Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cisco Command
Cisco Command
Uploaded by
GaLuh PurnamaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cisco Command
Cisco Command
Uploaded by
GaLuh PurnamaCopyright:
Available Formats
Command descriptions
switch>? The ? works here the same as in a router Used to get the list
of all available commands
switch>enable User mode, same as a router
switch# Privileged mode
switch#disable Leaves privileged mode
switch>exit Leaves user mode
switch#show version Displays information about software and hardware.
switch#show flash: Displays information about flash memory (will work only for
the 2900/2950 series).
switch#show mac-address-
table
Displays the current MAC address forwarding table
.
switch#show running-config Displays the current configuration in DRAM.
switch#show startup-config Displays the current configuration in NVRAM.
switch#show vlan Displays the current VLAN configuration.
switch#show interfaces Displays the interface configuration and status of line:
up/up, up/down, admin down.
switch#show interface vlan1 Displays setting of virtual interface VLAN 1, the default VLAN
on the switch.
To Reset Switch Configuration
Switch#delete flash:vlan.dat Removes the VLAN database from flash memory.
Delete filename [vlan.dat]? Press Enter
Delete flash:vlan.dat?
[confirm]
Press Enter
Switch#erase startup-config Erases the file from NVRAM.
Switch#reload Restarts the switch.
To Set Host Names
Switch#configure terminal Moves to global configuration mode
Switch(config)#hostname
Switch1
Creates a locally significant host name of the switch. This is
the same command as the router.
Switch1(config)#
To Set Passwords
Switch(config)#enable
password vinita
Sets the enable password to vinita
Switch(config)#enable
secret nikki
Sets the encrypted secret password to nikki
Switch(config)#line console
0
Enters line console mode
Switch(config-line)#login Enables password checking
Switch(config-
line)#password vinita
Sets the password to vinita
Switch(config-line)#exit Exits line console mode
Switch(config-line)#line vty
0 4
Enters line vty mode for all five virtual ports
Switch(config-line)#login Enables password checking
Switch(config-
line)#password vinita
Sets the password to vinita
Switch(config-line)#exit Exits line vty mode
Switch(config)#
To Set IP Addresses and Default Gateways
Switch(config)#interface
vlan1
Enters the virtual interface for VLAN 1, the default VLAN on
the switch
Switch(config-if)#ip address
192.168.0.10 255.255.255.0
Sets the IP address and netmask to allow for remote access
to the switch
Switch(config-if)#exit
Switch(config)#ip default-
gateway 192.168.0.5
Allows IP information an exit past the local network
To Set Interface Descriptions
Switch(config)#interface
fastethernet 0/1
Enters interface configuration mode
Switch(config-
if)#description Finance
VLAN
Adds a description of the interface
To Set Duplex Operation
Switch(config)#interface
fastethernet 0/1
Moves to interface configuration mode
Switch(config-if)#duplex
full
Forces full-duplex operation
Switch(config-if)#duplex
auto
Enables auto-duplex config
Switch(config-if)#duplex
half
Forces half-duplex operation
To Set Operation Speed
Switch(config)#interface
fastethernet 0/1
Switch(config-if)#speed 10 Forces 10-Mbps operation
Switch(config-if)#speed 100 Forces 100-Mbps operation
Switch(config-if)#speed
auto
Enables autospeed configuration
MAC Address Table
switch#show mac address-
table
Displays current MAC address forwarding table
switch#clear mac address-
table
Deletes all entries from current MAC address forwarding
table
switch#clear mac address-
table dynamic
Deletes only dynamic entries from table
ROUTERS
Some commands in the Cisco router configuration are just irreplaceable. The show
commands are the most widely used in Cisco routers. Here is a list of the 10 mostly used
of these show commands.
1. show running-config
This command is your true best friend. It shows the complete configuration that is
running currently.
2. show startup-config
This command shows the configuration that is saved on the NVRAM. It is helpful in
knowing the configuration that will be applied the next time the routers is reloaded.
3. show interface
This command shows status and statistics regarding interfaces. This command is almost
always needed in troubleshooting routing and link issues.
4. show ip route
This command shows the routing table. This table helps you in finding out the next hop
for each and every routable packet. It is the first indicator to point a problem in routing.
5. show ip protocols
This command shows the routing protocols used in the router and what networks are
these protocols advertising. It also shows the sources of routing updates received at
this router.
6. show access-list
This command shows the contents of each access-list. but not where each access-list is
applied.
7. show ip interface
This command displays information about IP protocol and the interface. Very quick way
to see the immediate status of your interfaces
8. show cdp neighbor detail
This command displays detailed information about the neighboring devices like IP
addresses, platforms, and host names. can be used in finding out how devices are
connected to each other when you have no clear drawn network map.
9. show version
This command shows detailed information about the IOS. It shows the file name of the
IOS along with the version of the IOS and value of the configuration register.
10. show flash or show slot0:
This command is used to view the contents of the flash and the size of the IOS file(s)
and the size of the flash and how much of it is free. It is necessary in upgrading or
installing the IOS file.
You might also like
- 18F CST8108 010 Network Programming Basics Algonquin College PDFDocument15 pages18F CST8108 010 Network Programming Basics Algonquin College PDFhenNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security Chapter 2 PowerpointDocument14 pagesCCNA Security Chapter 2 PowerpointEric NapholzNo ratings yet
- Point To Point Protocol Cisco Ccna Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePoint To Point Protocol Cisco Ccna Cheat SheetWalter ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Tes MikrotikDocument6 pagesTes MikrotikRian Wakhid50% (2)
- Basic Switch ConfigDocument11 pagesBasic Switch Configm2incyberNo ratings yet
- Cisco Switch ConfigurationDocument3 pagesCisco Switch ConfigurationKalp SengarNo ratings yet
- Cisco Commands - 2016-05-19Document26 pagesCisco Commands - 2016-05-19agaver2No ratings yet
- Basic Commands List 1Document5 pagesBasic Commands List 1John TrovoltaNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Basic Cisco Troubleshooting PDFDocument1 pageBasic Cisco Troubleshooting PDFshareefgs55600% (1)
- CCNA R&S Practical EbookDocument78 pagesCCNA R&S Practical EbookParvinderSinghNo ratings yet
- Boson Ccna CourseDocument33 pagesBoson Ccna Courseedara1234No ratings yet
- CCNA 200 301 June 2023 v1 2Document320 pagesCCNA 200 301 June 2023 v1 2kao kenNo ratings yet
- CCNA CheatSheet PDFDocument19 pagesCCNA CheatSheet PDFpranali50% (2)
- © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument37 pages© 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedmargubupolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Using The Command-Line InterfaceDocument22 pagesChapter 4. Using The Command-Line InterfacePoojitha NagarajaNo ratings yet
- 200 301 VCE Dumps (336 349)Document6 pages200 301 VCE Dumps (336 349)Edoardo NalinNo ratings yet
- Use Python CLASS and FUNCTION To Get and Process Data From RoutersDocument12 pagesUse Python CLASS and FUNCTION To Get and Process Data From RoutersCC DreamerNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab6-1 FHRP HSRP VRRP STUDENTDocument61 pagesCCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab6-1 FHRP HSRP VRRP STUDENTjerblic-1No ratings yet
- Ccna Lab UpdatedDocument144 pagesCcna Lab UpdatedSatya VasuNo ratings yet
- CCNA Routing Protocols OSPF Skills AssessmentDocument10 pagesCCNA Routing Protocols OSPF Skills AssessmentAntonio Adkins75% (4)
- Describing Routing Between Vlans: Implementing Inter-Vlan RoutingDocument42 pagesDescribing Routing Between Vlans: Implementing Inter-Vlan RoutingArun JoyNo ratings yet
- Lab 2.5.1 Basic Switching Configurationv3Document15 pagesLab 2.5.1 Basic Switching Configurationv3reza3691No ratings yet
- Ccna NotesDocument215 pagesCcna NotesPrasanth Jayasviji JsNo ratings yet
- Hardening ProCurve Switches White PaperDocument10 pagesHardening ProCurve Switches White PaperBlertin Haruni100% (2)
- Configuracion Switch Zyxel PDFDocument384 pagesConfiguracion Switch Zyxel PDFJulio Perez Ferrufino100% (1)
- Cisco Ios Basic SkillsDocument10 pagesCisco Ios Basic SkillsSasa MikiruniNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial: Cisco Inter-Network Operating SystemDocument11 pagesCisco Router Configuration Tutorial: Cisco Inter-Network Operating Systemheruye mulugetaNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security Final 100%Document14 pagesCCNA Security Final 100%Akbal Larios75% (8)
- CN Lab 3Document7 pagesCN Lab 3Esha JavaidNo ratings yet
- CCNP Encor - Udemy - Device AccessDocument88 pagesCCNP Encor - Udemy - Device AccessAHOUALAKOUNNo ratings yet
- TSHOOT 15min GuideDocument13 pagesTSHOOT 15min GuidejuliosistemasNo ratings yet
- CCNAv2 Chapter 05Document18 pagesCCNAv2 Chapter 05Linux HamzaNo ratings yet
- Basic Switch Part1Document6 pagesBasic Switch Part1BasilNo ratings yet
- CCNP ENARSI Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services Exam 300-410Document123 pagesCCNP ENARSI Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services Exam 300-410Alexey Fernández SuárezNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 - Configuring A RouterDocument26 pagesCh.3 - Configuring A RouterArad RezaNo ratings yet
- Mpls InertviewDocument22 pagesMpls InertviewAbu FadilahNo ratings yet
- CCNA Study Guide - Vir Lab 4 Lab MappingDocument4 pagesCCNA Study Guide - Vir Lab 4 Lab Mappingparthasn83No ratings yet
- Ansible Hands-OnDocument35 pagesAnsible Hands-Onarm_max78No ratings yet
- 2530 Switch PresentationDocument33 pages2530 Switch PresentationNgoc The NguyenNo ratings yet
- Juniper Cheat SheetDocument12 pagesJuniper Cheat SheetmikeNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial PDFDocument8 pagesCisco Router Configuration Tutorial PDFHamami InkaZoNo ratings yet
- Cisco RefrenceDocument11 pagesCisco RefrenceElizabeth HaunNo ratings yet
- Basic Cisco Router ConfigurationDocument6 pagesBasic Cisco Router ConfigurationKhan JamalNo ratings yet
- Cisco HSRP TroubleshootingDocument52 pagesCisco HSRP TroubleshootingSivakonalarao MandalapuNo ratings yet
- Ccna R&SDocument77 pagesCcna R&SarunNo ratings yet
- Shortnote LabDocument22 pagesShortnote LabSamiNo ratings yet
- CCNA Basic Switch Configuration Commands SheetDocument3 pagesCCNA Basic Switch Configuration Commands Sheetwnelson7No ratings yet
- Cisko Switch KomandeDocument6 pagesCisko Switch Komandegoran66bNo ratings yet
- Comandos Cisco SwitchDocument4 pagesComandos Cisco SwitchAlejandro GómezNo ratings yet
- Cisco Switch CommandsDocument4 pagesCisco Switch CommandsVikaas VermaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Quick ReferenceDocument10 pagesCisco Quick Referencegotek145No ratings yet
- CCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingDocument8 pagesCCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingHeribertus BudhihartoNo ratings yet
- Configuring Users and Passwords For The CCENT Certification ExamDocument12 pagesConfiguring Users and Passwords For The CCENT Certification ExamSarthakGuptaNo ratings yet
- Ccna Certifications BasiDocument4 pagesCcna Certifications BasiAnupam MishraNo ratings yet
- TCP Refresher - Part 1Document54 pagesTCP Refresher - Part 1Network JunkieNo ratings yet
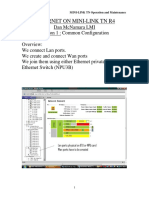
- Ethernet On Mini LinkDocument12 pagesEthernet On Mini LinkmohamedNo ratings yet
- Networking Appc, Appn, and HPR: Ibm I 7.2Document132 pagesNetworking Appc, Appn, and HPR: Ibm I 7.2testtest testNo ratings yet
- Server Linux NotesDocument35 pagesServer Linux NotesChand Basha100% (2)
- DP c5005df Error Code ListDocument46 pagesDP c5005df Error Code ListErik Bordenkircher77% (13)
- EVPN VXLAN Design GuideDocument45 pagesEVPN VXLAN Design Guidedeep kNo ratings yet
- OmniSwitch AOS Release 6 CLI Reference GuideDocument4,126 pagesOmniSwitch AOS Release 6 CLI Reference GuideEric GuttNo ratings yet
- LAN Switching and Bridges: Relates To Lab 6Document39 pagesLAN Switching and Bridges: Relates To Lab 6SujathaNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Lab2-2 EIGRP-Stub-Routing StudentDocument17 pagesCCNPv7 ROUTE Lab2-2 EIGRP-Stub-Routing StudentCarlos Alberto Pedraza CruzNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions 100-105: Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1 v3.0)Document18 pagesExam Questions 100-105: Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1 v3.0)semaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Design of IMAR Using Proxy Servers in Wireless NetworkDocument5 pagesDesign of IMAR Using Proxy Servers in Wireless NetworkNehru Veerabatheran100% (1)
- 7.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring A Point-To-Point GRE VPN TunnelDocument6 pages7.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring A Point-To-Point GRE VPN TunnelBlyiremk83% (6)
- TS 7.1.109-Rnloc 1.0Document109 pagesTS 7.1.109-Rnloc 1.0bouncetome2008No ratings yet
- Huawei S6720-LI Series Switches Product BrochureDocument9 pagesHuawei S6720-LI Series Switches Product BrochureRochdi BouzaienNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2MohammadNaseerBatlaNo ratings yet
- Mediant 500 MSBR DatasheetDocument2 pagesMediant 500 MSBR DatasheetChato PerezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 IPv4 AddressingDocument6 pagesLecture 5 IPv4 Addressingchuchu mangeusNo ratings yet
- A10 AX Confguration GuideDocument960 pagesA10 AX Confguration GuideRenataEMJNo ratings yet
- Configure Nat On MikrotikDocument4 pagesConfigure Nat On Mikrotiknazm basmNo ratings yet
- Manual IP Firewall NAT - MikroTik WikiDocument8 pagesManual IP Firewall NAT - MikroTik Wikikoulis123No ratings yet
- Maseno University Department of Information Technology CDIT 406: Web AuthoringDocument7 pagesMaseno University Department of Information Technology CDIT 406: Web AuthoringMayur Hitesh RabadiaNo ratings yet
- JNCIE SP v1.1 Technology Focused Workbook 2018Document28 pagesJNCIE SP v1.1 Technology Focused Workbook 2018Abhishek gargNo ratings yet
- Ethernet NumbersDocument13 pagesEthernet NumbersjohnbohnNo ratings yet
- Cisco Networking All-in-One For Dummies Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesCisco Networking All-in-One For Dummies Cheat SheetJ ChangNo ratings yet
- Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 6Document60 pagesCisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 6El MenyoNo ratings yet
- NSE4 Dumps Fortinet Network Security Expert 4 Written ExamDocument20 pagesNSE4 Dumps Fortinet Network Security Expert 4 Written Exammansoorali_af100% (1)
- Fortios v5.2.11 Log ReferenceDocument103 pagesFortios v5.2.11 Log ReferenceAndrew WebbNo ratings yet
- VPC CreateDocument376 pagesVPC CreateSorabh MohindruNo ratings yet