Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elec1111 01b Circuit Basics
Elec1111 01b Circuit Basics
Uploaded by
uploadingperson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views5 pagesThis document summarizes an introductory lecture on circuit basics for electrical engineering. It discusses how aircraft electrical systems work using generators connected to loads. It then covers some key concepts for circuit analysis, including current, voltage, power, and energy. Examples of direct and alternating current are shown. The document also defines voltage and resistance, and introduces conventions for denoting the polarity of voltage measurements between two nodes.
Original Description:
.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes an introductory lecture on circuit basics for electrical engineering. It discusses how aircraft electrical systems work using generators connected to loads. It then covers some key concepts for circuit analysis, including current, voltage, power, and energy. Examples of direct and alternating current are shown. The document also defines voltage and resistance, and introduces conventions for denoting the polarity of voltage measurements between two nodes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views5 pagesElec1111 01b Circuit Basics
Elec1111 01b Circuit Basics
Uploaded by
uploadingpersonThis document summarizes an introductory lecture on circuit basics for electrical engineering. It discusses how aircraft electrical systems work using generators connected to loads. It then covers some key concepts for circuit analysis, including current, voltage, power, and energy. Examples of direct and alternating current are shown. The document also defines voltage and resistance, and introduces conventions for denoting the polarity of voltage measurements between two nodes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
1
Electrical Engineering &
Telecommunications
Lecturer:
Ted Spooner
Lecture -
Intro to Circuit Basics
Elec1111 Elec1111
Rm124A EE email: e.spooner@unsw.edu.au
How is the Electrical system of
an Aircraft Powered?
One of 4 variable
frequency 150kVA
generators on the new
A380 Airbus
RamAir Turbine
Auxiliary
Power Unit
(APU)
How do we connect it all?
How do we go about designing and
evaluating the design?
Have to analyse circuits
How do we do that?
Possible Circuit solutions to a simplified
aircraft electrical system.
Generator
1 Generator
2
LOAD 1 LOAD 2
LOAD 3
LOAD 4
LOAD 5
Possible Circuit solutions to a simplified
aircraft electrical system.
Generator
1
Generator
2
LOAD 1
LOAD 2
LOAD 5
LOAD 4
LOAD 3
How do we analyze a circuit like
this?
Audio Power Amplifier
2
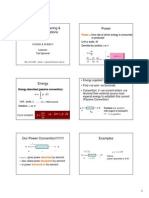
Electric Circuit Variables
Charge
Current
Voltage
Power
Energy
Need to Understand Concepts
How do we calculate current in
each element of this circuit?
10V
1000 10
87 20 3V
current
constant: direct current (dc)
time-varying: many forms
e.g. sinusoidal, also called
alternating current (ac)
t (s)
i
(A)
0
sinusoid (ac)
ramp
exponential
Time-varying current
t (s)
i
(A)
0
Direct current (dc)
t (s)
i
(A)
0
sinusoid (ac)
ramp
exponential
Time-varying current
t (s)
i
(A)
0
Direct current (dc)
VOLTAGE
When charge flows through an element
then energy is transferred either to or from
the element
a b
i
3
Voltage (potential difference) =measure
of the amount of energy transferred per
unit of charge.
Unit: volt, V
Notation: V, v(t) or v
energy
charge
dq
dw
v =
Voltage
As charge flows through an element then
energy is transferred either to or from the
element
a b
v
i
+
_
Must have a sense of direction.
If i and v are positive then: energy is being transferred to the element.
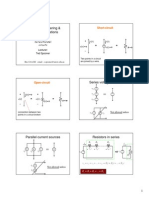
Voltage
Element absorbing energy
a b
i
+
_
i
v
a b
i
+
_
Element delivering energy
i
v
If i and v are positive.
Voltage is analogous to
pressure
PUMP
Resistance
to flow
Voltage is like pressure HV transmission lines: up to 500kV
Household supply: 230V
Car battery: 12V 13V
Flashlight battery: 1.5V
Electroencephalography (EEG):10V
4
Voltage Sign conventions
Voltage is a measure of potential
difference between two points.
ie Vab is the difference in potential
between nodes a and b.
Vab is the voltage of node a with respect
to node b.
a
b
+
_
ab
v
When we say voltage of node When we say voltage of node a a
relative to node relative to node b b we write it like: we write it like:
Voltage Sign
conventions
Voltage is a measure of
potential difference between two points.
Reference
Ground
v
a
+
_
v
b
+
_
v
ab
=v
a
- v
b
a
b
+
_
ba
v
When we say voltage of node When we say voltage of node b b
relative to node relative to node a a we write it like: we write it like:
Now voltage of b with respect
to a
Reference
Ground
v
b
+
_
v
a
+
_
v
ba
=v
b
- v
a
a b
+
_
ba
v
ab
v
+
_
a b
Then : Then :
If If 5
ab
v V =
5
ba
v V =
a b
+
_
ab
v
5
ab
v V =
COM V
+5V Reading
Measuring
V
ab
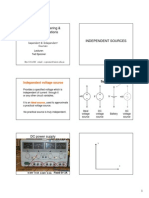
Sources =devices that supply energy to circuit
Voltage Voltage
sources sources
Current Current
sources sources
Sources Sources
2 types
Sources can be independent independent or dependent dependent.
5
Independent Voltage
source
DC
voltage
source
V
AC
voltage
source
v(t)
Ideal
voltage
source
v(t)
Battery
V
positive
terminal
Independent current source Independent current source
i(t)
You might also like
- Yashesve Summer Internship Report 2019Document71 pagesYashesve Summer Internship Report 2019Ankit TiwariNo ratings yet
- A Novel Pumped Hydro Combined With Compressed AirDocument45 pagesA Novel Pumped Hydro Combined With Compressed AirAndy Uc ChiNo ratings yet
- Electrical QuantitiesDocument34 pagesElectrical QuantitiesMika VaughnNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1 (Final Term)Document20 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1 (Final Term)Abdul Halil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Zuraini Dahari ROOM NO: 3.24 Ext: 6048: Eezuraini@usm - MyDocument56 pagesDr. Zuraini Dahari ROOM NO: 3.24 Ext: 6048: Eezuraini@usm - Myiman qasidahNo ratings yet
- EE 306 - Electrical Engineering LaboratoryDocument7 pagesEE 306 - Electrical Engineering LaboratoryMohammed KhouliNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument68 pagesELECTRICITYPrecious AgyeiNo ratings yet
- 1 - EE2001 Circuit Analysis Lectures 1-6 PDFDocument112 pages1 - EE2001 Circuit Analysis Lectures 1-6 PDFkoolkrish14No ratings yet
- EE42 100 Cch-Lecure2 062613-FDocument45 pagesEE42 100 Cch-Lecure2 062613-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Be-104 (Beee)Document69 pagesBe-104 (Beee)Sunil NamdevNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Interview Interview QuestionsDocument18 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview Interview QuestionsAta Ur Rahman Khalid100% (1)
- Chapter 1-1 - Intro and Part 1 and 2Document59 pagesChapter 1-1 - Intro and Part 1 and 2Hanis SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 DC Network TheoremsDocument76 pagesTopic 1 DC Network TheoremsASHISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- FE Exam Review - Circuits - 11182014Document80 pagesFE Exam Review - Circuits - 11182014Juan Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Physics 271 Physics 271Document32 pagesPhysics 271 Physics 271Michelle Anne TandocNo ratings yet
- Foundamental Circuit CH 1.Document53 pagesFoundamental Circuit CH 1.syumteame15161993No ratings yet
- BEE Electricity Basic PrinciplesDocument20 pagesBEE Electricity Basic PrinciplesMondaya, Jake Armond D.No ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis and Design Manual FinalDocument65 pagesCircuit Analysis and Design Manual Finalصدام حسینNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering: Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Hassan DawoodDocument183 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering: Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Hassan Dawoodbakhtawar saeedNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis: Adnan YousafDocument26 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis: Adnan Yousafsufyan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document33 pagesLecture 1tahiaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering EE-211: Electrical Network Analysis Lab 7: Capacitive Phase Shift and Reactive PowerDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering EE-211: Electrical Network Analysis Lab 7: Capacitive Phase Shift and Reactive PowerWaleed BajwaNo ratings yet
- 9 ElectricityDocument32 pages9 Electricityzzrnwdzpsmhs951003No ratings yet
- Questions and Answers of Viva of EEEDocument19 pagesQuestions and Answers of Viva of EEERubayetNo ratings yet
- Lecture-01 Basic Concepts - System of Units - Basic QuantitiesDocument25 pagesLecture-01 Basic Concepts - System of Units - Basic QuantitiesMuhammad Salman100% (1)
- Bakshi Basic ElectricalDocument196 pagesBakshi Basic Electricalprakash100% (6)
- Chapter1 FundamentalDocument96 pagesChapter1 FundamentalfrankieyiiNo ratings yet
- 19.1 Current and CircuitsDocument27 pages19.1 Current and CircuitsHasan AlzaghalNo ratings yet
- Basic Laws of Electric Circuits Fundamentals Lesson 1Document27 pagesBasic Laws of Electric Circuits Fundamentals Lesson 1Kkbhuvan KkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document117 pagesChapter 1badrilaminNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuit Lab ManualDocument46 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuit Lab ManualManu anand100% (1)
- Basics of Power SystemsDocument63 pagesBasics of Power SystemsAravind BalaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDocument101 pagesCircuit Theory 1 MidtermMcHaley HalNo ratings yet
- N 5 Eabb 57 B 5 FF 53Document9 pagesN 5 Eabb 57 B 5 FF 53bitseee RandDNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document78 pagesUnit 1Atharva RaksheNo ratings yet
- Bee LabDocument23 pagesBee Labdurgesh choudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 DC CircuitsDocument183 pagesUnit-1 DC CircuitsChannabasappa KudarihalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC Circuit Analysis PDF 1 8 MegDocument31 pagesUnit 1 DC Circuit Analysis PDF 1 8 MegJoshua Duffy67% (3)
- Det1013 - Electrical Technology: Introduction To Electric CircuitDocument118 pagesDet1013 - Electrical Technology: Introduction To Electric Circuitcaj7687No ratings yet
- Engr260-Lec1-Basics (Ink)Document34 pagesEngr260-Lec1-Basics (Ink)Nick RentschNo ratings yet
- NT Unit Part 1Document62 pagesNT Unit Part 1ece placementNo ratings yet
- ECET525 (Power Electronics) : Day 2-Bird's-Eye View of Power Electronics SystemsDocument32 pagesECET525 (Power Electronics) : Day 2-Bird's-Eye View of Power Electronics SystemsbuukieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 PDFDocument22 pagesLecture 2 PDFNathan KingNo ratings yet
- Lab#06 Ee-Lab....Document5 pagesLab#06 Ee-Lab....muhammad faheem ziaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering-PUPSTB ELEN 20024 Circuits 1Document3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communications Engineering-PUPSTB ELEN 20024 Circuits 1Bom ParkNo ratings yet
- Power System Representation - (Upto 09-02-16)Document16 pagesPower System Representation - (Upto 09-02-16)Shahab SaqibNo ratings yet
- NA Unit-1Document99 pagesNA Unit-1phani5016No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - AC and DC Circuit AnalysisDocument39 pagesLecture 2 - AC and DC Circuit AnalysisZoren MabungaNo ratings yet
- Al-Mansour University College Computer Technical Engineering First ClassDocument17 pagesAl-Mansour University College Computer Technical Engineering First ClassranjdarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Course Code: BT 104Document24 pagesBasic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Course Code: BT 104nehaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument23 pagesLaboratory ManualAnmol AhsaasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Circuit TheoremsDocument43 pagesLecture 5 - Circuit TheoremsYip Tuck WaiNo ratings yet
- University of Hormuud: Circuit Analysis IDocument49 pagesUniversity of Hormuud: Circuit Analysis ISalmaanCadeXaajiNo ratings yet
- Title:-: Measurement of PowerDocument5 pagesTitle:-: Measurement of Powermuhammad faheem ziaNo ratings yet
- Teknik Tenaga Listrik: Evizal Abdul KadirDocument45 pagesTeknik Tenaga Listrik: Evizal Abdul KadirYayan FunkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27.electDocument23 pagesChapter 27.electOsama HassanNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitDocument36 pagesElectric CircuitEzekiel MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document8 pagesExp 4MaazNo ratings yet
- EE331 Lecture1 NotesDocument21 pagesEE331 Lecture1 NotespaulamarieestrellalengascoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MidtermsDocument57 pagesModule 1 MidtermsKin Luther De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Bee Experiments: Pointers To FollowDocument35 pagesBee Experiments: Pointers To FollowPratik Mishra100% (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Rinciples of Lgorithm Nalysis: Sedgewick: Chapter 2Document20 pagesRinciples of Lgorithm Nalysis: Sedgewick: Chapter 2uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- PSE2Document1 pagePSE2uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Heaps and Priority QueuesDocument15 pagesLecture 6 Heaps and Priority QueuesuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- PSE9Document1 pagePSE9uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 11c A DigLogic KarnaughExampleDocument2 pagesElec1111 11c A DigLogic KarnaughExampleuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Compilation and Makefiles: Computing 2Document11 pagesCompilation and Makefiles: Computing 2uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 11a Digital Boolean AlgebraDocument4 pagesElec1111 11a Digital Boolean AlgebrauploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 12 TeleDocument5 pagesElec1111 12 TeleuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 11b Digital Function ImplementationDocument5 pagesElec1111 11b Digital Function ImplementationuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 11 Digital LogicDocument8 pagesElec1111 11 Digital LogicuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 10 Opamps2 PDocument7 pagesElec1111 10 Opamps2 PuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications Today: Elec1111Document6 pagesElectrical Engineering & Telecommunications Today: Elec1111uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 07 Sines BWDocument11 pagesElec1111 07 Sines BWuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 01d Charge CurrentDocument3 pagesElec1111 01d Charge CurrentuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications: Elec1111Document7 pagesElectrical Engineering & Telecommunications: Elec1111uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 10a Transformers PDocument7 pagesElec1111 10a Transformers PuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications Amplifiers - Why Do We Use Them?Document8 pagesElectrical Engineering & Telecommunications Amplifiers - Why Do We Use Them?uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 04 Thevenin B WDocument7 pagesElec1111 04 Thevenin B WuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 02c Dependent Sources PDocument5 pagesElec1111 02c Dependent Sources PuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 05 Superposition BWDocument6 pagesElec1111 05 Superposition BWuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Random QUIZ 1 - S2 2008: ELEC1111 - Electrical & Telecommunications EngineeringDocument4 pagesRandom QUIZ 1 - S2 2008: ELEC1111 - Electrical & Telecommunications EngineeringuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 02b Series Parallel PDocument4 pagesElec1111 02b Series Parallel PuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 03 Node Voltage Analysis PDocument9 pagesElec1111 03 Node Voltage Analysis PuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 01c Intro KCL KVL Resistive CircuitsDocument5 pagesElec1111 01c Intro KCL KVL Resistive CircuitsuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 02a Power EnergyDocument3 pagesElec1111 02a Power EnergyuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- How Do You Feel About The Statement?Document2 pagesHow Do You Feel About The Statement?Juliet ThingsNo ratings yet
- Use of Magnetic Levitation For:: Wind TurbinesDocument20 pagesUse of Magnetic Levitation For:: Wind TurbinesPrathamesh SheteNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Analysis of Rooftop Solar Photovoltaic For Non-Academic Building in An Educational Institution in MalaysiaDocument10 pagesFeasibility Analysis of Rooftop Solar Photovoltaic For Non-Academic Building in An Educational Institution in MalaysiaXavier BrownNo ratings yet
- PPA Format - IndiaDocument54 pagesPPA Format - Indiavineets058No ratings yet
- Earth Day Statement From Mayor MorseDocument3 pagesEarth Day Statement From Mayor MorseAnonymous CQcIutoYNo ratings yet
- Cross-Flow Turbine - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesCross-Flow Turbine - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaArif NurjiyantoNo ratings yet
- Heat EquationDocument12 pagesHeat EquationMokhammad Sanpradipto JaluntoroNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy StorageDocument4 pagesFlywheel Energy Storagetzw101No ratings yet
- Student Worksheet of Electrochemical Cells: Name: . Grade XII Semester 1 Sma 1 Bae KudusDocument10 pagesStudent Worksheet of Electrochemical Cells: Name: . Grade XII Semester 1 Sma 1 Bae KudusAuliaNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Status 290716Document3 pagesCommissioning Status 290716bidyut100No ratings yet
- Role of Solar Farm in Power Factor Improvement of Grid Connected SystemDocument11 pagesRole of Solar Farm in Power Factor Improvement of Grid Connected SystemAyush Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- SETR 10: Sustainable Energy TechnologiesDocument11 pagesSETR 10: Sustainable Energy TechnologiesHoover InstitutionNo ratings yet
- Tensotherm MaterialDocument4 pagesTensotherm MaterialMirceaNo ratings yet
- PX7103-Analysis and Design of InvertersDocument8 pagesPX7103-Analysis and Design of InvertersGabriel SanthoshkumarNo ratings yet
- Sanyal Classification of Geothermal Systems 2005 PDFDocument8 pagesSanyal Classification of Geothermal Systems 2005 PDFLevi OktaNo ratings yet
- 3M AdMD - GB - Study - Solar Heat Reflective Paint Using 3M Glass BubblesDocument12 pages3M AdMD - GB - Study - Solar Heat Reflective Paint Using 3M Glass BubblesEdin Krdžalić EdoNo ratings yet
- Ee8703-Res Question Bank..Document11 pagesEe8703-Res Question Bank..kanakaraj0% (1)
- Centrifugal Fans For Air Handling UnitsDocument36 pagesCentrifugal Fans For Air Handling UnitsMarijan MartinovićNo ratings yet
- De SiltingDocument6 pagesDe Siltingtarang001No ratings yet
- CB434C Kebp0157-09Document610 pagesCB434C Kebp0157-09Jorge Andres Arias Pairazaman100% (4)
- Chapter 10 Rotation of Rigid BodyDocument22 pagesChapter 10 Rotation of Rigid BodylozzzzzNo ratings yet
- Vingcard Energy Control DeviceDocument2 pagesVingcard Energy Control DeviceJonathan LukmanNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy: Paper 2: Structured Questions Instructions: Answer The Following Questions. Section A 1Document4 pagesSources of Energy: Paper 2: Structured Questions Instructions: Answer The Following Questions. Section A 1Santhiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- BNBC-2006 WIND CalculationDocument7 pagesBNBC-2006 WIND CalculationJahidul Islam0% (1)
- Wave Energy in EuropeDocument27 pagesWave Energy in EuropeCognosferaNo ratings yet
- ABB Circit Breaker Trip CurveDocument1 pageABB Circit Breaker Trip CurvebjeserviceNo ratings yet
- Prof. H. SahaDocument48 pagesProf. H. SahaKuldip SinghNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument5 pagesBusiness PlanSheryl HernandezNo ratings yet