Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Swing Lab: y (T) Pcos (Q (T+R) ) +S y (T) Psin (Q (T+R) ) +S
Swing Lab: y (T) Pcos (Q (T+R) ) +S y (T) Psin (Q (T+R) ) +S
Uploaded by
api-257891091Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Swing Lab: y (T) Pcos (Q (T+R) ) +S y (T) Psin (Q (T+R) ) +S
Swing Lab: y (T) Pcos (Q (T+R) ) +S y (T) Psin (Q (T+R) ) +S
Uploaded by
api-257891091Copyright:
Available Formats
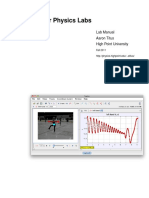
SwingLab
Tocompletethefollowingactivity,youwillneedaccesstothemoviefileoftheswingerandthedata
pointsfortheSwingLab.ThisdataisavailableinanExcelfileoraTICalculatorprogram.Apartialtable
ofdataisprovidedattheendofthishandout.
PreActivity:Watchthevideooftheswinger.Asyouwatchthevideo,thinkaboutbreakingupher
motionintoherverticalpositionandhorizontalpositionovertime.Forexample,thinkabouthowhigh
sheswingsorhowfarleftorrightsheisfromthecenterofherswing.Thedistancebetweenthetop
ofthetwoorangeconesisapproximately72inches.Thinkabouthowlongittakesfortheswingerto
makeonecompleteswing(fromfarlefttofarrightbacktofarleftagain).
PartI:ModelingtheVerticalPositionoftheSwinger
ThegoalforPartIofthelessonisforyoutocreateamathematicalmodelthatgivestheswingers
verticalpositionasafunctionoftime.
Letsconsiderthegraphbelow.Alongthehorizontalaxiswehavetimeinsecondsandalongthevertical
axiswehavetheverticalpositionoftheswinger,i.e.herheightoffthegroundmeasuredininches.
Usingyourknowledgeoftrigonometry,thegraphandadatatableofthepoints,createamodelofthe
form y(t)=Pcos(Q(t+R))+S or y(t)=Psin(Q(t+R))+S fortheverticalpositionfortheswingerasafunction
oftime(t)inseconds.
CarefullyexplainhowyouarriveateachofthevaluesfortheconstantsP,Q,RandS.
Usingtechnology,createagraphofthegivendataalongwithagraphofyourmodel.Discussthe
accuracyofyourmodel.Includeinformationaboutthephysicalproblemasyoudiscusstheaccuracyof
yourmodel.
PartII:ModelingtheHorizontalPositionoftheSwinger
ThegoalforPartIIofthelessonisforyoutocreateamathematicalmodelthatgivestheswingers
horizontalpositionasafunctionoftime.
Letsconsiderthegraphbelow.Alongthehorizontalaxiswehavetimeinsecondsandalongthevertical
axiswehavethehorizontalpositionoftheswinger.Ifweassumethatthehorizontalpositionofthe
swingeriszerowhentheswingisatrest,thenthevariableontheverticalaxisisherhorizontalposition
fromthatcenterpoint.Herhorizontalpositionispositivewhensheistotherightofthatcenterpoint
andnegativewhensheistotheleftofthatcenterpoint.
Usingyourknowledgeoftrigonometry,thegraphandadatatableofthepoints,createamodelofthe
form y(t)=Pcos(Q(t+R))+S or y(t)=Psin(Q(t+R))+S forthehorizontalpositionfortheswingerasa
functionoftime(t)inseconds.
CarefullyexplainhowyouarriveateachofthevaluesfortheconstantsP,Q,RandS.
Usingtechnology,createagraphofthegivendataalongwithagraphofyourmodel.Discussthe
accuracyofyourmodel.Includeinformationaboutthephysicalproblemasyoudiscusstheaccuracyof
yourmodel.
ComparetheperiodsofthemodelsyoufoundinPartsIandII.Explainwhytheperiodsofthe
trigonometricmodelsmakesenseinthecontextoftheproblem.
PartIII:ModelingtheMotionoftheSwingerParametrically
ThegoalforPartIIIofthelessonisforyoutocreateaparametricmodelthatgivestheswingersmotion
overtime.YouwillusetheworkyoudidinPartsIandII.
UsingaTICalculatororsomeotherparametricequationgraphingtool,enterthehorizontalposition
modelintothex(t)functionandtheverticalpositionintothey(t).Carefullychooseanappropriate
windowforthegraphoftheswingersmotionandcreateagraphoftheswingersmotion.
Discusstheaccuracyofyourparametricmodel.
SwingLabDataTable
Apartialtablethatincludesthetime(inseconds)andthehorizontalandverticalpositions(ininches)of
theswingerisgivenbelow.
Time
(sec)
Horizontal
Position(in)
Vertical
Position(in)
0.0 65.0 108.8
0.2 63.6 100.4
0.4 54.3 75.0
0.6 35.7 51.1
0.8 1.3 37.7
1.0 38.1 53.9
1.2 58.3 84.4
1.4 63.9 107.6
1.6 65.6 115.1
1.8 64.6 106.7
2.0 56.9 79.5
2.2 33.2 47.4
2.4 8.5 37.7
2.6 38.3 53.5
2.8 59 85.4
3.0 65.0 107.4
3.2 65.8 114
3.4 63.4 99.9
3.6 55.2 77.6
3.8 30.1 46.9
4.0 10.2 38.7
4.2 44.9 60.3
4.4 60.4 92.6
4.6 64.9 111.6
4.8 65.8 118.4
5.0 64.4 105.1
5.2 54.3 75.3
5.4 27.4 44.3
5.6 6.9 38
5.8 43.5 59.3
6.0 60.1 90.5
6.2 64.8 109.3
6.4 65.3 114
6.6 63.4 101.3
You might also like
- Autodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersFrom EverandAutodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersNo ratings yet
- Module-5 AnimationDocument12 pagesModule-5 AnimationAbdulkhaliq Nasher100% (2)
- Assignment 1: 11520G Data Capture and PreparationsDocument7 pagesAssignment 1: 11520G Data Capture and PreparationsagamdeepNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP - Final DemonstrationDocument8 pagesDetailed LP - Final DemonstrationGenaro Nocete de Mesa, Jr.67% (3)
- Design and Creation of Test-, QA-and Training Systems: White PaperDocument15 pagesDesign and Creation of Test-, QA-and Training Systems: White Paperkcvaka123100% (1)
- Circular Motion LabDocument4 pagesCircular Motion LabJasdeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Projectiles I MD I RnsDocument4 pagesProjectiles I MD I RnsKhabi Nada50% (2)
- Atego en 20100811Document131 pagesAtego en 20100811bocevski67% (3)
- Unit 1: Cs2203-Object Oriented Programming-Anna University Syllabus For CSEDocument3 pagesUnit 1: Cs2203-Object Oriented Programming-Anna University Syllabus For CSEvidhyahNo ratings yet
- Process Planning of Bearing Housing1Document22 pagesProcess Planning of Bearing Housing1Thota Sri K HarithaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Video Analysis WorksheetDocument21 pagesKinematics Video Analysis WorksheetSoonGiaprongNo ratings yet
- Pivot Interactives Motion Graphs of Positive and Negative AccelerationDocument2 pagesPivot Interactives Motion Graphs of Positive and Negative AccelerationSophiaNo ratings yet
- Lab 14report-2Document4 pagesLab 14report-2Hamza RehiouiNo ratings yet
- OpenFX TutorialsDocument59 pagesOpenFX Tutorialsrmm99rmm99No ratings yet
- Tracker Lab ManualDocument49 pagesTracker Lab ManualfakturkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Creating Animated AppsDocument19 pagesChapter 6 - Creating Animated AppsVin FajardoNo ratings yet
- Using Procedures Practices - OracleDocument3 pagesUsing Procedures Practices - OraclerudiawanNo ratings yet
- 1101 Lab 4 - Circular MotDocument18 pages1101 Lab 4 - Circular MotYi Wei OngNo ratings yet
- LAB02-2: Video Analysis of Projectile Motion: ObjectiveDocument11 pagesLAB02-2: Video Analysis of Projectile Motion: Objectivejumperpc3000No ratings yet
- Bungee Jump Accel LQDocument5 pagesBungee Jump Accel LQReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Final Project Guidelines Amber GDocument4 pagesFinal Project Guidelines Amber GspreemouseNo ratings yet
- CA SummaryDocument14 pagesCA Summarysab640887No ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Motion Analysis P61.1Document7 pagesExperiment 3 Motion Analysis P61.1zayn malikNo ratings yet
- D) AirDocument9 pagesD) AirKanokporn LeerungnavaratNo ratings yet
- Students Should Already Have Received Instruction On The Basic Principles of Seismic Waves. For Ideas On How To Provide This Instruction Please SeeDocument7 pagesStudents Should Already Have Received Instruction On The Basic Principles of Seismic Waves. For Ideas On How To Provide This Instruction Please SeeSantiago TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Using A Clinometer To Measure HeightDocument6 pagesUsing A Clinometer To Measure HeightangryhamsterNo ratings yet
- Charisma B Moving Man Phet LessonDocument7 pagesCharisma B Moving Man Phet Lessonapi-255910104No ratings yet
- 121-Ch3 Revised Fall 2013Document12 pages121-Ch3 Revised Fall 2013Swarnav BanikNo ratings yet
- H Apply Concepts of in BetweenDocument6 pagesH Apply Concepts of in BetweenSACATA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOLNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science: Unit - Going Downhill - Physics EEI (Extended Experimental Investigation)Document9 pagesYear 10 Science: Unit - Going Downhill - Physics EEI (Extended Experimental Investigation)Chad GardinerNo ratings yet
- Bungee Jump Accelerations: ExperimentDocument7 pagesBungee Jump Accelerations: ExperimentReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Memory Drawing and Quick Sketching.: Dr. Utpal BaruaDocument13 pagesMemory Drawing and Quick Sketching.: Dr. Utpal BaruaJabbar AljanabyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document12 pagesChapter 17javichuNo ratings yet
- Referencia Material TutorialDocument4 pagesReferencia Material TutorialWILFREDO OSPITIA GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- ENSC 102L - Module-I (Activity 1)Document6 pagesENSC 102L - Module-I (Activity 1)zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Velocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabDocument7 pagesVelocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabqweerNo ratings yet
- The Frog MazeDocument26 pagesThe Frog MazeimrayyantubeNo ratings yet
- Labatorial 8, Circular MotionDocument9 pagesLabatorial 8, Circular Motionmzbreezy808No ratings yet
- 04 COMP G On InclineDocument5 pages04 COMP G On InclinecfisicasterNo ratings yet
- Velocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabDocument7 pagesVelocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabGerlie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Velocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabDocument7 pagesVelocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabGerlieNo ratings yet
- Graph Matching New PhysicsDocument5 pagesGraph Matching New Physicsapi-269873615No ratings yet
- Tle - Animation: Quarter 3: Week 3 - 4Document12 pagesTle - Animation: Quarter 3: Week 3 - 4Erika C. Delos Santos100% (1)
- Multimedia Element AnimationDocument54 pagesMultimedia Element AnimationVennis Suzanne Bumanlag SacroNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion (Student Version)Document5 pagesProjectile Motion (Student Version)Ashley JohnsNo ratings yet
- Bucio - Projectile WS 1Document3 pagesBucio - Projectile WS 1ZhaeNo ratings yet
- World of AnimationDocument42 pagesWorld of Animationankur BoraNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument11 pagesProjectile Motionbastard100% (1)
- Chp6 - Animation and Surface RenderingDocument57 pagesChp6 - Animation and Surface RenderingMin ShahatNo ratings yet
- Bourret ScratchProgrammingDocument43 pagesBourret ScratchProgrammingjosef100% (1)
- An Introduction To Programming With Scratch: Ronald BourretDocument43 pagesAn Introduction To Programming With Scratch: Ronald BourretHazem Osman 2512No ratings yet
- ScratchDocument3 pagesScratchapi-249163109No ratings yet
- Projectiles/Projectile Simulator/Projectile Simulator InteractiveDocument4 pagesProjectiles/Projectile Simulator/Projectile Simulator InteractiveEldienGarciaBucol100% (1)
- P6 Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesP6 Projectile MotionKim ValdezNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of MovementDocument6 pagesBiomechanics of Movementعبدالرحمن الشهريNo ratings yet
- Unit 9Document14 pagesUnit 9Technical DipeshNo ratings yet
- Studio Physics IDocument4 pagesStudio Physics IStanley CampbellNo ratings yet
- Session 4Document13 pagesSession 4svchouhan4No ratings yet
- Digital Animation EquipmentDocument32 pagesDigital Animation EquipmentJoshua CondeNo ratings yet
- Few Random Q&aDocument4 pagesFew Random Q&aHiba AnisNo ratings yet
- 1A-Investigation Toy CarDocument5 pages1A-Investigation Toy CarMatthew OwenNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Logger?Document10 pagesWhat Is Data Logger?Nurshahirah ZulkipliNo ratings yet
- iPad Animation: - make stop motion movies on the iPad with iStopMotion, GarageBand, iMovieFrom EverandiPad Animation: - make stop motion movies on the iPad with iStopMotion, GarageBand, iMovieRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Day 1 Modeling NotesDocument1 pageDay 1 Modeling Notesapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Symmedian Application TriangulationDocument3 pagesSymmedian Application Triangulationapi-257891091No ratings yet
- 6 27 FractalsDocument2 pages6 27 Fractalsapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Day 3 Modeling NotesDocument2 pagesDay 3 Modeling Notesapi-257891091No ratings yet
- 6 25 Notes VideosDocument2 pages6 25 Notes Videosapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Day 3 Geometry NotesDocument4 pagesDay 3 Geometry Notesapi-257891091No ratings yet
- 6 27 Modeling NotesDocument3 pages6 27 Modeling Notesapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Pass The Candy Tally Sheet & Questions: Part I - Collecting & Analyzing DataDocument2 pagesPass The Candy Tally Sheet & Questions: Part I - Collecting & Analyzing Dataapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Class Notes 6 24 Fluid MathDocument1 pageClass Notes 6 24 Fluid Mathapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Day 2 Modeling NotesDocument4 pagesDay 2 Modeling Notesapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Suez Canal Class HandoutDocument3 pagesSuez Canal Class Handoutapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Alan NovemberDocument2 pagesAlan Novemberapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Suez Canal SolutionDocument7 pagesSuez Canal Solutionapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Dan TeagueDocument2 pagesDan Teagueapi-257891091No ratings yet
- MapsDocument2 pagesMapsapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Jonathan ChoateDocument2 pagesJonathan Choateapi-257891091No ratings yet
- Flatland 2Document2 pagesFlatland 2api-257891091No ratings yet
- Diana Tunnell Resume June 2014Document2 pagesDiana Tunnell Resume June 2014api-257891091No ratings yet
- GR-55 ManualDocument100 pagesGR-55 ManualJose RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Executive S&Op Effectiveness ChecklistDocument7 pagesThe Executive S&Op Effectiveness ChecklistSanjay KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Open Source IntelligenceDocument6 pagesOpen Source IntelligenceccodriciNo ratings yet
- JETI DC/DS Update Version 4.28 (May 2018) : New FeaturesDocument23 pagesJETI DC/DS Update Version 4.28 (May 2018) : New FeaturesPeter SchwarzNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Simrad AP50 AutopilotDocument188 pagesInstruction Manual: Simrad AP50 AutopilotARCESIO DOUMETNo ratings yet
- Harmony 21 Essentials Keyboard ShortcutsDocument52 pagesHarmony 21 Essentials Keyboard ShortcutsGretaNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Pressure SensorDocument4 pagesDiaphragm Pressure SensorSaumya GoelNo ratings yet
- Model: Slk-D10: Mini Dot Impact PrinterDocument26 pagesModel: Slk-D10: Mini Dot Impact Printerdann kurokiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database VLDB and Partitioning GuideDocument304 pagesOracle Database VLDB and Partitioning GuideHưng Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- QMS-04 REV 1 Procedure For Document ControlDocument26 pagesQMS-04 REV 1 Procedure For Document ControlbanglvhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operating SystemDocument62 pagesIntroduction To Operating SystemJunaid SayyedNo ratings yet
- EE0015 Lab Activity 4Document15 pagesEE0015 Lab Activity 4kyle vicenteNo ratings yet
- Industrial Maintenance: Status, Trends + Forecasts ReportDocument12 pagesIndustrial Maintenance: Status, Trends + Forecasts Reportzufriategui100% (1)
- Laboratory Report: Analogue ElectronicsDocument8 pagesLaboratory Report: Analogue ElectronicsWAN AHMAD AFIQ WAN HUZAIRUL AZRILNo ratings yet
- What Is A PCBDocument8 pagesWhat Is A PCBKhushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lab No 3Document4 pagesLab No 3Farhan Khan NiaZiNo ratings yet
- Scanscore 2 ManualDocument26 pagesScanscore 2 Manualcbsubscription2250No ratings yet
- Mie11169-Cba2000 Application GuideDocument149 pagesMie11169-Cba2000 Application GuideFuad BurhaniNo ratings yet
- The State of Pentesting 2023Document30 pagesThe State of Pentesting 2023bacbaphi88No ratings yet
- PROPOSAL EPSON M15140 and L15180Document3 pagesPROPOSAL EPSON M15140 and L15180IT ManNo ratings yet
- Check To Make Sure You Have The Most Recent Set of AWS Simple Icons Creating DiagramsDocument48 pagesCheck To Make Sure You Have The Most Recent Set of AWS Simple Icons Creating DiagramsarunchockanNo ratings yet
- Istr 23 Executive SummaryDocument4 pagesIstr 23 Executive SummaryPaulo SchullerNo ratings yet
- Status Profile Creation and Assignment To An Order Type in SAP PPDocument7 pagesStatus Profile Creation and Assignment To An Order Type in SAP PPHemant UNICHEMLLPNo ratings yet
- Implementation IntentionsDocument3 pagesImplementation IntentionsJoana ManahanNo ratings yet
- DH-IPC-HFW2531S-S-S2: 5MP Lite IR Fixed-Focal Bullet Network CameraDocument3 pagesDH-IPC-HFW2531S-S-S2: 5MP Lite IR Fixed-Focal Bullet Network CameraguestisorNo ratings yet
- Wise Masts ADocument120 pagesWise Masts ArkchdryNo ratings yet