Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Change Change Source: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Change Change Source: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
aja_sh99@yahoo.co.in0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views5 pagesThis document summarizes information about solar energy from Wikipedia. It describes solar energy as energy from sunlight that has been used for thousands of years in heating, cooking, and drying. Modern uses of solar energy include generating electricity through solar cells or heat engines. The document provides details on the amount of solar energy that reaches the Earth's surface and the types of solar energy technologies, including solar power plants, solar cooking, solar heating, and solar cells.
Original Description:
It gives a description of generation of electricity using wind power.
Original Title
Wind Power
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes information about solar energy from Wikipedia. It describes solar energy as energy from sunlight that has been used for thousands of years in heating, cooking, and drying. Modern uses of solar energy include generating electricity through solar cells or heat engines. The document provides details on the amount of solar energy that reaches the Earth's surface and the types of solar energy technologies, including solar power plants, solar cooking, solar heating, and solar cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views5 pagesChange Change Source: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Change Change Source: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
aja_sh99@yahoo.co.inThis document summarizes information about solar energy from Wikipedia. It describes solar energy as energy from sunlight that has been used for thousands of years in heating, cooking, and drying. Modern uses of solar energy include generating electricity through solar cells or heat engines. The document provides details on the amount of solar energy that reaches the Earth's surface and the types of solar energy technologies, including solar power plants, solar cooking, solar heating, and solar cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
The natural resource of wind powers these 5MW wind turbines on this wind farm in Belgium.
A natural resource is anything that people can use which comes from nature. People do not
make natural resources, but gather them from the earth. Examples of natural resources are air,
water, wood, oil, wind energy, hydro-electric energy, iron, and coal. Refined oil is not a
natural resource because people make it.
Contents
[hide]
1 Supply
2 Demand
3 Availability
4 References
5 Other websites
Supply[change | change source]
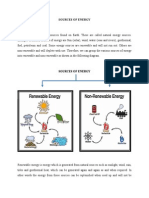
We often say there are two sorts of natural resources: renewable resources and non-renewable
resources.
A renewable resource grows again and comes back again after we use it. For example,
soil, sunlight, water and wood are renewable resources.
A non-renewable resource is a resource that does not grow and come back, or a
resource that would take a very long time to come back. For example, coal is a non-
renewable resource. When we use coal, there is less coal afterward. One day, there
will be no more of it to make goods. The non-renewable resource can be used directly
(for example, burning oil to cook), or we can find a renewable resource to use (for
example, using wind energy to make electricity to cook). It is important to conserve
(save) non-renewable resources, because if we use them too quickly there will not be
enough.
Most natural resources are limited. This means they will eventually run out. A perpetual
resource has a never-ending supply. Some examples of perpetual resources include solar
energy, tidal energy, and wind energy.
[1]
Other examples are salt, stone, magnesium, and
diamonds.
Some of the things influencing supply of resources include whether it is able to be recycled,
and the availability of suitable substitutes for the material. Non-renewable resources cannot
be recycled. For example, oil, minerals, and other non-renewable resources cannot be
recycled.
Demand[change | change source]
The demand for resources can change with new technology, new needs, and new economics
(e.g. changes in cost of the resources). Some material can go completely out of use, if people
do not want it any more. Demand of natural resources is very high, but availability is very
low .
Availability[change | change source]
All places have their own natural resources. When people do not have a certain resource they
need, they can either replace it with another resource, or trade with another country to get the
resource. Some resources are difficult to find, so people sometimes fight to have them (for
example, oil resources).
When people do not have some natural resources, their quality of life can get lower. So, we
need to protect our resources from pollution. For example, when they can not get clean water,
people may become ill; if there is not enough wood, trees will be cut and the forest will
disappear over time (deforestation); if there are not enough fish in a sea, people can die of
starvation. Some examples of renewable resources are wood, solar energy, trees, wind,
hydroelectric power, fish, and sunlight. So humans should begin saving their natural
resources. Or else, all will be lost and it will be difficult for humans to survive.
4. Mixed cropping, crop rotation, and proper use of fertilizer, insecticide and pesticides should be taught to farmers. Encourage
the use of manures, biofertilizers and organic fertilizers.
5. We should protect wildlife. Though hunting is not allowed even then the persons are doing so. For this educated young
should teach the lesson of wildlife act.
6. We must develop energy saving methods to avoid wastage of energy. We should remember "energy saved is energy
produced."
7. Use drip irrigation and sprinkling irrigation to improve irrigation efficiency and reduce evaporation.
8. Utilize renewable energy sources as much as possible. Encourage use of solar cooker, pump etc.
9. We should recycle the waste and waste water for agriculture purposes.
10. Install rain water harvesting system in houses, colonies.
11. Try to educate local people for the protection and judicious use of natural resources.
Solar energy
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
At the equator, the Sun provides approximately 1000 watts per square meter on Earth's surface.
The top diagram shows how the strength of sunlight is less nearer the Earth's poles. The lower map
shows how much solar energy hits the Earth's surface after clouds and dust have reflected and
absorbed some solar energy.
Solar Radiation Map: Global Horizontal Irradiation in Europe
Solar energy is energy that is present in sunlight. It has been used for thousands of years in
many different ways by people all over the world. As well as its traditional human uses in
heating, cooking, and drying, it is used today to make electricity where other power supplies
are absent, such as in remote places and in space. It is becoming cheaper to make electricity
from solar energy and in many situations it is now competitive with energy from coal or oil.
Contents
[hide]
1 Energy use
2 Energy from the Sun
3 Types of technologies
o 3.1 Solar power plants
o 3.2 Solar cooking
o 3.3 Solar heating
o 3.4 Solar cells
4 Other pages
5 References
6 Other websites
Energy use[change | change source]
Solar energy is used today in a number of ways:
As heat for making hot water, heating buildings, and cooking
To generate electricity with solar cells or heat engines
To take the salt away from seawater.
Energy from the Sun[change | change source]
After passing through the Earth's atmosphere, most of the Sun's energy is in the form of
visible light and infrared light radiation. Plants convert the energy in sunlight into chemical
energy (sugars and starches) through the process of photosynthesis. Humans regularly use
this store of energy in various ways, as when they burn wood or fossil fuels, or when simply
eating plants, fish and animals.
Solar radiation reaches the Earth's upper Earth's atmosphere with the power of 1366 watts per
square meter (W/m
2
). Since the Earth is round, the surface nearer its poles is angled away
from the sun and receives much less solar energy than the surface nearer the equator.
At present, solar cell panels convert, at best, about 15% of sunlight hitting them into
electricity.
[1]
The dark disks in the third diagram on the right are imaginary examples of the
amount of land that, if covered with 8% efficient solar panels, would produce slightly more
energy in the form of electricity than the world needed in 2003.
[2]
Types of technologies[change | change source]
Many technologies have been developed to make use of solar radiation. Some of these
technologies make direct use of the solar energy (e.g. to provide light, heat, etc.),
You might also like
- 51909-Doosan MOXY MT26 MT31 Articulated Dump Truck PDFDocument931 pages51909-Doosan MOXY MT26 MT31 Articulated Dump Truck PDFSimon C Mulgrew83% (6)
- Clocky Case Study - Group 1Document7 pagesClocky Case Study - Group 1Souhardya BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Microcell CalibrationDocument10 pagesMicrocell Calibrationprabhu0487No ratings yet
- Grading Rubric Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGrading Rubric Lesson Planapi-395707446No ratings yet
- Earth's Resources: 6 GradeDocument13 pagesEarth's Resources: 6 GradeJordyn IzenstarkNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources - Google DriveDocument20 pagesNatural Resources - Google DriveKajol HNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument8 pagesNatural ResourcesTigerNo ratings yet
- Final Report EnergyDocument52 pagesFinal Report EnergymangalamNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Psychology: EnergyDocument31 pagesPhilosophy and Psychology: EnergyDodelyn CeniaNo ratings yet
- Comprehension EnergyDocument3 pagesComprehension EnergyArlet SastreNo ratings yet
- Handout 2.10.f PDFDocument3 pagesHandout 2.10.f PDFToru -No ratings yet
- Module 3Document15 pagesModule 3SumanpalNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources Handout (C)Document3 pagesEnergy Resources Handout (C)PunchyDoodlesNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy SourcesDocument12 pagesAlternative Energy SourcesArodis GomezNo ratings yet
- JACK BREEDLOVE - TX - 4.7C - Resources - EXPLAIN - STEMscopediaDocument7 pagesJACK BREEDLOVE - TX - 4.7C - Resources - EXPLAIN - STEMscopediar9y8mn4kggNo ratings yet
- What Are Different Sources of EnergyDocument6 pagesWhat Are Different Sources of EnergyMeliza PugalNo ratings yet
- Examples of Nonrenewable Energy SourcesDocument4 pagesExamples of Nonrenewable Energy SourcesY D Amon GanzonNo ratings yet
- What Are Natural Resources?Document5 pagesWhat Are Natural Resources?Lucrari de LicentaNo ratings yet
- Uses of Renewable and Non Renewable Resources - 20240407 - 213637 - 0000Document53 pagesUses of Renewable and Non Renewable Resources - 20240407 - 213637 - 0000Hestia MendezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sistema Ni KaloyDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Sistema Ni KaloyJohn Carlo CericoNo ratings yet
- M4. Lab Different Energy FormsDocument8 pagesM4. Lab Different Energy FormsMyriam AkramNo ratings yet
- BBA-Semester III Course Name-Environment Management Topic-Natural ResourcesDocument3 pagesBBA-Semester III Course Name-Environment Management Topic-Natural ResourcesMitali GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sistema Ni Kaloy UpgradedDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Sistema Ni Kaloy UpgradedJohn Carlo CericoNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Is Energy Which: Enewable Nergy EsourcesDocument4 pagesRenewable Energy Is Energy Which: Enewable Nergy EsourcesJawwad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy and ResourcesDocument7 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable Energy and ResourcesChristine Rizza Ablao NavarroNo ratings yet
- Unit Energy Part 5Document20 pagesUnit Energy Part 5Maurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- Sources of EnergyDocument2 pagesSources of EnergyglechohNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources: and Their ConservationDocument18 pagesNatural Resources: and Their Conservationnihal_sawyerNo ratings yet
- Energy Renewable EnergyDocument16 pagesEnergy Renewable EnergyMd IshteyaqueNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Historical BackgroundDocument19 pages2.1 Historical BackgroundTransfiguration DailyNo ratings yet
- ResourcesDocument7 pagesResourcestereveNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument92 pagesIlovepdf MergedFiras 01No ratings yet
- EVS Chapter 2 Sem2Document17 pagesEVS Chapter 2 Sem2rishigoel284No ratings yet
- Green Planet Weekly FinalDocument2 pagesGreen Planet Weekly FinalDang PhamNo ratings yet
- 2.energy ResourseDocument38 pages2.energy Resoursearpit patilNo ratings yet
- Energy Engineering Unit 1Document6 pagesEnergy Engineering Unit 1SathishNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources: UsesDocument4 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable Resources: Usesyasri_yahyaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering NotesDocument3 pagesPower Plant Engineering NotesNeelesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument38 pagesRenewable EnergyRahul Kumar100% (1)
- Makapasar Sa Sci CutieDocument18 pagesMakapasar Sa Sci CutieChristian MonterroyoNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources and Their ManagementDocument24 pagesNatural Resources and Their Managementshilpaverma2106No ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument4 pagesRenewable EnergyErick ValdovinosNo ratings yet
- STEMAZINGDocument3 pagesSTEMAZINGrueza bontuyanNo ratings yet
- 10 Different Alterntive Sources of Energy (SolarDocument3 pages10 Different Alterntive Sources of Energy (Solarwhnqckt7nzNo ratings yet
- Sources of EnergyDocument15 pagesSources of EnergyHaze MaelstromNo ratings yet
- Toddle Dbcde904 132c 4afc b6b6 2a237bef7220 Renewable and NonrenewableDocument6 pagesToddle Dbcde904 132c 4afc b6b6 2a237bef7220 Renewable and Nonrenewable76t8n6vdg7No ratings yet
- EnergyDocument4 pagesEnergyAmmara RiazNo ratings yet
- JANUARY Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesJANUARY Lesson PlanKashyap MulukutlaNo ratings yet
- Vaishali Evs ProjectDocument32 pagesVaishali Evs Projectvaishali TMU studentNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesRenewable EnergyTamil VelNo ratings yet
- Goal:: Letter MatrixDocument1 pageGoal:: Letter MatrixPint EraNo ratings yet
- Energy and EnvironmentDocument17 pagesEnergy and EnvironmentGiridhar SankarNo ratings yet
- Renewable ResourcesDocument5 pagesRenewable ResourcessumitrochakrabortiNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument20 pagesNatural Resourcessana ali huabishiNo ratings yet
- Deffrent Type of EnergyDocument3 pagesDeffrent Type of EnergyImran SiddNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Technologies: MECH 200Document10 pagesRenewable Energy Technologies: MECH 200Bachir El FilNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Coal and PetroleumDocument5 pagesCh-5 Coal and PetroleumZara SmithNo ratings yet
- Krishna Sraf - Ix-A - Computer Practical Question 1.Document43 pagesKrishna Sraf - Ix-A - Computer Practical Question 1.Krishna SarafNo ratings yet
- Solar CollectorDocument62 pagesSolar CollectorJordanNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources: Energy From The SunDocument5 pagesEnergy Sources: Energy From The SunKyle SaberonNo ratings yet
- Las Module 3 Earth and LifeDocument7 pagesLas Module 3 Earth and LifeJames ivan ToledoNo ratings yet
- Alternative Sources of Energy EssayDocument4 pagesAlternative Sources of Energy EssayRaivat ShahNo ratings yet
- Types of Natural ResourcesDocument3 pagesTypes of Natural ResourcesSoumendra RoyNo ratings yet
- Life of Dorothy MillerDocument1 pageLife of Dorothy Milleraja_sh99@yahoo.co.inNo ratings yet
- Kantaka Shani RealDocument14 pagesKantaka Shani RealAbin Sasi100% (1)
- Final: Test Report StatusDocument1 pageFinal: Test Report Statusaja_sh99@yahoo.co.inNo ratings yet
- Uttar Haryana Bijli Vitran NigamDocument1 pageUttar Haryana Bijli Vitran Nigamaja_sh99@yahoo.co.inNo ratings yet
- Transit Chart KC From Original Natal ChartDocument2 pagesTransit Chart KC From Original Natal Chartaja_sh99@yahoo.co.inNo ratings yet
- Process Scheduling AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesProcess Scheduling AlgorithmsKartik VermaNo ratings yet
- 36 PneumaticDocument60 pages36 PneumaticQuynh Nguyen100% (1)
- 2014 Survey of Living Conditions QuestionnaireDocument59 pages2014 Survey of Living Conditions QuestionnaireabguyNo ratings yet
- Brosur JN 190253 PHIDocument12 pagesBrosur JN 190253 PHIanugrahjayainternusa100% (1)
- Hanlon Windows BrochureDocument9 pagesHanlon Windows BrochureBhairav DesaiNo ratings yet
- DD Security Configuration GuideDocument50 pagesDD Security Configuration GuideRatataNo ratings yet
- Power System Research PapersDocument5 pagesPower System Research Papersknztwaulg100% (1)
- App Inventor TutorialsDocument54 pagesApp Inventor TutorialsLolo Perez GarciaNo ratings yet
- High Performance MCB, ABBDocument53 pagesHigh Performance MCB, ABBUmang JainNo ratings yet
- The Messenger: No. 123 - March 2006Document80 pagesThe Messenger: No. 123 - March 2006European Southern ObservatoryNo ratings yet
- Sanken News: House of Fashion Shopping MallDocument10 pagesSanken News: House of Fashion Shopping Mallmalan_ubNo ratings yet
- Silent Hunter 3Document41 pagesSilent Hunter 3Ricardo DavisNo ratings yet
- Saving Reading UploadingDownloading Mechanism of CSV File and Text File Using Csharp AspnetDocument4 pagesSaving Reading UploadingDownloading Mechanism of CSV File and Text File Using Csharp AspnetLajapathy ArunNo ratings yet
- 05 10Document22 pages05 10gayathrisicwai100% (1)
- Cristians AlgorithmDocument13 pagesCristians AlgorithmJoao BorgesNo ratings yet
- 9Document37 pages9id7miNo ratings yet
- TM 55 1520 236 23 3Document1,427 pagesTM 55 1520 236 23 3Tod A. Wulff100% (2)
- Catalogo Athena Off Road e Atv PDFDocument248 pagesCatalogo Athena Off Road e Atv PDF851ducatiNo ratings yet
- Cloudera Administration Handbook Sample ChapterDocument22 pagesCloudera Administration Handbook Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Suspention BridgeDocument15 pagesSuspention BridgeMdrazi BilalNo ratings yet
- OAG PolicyDeveloperGuideDocument781 pagesOAG PolicyDeveloperGuideMatiasNo ratings yet
- PC-PRO+ Advanced 9 00 Release NotesDocument8 pagesPC-PRO+ Advanced 9 00 Release NotesBruno De BridaNo ratings yet
- PWM Solar Charge Contrller: RTC SeriesDocument1 pagePWM Solar Charge Contrller: RTC SeriesjedossousNo ratings yet
- OptiFDTD Tutorials PDFDocument36 pagesOptiFDTD Tutorials PDFKhải NguyễnNo ratings yet