Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHH Drug Study Week 3
CHH Drug Study Week 3
Uploaded by
maryxtine24Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Conzace Tranexamic MetoclopramideDocument5 pagesConzace Tranexamic MetoclopramideDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- BREX Pharmacy Review Module 1Document9 pagesBREX Pharmacy Review Module 1Kenneth DayritNo ratings yet
- Pharma Guide (Dhshan H. Dhshan) - 2018Document419 pagesPharma Guide (Dhshan H. Dhshan) - 2018A.E. Salih Unused Email100% (2)
- MCQ For FINAL (3&4)Document12 pagesMCQ For FINAL (3&4)api-2693862480% (5)
- ASCIA HP Penicillin Allergy Guide 2016Document1 pageASCIA HP Penicillin Allergy Guide 2016kkkssbbNo ratings yet
- CHH Drug Study Week 2Document25 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 2maryxtine24No ratings yet
- Drug Study ProjectDocument7 pagesDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Xi - Drug Study: Drugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument18 pagesXi - Drug Study: Drugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationlicservernoidaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Hepatic FailureDocument37 pagesHepatic FailureWinston Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- 1 DrugsDocument2 pages1 DrugsPatricia Lucero67% (3)
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoy Jarin100% (1)
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Drug StudDocument12 pagesDrug StudKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Rani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument10 pagesRani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyIv'z TandocNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Careplan 2Document11 pagesCareplan 2JulieRn2beNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument12 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyDeca TanNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument11 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Care Plan September 25 Med-SurgDocument19 pagesCare Plan September 25 Med-Surgapi-251516913No ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Tramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibDocument4 pagesTramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibEric de JulianNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification:: Source: Drug Handbook 27 Edition, Lippincot Williams & WilkinsDocument11 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Classification:: Source: Drug Handbook 27 Edition, Lippincot Williams & WilkinsVel Georgia-FrancoNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Presented by BSN Iii - A2Document90 pagesCase Presentation: Presented by BSN Iii - A2Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy DrugsDocument43 pagesChemotherapy Drugsbrigette_lagat100% (2)
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- FINAL DRUGS Pancreatic CancerDocument10 pagesFINAL DRUGS Pancreatic CancerfjorelynNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismDocument9 pagesDrug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AGEDocument5 pagesDrug Study AGEAna Mae ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocument12 pagesDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolDocument7 pagesName of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objectivechaoz09No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)Document2 pagesAcetaminophen (Tylenol)amelia hearonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Medication Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Intervention Generic Name: CNS: GIDocument4 pagesMedication Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Intervention Generic Name: CNS: GIKathleenDawalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RICUDocument10 pagesDrug Study RICUCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 pagesAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Last DutyDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDelivery Room Drug StudyChinimansiNo ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Penicillin Production Paper - FinalDocument31 pagesPenicillin Production Paper - Finalapi-508032756No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Antibiotics & Antiinfectives-1Document39 pagesLecture 10 Antibiotics & Antiinfectives-1Dr Haris AwanNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry of Beta-Lactam AntibioticsDocument13 pagesMedicinal Chemistry of Beta-Lactam AntibioticsJosiah O OmobaNo ratings yet
- Jama Shenoy 2019 RV 180010Document12 pagesJama Shenoy 2019 RV 180010GustavoCalderinNo ratings yet
- Soal UasDocument10 pagesSoal UasDila ZeinNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument9 pagesNursing DiagnosisSkyerexNo ratings yet
- PenicillinDocument75 pagesPenicillinJean CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Bio Process Problem 1Document1 pageBio Process Problem 1AshenafiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Neuropsychiatric Effects Psychotropic Interact IonsDocument13 pagesAntibiotics: Neuropsychiatric Effects Psychotropic Interact Ionsracm89No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyAnne Therese Bello Sibayan0% (1)
- Ef3 Advanced Short Films ScriptsDocument9 pagesEf3 Advanced Short Films Scriptskeyepat806No ratings yet
- Pil 11044Document3 pagesPil 11044an12al9008No ratings yet
- Alexander Fleming and The Discovery of PenicilinDocument3 pagesAlexander Fleming and The Discovery of PenicilinAlexandra HornetNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyCieLouie Cauilan-DomingoNo ratings yet
- 1 Historical Overview and Future Perspective: Bernhard Eikmanns, Marcella Eikmanns, and Christopher J. PaddonDocument22 pages1 Historical Overview and Future Perspective: Bernhard Eikmanns, Marcella Eikmanns, and Christopher J. PaddonDr. Laxman RautNo ratings yet
- Listening Activity. EIII G1docxDocument2 pagesListening Activity. EIII G1docxYeraldin Acevedo CastroNo ratings yet
- Cep Halo Sporin SDocument9 pagesCep Halo Sporin SJasper VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykakienz100% (7)
- 1ST - Microbiology and Parasitology (Laboratory)Document11 pages1ST - Microbiology and Parasitology (Laboratory)Krianne Chris DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Beta - Lactam AntibioticsDocument217 pagesBeta - Lactam AntibioticsEmre Yücel100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyArdy PadamadaNo ratings yet
- Bicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyDocument1 pageBicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyChristine Pialan Salimbagat100% (1)
- Pharma Lecture With Dr. Maria Yña Eluisia T. Pereyra-Borlongan 1Document13 pagesPharma Lecture With Dr. Maria Yña Eluisia T. Pereyra-Borlongan 1Sammy GirlNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document20 pagesExercise 1Huyen Trang NguyenNo ratings yet
- All (Introduction To Anti-MicDocument3 pagesAll (Introduction To Anti-MicMiki AberaNo ratings yet
- L9 Antibiotic For Gram PositiveDocument6 pagesL9 Antibiotic For Gram PositiveJennifer TanNo ratings yet
CHH Drug Study Week 3
CHH Drug Study Week 3
Uploaded by
maryxtine24Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHH Drug Study Week 3
CHH Drug Study Week 3
Uploaded by
maryxtine24Copyright:
Available Formats
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
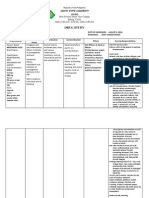
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Mannitol Pharmacologic Class:
Osmotic Diuretic
Therapeutic Class:
Diuretic
Test dose for marked oliguria or
suspected inadequate kidney
function.
Oliguria
To prevent oliguria or acute renal
impairment.
Edema; ascites caused by renal,
hepatic, o?r cardiac failure.
To reduce intraocular or
intracranial pressure
Diuresis in drug intoxication
Irrigation solution during
transurethral resection prostate
20% 150ml IV bolus every
4 hours
Assess patients condition before therapy and
regularly thereafter to monitor drugs
effectiveness.
Monitor vital signs, central venous pressure, and
fluid intake and output hourly.
Monitor weight and kidney function, as well as
serum and urine sodium and potassium levels.
Tell patient that he may feel thirsty or have a
dry mouth, and emphasize the importance of
drinking only the amount of fluid provided.
Instruct patient to immediately report pain in
chest, back, or legs, or shortness of breath.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Osmetrol Chemical Effect:
Increases osmotic pressure
of glomerular filtrate,
inhibiting tubular
reabsorption of water and
electrolytes. This elevates
blood osmolality, enhancing
water and sodium flow into
extracellular fluid.
Therapeutic Effect:
Increases water excretion,
decreases intracranial or
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to the drug or any of
its components, and in those with
anuria, severe pulmonary congestion,
frank pulmonary edema,severe heart
failure, severe dehydration, metabolic
edema, progressive renal disease or
dysfunction, or active intracranial
bleeding except during craniotomy.
CNS: headache, confusion,
seizures
CV: Circulatory overload,
heart failure, tachycardia,
chest pain
EENT: blurred vision,
rhinitis
GI: thirst, nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea
GU: urine retention
Metabolic: water
intoxication, cellular
dehydration, electrolyte
Patient maintains adequate hydration
throughout the therapy.
Adequate balance of patients fluid output noted.
Decrease evidence of elevated intracranial
pressure
Moderate to minimal drainage from patients JP
drain at right frontoparietal area.
intraocular pressure,
prevents or treats kidney
dysfunction, and promotes
excretion of drug
overdosage.
imbalance
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
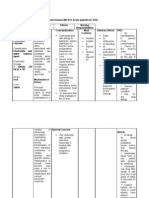
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Piperacillin
+Tazobactam
Pharmacologic Class: Beta
Lactamase Inhibitor,
extended spectrum penicillin
Therapeutic Class: antibiotic
Pregnancy Risk category : B
Treatment of moderate to severe
appendicitis, uncomplicated and
complicated skin and skin structure
infections, endometritis, pelvic
inflammatory disease, or
nosocomial or community-acquired
pneumonia caused by piperacillin-
resistant, piperacillin/tazobactam-
susceptible, beta-lactamase-
producing bacteria.
2.25grams IV every 8
hours
Obtain history of hypersensitivity to penicillins,
cephalosporins, or other drugs prior to
administration.
Lab tests: C&S prior to first dose of the drug; start
drug pending results.
Monitor hematologic status with prolonged
therapy (Hct and Hgb, CBC with differential and
platelet count).
Monitor patient carefully during the first 30 min
after initiation of the infusion for signs of
hypersensitivity.
Report rash, itching, or other signs of
hypersensitivity immediately.
Report loose stools or diarrhea as these may
indicate pseudomembranous colitis
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Tazocin It blocks the bacteria's cell
wall growth, which kills the
bacteria. Tazobactam
inhibits the action of
bacterial beta-lactamases. It
is added to the extended
spectrum beta-lactam
antibiotic piperacillin. It
Caution should be exercised in
patients with history of asthma; hay
fever; or kidney, liver, or
gastrointestinal disease (especially
colitis), during pregnancy and
breastfeeding.
Repeated electrolyte estimations
may be needed especially in
It may lead to increase
risk of fever, rashes in
patients with cystic
fibrosis, bleeding,
super infections,
convulsions, kidney
failure.
Allergic Reactions-
Patient is still closely monitored from infection.
Patient maintains adequate hydration throughout
the therapy.
Patient and Family state understanding of drug
therapy.
broadens the spectrum of
piperacillin by making it
effective against organisms
that express beta-lactamase
and would normally degrade
piperacillin.
patients with low potassium levels.
Monitor blood functions regularly.
Diarrhea, severe
allergic reactions, skin
rashes, itching,
occasionally platelet
mediated bleeding,
rigors, malaise,
inflammation in
stomach.
Local- Injection-site
reactions such as pain,
swelling, redness,
indurations and vein
inflammation.
GI- Inflammation of
stomach, hairy tongue,
inflammation of colon,
nausea and vomiting,
blood in stool.
GU- Urine retention,
painful urination.
Blood- Decrease in
white blood cells.
Lab- Increase in liver
enzymes, blood urea
nitrogen, and presence
of red blood cells in
urine.
Misc- Chills, facial
swelling, mucosal
bleeding, tightness in
throat.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
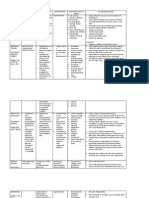
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Paracetamol Pharmacologic Class:
para-aminophenol derivative
Therapeutic Class: nonopiod
analgesic, antipyretic
Pregnancy Risk category : B
Mild pain or fever
Osteoarthritis
500mg tablet every 6
hours
Assess patients pain or temperature before and
during therapy.
Assess patients drug history, and calculate total
daily dosage accordingly.
Give oral form early in the morning and the
second dose early in the afternoon to avoid
nocturia.
Teach patient to monitor fluid volume by
measuring weight, intake, and output daily.
Enourage patient to avoid high-sodium foods and
to choose high-potassium foods.
Teach patient to recognize and report signs and
symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalance..
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Biogesic Chemical Effect:
Blocks pain impulses, probably
by inhibiting prostaglandin or
pain receptor sensitizers. May
relieve fever by acting in
hypothalamic heat-regulating
center.
Therapeutic Effect:
Relieves pain and reduces fever.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug.
Use cautiously in patients with
a history of chronic alcohol
abuse because hepatotoxicity
may occur after therapeutic
doses.
Hematologic: hemolytic
anemia, leucopenia,
neutopenia,
pancytopenia,
thrombocytopenia.
Hepatic: liver damage
(with toxic doses),
jaundice.
Metabolic: hypoglycemia
Patients temperature is already within normal
range and is thermoregulated
Slight grade 1 pitting edema noted from patient.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
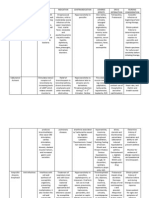
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Paracetamol Pharmacologic Class:
para-aminophenol derivative
Therapeutic Class: nonopiod
analgesic, antipyretic
Pregnancy Risk category : B
Mild pain or fever
Osteoarthritis
300mg IV for 6 doses Assess patients pain or temperature before and
during therapy.
Assess patients drug history, and calculate total
daily dosage accordingly.
Give oral form early in the morning and the
second dose early in the afternoon to avoid
nocturia.
Teach patient to monitor fluid volume by
measuring weight, intake, and output daily.
Enourage patient to avoid high-sodium foods and
to choose high-potassium foods.
Teach patient to recognize and report signs and
symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalance..
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Aeknil Chemical Effect:
Blocks pain impulses, probably
by inhibiting prostaglandin or
pain receptor sensitizers. May
relieve fever by acting in
hypothalamic heat-regulating
center.
Therapeutic Effect:
Relieves pain and reduces fever.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug.
Use cautiously in patients with
a history of chronic alcohol
abuse because hepatotoxicity
may occur after therapeutic
doses.
Hematologic: hemolytic
anemia, leucopenia,
neutopenia,
pancytopenia,
thrombocytopenia.
Hepatic: liver damage
(with toxic doses),
jaundice.
Metabolic: hypoglycemia
Patients temperature is already within normal
range and is thermoregulated
Slight grade 1 pitting edema noted from patient.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Potassium
Chloride
Pharmacologic Class:
Potassium supplement
Therapeutic Class: mineral
Pregnancy Risk category : C
Prevention of hypokalemia
Hypokalemia
Severe hpokalemia
Acute MI
1 durule per NGT Assess patients pain or temperature before and
during therapy.
During therapy, monitor ECG, renal function, fluid
intake and output, and potassium, creatinine and
BUN levels.
Give cautiously because different potassium
supplements deliver varying amounts of
potassium. Never switch products without
prescribers order.
Give potassium with or after meals with full glass
of water or fruit juice to lessen GI distress.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Kalium Durule Chemical Effect:
Aids in transmitting nerve
impulses, contracting cardiac
and skeletal muscle, and
maintaining intracellular
tonicity, cellular metabolism,
acid-base balance, and normal
renal function
Therapeutic Effect:
Replaces and maintains
potassium level
Contraindicated in patients
with untreated Addison
disease, adrenocortical
insufficiency, acute
dehydration, heat cramps,
hyperkalemia, hyperkalemic
form of familial periodic
paralysis, other conditions
linked to extensive tissue
breakdown, or severe renal
impairment with oliguria,
anuria, or azotemia
Hematologic: hemolytic
anemia, leucopenia,
neutopenia,
pancytopenia,
thrombocytopenia.
Hepatic: liver damage
(with toxic doses),
jaundice.
Metabolic: hypoglycemia
Patients potassium level returns to normal
Patient is free from hyperkalemia
Patient and family state understanding of drug
therapy.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Oxacillin Penicillins Systemic infections caused by
penicillinase-producing
staphylococci
1gm per IVTT Use cautiously in patients with other drug allergy,
especially to cephalosporins.
Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivity tests
before first dose.
To prevent vein irritation, avoid continuous
infusions. Change site every 48 hours.
Give 1-2 hours before or 2-3 hours after meals to
prevent gastric irritation.
Instruct patient to report the following signs of
superinfection: black, furry tongue, loose or
foul-smelling stools, vaginal itching or discharge.
Instruct patient to discard any liquid forms of
medication after 7 days if stored at room
temperature; after 14 days if refrigerated
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Wydox A penicillinase resistant
penicillin that inhibits cell-wall
synthesis during
microorganism multiplication;
bacteria resists penicillins by
producing penicilllinase
enzymes that convert
penicillins to inactivate
penecillic acids. Oxacillin resists
these enzymes.
Common: Thrombophebitis
Uncommon: Neuropathy,
neuromuscular irritability,
lethargy, hallucination,
anxiety, confusion, agitation,
depression, dizziness, fatigue,
oral lesions, nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea, enterocolitis,
interstitial nephritis,
nephropathy,
thrombocytopenia, hemolytic
anemia, anemia,
CNS
Neurotoxicity (eg,
lethargy, neuromuscular
irritability,
hallucinations,
convulsions and
seizures); dizziness;
fatigue; insomnia;
reversible hyperactivity;
prolonged muscle
relaxation.
Dermatologic
Ecchymosis.
Patient showed no signs of hypersensitivity
Patient is free from infection
Patient maintains adequate hydration.
hypersensitivity reactions EENT
Itchy eyes; abnormal
taste perception.
GI
Glossitis; stomatitis;
gastritis; sore mouth or
tongue; dry mouth; furry
tongue; black hairy
tongue; nausea;
anorexia; vomiting;
abdominal pain or
cramp; diarrhea or
bloody diarrhea; rectal
bleeding; flatulence;
enterocolitis;
pseudomembranous
colitis; anorexia.
Genitourinary
Interstitial nephritis (eg,
oliguria, proteinuria,
hematuria, hyaline casts,
pyuria); nephropathy;
increased creatinine and
BUN; vaginitis.
Hematologic
Deep vein thrombosis;
hematomas; phlebitis;
anemias;
thrombocytopenia;
eosinophilia; leukopenia;
granulocytopenia;
neutropenia; bone
marrow depression;
agranulocytosis; reduced
Hgb or Hct; prolongation
of bleeding and PT.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Metronidazole Pharmacologic Class:
nitroimidazole
Therapeutic Class:
Antibacterial, antiprotozoal,
amebicide
Pregnancy Risk Category: B
Amebic hepatic abscess
Intestinal Amebiasis
Trichomoniasis
Refractory trichomoniasis
Bacterial infections caused by
anaerobic microorganisms
To prevent postoperative infection
in contaminated colorectal surgery
Inflammatory papules and pustules
of acne rosacea
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Bacterial vaginosis
Active Crohn disease
500mg IV Assess patients infection before and regularly
thereafter to monitor drug effectiveness.
Watch carefully for edema, especially in
patients also receiving corticosteroids, because
Flagyl I.V. RTU may cause sodium retention.
Record number of stools when used in
amebiasis.
I.V. infusion may cause thrombophlebitis at
site; observe closely.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Dazomet Chemical Effect:
Direct-acting trichomonacide
and amebicide that works at
both intestinal and
extraintestinal sites.
Therapeutic Effect:
Hinders growth of selected
organims, including most
anaerobic and protozoa.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to the drug or other
nitroimidazole derivatives.
Use cautiously in patients receiving
hepatotoxic drugs and in patients
with history or blood dyscrasia or
CNS disorder, retinal or visual field
changes, hepatic disease, or
alcholism.
CNS: ataxia, confusion,
depression, drowsiness,
fatigue headache,
incoordination insomnia,
irritability, seizures,
vertigo, weakness.
CV: edema, flattened T
wave, flushing,
thrombophlebitis.
EENT: eye tearing.
GI: abdominal cramping,
Patient is still closely monitored from infection.
Patient maintains adequate hydration
throughout the therapy.
Patient and Family state understanding of drug
therapy.
anorexia, constipation,
diarrhea, dry mouth,
metallic taste, nausea,
vomiting. GU: cystitis,
darkened urine, dry
vagina and vulva,
dyspareunia.
Hematologic:
neutropenia,
thrombocytopenia,
transient leucopenia.
Skin: burning and
stinging, contact
dermatitis, dry skin, local
allergic reaction or
irritation.
Other: decreased libido,
glossitis, gynecomastia,
overgrowth of
nonsusceptible
organisms.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Clopidogrel
Bisulfate
Pharmacologic Class:
Inhibitor of adenosine
diphosphate (ADP)-induced
platelet aggregation
Therapeutic Class:
Antiplatelet
Pregnancy Risk Category: B
Reduce atherosclerotic events in
patients with atherosclerosis
documented by recent stroke, MI,
or peripheral arterial disease.
ST-segment elevation acute MI.
500mg IV Assess current use of OTC drugs, such as
aspirin, or NSAIDS, and herbal remedies.
Assess patient for increased bleeding or
bruising tendencies before and during drug
therapy.
Assess for history of gastric upset, bleeding or
liver disease.
Always inspect skin and mucous membrane for
signs of bleeding, monitor vital signs, monitor
blood counts.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Plavix Chemical Effect:
Drugs that inhibit platelet
aggregation thereby preventing
blood clots, inhibits the binding
of adenosine diphosphate to its
platelet receptor.
Therapeutic Effect:
Prevents clot formation
Contraindicated in patients
Hypersensitivity to the drug substance
or any component of the product.
Active pathologic bleeding, such as
peptic ulcer or intracranial
hemorrhage.
CNS: depression,
dizziness, fatigue,
headache, pain.
CV: edema, chest pain,
hypertension
EENT: epistaxis, rhinitis.
GI: abdominal pain,
constipation, diarrhea,
dyspepsia, gastritis,
hemorrhage, ulcers
Hematologic: purpura
Patient has less risk of stroke, MI, and vascular
death.
No signs of bleeding or bruising noted from
patient.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Ferrous Sulfate +
Folic Acid
Pharmacologic Class:
Oral iron supplement
Therapeutic Class:
Hematinic
Pregnancy Risk Category: A
Iron deficiency 500mg IV Obtain baseline assessment of patients iron
deficiency before starting therapy.
Evaluate hemoglobin level, hematocrit, and
reticulocyte count during therapy.
Give tablets with juice or water, but not with
milk or antacids.
To avoid staining of teeth, give suspension or
elixir with straw and place drops at back of
throat.
To prevent GI upset; give drug between meals
but if GI upset continues may give with food
Inform patient that oral iron turn stools into
black.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Iberet Folic Chemical Effect:
Provides elemental iron, an
essential component in
formation of hemoglobin.
Therapeutic Effect:
Relieves iron deficiency
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitivity to the drug or
ingredients; patients with primary
hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis,
hemolytic anemia, peptic ulcer disease,
regional enteritis, or ulcerative colitis;
and patients receiving repeated blood
transfusions.
GI:anorexia, black stools,
constipation, diarrhea,
epigastric pain, nausea,
vomiting.
Other: temporary staining
of teeth (drops,
suspension).
Decreased observations of fatigue noted from
patient
Assessed capillary refill time of <2 seconds
Patient and family state understanding of drug
therapy.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Acarbose Pharmacologic Class:
Alpha-glucosidae inhibitor
Therapeutic Class:
antidiabetic
Pregnancy Risk Category: B
To lower glucose level in
patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus, along with diet,
exercise, and possibly a
sulfonylurea, metformin or
insulin.
1gm per IVTT Obtain baseline creatinine level. Drug isnt
recommended in patient with a creatinine level
greater than 2 mg/dl.
Monitor glucose level 1 hour after a meal to
determine effectiveness and to identify
appropriate dose.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Glucobay Chemical Effect:
Delays carbohydrate digestion
and glucose absorption. Inhibits
the metabolism and sucrose to
glucose and fructose.
Therapeutic Effect:
Lessens postprandial
hyperglycemia.
Hypersensitivity to acarbose
or any of the excipients,
pregnancy and in nursing
mothers.
Glucobay is also contra-
indicated in patients with
inflammatory bowel disease,
colonic ulceration, partial
intestinal obstruction or in
patients predisposed to
GI: abdominal pain,
diarrhea, flatulence.
Patient maintains adequate fluid volume balance
Patient doesnt experience hypoglycemia.
Patient and family state understanding of drug
therapy.
intestinal obstruction. In
addition, Glucobay should not
be used in patients who have
chronic intestinal diseases
associated with marked
disorders of digestion or
absorption and in patients who
suffer from states which may
deteriorate as a result of
increased gas formation in the
intestine, e.g. larger hernias.
Glucobay is contra-indicated in
patients with severe hepatic
impairment.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Essential Amino
Acids
Pharmacologic Class:
Ketoanalogs; Essential amino
acids
Therapeutic Class:
Essential amino acids
Pregnancy Risk Category: B
Constipation
To prevent and treat hepatic
encephalopathy, including
heapatic precoma and coma in
patients with severe hepatic
disease.
To induce bowel evacuation in
geriatric patients with colonic
retention in barium and severe
constipation after a barium
meal examination.
To restore bowel movements
after hemorhoidectomy
30ml per orem
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Ketosteril
Chemical Effect:
Delays carbohydrate digestion
and glucose absorption. Inhibits
the metabolism and sucrose to
glucose and fructose.
Therapeutic Effect:
Lessens postprandial
hyperglycemia.
Contraindicated in paients on
low-galactose diet
Use cautiously in patients with
diabetes mellitus because drug
contains lactose, galactose, and
other sugars.
GI: abdominal carmps
and distention, belching,
diarrhea, flatulence,
nausea, vomiting.
Patient maintains adequate fluid volume balance
Patient doesnt experience hypoglycemia.
Patient and family state understanding of drug
therapy.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Lactulose Pharmacologic Class:
Disaccharide
Therapeutic Class:
Laxative
To lower glucose level in
patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus, along with diet,
exercise, and possibly a
sulfonylurea, metformin or
insulin.
1gm per IVTT Assess patients condition before starting therapy
and regularly thereafter to monitor drug
effectiveness. If patient has hepatic
encephalopathy, assess mental condition.
Monitor patients electrolyte levels during long-
term use.
In patient with hepatic disease, monitor ammonia
level.
Be alert for adverse reactions and drug
interactions.
Assess patients and familys knowledge of drug
therapy.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Lilac
Chemical Effect:
Delays carbohydrate digestion
and glucose absorption. Inhibits
the metabolism and sucrose to
glucose and fructose.
Therapeutic Effect:
Lessens postprandial
hyperglycemia.
Contraindicated in patients on
low-galactose diet.
use cautiously in patients with
diabetes mellitus because drug
contains lactose, galactose, and
other sugars.
GI: abdominal pain,
diarrhea, flatulence.
Patients constipation is relieved
Decreased distention of patients abdomen
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Ranitidine
Pharmacologic Class:
H2-receptor antagonist
Therapeutic Class:
Antiulcerative
Pregnancy Risk Category: B
Short-term treatment of active
duodenal ulcer
Maintenance therapy for
duodenal ulcer at reduced
dosage
Short-term treatment of
active, benign gastric ulcer
Short-term treatment of GERD
Pathologic hypersecretory
conditions (eg, Zollinger-
Ellison syndrome)
Treatment of erosive
esophagitis
Treatment of heartburn, acid
indigestion, sour stomach
50mg tab once a day Take drug with meals and at bedtime. Therapy
may continue for 46 weeks or longer.
If you also are using an antacid, take it exactly as
prescribed, being careful of the times of
administration.
Have regular medical follow-up care to evaluate
your response.
You may experience these side effects:
Constipation or diarrhea (request aid from your
health care provider); nausea, vomiting (take
drug with meals); enlargement of breasts,
impotence or decreased libido (reversible);
headache (adjust lights and temperature and
avoid noise).
Report sore throat, fever, unusual bruising or
bleeding, tarry stools, confusion, hallucinations,
dizziness, severe headache, muscle or joint pain.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Zantac
Chemical Effect:
Delays carbohydrate digestion
and glucose absorption. Inhibits
the metabolism and sucrose to
glucose and fructose.
Therapeutic Effect:
Lessens postprandial
hyperglycemia.
Contraindicated with allergyto
ranitidine, lactation Use
cautiously with impairedrenalor
hepatic function, pregnancy
Headache, dizziness.
Rarely hepatitis,
thrombocytopaenia,
leucopaenia,
hypersensitivity,
confusion,
gynecomastia,
impotence,
somnolence, vertigo,
hallucinations.
Patient states that GI discomfort is relieved.
Patient sustains no injury as result of drug
induced adverse CNS reactions.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Digoxin
Pharmacologic Class: cardiac
glycoside
Therapeutic Class:
antiarrhythmic, inotropic
Pregnancy Risk Category: C
Heart failure, paroxysmal
supraventricular tachycardia,
atrial fibrillation and flutter.
250 mcg tablet tablet
daily
Monitor effectiveness by taking apical pulse for 1
full minute before giving dose. Evaluate ECG, and
regularly assess patients cardiopulmonary
condition for signs of improvement.
Monitor drug level. Therapeutic level ranges from
0.5 to 2 nanograms/ml.
Monitor potassium level carefully.
Adjust doses as needed. Hypothyroid patients are
extremely sensitive to drug, and hyperthyroid
patients may need larger dosage. Reduce dose in
patients with renal impairment.
Before giving loading dose, obtain baseline data
and question about the use of drug for the past 2-3
weeks.
Withhold drug if pulse rate slows to 60bpm and
notify prescriber.
Withhold dose for 1-2 days before elective
cardioversion and adjust the dose afterwards
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Lanoxin
Inhibits sodium-potassium-
activated adenosine
triphosphate, thereby
promoting movement of
calcium from extracellular
to intracellular cytoplasm
and strengthening
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug or any
of its components and in those
with digoxin-induced toxicity,
ventricular fibrillation, or
ventricular tachycardia unless
caused by heart failure.
CNS: agitation, dizziness,
fatigue, generalized
muscle weakness,
hallucinations, headache,
malaise, paresthesia,
stupor, vertigo
CV: arrhythmias, heart
Patient had adequate cardiac output
Patient had no signs of digoxin toxicity
Rare episodes of cardiac arrythmia
myocardial contraction.
Also acts on CNS to enhance
vagal tone, slowing
conduction through SA and
AV node and providing
antiarrhythmic effect
Strengthens myocardial
contractions and slows
conduction through SA and
Av node.
Use cautiously in patients with
acute MI, incomplete AV block,
sinus bradycardia, PVCs,
chronic constrictive
pericarditis, hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy, renal
insufficiency, severe
pulmonary disease, or
hypothyroidism.
failure, hypotension
EENT: blurred vision,
diplopia, light flashes,
photophobia, yellow-
green halos around
visual images
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Phenobarbital Pharmacologic Class:
barbiturate
Therapeutic Class:
anticonvulsant, sedative-
hypnotic
Pregnancy Risk Category: D
All forms of epilepsy except
absence seizures; febrile seizures in
children.
Status epilepticus
Sedation
Insomnia
Preoperative sedation
Prevention and treatment of
hyperbilirubinemia
To lower serum bilirubin or serum
lipid levels in the treatment of
chronic cholestasis.
500mg IV Assess patients infection before and regularly
thereafter to monitor drug effectiveness.
Watch carefully for edema, especially in patients
also receiving corticosteroids, because Flagyl I.V.
RTU may cause sodium retention.
Record number of stools when used in amebiasis.
I.V. infusion may cause thrombophlebitis at site;
observe closely.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Luminal Chemical Effect:
Direct-acting trichomonacide
and amebicide that works at
both intestinal and
extraintestinal sites.
Therapeutic Effect:
Hinders growth of selected
organims, including most
anaerobic and protozoa.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to barbiturates and
in those with hepatic dysfunction,
respiratory disease with dyspnea or
obstruction, nephritis, or a history
of manifest or latent porphyria.
Use cautiously in debilitated
patients and in patients with acute
or chronic pain, depression, suicidal
tendencies, history of drug abuse,
altered blood pressure, CV disease,
shock, or uremia
CNS: drowsiness,
hangover, lethargy.
CV: bradycardia,
hypotension,
thrombophlebitis
GI: nausea, vomiting
Hematologic:
exacerbation or
porphyria.
Respiratory: apnea,
respiratory depression.
Skin: erythema
multiforme, rash.
Patient is free from seizure activity
Patient has no injury from drug-induced adverse
CNS reactions.
You might also like
- Conzace Tranexamic MetoclopramideDocument5 pagesConzace Tranexamic MetoclopramideDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- BREX Pharmacy Review Module 1Document9 pagesBREX Pharmacy Review Module 1Kenneth DayritNo ratings yet
- Pharma Guide (Dhshan H. Dhshan) - 2018Document419 pagesPharma Guide (Dhshan H. Dhshan) - 2018A.E. Salih Unused Email100% (2)
- MCQ For FINAL (3&4)Document12 pagesMCQ For FINAL (3&4)api-2693862480% (5)
- ASCIA HP Penicillin Allergy Guide 2016Document1 pageASCIA HP Penicillin Allergy Guide 2016kkkssbbNo ratings yet
- CHH Drug Study Week 2Document25 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 2maryxtine24No ratings yet
- Drug Study ProjectDocument7 pagesDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Xi - Drug Study: Drugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument18 pagesXi - Drug Study: Drugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationlicservernoidaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Hepatic FailureDocument37 pagesHepatic FailureWinston Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- 1 DrugsDocument2 pages1 DrugsPatricia Lucero67% (3)
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoy Jarin100% (1)
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Drug StudDocument12 pagesDrug StudKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Rani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument10 pagesRani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyIv'z TandocNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Careplan 2Document11 pagesCareplan 2JulieRn2beNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument12 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyDeca TanNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument11 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Care Plan September 25 Med-SurgDocument19 pagesCare Plan September 25 Med-Surgapi-251516913No ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Tramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibDocument4 pagesTramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibEric de JulianNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification:: Source: Drug Handbook 27 Edition, Lippincot Williams & WilkinsDocument11 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Classification:: Source: Drug Handbook 27 Edition, Lippincot Williams & WilkinsVel Georgia-FrancoNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Presented by BSN Iii - A2Document90 pagesCase Presentation: Presented by BSN Iii - A2Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy DrugsDocument43 pagesChemotherapy Drugsbrigette_lagat100% (2)
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- FINAL DRUGS Pancreatic CancerDocument10 pagesFINAL DRUGS Pancreatic CancerfjorelynNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismDocument9 pagesDrug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AGEDocument5 pagesDrug Study AGEAna Mae ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocument12 pagesDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolDocument7 pagesName of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objectivechaoz09No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)Document2 pagesAcetaminophen (Tylenol)amelia hearonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Medication Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Intervention Generic Name: CNS: GIDocument4 pagesMedication Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Intervention Generic Name: CNS: GIKathleenDawalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RICUDocument10 pagesDrug Study RICUCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 pagesAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Last DutyDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDelivery Room Drug StudyChinimansiNo ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Penicillin Production Paper - FinalDocument31 pagesPenicillin Production Paper - Finalapi-508032756No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Antibiotics & Antiinfectives-1Document39 pagesLecture 10 Antibiotics & Antiinfectives-1Dr Haris AwanNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry of Beta-Lactam AntibioticsDocument13 pagesMedicinal Chemistry of Beta-Lactam AntibioticsJosiah O OmobaNo ratings yet
- Jama Shenoy 2019 RV 180010Document12 pagesJama Shenoy 2019 RV 180010GustavoCalderinNo ratings yet
- Soal UasDocument10 pagesSoal UasDila ZeinNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument9 pagesNursing DiagnosisSkyerexNo ratings yet
- PenicillinDocument75 pagesPenicillinJean CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Bio Process Problem 1Document1 pageBio Process Problem 1AshenafiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Neuropsychiatric Effects Psychotropic Interact IonsDocument13 pagesAntibiotics: Neuropsychiatric Effects Psychotropic Interact Ionsracm89No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyAnne Therese Bello Sibayan0% (1)
- Ef3 Advanced Short Films ScriptsDocument9 pagesEf3 Advanced Short Films Scriptskeyepat806No ratings yet
- Pil 11044Document3 pagesPil 11044an12al9008No ratings yet
- Alexander Fleming and The Discovery of PenicilinDocument3 pagesAlexander Fleming and The Discovery of PenicilinAlexandra HornetNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyCieLouie Cauilan-DomingoNo ratings yet
- 1 Historical Overview and Future Perspective: Bernhard Eikmanns, Marcella Eikmanns, and Christopher J. PaddonDocument22 pages1 Historical Overview and Future Perspective: Bernhard Eikmanns, Marcella Eikmanns, and Christopher J. PaddonDr. Laxman RautNo ratings yet
- Listening Activity. EIII G1docxDocument2 pagesListening Activity. EIII G1docxYeraldin Acevedo CastroNo ratings yet
- Cep Halo Sporin SDocument9 pagesCep Halo Sporin SJasper VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykakienz100% (7)
- 1ST - Microbiology and Parasitology (Laboratory)Document11 pages1ST - Microbiology and Parasitology (Laboratory)Krianne Chris DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Beta - Lactam AntibioticsDocument217 pagesBeta - Lactam AntibioticsEmre Yücel100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyArdy PadamadaNo ratings yet
- Bicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyDocument1 pageBicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyChristine Pialan Salimbagat100% (1)
- Pharma Lecture With Dr. Maria Yña Eluisia T. Pereyra-Borlongan 1Document13 pagesPharma Lecture With Dr. Maria Yña Eluisia T. Pereyra-Borlongan 1Sammy GirlNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document20 pagesExercise 1Huyen Trang NguyenNo ratings yet
- All (Introduction To Anti-MicDocument3 pagesAll (Introduction To Anti-MicMiki AberaNo ratings yet
- L9 Antibiotic For Gram PositiveDocument6 pagesL9 Antibiotic For Gram PositiveJennifer TanNo ratings yet