals: Instructor: Sehar Javaid Lecture # 04 & 05Document45 pagesComputer Fundamentals: Instructor: Sehar Javaid Lecture # 04 & 05RajaishNo ratings yet
- Number System ReviewerDocument5 pagesNumber System ReviewerGerthie EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Number System: Chapter - 3Document16 pagesNumber System: Chapter - 3lvsaruNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 1 Number SystemDocument3 pagesQ4 Lesson 1 Number SystemBilly SalameroNo ratings yet
- Binary Numbers OverviewDocument9 pagesBinary Numbers OverviewHolsworth WilsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Base NumberDocument13 pagesChapter 3 - Base NumberZufayri Peyi100% (1)
- Coma STD LecturesDocument44 pagesComa STD LecturesMusonda MwenyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Number SystemDocument60 pagesChapter 2: Number SystemAnup Shukla100% (1)
- Number System in Digital LogicDocument26 pagesNumber System in Digital Logicnoxase8709No ratings yet
- Digital ElectronicsDocument58 pagesDigital Electronicspradyot swainNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Rlog 2Document38 pagesKuliah Rlog 2Alhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Numbering SystemDocument10 pagesNumbering SystemSolomon TekluNo ratings yet
- Lesson4 Number SystemsDocument65 pagesLesson4 Number SystemsJennifer Diaz PendonNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument10 pagesNumber SystemsRaymond John Rodriguez VergaraNo ratings yet
- CMA101 - Chapter 1Document13 pagesCMA101 - Chapter 1Kenzo TanNo ratings yet
- As Chapter 1 Information RepresentationDocument157 pagesAs Chapter 1 Information RepresentationhijabNo ratings yet
- SBSA1101Document97 pagesSBSA1101omotolani ololadeNo ratings yet
- Floating Point Representation Latest by MR SaemDocument69 pagesFloating Point Representation Latest by MR SaemMr SaemNo ratings yet
- BinaryDocument11 pagesBinaryAxl Pring100% (1)
- Binary NumbersDocument10 pagesBinary NumbersorbitalroNo ratings yet
- Y9 Computer Science 2020Document78 pagesY9 Computer Science 2020PegNo ratings yet
Decimal Binary
Decimal Binary
Uploaded by
Jyoti Arya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesIn a base 10 (or decimal) number, each column in the number stands for a power of 10. Because information in a computer is stored in bits, it's easiest to work in base 2. We will consider two methods for converting between decimal and binary numbers.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIn a base 10 (or decimal) number, each column in the number stands for a power of 10. Because information in a computer is stored in bits, it's easiest to work in base 2. We will consider two methods for converting between decimal and binary numbers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesDecimal Binary
Decimal Binary
Uploaded by
Jyoti AryaIn a base 10 (or decimal) number, each column in the number stands for a power of 10. Because information in a computer is stored in bits, it's easiest to work in base 2. We will consider two methods for converting between decimal and binary numbers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Converting between Decimal (Base 10) and Binary (Base 2)
Base 10 vs. Base 2
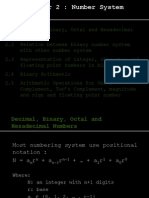
Were used to thinking about numbers in base 10. People probably started using base 10 because we
have 10 ngers so its easiest for us to count in groups of 10. In a base 10 (or decimal) number, each
column in the number stands for a power of 10. Numbers have a 1s column (= 10
0
), 10s column (=
10
1
), 100s column(= 10
2
), etc. We write numbers with the most signicant column (the one with the
highest value) at the left. We can determine the value of number by multiplying the digit in the column
by how much the column is worth:
1000 100 10 1
----------------
2 0 3 6
Total: 2 * 1000 + 0 * 100 + 3 * 10 + 6 * 1 = 2036
Were all used to working with base 10, but because information in a computer is stored in bits (just 0
or 1, so its kind of like just having two ngers to count on), its easiest to work in base 2. In a base 2
(or binary) number, each column stands for a power of 2: 2
0
(= 1), 2
1
(= 2), 2
2
(= 4), 2
3
(= 8), etc.
16 8 4 2 1
------------------
1 0 1 1 0
Total: 1 * 16 + 0 * 8 + 1 * 4 + 1 * 2 + 0 * 1 = 22
We will consider two methods for converting between decimal and binary numbers, the table method
and the division/multiplication by 2 method.
Table Method
Decimal to Binary with a Table
1. Create a table whose leftmost column is the greatest power of 2 less than the number you want
to convert. If the number is between 64 and 127, the leftmost column will be 64. If the number is
between 128 and 255, the leftmost column will be 128. Each column in the table is a power of 2.
The rightmost column is 2
0
(= 1), the next one to the left is 2
1
(= 2), the next is 2
2
(= 4), etc.
Instead of thinking about powers of 2, you can just think about doubling each number to get the
value for the next column to the left. This will typically look like:
64 32 16 8 4 2 1
--------------------------
2. Start by comparing the number you want to convert to the value leftmost column. If youve set
up the table correctly, it should be less than the column value, so put a 1 in the column.
3. Add up the values of all the columns youve put 1s in so far. This is your running total. Take
the running total and add the value of the next column. If the result is less than the number you
want to convert, put a 1 in this column. If the result is greater than the number you want to
convert, put a 0 in this column.
4. Repeat the previous step until all columns are lled.
Decimal number: 87
64 32 16 8 4 2 1
--------------------------
1 (64 < 87 ? yes)
0 (64 + 32 < 87 ? no)
1 (64 + 16 < 87 ? yes)
0 (64 + 16 + 8 < 87 ? no)
1 (64 + 16 + 4 < 87 ? yes)
1 (64 + 16 + 4 + 2 < 87 ? yes)
1 (64 + 16 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 87, yes, done)
Binary number: 1010111
Decimal number: 105
64 32 16 8 4 2 1
--------------------------
1 (64 < 105 ? yes)
1 (64 + 32 < 105 ? yes)
0 (64 + 32 + 16 < 105 ? no)
1 (64 + 32 + 8 < 105 ? yes)
0 (64 + 32 + 8 + 4 < 105? no)
0 (64 + 32 + 8 + 2 < 105? no)
1 (64 + 32 + 8 + 1 = 105, yes, done)
Binary number: 1101001
Binary to Decimal with a Table
1. Create a table with enough columns for your binary number. (See instructions in the previous
section.)
64 32 16 8 4 2 1
--------------------------
2. Fill in the binary number in the table making sure that the rightmost digit is aligned under 1.
3. For each column containing a 1, take the value of that column (e.g., 64, 32, etc.) and add it to
the total.
Binary number: 1010111
64 32 16 8 4 2 1
--------------------------
1 0 1 0 1 1 1
Total: 64 + 16 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 87
Binary number: 1101001
64 32 16 8 4 2 1
--------------------------
1 1 0 1 0 0 1
Total: 64 + 32 + 8 + 1 = 105
Division/Multiplication by 2 Method
Decimal to Binary: Divide by 2
1. Take the decimal number and divide it by two keeping track of the remainder (instead of decimal
place). For example, 10 / 2 is 5 r 0. 11 / 2 is 5 r 1. The result for both is 5. The remainder for
10 / 2 is 0 and the remainder for 11 / 2 is 1.
2. Take the result and divide it by two in the same way, always keeping track of the remainder.
3. Repeat Step 2 until you reach a result of 0. Your last step should always look like 1 / 2 = 0 r 1.
4. Read the remainders (all 0 or 1) o in reverse order starting at the bottom with the one you just
nished. This is the answer.
Decimal number:
87 105
87 / 2 = 43 r 1 105 / 2 = 52 r 1
43 / 2 = 21 r 1 52 / 2 = 26 r 0
21 / 2 = 10 r 1 26 / 2 = 13 r 0
10 / 2 = 5 r 0 13 / 2 = 6 r 1
5 / 2 = 2 r 1 6 / 2 = 3 r 0
2 / 2 = 1 r 0 3 / 2 = 1 r 1
1 / 2 = 0 r 1 1 / 2 = 0 r 1
Result (read remainders bottom to top):
1010111 1101001
Binary to Decimal: Multiply by 2
1. Start with 0 as the result. Add to 0 the digit from the leftmost column in the binary number.
2. Take the result, multiply it by 2, and add the next digit following left-to-right in the binary
number.
3. Repeat Step 2 until you have used all digits in the binary number. The nal result is your answer.
Binary number:
1010111 1101001
0 + 1 = 1 0 + 1 = 1
1 * 2 + 0 = 2 1 * 2 + 1 = 3
2 * 2 + 1 = 5 3 * 2 + 0 = 6
5 * 2 + 0 = 10 6 * 2 + 1 = 13
10 * 2 + 1 = 21 13 * 2 + 0 = 26
21 * 2 + 1 = 43 26 * 2 + 0 = 52
43 * 2 + 1 = 87 52 * 2 + 1 = 105
Decimal number:
87 105
Checks
The best way to check your answer is to convert it back and make sure you get what you started with.
A few quick checks might also help you catch mistakes:
1. If the decimal number is even, the equivalent binary number should end in 0. If the decimal
number is odd, the binary number should end in 1.
2. If the binary number ends in 1, the equivalent decimal number should be odd. If the binary
number ends in 0, the decimal should be even.
3. If the decimal number is between 64 and 127, the equivalent binary number should contain 7
digits (ignoring any leading 0s).
4. If the decimal number is between 128 and 255, the equivalent binary number should contain 8
digits (ignoring any leading 0s).
You might also like
- Практика IctDocument39 pagesПрактика IctNurzat SharipNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Number SystemsDocument30 pagesUnit 1 Number SystemsAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- Conveconvconverting Between Decimal (Base 10) and Binary (Base 2)Document26 pagesConveconvconverting Between Decimal (Base 10) and Binary (Base 2)Himanshu VohraNo ratings yet
- Digital Number SystemDocument44 pagesDigital Number SystemNicholas SaweNo ratings yet
- How To Add Binary NumbersDocument99 pagesHow To Add Binary NumbersRafael Taylor100% (1)
- Number RepresentationDocument25 pagesNumber RepresentationsegdeadeyeytNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Number SystemsDocument70 pagesModule 1 - Number SystemsGrant GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Subnetting?! You Can Do It!: Example 1 (Binary To Decimal) 11001011 203 orDocument2 pagesSubnetting?! You Can Do It!: Example 1 (Binary To Decimal) 11001011 203 orRipunjay MishraNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument35 pagesNumber SystemshasithrNo ratings yet
- CSA Unit 1 NotesDocument46 pagesCSA Unit 1 Notes6747 mohammedjeelaniNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument24 pagesNumber SystemsShishupal SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 and 2. DfaDocument43 pagesUnit 1 and 2. DfaVanchima Devi0% (1)
- Number Systems, Operations, and CodesDocument50 pagesNumber Systems, Operations, and CodesManqoba Muntu MasukuNo ratings yet
- Data Representation Inside Computer SystemDocument32 pagesData Representation Inside Computer SystemOmar KamilNo ratings yet
- Lres 125Document123 pagesLres 125vijay kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming in Java Binary and Hexadecimal Numeration and Logical OperationsDocument12 pagesObject Oriented Programming in Java Binary and Hexadecimal Numeration and Logical Operationsaqil_shamsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Csa SummaryDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Csa Summarycsa94No ratings yet
- 6787 Yhy HHH HHGHDocument10 pages6787 Yhy HHH HHGHmyschoolonthegoNo ratings yet
- CS2Document15 pagesCS2akshat1apsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 NumbersystemDocument13 pagesLecture 4 NumbersystemMuhammad IshaqNo ratings yet
- Electronics-1-Chap 2-17 - 11 - 2021Document5 pagesElectronics-1-Chap 2-17 - 11 - 2021Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- M.C.a. (Sem - I) Discrete MathematicsDocument177 pagesM.C.a. (Sem - I) Discrete MathematicsSomya SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Hand Notes On Number System 1 1Document6 pagesClass 7 Hand Notes On Number System 1 1zannateen nayeemNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument4 pagesNumber Systemdiljithdinesh1501No ratings yet
- A Freshman C++ Programming Course: Dr. Ali H. Al-Saedi Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, IraqDocument86 pagesA Freshman C++ Programming Course: Dr. Ali H. Al-Saedi Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, IraqJibril DefooNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Binary Numbers and ArithmeticDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - Binary Numbers and ArithmeticTraian VladuNo ratings yet
- 01 Ec2106 Unit I-4Document68 pages01 Ec2106 Unit I-4lekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Numsys 2Document13 pagesNumsys 2Abhishek VijayNo ratings yet
- IB - Number Systems and ConversionsDocument30 pagesIB - Number Systems and ConversionsMd Sifat KhanNo ratings yet
- Number System: After Studying Chapter 1, You Should Be Able ToDocument9 pagesNumber System: After Studying Chapter 1, You Should Be Able ToOdrie Audrey NalaunanNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: Kwame Oteng Gyasi Lecture 2: Number SystemDocument28 pagesDigital Electronics: Kwame Oteng Gyasi Lecture 2: Number SystemOperation ResearchNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument7 pagesNumber SystemsAna DshNo ratings yet
- 1.number SystemDocument73 pages1.number SystemOmkar KaleNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMMING 11 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2 PDFDocument13 pagesPROGRAMMING 11 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2 PDFDianne Brucal - MatibagNo ratings yet
- Lab 1.5.9: Converting Numbers Overview: Estimated Time: 25 Minutes ObjectiveDocument5 pagesLab 1.5.9: Converting Numbers Overview: Estimated Time: 25 Minutes ObjectiveHamzaSpahijaNo ratings yet
- C Notes 2 - Number SystemDocument9 pagesC Notes 2 - Number SystemabeetpaulNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals: Instructor: Sehar Javaid Lecture # 04 & 05Document45 pagesComputer Fundamentals: Instructor: Sehar Javaid Lecture # 04 & 05RajaishNo ratings yet
- Number System ReviewerDocument5 pagesNumber System ReviewerGerthie EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Number System: Chapter - 3Document16 pagesNumber System: Chapter - 3lvsaruNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 1 Number SystemDocument3 pagesQ4 Lesson 1 Number SystemBilly SalameroNo ratings yet
- Binary Numbers OverviewDocument9 pagesBinary Numbers OverviewHolsworth WilsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Base NumberDocument13 pagesChapter 3 - Base NumberZufayri Peyi100% (1)
- Coma STD LecturesDocument44 pagesComa STD LecturesMusonda MwenyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Number SystemDocument60 pagesChapter 2: Number SystemAnup Shukla100% (1)
- Number System in Digital LogicDocument26 pagesNumber System in Digital Logicnoxase8709No ratings yet
- Digital ElectronicsDocument58 pagesDigital Electronicspradyot swainNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Rlog 2Document38 pagesKuliah Rlog 2Alhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Numbering SystemDocument10 pagesNumbering SystemSolomon TekluNo ratings yet
- Lesson4 Number SystemsDocument65 pagesLesson4 Number SystemsJennifer Diaz PendonNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument10 pagesNumber SystemsRaymond John Rodriguez VergaraNo ratings yet
- CMA101 - Chapter 1Document13 pagesCMA101 - Chapter 1Kenzo TanNo ratings yet
- As Chapter 1 Information RepresentationDocument157 pagesAs Chapter 1 Information RepresentationhijabNo ratings yet
- SBSA1101Document97 pagesSBSA1101omotolani ololadeNo ratings yet
- Floating Point Representation Latest by MR SaemDocument69 pagesFloating Point Representation Latest by MR SaemMr SaemNo ratings yet
- BinaryDocument11 pagesBinaryAxl Pring100% (1)
- Binary NumbersDocument10 pagesBinary NumbersorbitalroNo ratings yet
- Y9 Computer Science 2020Document78 pagesY9 Computer Science 2020PegNo ratings yet