Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Use The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit How To User The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit
How To Use The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit How To User The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit
Uploaded by
nabil1608740 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
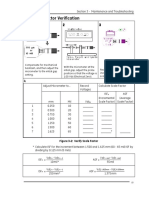
121 views2 pages3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit Part Number 140273-01, Rev. C Setup Option 1 - Transducer System Verification Set up the shaft micrometer using a power supply, multimeter, and transducer system with the probe viewing a Bently Nevada(tm) 4140 target button. To obtain your first measuring point, X1, back off the micrometer to the beginning of the linear range of the probe in use.
Original Description:
Original Title
0273C1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit Part Number 140273-01, Rev. C Setup Option 1 - Transducer System Verification Set up the shaft micrometer using a power supply, multimeter, and transducer system with the probe viewing a Bently Nevada(tm) 4140 target button. To obtain your first measuring point, X1, back off the micrometer to the beginning of the linear range of the probe in use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
121 views2 pagesHow To Use The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit How To User The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit
How To Use The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit How To User The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit
Uploaded by
nabil1608743300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit Part Number 140273-01, Rev. C Setup Option 1 - Transducer System Verification Set up the shaft micrometer using a power supply, multimeter, and transducer system with the probe viewing a Bently Nevada(tm) 4140 target button. To obtain your first measuring point, X1, back off the micrometer to the beginning of the linear range of the probe in use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
How to Use the 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit
Part Number 140273-01, Rev. C
Setup Option 1 Transducer System
Verification
Set up the shaft micrometer using a power
supply, multimeter, and transducer system with
the probe viewing a Bently Nevada 4140
target button. Note: Be sure the target is visible
through the hole in the collet before you insert
the probe.
POWER SUPPLY MULTIMETER
-3.00 Vdc
Vin
10 kO
Com
-24 Vdc
+ -
Setup Option 2 Shaft Verification in
Hazardous Areas
To verify the transducer system curve in an
intrinsically safe application when viewing a
shaft or piston rod, set up the transducer
system, micrometer, and multimeter as shown
below.
MULTIMETER
-3.00 Vdc
Vin Com
IN
MONITOR
COM
VT
BUFFERED
TRANSDUCER OUTPUT
(BNC CONNECTION)
Setup Option 3 Shaft Verification in
Non-Hazardous Areas
To verify the transducer system curve when
viewing the shaft or piston rod in a
non-hazardous area application, set up the
transducer system, shaft micrometer, power
supply, and multimeter as shown below.
POWER SUPPLY MULTIMETER
-3.00 Vdc
Vin
10 kO
Com
-24 Vdc
+ -
Step 1 Verifying the Transducer
While compensating for backlash, adjust the
micrometer position until the transducer system
is at electrical zero. The position of the
micrometer at this point is X0. To obtain your
first measuring point, X1, back off the
micrometer to the beginning of the linear range
of the probe in use. For example, for 5 & 8 mm
3300 probes, back off the micrometer 12 mil
(300m) from X0 and then adjust forward to 10
mil (250m) from X0. This will give you X1.
Xo-12 mil
Xo-300 um
or
Xo-250 um
Xo-10 mil
or
How to User the 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit
Part Number 140273-01, Rev. C
Setup Option 1 Transducer System
Verification
Set up the shaft micrometer using a power
supply, multimeter, and transducer system with
the probe viewing a Bently Nevada 4140 target
button. Note: Be sure the target is visible through
the hole in the collet before inserting the probe.
POWER SUPPLY MULTIMETER
-3.00 Vdc
Vin
10 kO
Com
-24 Vdc
+ -
Setup Option 2 Shaft Verification in
Hazardous Areas
To verify the transducer system curve in an
intrinsically safe application when viewing a
shaft or piston rod, set up the transducer
system, micrometer, and multimeter as shown
below.
MULTIMETER
-3.00 Vdc
Vin Com
IN
MONITOR
COM
VT
BUFFERED
TRANSDUCER OUTPUT
(BNC CONNECTION)
Setup Option 3 Shaft Verification in Non-
Hazardous Areas
To verify the transducer system curve when
viewing the shaft or piston rod in a non-
hazardous area application, set up the
transducer system, shaft micrometer, power
supply, and multimeter as shown below.
POWER SUPPLY MULTIMETER
-3.00 Vdc
Vin
10 kO
Com
-24 Vdc
+ -
Step 1 Verifying the Transducer
While compensating for backlash, adjust the
micrometer position until the transducer
system is at electrical zero. The position of the
micrometer at this point is X0. To obtain your
first measuring point, X1, back off the
micrometer to the beginning of the linear range
of the probe in use. For example, for 5 & 8 mm
3300 probes, back off the micrometer 12 mil
(300m) from X0 and then adjust forward to 10
mil (250m) from X0. This will give you X1.
Xo-12 mil
Xo-300 um
or
Xo-250 um
Xo-10 mil
or
Step 2 Take Readings
Take readings until end of linear range in 250m
(10 mil) increments, assuming X1 is approximately
equal to 250m (10 mil). All voltages should be
negative voltages.
xn Probe Gap
Record
Voltages
n mn miln Vdcn
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Step 3 Calculate ISF
Calculate Incremental Scale Factors (ISFn),
Average Scale Factor (ASF), and difference
voltages (Vdiffn).
25 . 0
Vdc - Vdc
= ISF
n 1 - n
) m / mV ( n
01 . 0
Vdc - Vdc
= ISF
n 1 - n
) mil / mV ( n
2
Vdc - Vdc
= ASF
m 2250 m 250
) m / mV (
08 . 0
Vdc - Vdc
= ASF
mil 90 mil 10
) mil / mV (
) 0079 . 0 m ( + Vdc = Vdiff n n n
) 2 . 0 l mi ( + Vdc = Vdiff n n n
Step 4a Record Scale Factors and
Difference Voltages
n
ISFn
(Incremental
Scale
Factor)
ASF
(Average
Scale
Factor)
Vdiffn
(Difference
Voltage)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Step 4b Determine Maximum Deviation
From Straight Line (DSL)
Use the following formulas to determine
maximum DSL:
m ____ =
0157 . 0
Vdiff - Vdiff
= DSL
(min) (max)
) m (
mil ____ =
40 . 0
Vdiff - Vdiff
= DSL
(min) (max)
) mil (
Notes
1. The numbers shown are only for
3300 5mm or 8mm, or 7200 5mm or
8mm systems. Check your
Transducer Manual for other values
for other systems.
2. Periodically coat target face with a
thin coat of paraffin wax to avoid
corrosion.
3. It is possible for the target to become
magnetized, which can effect scale
factor readings. Avoid strong
magnetic fields and degauss target if
necessary.
Copyright 1999. Bently Nevada LLC.
Bently Nevada is a trademark of General
Electric Company.
Step 2 Take Readings
Take readings until end of linear range in 250m
(10 mil) increments, assuming X1 is approximately
equal to 250m (10 mil). All voltages should be
negative voltages.
xn Probe Gap
Record
Voltages
n mn miln Vdcn
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Step 3 Calculate ISF
Calculate Incremental Scale Factors (ISFn),
Average Scale Factor (ASF), and difference
voltages (Vdiffn).
25 . 0
Vdc - Vdc
= ISF
n 1 - n
) m / mV ( n
01 . 0
Vdc - Vdc
= ISF
n 1 - n
) mil / mV ( n
2
Vdc - Vdc
= ASF
m 2250 m 250
) m / mV (
08 . 0
Vdc - Vdc
= ASF
mil 90 mil 10
) mil / mV (
) 0079 . 0 m ( + Vdc = Vdiff n n n
) 2 . 0 l mi ( + Vdc = Vdiff n n n
Step 4a Record Scale Factors and
Difference Voltages
n
ISFn
(Incremental
Scale
Factor)
ASF
(Average
Scale
Factor)
Vdiffn
(Difference
Voltage)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Step 4b Determine Maximum Deviation
From Straight Line (DSL)
Use the following formulas to determine
maximum DSL:
m ____ =
0157 . 0
Vdiff - Vdiff
= DSL
(min) (max)
) m (
mil ____ =
40 . 0
Vdiff - Vdiff
= DSL
(min) (max)
) mil (
Notes
1. The numbers shown are only for
3300 5mm or 8mm, or 7200 5mm or
8mm systems. Check your
Transducer Manual for other values
for other systems.
2. Periodically coat target face with a
thin coat of paraffin wax to avoid
corrosion.
3. It is possible for the target to become
magnetized, which can effect scale
factor readings. Avoid strong
magnetic fields and degauss target if
necessary.
Copyright 1999. Bently Nevada LLC.
Bently Nevada is a trademark of General
Electric Company.
You might also like
- BMW x3 E83 2003 2010 Workshop Service ManualDocument5,817 pagesBMW x3 E83 2003 2010 Workshop Service Manualmegaady100% (4)
- Portable Vibration CalibratorDocument23 pagesPortable Vibration CalibratorNovato300% (1)
- CNC Machine Operator MVDocument6 pagesCNC Machine Operator MVAfif Effendi100% (1)
- Form 4 - Physics ExercisesDocument9 pagesForm 4 - Physics Exercisesnik mohamad solehin100% (3)
- Manual For Wire RopesDocument25 pagesManual For Wire RopesAnand Agrawal0% (1)
- Kistler 9602AADocument6 pagesKistler 9602AAJenni JosephNo ratings yet
- 1Document30 pages1Amarnath YadavNo ratings yet
- Bently Nevada MmsDocument30 pagesBently Nevada MmsMohamed Hamed100% (1)
- 990 and 991 TransmitterDocument5 pages990 and 991 TransmitterTrần Văn ViễnNo ratings yet
- Micrometer: ProbeDocument27 pagesMicrometer: ProbeJêmš NavikNo ratings yet
- Ssm2120 2 ExpanderDocument12 pagesSsm2120 2 ExpandershirtquittersNo ratings yet
- Bently Nevada MmsDocument30 pagesBently Nevada MmsAmarnath Yadav100% (6)
- Descriptio: FeaturesDocument12 pagesDescriptio: FeaturesgdfsndhgfdvhjzdNo ratings yet
- AC30 Technical Description - Rev03Document13 pagesAC30 Technical Description - Rev03Lizardo Ramos100% (1)
- 1 Kmy10 PDFDocument5 pages1 Kmy10 PDFYilmaz Murat AhmetNo ratings yet
- Vibration MonitoringDocument8 pagesVibration MonitoringKrzysiek PodsiadłoNo ratings yet
- Series Industrial Transmitter, With Dynamic Signal SensorDocument19 pagesSeries Industrial Transmitter, With Dynamic Signal Sensorfreddy kurniawanNo ratings yet
- T2 - Proximity Transducer System OperationDocument34 pagesT2 - Proximity Transducer System OperationarijitnagNo ratings yet
- Features Description: Sbfs017A - December 1995 - Revised December 2004Document15 pagesFeatures Description: Sbfs017A - December 1995 - Revised December 2004LasithaNo ratings yet
- MC 1496Document12 pagesMC 1496Alejandro GarciaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Vibration VelocityDocument4 pagesInstruction Manual Vibration VelocityzakariaNo ratings yet
- VIF/SIF/Y/C/Deflection Implemented in A Single Chip: For NTSC Color Television SetsDocument35 pagesVIF/SIF/Y/C/Deflection Implemented in A Single Chip: For NTSC Color Television SetsLuz Rito Gomez ColungaNo ratings yet
- DPM 1As-Bl: Product DescriptionDocument4 pagesDPM 1As-Bl: Product DescriptionFane PelinNo ratings yet
- Digital Protective RelaysDocument34 pagesDigital Protective Relayssubho7297648100% (3)
- Sensors High PressureDocument5 pagesSensors High PressureGiuseppe DonatoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocument6 pagesMaintenance and TroubleshootingSilo LibraNo ratings yet
- 10.709 Gbps Laser Diode Driver Chipset: A To 1200 ADocument12 pages10.709 Gbps Laser Diode Driver Chipset: A To 1200 ABanyugeaNo ratings yet
- HS-2420RH - Fast Sample and HolDocument8 pagesHS-2420RH - Fast Sample and HolDeepa DevarajNo ratings yet
- CN0217Document6 pagesCN0217alraca1234No ratings yet
- LTC 6102Document20 pagesLTC 6102Martin CraysNo ratings yet
- MS4600 Datasheet en 201507 F266I-E-01Document7 pagesMS4600 Datasheet en 201507 F266I-E-01Eliezer DominguezNo ratings yet
- G02Document114 pagesG02Anonymous nC9gpUWPNo ratings yet
- Me170a - Lab 01 - Instrumentation Handout - Edited2015Document8 pagesMe170a - Lab 01 - Instrumentation Handout - Edited2015andman753No ratings yet
- Voltage Divider ExperimentDocument9 pagesVoltage Divider ExperimentJAINo ratings yet
- CXD3400N: 6-Channel CCD Vertical Clock DriverDocument9 pagesCXD3400N: 6-Channel CCD Vertical Clock DriverJaffer SultanNo ratings yet
- High Speed Can Bus Transceiver: DescriptionDocument9 pagesHigh Speed Can Bus Transceiver: Descriptionsweety987No ratings yet
- High Accuracy Impedance Measurements Using 12-Bit Impedance ConvertersDocument6 pagesHigh Accuracy Impedance Measurements Using 12-Bit Impedance Converterschristobal_huntaNo ratings yet
- An 23Document12 pagesAn 23ディエゴ水上No ratings yet
- Metrahit 15 SDocument12 pagesMetrahit 15 SJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Level SensorDocument20 pagesUltrasonic Level SensorEd CalheNo ratings yet
- Users Guide Digital Inductive Loop Sensors: MatrixDocument6 pagesUsers Guide Digital Inductive Loop Sensors: MatrixEliseu DiasNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi SemiconductorDocument8 pagesMitsubishi Semiconductoredgardo2004No ratings yet
- Ad8421 PDFDocument28 pagesAd8421 PDFsoft4gsmNo ratings yet
- Medical Ecg Ina326Document23 pagesMedical Ecg Ina326ronny5525No ratings yet
- Tektronix DMM4020 Digital Multimeter Datasheet 6Document12 pagesTektronix DMM4020 Digital Multimeter Datasheet 6JumbosizeNo ratings yet
- Opa381 PDFDocument19 pagesOpa381 PDFVictoria Guerrero100% (1)
- ECE250 Lab 8 MOSFET Audio PA Amp DemoDocument6 pagesECE250 Lab 8 MOSFET Audio PA Amp DemodrhammoudaNo ratings yet
- MIC94305 500ma Switch With Ripple BlockerDocument20 pagesMIC94305 500ma Switch With Ripple BlockerHaidong KimNo ratings yet
- ADZ - SMH DatasheetDocument4 pagesADZ - SMH DatasheettamanogNo ratings yet
- High Accuracy, Low I, Anycap Adjustable Low Dropout RegulatorDocument12 pagesHigh Accuracy, Low I, Anycap Adjustable Low Dropout Regulatortrillion5No ratings yet
- 0 2300 Dual Channel Monitor Datasheet 105m0340lDocument13 pages0 2300 Dual Channel Monitor Datasheet 105m0340lAdhitya ReNo ratings yet
- Single 2013 MI 3102 BT EurotestXE AngDocument2 pagesSingle 2013 MI 3102 BT EurotestXE AngYajaira RuizNo ratings yet
- Commissioning of DAVRDocument70 pagesCommissioning of DAVRPMG Bhuswal Project100% (1)
- Twa 40 DDocument4 pagesTwa 40 Dkenlavie2No ratings yet
- Saturn GeoDocument4 pagesSaturn GeoAlexandre EstevesNo ratings yet
- Curve Tracer HM 6042: SpecificationsDocument1 pageCurve Tracer HM 6042: Specificationsmkdir911No ratings yet
- NS2000 ManualDocument16 pagesNS2000 ManualABDULMALIK NASIRUNo ratings yet
- DS90LV018A 3V LVDS Single CMOS Differential Line Receiver: General Description FeaturesDocument9 pagesDS90LV018A 3V LVDS Single CMOS Differential Line Receiver: General Description FeaturesIan McNairNo ratings yet
- DPM 1as-BlDocument4 pagesDPM 1as-BlNarendra BholeNo ratings yet
- MC1458 OnDocument8 pagesMC1458 OnDanteLupuNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- AbreviationDocument2 pagesAbreviationnabil160874No ratings yet
- Customer Course CatalogDocument102 pagesCustomer Course Catalognabil160874No ratings yet
- 109T7219 - E - Network Topology PDFDocument12 pages109T7219 - E - Network Topology PDFnabil160874No ratings yet
- 109T7219 - E - Network Topology PDFDocument12 pages109T7219 - E - Network Topology PDFnabil160874100% (1)
- Med Riad: Sponsored by Control Technology Corp. ..Document8 pagesMed Riad: Sponsored by Control Technology Corp. ..nabil160874No ratings yet
- 389b3172ae B PDFDocument31 pages389b3172ae B PDFnabil160874No ratings yet
- 09 IGV SystemDocument5 pages09 IGV Systemnabil160874100% (1)
- GT Fuel Nozzle RefurbishmentDocument3 pagesGT Fuel Nozzle Refurbishmentnabil160874No ratings yet
- ABB Protection CurvesDocument60 pagesABB Protection Curvesnabil160874No ratings yet
- Spectra RMS Molded Case Circuit Breakers: GEH-702 Users ManualDocument52 pagesSpectra RMS Molded Case Circuit Breakers: GEH-702 Users Manualnabil160874100% (1)
- MCT Mkvie OmDocument4 pagesMCT Mkvie Omnabil160874No ratings yet
- MCT Mkvie OmDocument4 pagesMCT Mkvie Omnabil160874No ratings yet
- CS18214 Orbit - Q32019 - R1Document8 pagesCS18214 Orbit - Q32019 - R1nabil160874No ratings yet
- Feeder Protection and Control REF620: Application ManualDocument164 pagesFeeder Protection and Control REF620: Application Manualnabil160874No ratings yet
- Geh 6811 - 2Document30 pagesGeh 6811 - 2nabil160874No ratings yet
- How Does A MOOG Servo Valve OperatesDocument5 pagesHow Does A MOOG Servo Valve OperatesMikoto Rifky100% (1)
- Exhaust Temperature Spread 2Document5 pagesExhaust Temperature Spread 2nabil160874100% (1)
- Frame 9a5 DifinitionDocument2 pagesFrame 9a5 Difinitionnabil160874No ratings yet
- 7fatripoildualfuel 140301161154 Phpapp01Document28 pages7fatripoildualfuel 140301161154 Phpapp01Jeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 6 FAswchtDocument6 pages6 FAswchtnabil160874No ratings yet
- Functional Description AlrarDocument57 pagesFunctional Description Alrarnabil160874No ratings yet
- Start PDFDocument1 pageStart PDFnabil160874No ratings yet
- Gas Turbine and Auxiliaries AlstomDocument54 pagesGas Turbine and Auxiliaries Alstomnabil160874100% (8)
- DLN Controls Code Development 9fa+ EnhancedDocument28 pagesDLN Controls Code Development 9fa+ Enhancednabil160874100% (1)
- System 1: Bently NevadaDocument4 pagesSystem 1: Bently Nevadanabil1608740% (1)
- System 1Document4 pagesSystem 1nabil160874No ratings yet
- DLN2+ HRDWDocument21 pagesDLN2+ HRDWnabil160874100% (4)
- Rack 1 3500 Relay ReportDocument1 pageRack 1 3500 Relay Reportnabil160874No ratings yet
- System 1: Bently NevadaDocument4 pagesSystem 1: Bently Nevadanabil160874No ratings yet
- American Machinists Handbook 1000165626Document586 pagesAmerican Machinists Handbook 1000165626Juan Pedreno Bernal100% (9)
- Cource Outline MeasuremntDocument3 pagesCource Outline Measuremntmuru0105No ratings yet
- Dimensions and Tolerances For Plastic BottlesDocument16 pagesDimensions and Tolerances For Plastic Bottlesfqueiroz75No ratings yet
- Sub-Spec 022 - Vam CDS, EIS, VAM Express: Visual InspectionDocument3 pagesSub-Spec 022 - Vam CDS, EIS, VAM Express: Visual InspectionJosue FishNo ratings yet
- Sejarah MikrometerDocument32 pagesSejarah MikrometerReza BudimanNo ratings yet
- UNIT VII Angular MeasurementsDocument99 pagesUNIT VII Angular MeasurementsAkash PatilNo ratings yet
- Microscope CalibrationDocument5 pagesMicroscope CalibrationInuyashayahooNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010Document16 pagesTrial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010lilysuhanyNo ratings yet
- Geological Description of InstrumentDocument8 pagesGeological Description of InstrumentsrinivignaNo ratings yet
- ISO IEC 17025 Accreditation Cert+Scope-GCC AccreditationDocument23 pagesISO IEC 17025 Accreditation Cert+Scope-GCC AccreditationebbasinghNo ratings yet
- MD Yellow BookDocument385 pagesMD Yellow BookRockydel MontesNo ratings yet
- BS en ISO 9513-2000 (Calibration of Extensometers in UniaxialDocument19 pagesBS en ISO 9513-2000 (Calibration of Extensometers in UniaxialMohamed Farag100% (1)
- Physics Paper 1 KBSMDocument14 pagesPhysics Paper 1 KBSMyudrea88No ratings yet
- Hornady Powder Measure FeederDocument4 pagesHornady Powder Measure Feederp317No ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Methods of Physical Testing of LeatherDocument98 pagesIndian Standard: Methods of Physical Testing of LeatherAshish Dixit100% (3)
- AR860 English ManualDocument10 pagesAR860 English ManualMARIO SALVATORE SANDOVAL PAIPAYNo ratings yet
- JJ204 Workshop Technology Semester 2Document150 pagesJJ204 Workshop Technology Semester 2Ye ChonnNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 03 EXPERIMENT: Measurement of Different Parameters of A Machine Component Using The Optical ComparatorDocument7 pagesExperiment No: 03 EXPERIMENT: Measurement of Different Parameters of A Machine Component Using The Optical ComparatorAbienash Thangavel100% (1)
- DP200 en 10037833Document6 pagesDP200 en 10037833Carlos RamirezNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Screw Thread ElementDocument33 pagesMeasurement of Screw Thread ElementPK SinghNo ratings yet
- Sop Iii-100 R00Document28 pagesSop Iii-100 R00BepdjNo ratings yet
- Repair Parts Catalogue V1.4 en 12 2018Document56 pagesRepair Parts Catalogue V1.4 en 12 2018silverdollar100% (3)
- Pressure GaugesDocument36 pagesPressure GaugessenthilrsenthilNo ratings yet
- 7 Methods of Coating Thickness MeasurementDocument7 pages7 Methods of Coating Thickness MeasurementRauf AliyevNo ratings yet
- ELC311201 - Perform Mensuration and CalculationDocument31 pagesELC311201 - Perform Mensuration and CalculationGie KoNo ratings yet