Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.3.2 - Report Annual Plan - Form 5
1.3.2 - Report Annual Plan - Form 5
Uploaded by
Mimie SulaimanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physics Workbook AnswersDocument58 pagesPhysics Workbook Answersbright hero88% (16)
- Force Diagrams & Statics: Free Particle Model Worksheet 4Document7 pagesForce Diagrams & Statics: Free Particle Model Worksheet 4api-292718088No ratings yet
- Eastern Philosophy of EducationDocument61 pagesEastern Philosophy of EducationMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Expt-2: Bouncing Ball Experiment: ObjectiveDocument9 pagesExpt-2: Bouncing Ball Experiment: ObjectiveNilima Ayoub DiptyNo ratings yet
- M Schemes 04Document3 pagesM Schemes 04Pathmanathan Nadeson0% (2)
- Sukatan FizikDocument26 pagesSukatan FizikAhmad MohsinNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5Document17 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5Salmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Physics Form 5 2013Document17 pagesYearly Plan Physics Form 5 2013qq2350% (1)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiDocument16 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 Smktpihelmi_tarmiziNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work f5Document22 pagesScheme of Work f5Asma AliasNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiDocument16 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiHelmi TarmiziNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work f5Document21 pagesScheme of Work f5Eunice TangNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Revision ChecklistDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Revision ChecklistShafkat Sakeebur Rahman100% (2)
- Physics Form 5: Yearly Plan 2015 Notes and VocabularyDocument14 pagesPhysics Form 5: Yearly Plan 2015 Notes and VocabularySue Suraya NazaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 Year 2016: Learning Area: WavesDocument19 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 Year 2016: Learning Area: WavesRed KiteNo ratings yet
- SMK Iskandar Shah Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015: Learning Area: 1. WavesDocument15 pagesSMK Iskandar Shah Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015: Learning Area: 1. WavesTee Ting QINo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan - Physics Form 5: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. VDocument16 pagesYearly Plan - Physics Form 5: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. VSalmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- 3 & 4 Marks Physics IMPDocument69 pages3 & 4 Marks Physics IMPNahush sarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Maths Revison List Year 10 All Sets Dec 15Document10 pagesMaths Revison List Year 10 All Sets Dec 15ollie deanNo ratings yet
- Emfw NotesDocument2 pagesEmfw NotesNaushad SheikNo ratings yet
- RPT Physics Form 5Document12 pagesRPT Physics Form 5SazlinAinaNo ratings yet
- Aman Dhattarwal's Physics IMP Questions (Class 12)Document4 pagesAman Dhattarwal's Physics IMP Questions (Class 12)Bhakta Kishor80% (10)
- Xii-Cbsephysicsimportant Derivations Question - Chapter WiseDocument4 pagesXii-Cbsephysicsimportant Derivations Question - Chapter WiseSharulathaNo ratings yet
- SMK Jalan Tiga Bandar Baru Bangi Physics Form 5 Yearly Lesson Plan 2009 Week Learning Area Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities Notes and VocabularyDocument25 pagesSMK Jalan Tiga Bandar Baru Bangi Physics Form 5 Yearly Lesson Plan 2009 Week Learning Area Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities Notes and VocabularyGerardo Lozano GuetaNo ratings yet
- Most Expected PU - II Physics Questions For 2020-2021Document16 pagesMost Expected PU - II Physics Questions For 2020-2021Navaneeth MsNo ratings yet
- Important Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Aman Dhattarwal S Physics IMP Questions Class 12Document5 pagesAman Dhattarwal S Physics IMP Questions Class 12Krishan Lohan100% (1)
- Applied Physics 2 Practical Viva Voce QDocument16 pagesApplied Physics 2 Practical Viva Voce QAnish MuraliNo ratings yet
- Derivations Class 12Document7 pagesDerivations Class 1228092008pragyana2382No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument180 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesGurusreenuNo ratings yet
- Lessonsections 2Document12 pagesLessonsections 2Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Physics Essential Unit 9 (E09)Document5 pagesPhysics Essential Unit 9 (E09)Jaxon FlameNo ratings yet
- 12thQuestionBank (KSU)Document9 pages12thQuestionBank (KSU)sohailmushtaq1001No ratings yet
- Physical Sciences GR 10 Assessent Frame June 2024Document5 pagesPhysical Sciences GR 10 Assessent Frame June 2024catlynnferreiraNo ratings yet
- Emtl r15 II II Jntu A SyllabusDocument1 pageEmtl r15 II II Jntu A SyllabussubramanyamNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics EMDocument8 pages12 Physics EMAniketNo ratings yet
- PHY 101 PowerpointDocument233 pagesPHY 101 PowerpointSyed ShahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Sections 1Document13 pagesLesson Sections 1Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Yearly Fizik 2013 Form 5Document18 pagesYearly Fizik 2013 Form 5Fazillah AziziNo ratings yet
- PH 110 Course Outline 2019-2020 Academic YearDocument4 pagesPH 110 Course Outline 2019-2020 Academic Yearmusamugabazi68No ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument26 pagesImportant QuestionsAyush TomarNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electricity 1 Whole Unit Overview: Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities ResourcesDocument2 pagesPhysics: Electricity 1 Whole Unit Overview: Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities ResourceszahraNo ratings yet
- BEEE Question Bank Unit 1,2Document13 pagesBEEE Question Bank Unit 1,2Upender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- Xii Derivation List-2023-24 2Document3 pagesXii Derivation List-2023-24 2prachurjyapadhiNo ratings yet
- Derivation of All ChapterDocument6 pagesDerivation of All Chapterplutouec86% (14)
- 12th Physics Worksheet (ch3 To ch7)Document3 pages12th Physics Worksheet (ch3 To ch7)lovecatsaninalsNo ratings yet
- H Physics XIIDocument33 pagesH Physics XIIMuzammil AfsarNo ratings yet
- Sfra For Condition Monitoring of Power TransformerDocument3 pagesSfra For Condition Monitoring of Power TransformerSarojakanti SahooNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2012Document7 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2012Cikgu EnaNo ratings yet
- Physics Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesPhysics Important QuestionsLaxman KumawatNo ratings yet
- Cbse Paper Leak PDFDocument7 pagesCbse Paper Leak PDFRohan AroraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Electric CurrentDocument14 pagesModule 2 Electric Currentjovy dulay100% (2)
- Planner For Preparatory Exam.Document3 pagesPlanner For Preparatory Exam.RaonarNo ratings yet
- Unit C: Electromagnetic EnergyDocument2 pagesUnit C: Electromagnetic EnergyticoninxNo ratings yet
- Important Questions PhysicsDocument12 pagesImportant Questions PhysicsNaziaParveenNo ratings yet
- 12 TH Physics Cbse SyllabusDocument7 pages12 TH Physics Cbse Syllabussandipsujata100% (1)
- 2014 Physics XII Cbse Sample PaperDocument37 pages2014 Physics XII Cbse Sample PaperVijaykumar Shukla100% (1)
- Phy 1 PG 2Document1 pagePhy 1 PG 2api-20001111No ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum in Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pagesEnergy and Momentum in Electromagnetic WavesEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics HWDocument33 pagesClass Xii Physics HWDhruv PandeyNo ratings yet
- Charles Steinmetz - Elementary Lectures On Electric Discharges, Waves and ImpulsesDocument172 pagesCharles Steinmetz - Elementary Lectures On Electric Discharges, Waves and Impulsesdawsecs100% (1)
- Understanding Phase As A Key Concept in Physics and Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Phase As A Key Concept in Physics and Electrical EngineeringJavier PNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsFrom EverandPrinciples of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Principles of Electrical Transmission Lines in Power and Communication: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandPrinciples of Electrical Transmission Lines in Power and Communication: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Generation and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandGeneration and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Luminescent Properties of Rare Earth (Er, Yb) Doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet Thin Films and Bulk Samples Synthesised by An Aqueous Sol-Gel TechniqueDocument9 pagesLuminescent Properties of Rare Earth (Er, Yb) Doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet Thin Films and Bulk Samples Synthesised by An Aqueous Sol-Gel TechniqueMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Isi Padu PepejalDocument1 pageIsi Padu PepejalMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 Philosophy and BranchesDocument30 pagesSlide 1 Philosophy and BranchesMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Islamic Philosophy of AduDocument33 pagesIslamic Philosophy of AduMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Design GuidelinesDocument38 pagesLaboratory Design GuidelinesMark MoldezNo ratings yet
- Rotation (Grotto)Document7 pagesRotation (Grotto)Chandru ANo ratings yet
- 04 Laws of Motion Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFDocument7 pages04 Laws of Motion Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFAryan DeNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Circular Motion Abd Gravitation MCQDocument14 pagesTopic 6 Circular Motion Abd Gravitation MCQAmit BarateNo ratings yet
- Tractive Effort For Propulsion of TrainDocument4 pagesTractive Effort For Propulsion of TrainSandip MondalNo ratings yet
- Bookacceleration Probs PDFDocument6 pagesBookacceleration Probs PDFMukul KumawatNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics - Gravitation - NotesDocument5 pages11 Physics - Gravitation - Notesrahul pingaleNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Resultant ForceDocument30 pages1.1 Resultant ForceLim Yan JoeNo ratings yet
- Physics Cutnell 9th Edition Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPhysics Cutnell 9th Edition Solutions Manualgraphitehamous.22x7100% (54)
- Physics MidtermDocument14 pagesPhysics MidtermPrecious015100% (1)
- CON3301 - PPT 1 SI Unit and Force As Vector (2017) - Basic PhysicsDocument56 pagesCON3301 - PPT 1 SI Unit and Force As Vector (2017) - Basic PhysicsJoseph ChanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstituteDocument5 pagesElectromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstitutecisnarFNo ratings yet
- Definition Sem 1 PSTDocument8 pagesDefinition Sem 1 PSTNurul ShaiedahNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument1 pageNewton's First LawSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Exam Study Guide: Demond CarterDocument5 pagesPhysics Final Exam Study Guide: Demond CarterDemond CarterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Motion - Question For ThoughtDocument2 pagesChapter 2 - Motion - Question For Thoughtsuhughes100% (3)
- 1 Kane Equations - Example 1Document8 pages1 Kane Equations - Example 1Khisbullah HudhaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Homework - RautDocument7 pagesKinematics Homework - RautEull RautNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion MCQs Sheet 1Document6 pagesLaws of Motion MCQs Sheet 1eka123100% (1)
- Test-4 1Document6 pagesTest-4 1Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PPT - RadioactivityDocument23 pagesChemistry PPT - RadioactivityRishita SinghNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 - KinematicsDocument81 pagesCH - 4 - KinematicsVISHESH SEHRAWATNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line WorksheetDocument2 pagesMotion in A Straight Line WorksheetWoah NitinNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration Card Sort Task CardDocument4 pagesSpeed, Velocity, and Acceleration Card Sort Task CardDaryl DunneNo ratings yet
- 5 Newtons LawsDocument29 pages5 Newtons LawsMehwish IsrarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 HSC Physics NotesDocument8 pagesModule 5 HSC Physics NotesLiam KorngoldNo ratings yet
- Course Outline in General Physics 1Document5 pagesCourse Outline in General Physics 1Jin SenpaiNo ratings yet
1.3.2 - Report Annual Plan - Form 5
1.3.2 - Report Annual Plan - Form 5
Uploaded by
Mimie SulaimanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.3.2 - Report Annual Plan - Form 5
1.3.2 - Report Annual Plan - Form 5
Uploaded by
Mimie SulaimanCopyright:
Available Formats
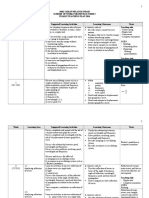
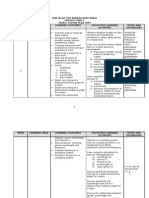
Table 2.
4 Annual Plans For Physics Form 5
WEEK/
DATE
CHAPTER
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
A student is able to:
NOTES
1
(2-3/1/14)
CHAPTER 1:
WAVE
Understanding wave
Describe what is meant by wave motion.
Recognize that waves transfer energy
without transferring matter
Compare transverse and longitudinal
waves.
State what is meant by a wave front.
State the direction of propagation of waves
in relation to wave fronts.
Carry out activities using a ripple
tank and slinky spring to
demonstrate:
a) That waves transfer energy
without transferring matter.
b) transverse and longitudinal
waves
c) wave fronts
d) the direction of propagation of
waves in relation to wave fronts
2
(6-
10/1/14)
Define
I. Amplitude
II. Period
III. Frequency
IV. Wavelength
V. Wave speed
Sketch and interpret a displacement time
graph for a wave.
Sketch and interpret a displacement time
graph for a wave.
Clarify the relationship between speed,
wavelength, and frequency.
Solve the problems involving speed,
wavelength, and frequency.
Describe damping in a oscillating system.
Describe a resonance in a oscillating
system.
3
(13-
17/1/14)
Analysing reflection of
waves
Describe reflection of waves in term of
angle of incident, angle of reflection,
wavelength, frequency, speed and direction
of propagation
Draw a diagram to show reflection of
waves.
14/1-
Maulidur Rasul
Carry out activities to observe
reflection of:
a) plane waves in a ripple tank,
b) light,
c) Sound waves.
Analysing refraction of
waves
Describe refraction of waves in terms of
the angle of incidence, angle of refraction,
wavelength, frequency, speed and direction
of propagation.
Draw a diagram to show refraction of
waves.
Carry out activities to observe
refraction of :
a) plane water waves in a ripple
tank,
b) light waves,
c) Sound waves.
4
(20-
24/1/14)
Analysis diffraction of
waves
Describe diffraction of waves in term of
wavelength, frequency, speed, direction of
propagation, and shape of the waves.
Draw a diagram to show diffraction of
waves.
25/1-
Alternate school for 3/2
Carry out activities to observe
refraction of :
a) water waves in a ripple tank,
b) light waves,
c) sound wave
5
(27/1/14-
29/1/14)
Analysing interference of
waves
State the principle of superposition.
Explain the interference of waves.
Draw interference patterns.
Interpret interference patterns.
Solve problems involving
30/1-4/2/14
Chinese New Year
Carry out activities to observe
interference patterns of:
a) water waves in a ripple tank,
b) light waves,
c) sound waves
6
(5-7/2/14)
Analysing sound wave
Describe sound waves.
Explain how the loudness relates to
amplitude.
Explain how the pitch relates to frequency.
Describe applications of reflection of
sound waves.
Calculate distances using the reflection of
sound waves.
7
(10-
15/2/14)
Analysing electromagnetic
waves
Describe the electromagnetic spectrum.
State that visible light is a part of
electromagnetic spectrum.
List sources of electromagnetic waves.
Describe the properties of electromagnetic
waves.
Describe applications of electromagnetic
15/2 Alternate school for 4/2
waves.
Describe the detrimental effects of
excessive exposure to certain components
of the electromagnetic spectrum.
8
(17-
21/2/14)
CHAPTER 2:
ELECTRICITY
Analysing electric fields
and charge flow
State the relationship between electron
flow and electric current.
Define electric current.
Describe an electric field.
Sketch electric field lines showing the
direction of the field.
Describe the effect of an electric field on a
charge.
Solve problem involving electric charge
and current
February Test
Recall the activity carried out
using a Van de Graff generator to
show the relationship between
electric charge and current flow.
I current
Q charge
T - time
Carry out activities/view
computer simulations to study
electric field lines for different
arrangements of charges.
9
(24/2/14-
28/2/14)
Analysing the relationship
between electric current and
potential difference
Define potential difference.
Plan and conduct an experiment to find the
relationship between current and potential
difference.
Describe the relationship between current
and potential difference.
State Ohms law.
*submission of test paper
Plan and conduct an experiment
to find the relationship between
current and potential difference
for an ohmic conductor.
PEKA 1:
Define resistance.
Explain factors that affect resistance.
Solve problem involving potential
difference, current and resistance.
Describe superconductors
Ohms Law
Conduct experiments to study and
discuss factors that affect
resistance, i.e. the type of
material, cross-sectional area,
length and temperature.
PEKA 2:
Factors affecting the resistance
10
(3-7/3/14)
Analysing series and
parallel circuits
Identify series and parallel circuits.
Compare the current and potential
difference of series circuits and parallel
circuits.
Determine the effective resistance of
resistors connected in series.
Determine the effective resistance of
resistors connected in parallel.
Solve problems involving current, potential
difference and resistance in series circuits,
parallel circuits and their combinations
Carry out activities to identify
series and parallel circuits.
Carry out activities to study the
current, I and potential difference,
V in series and parallel circuits
using ammeters and voltmeters to
show the value of I and V.
11
(10-
14/3/14)
Analysing electromotive
force and internal resistance
Define electromotive force (e.m.f).
Compare e.m.f and potential difference.
Explain internal resistance.
Determine e.m.f and internal resistance.
*test 1 start/ PPT draft
Carry out activities to distinguish
between e.m.f and potential
difference.
Solve problem involving e.m.f and internal
resistance.
Carry out an activity to study
internal resistance.
Carry out an activity to determine
e.m.f and internal resistance.
Analysing electrical energy
and power
Define electrical energy.
Define electric power.
Solve problems involving electrical energy
and power.
Compare power rating and energy
consumption of various electrical
appliances.
Compare various electrical appliances in
terms of efficient.
Describe ways of increasing energy
efficiency.
Carry out activities to compare
household electrical appliances
that perform the same function
such as a tungsten-filament light
bulb in terms of efficient use of
energy.
12
(17-
21/3/14)
CHAPTER 3:
ELECTRO-
MAGNETISM
Analysing the magnetic
effect of current carrying
conductor
State what an electromagnet is.
Draw the magnetic field pattern due to a
current in a :
i. Straight wire
ii. Coil
iii. Solenoid
Plan conducts experiment to study factors
that affect the strength to the magnetic
Carry out activities to study the
pattern and direction of the
magnetic field due to the current
in a
i. Straight wire
ii. Coil
iii. Solenoid
Plan conduct experiment to study
field of an electromagnet.
factors that effect the strength to
the magnetic field of an
electromagnet example:
a) The number of turns on the coil
b) The size of current carried by
the coil
c) The use of a soft iron core
22 -
30/3/14
MID-TERM BREAK 1
13
(1-5/4/14)
Understanding the force
and a current-carrying
conductor in a magnetic
field
Describe what happen to a current-carrying
conductor in a magnetic field.
Draw a pattern of the combined magnetic
field due to current carrying conductor in
a magnetic field.
Describe how a current carrying
conductor in a magnetic field experiences a
force.
Explain the factors that affect the
magnitude of the force on a current-
carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
Describe how a current carrying coil in a
magnetic field experiences a turning force.
Describe how a direct current motor works.
State factors that affect the speed of
rotation of an electric motor.
*Semak PPT
5/4- Alternate school for 31/7
Carry out activities to show the
force on a current carrying
conductor in a magnetic field
including the effect of reversing
the direction of the current and a
magnetic field.
Carry out experiments to study
factors that affect the force on a
current-carrying conductor in a
magnetic field and discuss how
the effect the force on a current-
carrying conductor in a magnetic
field.
Carry out activities to observe the
turning effect of a current
carrying coil in a magnetic field.
14
(7-
11/4/14)
Analysing electromagnetic
induction
Describe electromagnetic induction.
Indicate the direction of the induced
current in a :
i. Straight wire
Ii. Solenoid
Explain factors that affect the magnitude
of the current.
Describe applications of electromagnetic
induction.
Compare direct current and alternating
current
Carry out activities to observe
electromagnetic induction in a :
a) straight wire
b) solenoid
Carry out activities to study
factors that affect the magnitude
of the induced current and discuss
how they affect the magnitude of
the induced current
15
(14-
18/4/14)
Analysing transformer
Describe the structure and the operating
principle of a simple transformer.
Compare and contrast a step up and step
down transformer.
State that
for an ideal transformer.
State that
for an ideal
transformer.
Describe the energy losses in a
Carry out activities to gain an
understanding of the structure
and the operating principle of a
simple step up and a step down
transformer.
Carry out the activities to study
the relationship between number
of turns of the primary coil (
),
transformer.
Describe ways to improve the efficiency
of a transformer.
Solve the problems involving transformer.
number of turns of the secondary
coil (
), primary voltage (
and secondary voltage
.
16
(21-
25/4/14)
Understanding the
generation and transmission
of electricity
List sources of energy used to generate
electricity.
Describe the various ways of generating
electricity.
Describe the transmission of electricity.
Describe the energy loss in electricity
transmission cables and deduce the
advantage of high voltage transmission.
State the importance of the National Grid
Network.
Solve problems involving electricity
transmission.
Explain the importance of renewable
energy.
Explain the effects on the environment
caused by the use of various sources to
generate electricity.
17
(28/4/14-
2/5/14)
PPT Revision Week *submit PPT for RISO
1/5-
Labor Day
18
(5-
10/5/14)
MID-YEAR EXAM 10/5-
Alternate school 1/8
19
(12-
16/5/14)
MID-YEAR EXAM 13/5-
Wesak Day
20&21
(19-
26/5/14)
CHAPTER 9:
ELECTRONICS
Understanding the uses of
the Cathode Ray
Oscilloscope (C.R.O)
Explain thermionic emission.
Describe the properties of cathode rays.
Describe the working principle of the
cathode ray oscilloscope.
Measure potential difference using the
C.R.O.
Measure short time intervals using the
C.R.O.
Display wave forms using the C.R.O.
Solve problems based on the C.R.O.
display
Carry out activities to study the
properties of cathode rays using
apparatus such as the Maltese
Cross tube
Understanding
semiconductor diodes
Describe semiconductors in terms of
resistance and free electrons.
Describe n-type and p-type
semiconductors.
Describe semiconductor diodes.
Describe the function of diodes.
Describe the use of diodes as rectifiers.
Describe the use of capacitor to smooth
out output current and output voltage in a
Carry out activities to observe
current flow through a
semiconductor diode ( p-n
junction) in forward bias or
reverse bias.
rectifier circuit.
28/5-
15/6/14
MID-YEAR BREAK
22
(16-
20/6/14)
PPT discussion
23
(23-
27/6/14)
Understanding transistors
Describe a transistor in terms of its
terminals.
Describe how a transistor can be used as a
current amplifier.
Describe how a transistor can be used as
an automatic switch.
Carry out activities to show a
transistor as a current amplifier.
24
(30/6/14-
4/7/14)
Analysing logic gates
State that logic gates are switching circuits
in computers and other electronic systems.
List and draw symbols for the following
logic gates :
i) AND,
ii) OR,
iii) NOT,
iv) NAND,
v) NOR
State the action of the following logic
gates in a truth table :
Carry out activities to study the
action of the following logic gates
:
a) AND,
b) OR,
c) NOT,
d) NAND,
e) NOR.
i) AND,
ii) OR,
iii) NOT,
iv) NAND,
v) NOR.
Build truth tables for logic gates in
combination for a maximum of 2 inputs.
Describe applications of logic gate control
systems
25
(7-
11/7/14)
CHAPTER 10:
RADIO-
ACTIVITY
Understanding the nucleus
of an atom
Describe the composition of the nucleus of
an atom in terms of protons and neutrons.
Define proton number (Z) and nucleon
number (A).
Explain the term nuclide.
Use the nuclide notation
Define the term isotope.
26
(14-
18/7/14)
Analysing radioactive
decay
State what radioactivity is
Name common detectors for radioactive
emissions.
Compare the 3 kinds of radioactive
emissions in term of their nature.
Explain what radioactive decay is.
Use equations to represent changes in the
composition of the nucleus when particles
are emitted.
14/7- Test 2 start
15/7- Nuzul Quran leave
The structure of detectors are not
required
Explain half-life
determine half-life from a decay curve
solve problems involving half-life
Understanding the uses of
radioisotopes
Define radioisotopes.
Name examples of radioisotopes.
Describe applications of radioisotopes
27
(21-
25/7/14)
Understanding nuclear
energy
Define atomic mass unit (a.m.u).
Describe nuclear fission.
Give examples of nuclear fission.
Describe chain reactions.
Describe nuclear fusion.
Give examples of nuclear fusion.
Relate the release of energy in a nuclear
reaction with a change of mass according
to the equation
.
Describe the generation of electricity from
nuclear fission.
Justify the use of nuclear fission in the
generation of electricity.
Solve problems involving nuclear energy.
28/7-
3/8/14
HARI RAYA AIDILFITRI LEAVE
28
(4-8/8/14)
Releasing the importance of
proper management of
Describe the negative effects of
radioactive substances.
radioactive substances
Describe safety precautions needed in the
handling of radioactive substances.
Describe the management of radioactive waste
29
(11-
16/8/14)
REVISION FOR TRIAL SPM
16/8- Alternate school 21/10
30
(18-
22/8/14)
TRIAL SPM .
31
(25-
29/8/14)
TRIAL SPM 31/8-
Independents Day
32
(1-5/9/14)
DISCUSSION AND CORRECTION OF
TRIAL SPM
33
(8-
12/9/14)
DISCUSSION AND CORRECTION OF
TRIAL SPM
13-
21/9/14
MID-TERM BREAK 2
34
(22-
27/9/14)
REVISION
27/9- Alternate School 24/10
35
(29/9/14-
3/10/14)
REVISION
5/10- Hari Aidiladha Leave
36
(6-
10/10/14)
REVISION
37
(13/10/14
-
17/10/14)
REVISION
38
(20/10/14
-
24/10/14)
REVISION
21/10 25/10
Depavali Leave
Maal Hijrah
39
(27/10-
31/10/14)
REVISION
40
(3-
10/11/14)
SPM EXAM
41
(11-
14/11)
SPM EXAM
42
(17-
21/11)
SPM EXAM
43
(24-
29/11)
SPM EXAM YEAR END BREAK START
44
(1-5/12)
SPM EXAM
8/12-
31/12
YEAR END BREAK
You might also like
- Physics Workbook AnswersDocument58 pagesPhysics Workbook Answersbright hero88% (16)
- Force Diagrams & Statics: Free Particle Model Worksheet 4Document7 pagesForce Diagrams & Statics: Free Particle Model Worksheet 4api-292718088No ratings yet
- Eastern Philosophy of EducationDocument61 pagesEastern Philosophy of EducationMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Expt-2: Bouncing Ball Experiment: ObjectiveDocument9 pagesExpt-2: Bouncing Ball Experiment: ObjectiveNilima Ayoub DiptyNo ratings yet
- M Schemes 04Document3 pagesM Schemes 04Pathmanathan Nadeson0% (2)
- Sukatan FizikDocument26 pagesSukatan FizikAhmad MohsinNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5Document17 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5Salmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Physics Form 5 2013Document17 pagesYearly Plan Physics Form 5 2013qq2350% (1)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiDocument16 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 Smktpihelmi_tarmiziNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work f5Document22 pagesScheme of Work f5Asma AliasNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiDocument16 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiHelmi TarmiziNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work f5Document21 pagesScheme of Work f5Eunice TangNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Revision ChecklistDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Revision ChecklistShafkat Sakeebur Rahman100% (2)
- Physics Form 5: Yearly Plan 2015 Notes and VocabularyDocument14 pagesPhysics Form 5: Yearly Plan 2015 Notes and VocabularySue Suraya NazaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 Year 2016: Learning Area: WavesDocument19 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 Year 2016: Learning Area: WavesRed KiteNo ratings yet
- SMK Iskandar Shah Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015: Learning Area: 1. WavesDocument15 pagesSMK Iskandar Shah Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015: Learning Area: 1. WavesTee Ting QINo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan - Physics Form 5: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. VDocument16 pagesYearly Plan - Physics Form 5: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. VSalmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- 3 & 4 Marks Physics IMPDocument69 pages3 & 4 Marks Physics IMPNahush sarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Maths Revison List Year 10 All Sets Dec 15Document10 pagesMaths Revison List Year 10 All Sets Dec 15ollie deanNo ratings yet
- Emfw NotesDocument2 pagesEmfw NotesNaushad SheikNo ratings yet
- RPT Physics Form 5Document12 pagesRPT Physics Form 5SazlinAinaNo ratings yet
- Aman Dhattarwal's Physics IMP Questions (Class 12)Document4 pagesAman Dhattarwal's Physics IMP Questions (Class 12)Bhakta Kishor80% (10)
- Xii-Cbsephysicsimportant Derivations Question - Chapter WiseDocument4 pagesXii-Cbsephysicsimportant Derivations Question - Chapter WiseSharulathaNo ratings yet
- SMK Jalan Tiga Bandar Baru Bangi Physics Form 5 Yearly Lesson Plan 2009 Week Learning Area Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities Notes and VocabularyDocument25 pagesSMK Jalan Tiga Bandar Baru Bangi Physics Form 5 Yearly Lesson Plan 2009 Week Learning Area Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities Notes and VocabularyGerardo Lozano GuetaNo ratings yet
- Most Expected PU - II Physics Questions For 2020-2021Document16 pagesMost Expected PU - II Physics Questions For 2020-2021Navaneeth MsNo ratings yet
- Important Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Aman Dhattarwal S Physics IMP Questions Class 12Document5 pagesAman Dhattarwal S Physics IMP Questions Class 12Krishan Lohan100% (1)
- Applied Physics 2 Practical Viva Voce QDocument16 pagesApplied Physics 2 Practical Viva Voce QAnish MuraliNo ratings yet
- Derivations Class 12Document7 pagesDerivations Class 1228092008pragyana2382No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument180 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesGurusreenuNo ratings yet
- Lessonsections 2Document12 pagesLessonsections 2Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Physics Essential Unit 9 (E09)Document5 pagesPhysics Essential Unit 9 (E09)Jaxon FlameNo ratings yet
- 12thQuestionBank (KSU)Document9 pages12thQuestionBank (KSU)sohailmushtaq1001No ratings yet
- Physical Sciences GR 10 Assessent Frame June 2024Document5 pagesPhysical Sciences GR 10 Assessent Frame June 2024catlynnferreiraNo ratings yet
- Emtl r15 II II Jntu A SyllabusDocument1 pageEmtl r15 II II Jntu A SyllabussubramanyamNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics EMDocument8 pages12 Physics EMAniketNo ratings yet
- PHY 101 PowerpointDocument233 pagesPHY 101 PowerpointSyed ShahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Sections 1Document13 pagesLesson Sections 1Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Yearly Fizik 2013 Form 5Document18 pagesYearly Fizik 2013 Form 5Fazillah AziziNo ratings yet
- PH 110 Course Outline 2019-2020 Academic YearDocument4 pagesPH 110 Course Outline 2019-2020 Academic Yearmusamugabazi68No ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument26 pagesImportant QuestionsAyush TomarNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electricity 1 Whole Unit Overview: Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities ResourcesDocument2 pagesPhysics: Electricity 1 Whole Unit Overview: Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities ResourceszahraNo ratings yet
- BEEE Question Bank Unit 1,2Document13 pagesBEEE Question Bank Unit 1,2Upender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- Xii Derivation List-2023-24 2Document3 pagesXii Derivation List-2023-24 2prachurjyapadhiNo ratings yet
- Derivation of All ChapterDocument6 pagesDerivation of All Chapterplutouec86% (14)
- 12th Physics Worksheet (ch3 To ch7)Document3 pages12th Physics Worksheet (ch3 To ch7)lovecatsaninalsNo ratings yet
- H Physics XIIDocument33 pagesH Physics XIIMuzammil AfsarNo ratings yet
- Sfra For Condition Monitoring of Power TransformerDocument3 pagesSfra For Condition Monitoring of Power TransformerSarojakanti SahooNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2012Document7 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2012Cikgu EnaNo ratings yet
- Physics Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesPhysics Important QuestionsLaxman KumawatNo ratings yet
- Cbse Paper Leak PDFDocument7 pagesCbse Paper Leak PDFRohan AroraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Electric CurrentDocument14 pagesModule 2 Electric Currentjovy dulay100% (2)
- Planner For Preparatory Exam.Document3 pagesPlanner For Preparatory Exam.RaonarNo ratings yet
- Unit C: Electromagnetic EnergyDocument2 pagesUnit C: Electromagnetic EnergyticoninxNo ratings yet
- Important Questions PhysicsDocument12 pagesImportant Questions PhysicsNaziaParveenNo ratings yet
- 12 TH Physics Cbse SyllabusDocument7 pages12 TH Physics Cbse Syllabussandipsujata100% (1)
- 2014 Physics XII Cbse Sample PaperDocument37 pages2014 Physics XII Cbse Sample PaperVijaykumar Shukla100% (1)
- Phy 1 PG 2Document1 pagePhy 1 PG 2api-20001111No ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum in Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pagesEnergy and Momentum in Electromagnetic WavesEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics HWDocument33 pagesClass Xii Physics HWDhruv PandeyNo ratings yet
- Charles Steinmetz - Elementary Lectures On Electric Discharges, Waves and ImpulsesDocument172 pagesCharles Steinmetz - Elementary Lectures On Electric Discharges, Waves and Impulsesdawsecs100% (1)
- Understanding Phase As A Key Concept in Physics and Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Phase As A Key Concept in Physics and Electrical EngineeringJavier PNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsFrom EverandPrinciples of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Principles of Electrical Transmission Lines in Power and Communication: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandPrinciples of Electrical Transmission Lines in Power and Communication: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Generation and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandGeneration and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Luminescent Properties of Rare Earth (Er, Yb) Doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet Thin Films and Bulk Samples Synthesised by An Aqueous Sol-Gel TechniqueDocument9 pagesLuminescent Properties of Rare Earth (Er, Yb) Doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet Thin Films and Bulk Samples Synthesised by An Aqueous Sol-Gel TechniqueMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Isi Padu PepejalDocument1 pageIsi Padu PepejalMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 Philosophy and BranchesDocument30 pagesSlide 1 Philosophy and BranchesMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Islamic Philosophy of AduDocument33 pagesIslamic Philosophy of AduMimie SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Design GuidelinesDocument38 pagesLaboratory Design GuidelinesMark MoldezNo ratings yet
- Rotation (Grotto)Document7 pagesRotation (Grotto)Chandru ANo ratings yet
- 04 Laws of Motion Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFDocument7 pages04 Laws of Motion Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFAryan DeNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Circular Motion Abd Gravitation MCQDocument14 pagesTopic 6 Circular Motion Abd Gravitation MCQAmit BarateNo ratings yet
- Tractive Effort For Propulsion of TrainDocument4 pagesTractive Effort For Propulsion of TrainSandip MondalNo ratings yet
- Bookacceleration Probs PDFDocument6 pagesBookacceleration Probs PDFMukul KumawatNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics - Gravitation - NotesDocument5 pages11 Physics - Gravitation - Notesrahul pingaleNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Resultant ForceDocument30 pages1.1 Resultant ForceLim Yan JoeNo ratings yet
- Physics Cutnell 9th Edition Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPhysics Cutnell 9th Edition Solutions Manualgraphitehamous.22x7100% (54)
- Physics MidtermDocument14 pagesPhysics MidtermPrecious015100% (1)
- CON3301 - PPT 1 SI Unit and Force As Vector (2017) - Basic PhysicsDocument56 pagesCON3301 - PPT 1 SI Unit and Force As Vector (2017) - Basic PhysicsJoseph ChanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstituteDocument5 pagesElectromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstitutecisnarFNo ratings yet
- Definition Sem 1 PSTDocument8 pagesDefinition Sem 1 PSTNurul ShaiedahNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument1 pageNewton's First LawSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Exam Study Guide: Demond CarterDocument5 pagesPhysics Final Exam Study Guide: Demond CarterDemond CarterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Motion - Question For ThoughtDocument2 pagesChapter 2 - Motion - Question For Thoughtsuhughes100% (3)
- 1 Kane Equations - Example 1Document8 pages1 Kane Equations - Example 1Khisbullah HudhaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Homework - RautDocument7 pagesKinematics Homework - RautEull RautNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion MCQs Sheet 1Document6 pagesLaws of Motion MCQs Sheet 1eka123100% (1)
- Test-4 1Document6 pagesTest-4 1Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PPT - RadioactivityDocument23 pagesChemistry PPT - RadioactivityRishita SinghNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 - KinematicsDocument81 pagesCH - 4 - KinematicsVISHESH SEHRAWATNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line WorksheetDocument2 pagesMotion in A Straight Line WorksheetWoah NitinNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration Card Sort Task CardDocument4 pagesSpeed, Velocity, and Acceleration Card Sort Task CardDaryl DunneNo ratings yet
- 5 Newtons LawsDocument29 pages5 Newtons LawsMehwish IsrarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 HSC Physics NotesDocument8 pagesModule 5 HSC Physics NotesLiam KorngoldNo ratings yet
- Course Outline in General Physics 1Document5 pagesCourse Outline in General Physics 1Jin SenpaiNo ratings yet