Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arthritis
Arthritis
Uploaded by
Sherley Meiske PakasiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arthritis
Arthritis
Uploaded by
Sherley Meiske PakasiCopyright:
Available Formats
Arthritis.
com
What is it ?
Rheumatoid arthritis (rue-ma-TOYD arth-write-tis) is a chronic disease, mainly characterized by inflammation of
the linin, or syno!ium, of the "oints. #t can lead to lon-term "oint damae, resultin in chronic $ain, loss of
function and disability.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) $roresses in three staes. The first stae is the swellin of the syno!ial linin, causin
$ain, warmth, stiffness, redness and swellin around the "oint. %econd is the ra$id di!ision and rowth of cells, or
$annus, which causes the syno!ium to thic&en. #n the third stae, the inflamed cells release enzymes that may diest
bone and cartilae, often causin the in!ol!ed "oint to lose its sha$e and alinment, more $ain, and loss of
mo!ement.
'ecause it is a chronic disease, RA continues indefinitely and may not o away. (re)uent flares in disease acti!ity
can occur. RA is a systemic disease, which means it can affect other orans in the body. *arly dianosis and
treatment of RA is critical if you want to continue li!in a $roducti!e lifestyle. %tudies ha!e shown that early
aressi!e treatment of RA can limit "oint damae, which in turn limits loss of mo!ement, decreased ability to wor&,
hiher medical costs and $otential surery.
RA affects +., million Americans. -urrently, the cause of RA is un&nown, althouh there are se!eral theories. And
while there is no cure, it is easier than e!er to control RA throuh the use of new drus, e.ercise, "oint $rotection
techni)ues and self-manaement techni)ues. /hile there is no ood time to ha!e rheumatoid arthritis, ad!ancements
in research and dru de!elo$ment mean that more $eo$le with RA are li!in ha$$ier, healthier and more fulfillin
li!es.
What causes it ?
The e.act cause of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) currently is un&nown. #n fact, there $robably isn0t an e.act cause for
RA. Researchers now are debatin whether RA is one disease or se!eral different diseases with common features.
Immune System
/e do &now that the body0s immune system $lays an im$ortant role in rheumatoid arthritis. #n fact, RA is referred to
as an autoimmune disease because $eo$le with RA ha!e an abnormal immune system res$onse.
#n a healthy immune system, white blood cells $roduce antibodies that $rotect the body aainst forein substances.
1eo$le who ha!e RA ha!e an immune system that mista&es the body0s healthy tissue for a forein in!ader and
attac&s it.
One e.am$le of this miscommunication in the body is &nown as rheumatoid factor. Rheumatoid factor is an
antibody that is directed to reulate normal antibodies made by the body. #t wor&s well in $eo$le with small
)uantities of rheumatoid factor. 1eo$le with hih le!els of rheumatoid factor, howe!er, may ha!e a malfunctionin
immune system. This is why your doctor often will re)uest a test measurin rheumatoid factor when tryin to
dianose RA. #n eneral, the hiher the le!el of rheumatoid factor $resent in the body, the more se!ere the disease
acti!ity is.
#t is im$ortant to note that not all $eo$le with RA ha!e an ele!ated rheumatoid factor and not all $eo$le with an
ele!ated rheumatoid factor ha!e RA. The test also can come out neati!e if it is done too early in the course of the
disease. A$$ro.imately 23 $ercent of $eo$le with RA will ha!e a neati!e rheumatoid factor test and some $eo$le
who don0t ha!e RA will test $ositi!e.
4earn more about the immune system.
Gender
/omen et rheumatoid arthritis two to three times more often then men and their RA ty$ically oes into remission
when they et $renant. /omen de!elo$ RA more often than e.$ected in the year after $renancy and sym$toms
can increase after a baby is born. These facts lead researchers to belie!e that ender miht $lay a role in the
de!elo$ment and $roression of RA. 5any are tryin to understand the effects female hormones miht ha!e in the
de!elo$ment of RA. -urrently, there are limited answers to these )uestions. (or more information on $renancy and
arthritis, see 1renancy 1ronoisis.
Genetics
5ost researchers belie!e there are enes in!ol!ed in the cause of RA. The s$ecific enetic mar&er associated with
RA, 64A-DR7, is found in more than two-thirds of -aucasians with RA while it is only found in 23 $ercent of the
eneral $o$ulation. /hile $eo$le with this mar&er ha!e an increased ris& of de!elo$in RA, it is not a dianostic
tool. 5any $eo$le who ha!e the mar&er either don0t ha!e or will ne!er et RA. /hile this mar&er can be $assed
from $arent to child, it is not definite that if you ha!e RA, your child will too. 4earn more about enetics and RA.
Infection
%ome $hysicians and scientists belie!e that RA is triered by a &ind of infection. There is currently no $roof of this.
Rheumatoid arthritis is not contaious, althouh it is $ossible that a erm to which almost e!eryone is e.$osed may
cause an abnormal reaction from the immune system in $eo$le who already carry a susce$tibility for RA.
What are the effect ?
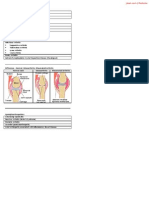
Rheumatoid arthritis can start in any "oint, but it most commonly beins in the smaller "oints of the finers, hands
and wrists. 8oint in!ol!ement is usually symmetrical, meanin that if a "oint hurts on the left hand, the same "oint
will hurt on the riht hand. #n eneral, more "oint erosion indicates more se!ere disease acti!ity.
Other common $hysical sym$toms include9
(atiue
%tiffness, $articularly in the mornin and when sittin for lon $eriods of time. Ty$ically, the loner the
mornin stiffness lasts, the more acti!e your disease is.
/ea&ness
(lu-li&e sym$toms, includin a low-rade fe!er
1ain associated with $roloned sittin
The occurrence of flares of disease acti!ity followed by remission or disease inacti!ity
Rheumatoid nodules, or lum$s of tissue under the s&in, a$$ear in about one-fifth of $eo$le with RA.
Ty$ically found on the elbows, they can indicate more se!ere disease acti!ity.
5uscle $ain
4oss of a$$etite, de$ression, weiht loss, anemia, cold and:or sweaty hands and feet
#n!ol!ement of the lands around the eyes and mouth, causin decreased $roduction of tears and sali!a
(%";ren0s syndrome)
Ad!anced chanes to loo& out for include damae to cartilae, tendons, liaments and bone, which causes deformity
and instability in the "oints. The damae can lead to limited rane of motion, resultin in daily tas&s (ras$in a for&,
combin hair, buttonin a shirt) becomin more difficult. You also may see s&in ulcers and a eneral decline in
health. 1eo$le with se!ere RA are more susce$tible to infection.
The effects of rheumatoid arthritis can !ary from $erson to $erson. #n fact, there is some rowin belief that RA isn0t
one disease, but it may be se!eral different diseases that share commonalities.
How is it diagnosed ?
Dianosin rheumatoid arthritis is a $rocess. There isn0t a sure-fire test that can tell you $ositi!ely that you ha!e
RA. #nstead your doctor relies on a number of tools to hel$ him determine the best treatment for your sym$toms.
A dianosis will be made from a medical history, a $hysical e.am, lab tests and <-rays.
Medical History
5edical history $robably is your doctor0s best tool for dianosin rheumatoid arthritis. The more your doctor &nows
about you, the faster and better he will be able to dianose your condition and determine the best treatment for you.
Ta&in a medical history is the first line to findin out if you ha!e rheumatoid arthritis. /hat you tell him will allow
him to determine if RA should be considered a $ossible dianosis or if he should loo& in another direction.
(ollowin is a list of )uestions your doctor miht as& in a medical history9
Do you ha!e "oint $ain in many "oints=
Does the $ain occur symmetrically > that is, do the same "oints on both sides of your body hurt at the same
time= Or is the $ain one-sided=
Do you ha!e stiffness in the mornin=
/hen is the $ain most se!ere=
Do you ha!e $ain in your hands, wrists and:or feet=
#f you ha!e $ain in your hands, which "oints hurt the most=
6a!e you had $eriods of feelin wea& and uncomfortable all o!er= Do you feel fatiued=
You may ha!e to answer these )uestions at e!ery office !isit so your doctor can best e!aluate your $ain and
functionality status. You also miht find yourself ta&in a self-re$ort )uestionnaire. These are de!elo$ed to hel$ the
doctor assess the im$act of RA on your daily life. Two of the most common are the 6ealth Assessment
?uestionnaire (6A?) and the Arthritis #m$act 5easurement %cales (A#5%).
Physical Exam
Your doctor also will $erform a $hysical e.am to determine dianosis and at most followin office !isits. 6e will be
loo&in for common features re$orted in RA, includin9
8oint swellin
8oint tenderness
4oss of motion in your "oints
8oint malalinment
%ins of rheumatoid arthritis in other orans, includin your s&in, luns and eyes.
Lab ests
/hile there is no one test to confirm whether or not you ha!e rheumatoid arthritis, your doctor may use se!eral
different tests and imain studies to hel$ ma&e a dianosis. The most commonly used tests are listed below, but not
all doctors will use e!ery test and some may use tests not described. You should feel free to fully )uestion your
doctor for any tests he or she orders so you understand what it is measurin and why. 5ost tests ordered to hel$ with
dianosis will only ha!e to be ta&en once. Tests desined to measure im$ro!ement or to chec& for dru side effects
may need to be re$eated reularly. (or additional information about lab tests, !isit @uide to 4ab Tests.
!om"lete #lood !ount
There are three ty$es of cells in your blood9 red blood cells, which carry o.yen to tissuesA white blood cells, which
hel$ fiht infectionsA and $latelets, which hel$ the blood clot. *ach may be tested to chec& for abnormalities that
miht e.ist or to monitor side effects of drus and chec& $roress.
1eo$le with rheumatoid arthritis often ha!e a low red blood count, sinally anemia, a common $roblem for $eo$le
with RA. Anemia can contribute to feelins of fatiue. 1eo$le with more aressi!e disease tend to ha!e more
se!ere anemia.
/hite blood cells may be hih, sinalin that infection is $resent in your body. A low white blood cell count could
suest (elty0s syndrome, a com$lication of RA, or may be caused by some medications.
Your $latelet count is ele!ated when you ha!e inflammation $resent in the body. #t can also be lowered by certain
drus.
#f you ta&e nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drus (B%A#Ds), your $latelet and white blood cell count will be
monitored e!ery si. months. 1eo$le ta&in disease-modifyin antirhuematic drus (D5ARDs), will be chec&ed
e!ery two to +2 wee&s.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation $ate %ES$ or sed rate&
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (*%R) measures the s$eed at which red blood cells fall to the bottom of a test
tube. The more ra$idly your red blood cells dro$, the more inflammation is $resent in the body. A hih sed rate
indicates inflammation and the hiher it is, the more se!ere the RA is. Your sed rate will be chec&ed fre)uently to
see if treatment is wor&in successfully.
You should note that only about C3 $ercent $eo$le with RA ha!e an ele!ated sed rate. 'ecause your treatment is
based $rimarily on clinical sym$toms, a normal sed rate doesn0t mean that you are cured and no loner need
treatment for RA.
!'$eacti(e Protein
--reacti!e $rotein (-R1) is found in the body and is ele!ated when inflammation is found in the body. The hiher
the le!el of -R1 the more disease acti!ity is in!ol!ed. Althouh *%R and -R1 reflect similar derees of
inflammation, sometimes one will be raised when the other isn0t. This test may be re$eated reularly to monitor your
inflammation and your res$onse to medication.
$heumatoid )actor
A$$ro.imately D3 to E3 $ercent of $eo$le with rheumatoid factor (R() also ha!e rheumatoid arthritis. #t is tested by
measurin the amount of R( in your body. The hiher the amount of R6 $resent in the body, the more acti!e and
se!ere your disease is.
%ome $eo$le with RA do not ha!e R( in their blood. They are called Fseroneati!e.G 1eo$le with R( in there blood
are called Fsero$ositi!e.G
*ntinuclear *ntibodies %*+*&
This test detects a rou$ of autoantibodies (antibodies aainst self), which is seen in about ,3 to 73 $ercent of $eo$le
with RA. Althouh it commonly is used as a screenin tool, ABA testin isnHt used as a dianostic tool because
many $eo$le without RA or with other diseases can ha!e ABAs.
ImagingStudies
$adiogra"hs %,'rays&
Your doctor may ta&e <-rays of your bones and "oints u$on dianosis with RA to $ro!ide a !aluable baseline for
com$arison with later <-rays. They show the swellin of the soft tissues and the loss of bone density around the
"oints > the result of your reduced acti!ity and inflammation. As your disease $roresses, your <-rays can show
small holes or erosions near the ends of bone s and narrowin of the "oint s$ace due to loss of cartilae. Doctors
used to wait until the a$$earance of erosion before beinnin aressi!e treatment of RA. Bow it is widely belie!ed
that it is better to treat aressi!ely before the de!elo$ment of erosion.
Magnetic $esonance Imaging %M$I&
A 5R# can detect early inflammation before it is !isible on an <-ray, and are $articularly ood at $in$ointin
syno!itis (inflammation of the linin of the "oint)
-oint .ltrasound
8oint ultrasound is a much less e.$ensi!e way to loo& for "oint inflammation before <-rays show damae. Althouh
not currently used often, this $rocedure may ain wider use o!er the ne.t few years as doctors increase their efforts
to document early e!idence of the disease.
#one /ensitometry %/E,*&
'one densitometry is an im$ortant imain study for measurin bone density, used $rimarily to detect osteo$orosis.
Osteo$orosis may be es$ecially se!ere in $eo$le with RA due to "oint immobilization, the inflammatory res$onse
itself and the use of certain thera$ies (such as lucocorticoids) that may hasten bone loss. %ome doctors suest that
a bone density test should be $art of the e!aluation and monitorin of all $eo$le with RA, $articularly for women
after meno$ause.
reatment o"tions
'ecause rheumatoid arthritis $resents itself on many different fronts and in many different ways, treatment must be
tailored to the indi!idual, ta&in into account the se!erity of your arthritis, other medical conditions you may ha!e
and your indi!idual lifestyle. -urrent treatment methods focus on relie!in $ain, reducin inflammation, sto$$in or
slowin "oint damae and im$ro!in your functionin and sense of well-bein.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a serious disease. #t is crucial that you et an early dianosis and wor& with your doctor to
find the best treatment for you so that you can li!e well with it. 8ust a few years ao, your doctor miht ha!e only
$rescribed an o!er-the-counter $ain relie!er, li&e an analesic or non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory dru (B%A#D),
until you e.$erienced increased disease $roression. Bow, with the im$ro!ement of a!ailable medications, doctors
&now that they ha!e to be more aressi!e early on in order to $re!ent se!ere deformity and "oint erosion.
Health'!are Professionals
#n order to et the $ro$er treatment for RA, you need to ma&e sure you ha!e the $ro$er health-care team. Your
$rimary doctor for treatin RA should be a rheumatoloist (ROO-ma-tall-o-"ist), a $hysician with s$ecial trainin in
arthritis and other disease in!ol!in diseases of the bone, muscles and "oints. Your rheumatoloist will coordinate
with your $rimary care $hysician. Other team members may include a $hysical thera$ist, an occu$ational thera$ist, a
nurse, a $sycholoist, an ortho$aedic sureon, a $hysiatrist, and a social wor&er. 4earn more about these s$ecialists
in the @lossary of 6ealth 1rofessionals.
Medications
The $ro$er medication reimen is im$ortant in controllin your RA. You must hel$ your doctor determine the best
combination for you. The main cateories of drus used to treat RA are9
+onsteroidal *nti'Inflammatory /rugs %+S*I/s& > These drus are used to reduce inflammation and
relie!e $ain. These are medications such as as$irin, ibu$rofen, indomethacin and -O<-2 inhibitors such as
!aldeco.ib and celeco.ib.
*nalgesic /rugs > These drus relie!e $ain, but don0t necessarily ha!e an effect on inflammation.
*.am$les of these medications are acetamino$hen, $ro$o.y$hene, me$eidine and mor$hine.
Glucocorticoids or Prednisone > These are $rescribed in low maintenance doses to slow "oint damae
caused by inflammation.
/isease Modifying *ntirheumatic /rugs %/M*$/s& > These are used with B%A#Ds and:or $rednisone
to slow "oint destruction caused by RA o!er time. *.am$les of these drus are methotre.ate, in"ectable old,
$enicillamine, azathio$rine, chloro)uine, hydro.ychloro)uine, sulfasalazine and oral old.
#iologic $es"onse Modifiers > These drus directly modify the immune system by inhibitin $roteins
called cyto&ines, which contribute to inflammation. *.am$les of these are abatace$t, etanerce$t, infli.imab,
adaliumumab and ana&inra.
Protein'* Immuoadsor"tion hera"y > This is not a dru, but a thera$y that filters your blood to remo!e
antibodies and immune com$le.es that $romote inflammation.
D5ARDs, $articularly methotre.ate, ha!e been the standard for aressi!ely treatin RA. Recently, studies ha!e
shown that the most aressi!e treatment for controllin RA may be the combination of methotre.ate and another
dru, $articularly bioloic res$onse modifiers. The dual dru treatment seems to create a more effecti!e treatment,
es$ecially for $eo$le who may not ha!e success with or who ha!e built u$ a resistance to, methotre.ate or another
dru alone. Doctors now are $rescribin combination dru thera$y more often and studies continue. #t a$$ears that
these combination dru thera$ies miht become the new road to follow in treatin RA. 6ere are some medications
your doctor may suest you combine with methotre.ate9 lefluonomide (Ara!a), etanerce$t (*nbrel), adalimumab
(6umira) and infli.imab (Remicade).
(or more information on these drus, !isit the Dru @uide.
Surgery
5any $eo$le with rheumatoid arthritis miht consider surery as $art of their treatment $lan. The surical o$tions
a!ailable today can contribute reatly to im$ro!in your )uality of life with RA. The followin are different surical
o$tions a!ailable to $eo$le with RA. (or more in-de$th information, !isit the %urery -enter.
Syno(ectomy > /hen one or two "oints are affected more se!erely than others, this $rocedure is used to reduce the
amount of inflammatory tissue by remo!in the diseased syno!ium or linin of the "oint. #t may result in less
swellin and $ain and the slowin or $re!ention of further "oint damae.
*rthrosco"ic Surgery > #n this $rocedure, the sureon inserts a !ery thin tube with a liht at the end into the "oint
throuh a small incision. #t is connected to a closed-circuit tele!ision and allows the sureon to see the e.tent of the
damae in the "oint. Once there, the doctor can ta&e tissue sam$les, remo!e loose cartilae, re$air tears, smooth a
rouh surface or remo!e diseased syno!ial tissue. #t is most commonly $erformed on the &nee and shoulder.
0steotomy > 4iterally meanin, Fto cut bone,G this $rocedure is used to increase stability by redistributin the
weiht on the "oint. Osteotomy isn0t often used with RA because there are other o$tions a!ailable besides cuttin the
bones.
-oint $e"lacement Surgery or *rthro"lasty - This is the surical reconstruction or re$lacement of a "oint.
%uccessfully used to hel$ $eo$le who otherwise miht be in a wheelchair, "oint re$lacement surery in!ol!es the
remo!al of the "oint, resurfacin and relinin of the ends of bones and re$lacin the "oint with a man-made
com$onent. This $rocedure is usually recommended for $eo$le o!er I3 or who ha!e se!ere disease $roression.
Ty$ically a new "oint will last between 23 and ,3 years.
*rthrodesis or fusion > This $rocedure fuses two bones toether. /hile it limits mo!ement, it does decrease $ain
and increase stability of the "oints in the an&les, wrists, finers, toes and s$ine.
L*# ES
Ma1ing a /iagnosis
/hile lab tests aren0t needed for e!ery form of arthritis, they are !ery im$ortant to !erify and confirm the $resence
of some diseases, accordin to Robert 4ahita, 5D, chief of rheumatoloy at %t. 4u&e0s:Roose!elt 6os$ital and
associate $rofessor of medicine at -olumbia Jni!ersity. #f your sym$toms and $hysical e.amination
suest rheumatoid arthritis, lu$us, %"oren0s syndrome, 4yme disease or one of a few other inflammatory forms of
arthritis, the followin tests can often confirm your doctor0s sus$icions9
*ntinuclear antibody %*+*& 2 -ommonly found in the blood of $eo$le who ha!e lu$us, ABAs (abnormal
antibodies directed aainst the cells0 nuclei) can also suest the $resence of $olymyositis, scleroderma, %"oren0s
syndrome, mi.ed connecti!e tissue disease or rheumatoid arthritis. Tests to detect s$ecific subsets of these
antibodies can be used to confirm the dianosis of a $articular disease or form of arthritis.
$heumatoid factor %$)& 2 Desined to detect and measure the le!el of an antibody that acts aainst the blood
com$onent amma lobulin, this test is often $ositi!e in $eo$le with rheumatoid arthritis.
.ric acid 2 'y measurin the le!el of uric acid in the blood, this test hel$s doctors dianose out, a condition that
occurs when e.cess uric acid crystallizes and forms de$osits in the "oints and other tissues, causin inflammation
and se!ere $ain.
HL* tissue ty"ing 2 This test, which detects the $resence of certain enetic mar&ers in the blood, can often confirm
a dianosis of an&ylosin s$ondylitis (a disease in!ol!in inflammation of the s$ine and sacroiliac "oint) or Reiter0s
syndrome (a disease in!ol!in inflammation of the urethra, eyes and "oints). The enetic mar&er 64A-'2D is almost
always $resent in $eo$le with either of these diseases.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 2 Also called *%R or Fsed rate,G this test measures how fast red blood cells clin
toether, fall and settle (li&e sediment) in the bottom of a lass tube o!er the course of an hour. The hiher the rate,
the reater the amount of inflammation.
Lyme serology 2 This test detects an immune res$onse to the infectious aent that causes 4yme disease and thus can
be used to confirm a dianosis of the disease.
S1in bio"sy 2 Ta&in small sam$les of s&in and e.aminin them under a microsco$e can hel$ doctors dianose
forms of arthritis that in!ol!e the s&in, such as lu$us, !asculitis (inflammation of the blood !essels) and $soriatic
arthritis.
Muscle bio"sy 2 'y oin a little dee$er into the tissue than with the s&in bio$sy, the sureon can ta&e a sam$le of
muscle to be e.amined for sins of damae to the muscle fibers. (indins can confirm a dianosis of $olymyositis
or !asculitis.
-oint fluid tests > #n this $rocedure, which is similar to drawin blood, the doctor inserts a needle into a "oint s$ace
and remo!es fluid. An e.amination of the fluid may re!eal uric acid crystals, confirmin a dianosis of out or
bacteria, suestin that the "oint inflammation is caused by infection.
WI3IPE/I*
*rthritis (from @ree& arthro-, "oint K -itis, inflammationA $lural9 arthritides) is a rou$ of conditions in!ol!in
damae to the "oints of the body.
There are o!er +33 different forms of arthritis
L+ML2M
. The most common form,osteoarthritis (deenerati!e "oint disease)
is a result of trauma to the "oint, infection of the "oint, or ae. Other arthritis forms are rheumatoid arthritis,$soriatic
arthritis, and related autoimmune diseases in which the body attac&s itself. %e$tic arthritis is caused by
"oint infection.
The ma"or com$laint by indi!iduals who ha!e arthritis is $ain. 1ain is often a constant and daily feature of the
disease. The $ain may be localized to thebac&, nec&, hi$, &nee or feet. The $ain from arthritis occurs due
to inflammationthat occurs around the "oint, damae to the "oint from disease, daily wear and tear of "oint,
muscles strains caused by forceful mo!ements aainst stiff, $ainful "oints and fatiue. The most im$ortant factor in
treatment is to understand the disorder and find ways to o!ercome the obstacles which $re!ent $hysical e.ercise.
!lassification
1rimary forms of arthritis9
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
%e$tic arthritis
@out and $seudo-out
8u!enile idio$athic arthritis
%tillHs disease
An&ylosin s$ondylitis
%econdary to other diseases9
*hlers-Danlos %yndrome
%arcoidosis
6enoch-%ch;nlein $ur$ura
1soriatic arthritis
Reacti!e arthritis
6aemochromatosis
6e$atitis
/eenerHs ranulomatosis (and many other !asculitis syndromes)
4yme disease
(amilial 5editerranean fe!er
6y$erimmunolobulinemia D with recurrent fe!er
TB( rece$tor associated $eriodic syndrome
#nflammatory bowel disease (#ncludin -rohnHs Disease and Jlcerati!e -olitis)
Diseases that can mimic arthritis include9
6y$ertro$hic osteoarthro$athy (nail clubbin)
5ulti$le myeloma
Osteo$orosis
(ifth disease ($ar!o!irus infection)
4edit5$heumatoid *rthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disorder where, for some un&nown reason, the bodyHs own immune system starts to attac&
body tissues. The attac& is not only directed at the "oint but to many other $arts of the body. #n rheumatoid arthritis,
most damae occurs to the "oint linin andcartilae which e!entually results in erosion of two o$$osin bones.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects "oints in the finers, wrists, &nees and elbows. The disease is symmetrical and can lead
to se!ere deformity in a few years if not treated. Rheumatoid arthritis occurs mostly in $eo$le aed 23 and abo!e. #n
children, the disorder can $resent with a s&in rash, fe!er, $ain, disability, and limitations in daily acti!ities. Bo one
&nows why rheumatoid arthritis occurs and all treatments are focused on easin the sym$toms. /ith earlier
dianosis and aressi!e treatment, many indi!iduals can lead a decent )uality of life. The drus to treat rheumatoid
arthritis rane from corticosteroids to monoclonal antibodies i!en intra!enously. The latest drus
li&e Remicade can sinificantly im$ro!e )uality of life in the short term. #n rare cases, surery may be re)uired to
re$lace "oints but there is no cure for the illness.
L,M
Rheumatic fe!er has now seen resurence in America $rimarily because of mass immiration of $eo$le from
de!elo$in countries
Lcitation neededM
. The disorder can $resent with a miratory nature of arthritis with many other
features li&e heart $roblems, s&in rash,ait abnormality and s&in nodules.
4edit50steoarthritis
Jnli&e rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis can affect both the larer and the smaller "oints of the body, includin the
hands, feet, bac&, hi$ or &nee. The disease is essentially one ac)uired from daily wear and tear of the "oint.
Osteoarthritis beins in the cartilae and e!entually leads to the two o$$osin bones erodin into each other.
#nitially, the condition starts with minor $ain while wal&in but soon the $ain can be continuous and e!en occur at
niht. The $ain can be debilitatin and $re!ent one from doin any ty$e of acti!ity. Osteoarthritis ty$ically affects
the weiht bearin "oints li&e the bac&, s$ine and $el!is. Jnli&e rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis is a disease of the
elderly. 5ore than ,3 $ercent of females ha!e some deree of osteoarthritis by ae CI.
$is1 factors for osteoarthritis6
1rior "oint trauma
Obesity
Re$etiti!e "oint use
%edentary lifestyle
Osteoarthritis, li&e rheumatoid arthritis, cannot be cured but one can $re!ent the condition from worsenin. /eiht
loss is the &ey to im$ro!in sym$toms and $re!entin $roression. 1hysical thera$y to strenthen muscles and
"oints is !ery hel$ful. 1ain medications are widely re)uired by indi!iduals with osteoarthritis. /hen the disease is
far ad!anced and the $ain is continuous, surery may be an o$tion. Jnli&e rheumatoid arthritis, "oint re$lacement
does hel$ many indi!iduals with osteoarthritis.
L7M
4edit5Lu"us
This is a common collaen !ascular disorder that can be $resent with se!ere arthritis. Other features of lu$us include
a s&in rash, e.treme$hotosensiti!ity, hair loss, &idney $roblems, emotional lability, lun fibrosis and constant "oint
$ain.
LIM
4edit5Gout
@out is caused by de$osition of uric acid crystals in the "oint, causin inflammation. There is also an uncommon
form of outy arthritis caused by the formation of rhomboid crystals of calcium $yro$hos$hate. This out is &nown
as $seudoout. #n the early staes, the outy arthritis usually occur in one "oint, but with time, it can occur in many
"oints and be )uite cri$$lin. The "oints in out can often become swollen and lose function.
LCM
4edit50ther
#nfectious arthritis is another se!ere form of arthritis. #t $resents with sudden onset of chills, fe!er and "oint $ain.
The condition is caused by bacteria elsewhere in the body. #nfectious arthritis must be ra$idly dianosed and treated
$rom$tly to $re!ent irre!ersible and $ermanent "oint damae.
LDM
1soriasis is another ty$e of arthritis. /ith $soriasis, most indi!iduals de!elo$ the s&in $roblem first and then the
arthritis. The ty$ical features are of continuous "oint $ains, stiffness and swellin. The disease does recur with
$eriods of remission but there is no cure for the disorder. A small $ercentae de!elo$ a se!ere $ainful and
destructi!e form of arthritis which destroys the small "oint in the hands and can lead to $ermanent disability and loss
of hand function
LEM
4edit5Signs and sym"toms
Reardless of the ty$e of arthritis, the common sym$toms for all arthritis disorders include !aried le!els of
$ain, swellin, "oint stiffness and sometimes a constant ache around the "oint(s). Arthritic disorders li&e lu$us and
rheumatoid can also affect other orans in the body with a !ariety of sym$toms.
LNM
#nability to use the hand or wal&
5alaise and a feelin of tiredness
(e!er
/eiht loss
1oor slee$
5uscle aches and $ains
Tenderness
Difficulty mo!in the "oint
#t is common in ad!anced arthritis for sinificant secondary chanes to occur. (or e.am$le, in someone who has
limited their $hysical acti!ity9
5uscle wea&ness
4oss of fle.ibility
Decreased aerobic fitness
These chanes can also im$act on life and social roles, such as community in!ol!ement.
4edit5/isability
Arthritis is the most common cause of disability in the J%A. 5ore than 23 million indi!iduals with arthritis ha!e
se!ere limitations in function on a daily basis. Absenteeism and fre)uent !isits to the $hysician are common in
indi!iduals who ha!e arthritis. Arthritis ma&es it !ery difficult for indi!iduals to be $hysically acti!e and soon
become home bound.
L+3M
#t is estimated that the total cost of arthritis cases is close to O+33 billion of which nearly I3P accounts from lost
earnins. *ach year, arthritis results in nearly + million hos$italizations and close to 7I million out$atient !isits
to health care centers.
L++M
Arthritis ma&es it !ery difficult for the indi!idual to remain $hysically acti!e. 5any indi!iduals who ha!e arthritis
also suffer from obesity, hihcholesterol or ha!e heart disease. #ndi!iduals with arthritis also become de$ressed and
ha!e fear of worsenin sym$toms.
4edit5/iagnosis
Dianosis is made by clinical e.amination from an a$$ro$riate health $rofessional, and may be su$$orted by other
tests such as radioloy and blood tests, de$endin on the ty$e of sus$ected arthritis. All arthritides $otentially
feature $ain. 1ain $atterns may differ de$endin on the arthritides and the location. Rheumatoid arthritis is enerally
worse in the mornin and associated with stiffnessA in the early staes, $atients often ha!e no sym$toms after a
mornin shower. Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, tends to be worse after e.ercise. #n the aed and children, $ain
miht not be the main $resentin featureA the aed $atient sim$ly mo!es less, the infantile $atient refuses to use the
affected limb.
*lements of the history of the disorder uide dianosis. #m$ortant features are s$eed and time of onset, $attern of
"oint in!ol!ement, symmetry of sym$toms, early mornin stiffness, tenderness, ellin or loc&in with inacti!ity,
ara!atin and relie!in factors, and other systemic sym$toms. 1hysical e.amination may confirm the dianosis,
or may indicate systemic disease. Radiora$hs are often used to follow $roression or hel$ assess se!erity.
4edit5Pre(ention
/hile neither Rheumatoid arthritis nor osteoarthritis can be com$letely $re!ented, one can reduce the ris&s by
becomin $hysically acti!e, $artici$atin in $hysical thera$y, losin weiht and eatin healthily. All indi!iduals who
ha!e $ain in the "oints should see& early dianosis because the earlier the treatment is started, the better is
the $ronosis.
4edit5reatment
Once the dianosis of arthritis is made, treatments are a!ailable for a !ariety of sym$toms. There is no cure for
either rheumatoid or osteoarthritis.
Treatment o$tions !ary de$endin on the ty$e of arthritis and include $hysical thera$y, lifestyle chanes (includin
e.ercise and weiht control), ortho$edic bracin, medications, and dietary su$$lements (sym$tomatic or tareted at
the disease $rocess causin the arthritis).Arthro$lasty ("oint re$lacement surery) may be re)uired in erodin forms
of arthritis. 5edications can hel$ reduce inflammation in the "oint which decreases $ain. 5oreo!er, by decreasin
inflammation, the "oint damae is slowed.
L+2M
#n eneral, studies ha!e shown that $hysical e.ercise of the affected "oint can ha!e noticeable im$ro!ement in terms
of lon-term $ain relief. (urthermore, e.ercise of the arthritic "oint is encouraed to maintain the health of the
$articular "oint and the o!erall body of the $erson.
L+,M
4edit5Physical hera"y
#ndi!iduals with arthritis can definitely benefit from both $hysical and occu$ational thera$y. #n arthritis the "oints
become stiff and the rane of mo!ement can be limited. 1hysical thera$y has been shown to sinificantly im$ro!e
function, decrease $ain, and delay need for surical inter!ention in ad!anced cases
L+7M
. *.ercise $rescribed by a
$hysical thera$ist has been shown to be more effecti!e than medications in treatin osteoarthritis of the &nee.
*.ercise often focusses on im$ro!in muscle strenth, endurance and fle.ibility. #n some cases, e.ercises may be
desined to train balance. Occu$ational thera$y can teach you how to reduce stress on your "oint from daily li!in
acti!ities. Occu$ation thera$y can also teach you how to modify your home and wor& en!ironment so that you do
reduce mo!ements that may worsen your arthritis. There are also assist de!ices a!ailable that can hel$ you dri!e,
ettin a bath, dressin and also in house&ee$in labors.
As well as e.ercise, $hysical thera$y may include education about modifyin acti!ities, and other self-manaement
s&ills such as usin ice or heat, and ultrasound. 1hysical thera$ists will routinely educate $atients to manae their
$roblems related to arthritis themsel!es. Other as$ects of $hysical thera$y means learnin how to maintain ood
$osture, conser!in enery by allowin rest before and after acti!ity.
Occu$ational thera$y can hel$ you do e!eryday acti!ities without worsenin $ain or causin "oint damae. The
techni)ues can hel$ you distribute $ressures to minimize stress on any one "oint. /ays to accom$lish daily li!in
tas&s are made easier.
L+IM
4edit5Medications
1hysicians usually start with drus which ha!e the fewest side effects and shift to stroner medications as the
disease $roresses.
L+CM
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (B%A#Ds) are usually the drus of first choice. These drus hel$ decrease
inflammation and reduce $ain. O!er the counter medications li&e #bu$rofen or Ale!e do hel$ but most $eo$le
re)uire stroner $rescri$tion $ain&illers li&e -elebre. ortramadol. /hile these drus are effecti!e, they are also
associated with a !ariety of side effects li&e abdominal $ain, bleedin, ulcers, li!er and &idney damae. Bon
steroidal anti inflammatory drus should not be used for $roloned $eriods without $ro$er $hysician su$er!ision.
L+DM
Corticosteroids are fre)uently $rescribed for indi!iduals with arthritis. These $otent drus can hel$ reduce
inflammation and slow down "oint damae. 6owe!er, corticosteroids ha!e $otent side effects which rane from
ulcer, s&in bruisin, weiht ain, cataracts, bone thinnin,diabetes and hy$ertension. -orticosteroids are usually
i!en for a short time to hel$ reduce acute sym$toms.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (D5ARDs) can hel$ slow down $roression of rheumatoid arthritis and
"oint damae. The most common D5ARDs include methotre.ate (Rheumatre.,
Tre.all), leflunomide (Ara!a), hydro.ychloro)uine (1la)uenil), sulfasalazine (Azulfidine)
and minocycline (Dynacin, 5inocin). All these drus ha!e side effects which include li!er damae, bone marrow
su$$ression and $ossibility of o$$ortunistic infections.
Immunosuppressants li&e cyclos$orine and cyclo$hos$hamide su$$ress $otent cells of the body and hel$ decrease
the inflammation. These medications do hel$ treat se!ere arthritis but also ma&e one $rone to infections.
Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors ha!e been shown to reduce inflammation, $ain, mornin stiffness and swellin of
"oints. Drus li&e etanerce$t(*nbrel), infli.imab (Remicade) and adalimumab (6umira) can sinificantly im$ro!e
)uality of life. The most common side effects from these drus include $ain at site of in"ection, heart failure and
increased ris& of infection.
L+EM
You might also like
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument24 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisJeanessa Delantar QuilisadioNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis & GoutDocument51 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis & GoutКеиNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis of Data With Report WritingDocument16 pagesStatistical Analysis of Data With Report WritingUsmansiddiq1100% (1)
- ArthritisDocument7 pagesArthritisGerardLum100% (1)
- OsteoarthritisDocument4 pagesOsteoarthritisDharti PatelNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument17 pagesOsteoarthritisNishaThakuri100% (1)
- Osteoarthritis in The Geriatric Population 1Document7 pagesOsteoarthritis in The Geriatric Population 1api-532703094No ratings yet
- Arthritis: By: Charmaine BaniquedDocument106 pagesArthritis: By: Charmaine BaniquedGemgem Acosta100% (1)
- Psoriatic ArthritisDocument12 pagesPsoriatic ArthritisSelvia RosadiNo ratings yet
- What Is PolymyositisDocument24 pagesWhat Is PolymyositisAshraf MobyNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs OsteoarthritisDocument10 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis Vs OsteoarthritisPratyusha100% (1)
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument6 pagesCardiovascular DiseaseDominique Excelsis J. DegamoNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument25 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisGandung PrakosoNo ratings yet
- Arthritis PPT For ClassDocument62 pagesArthritis PPT For ClassMayank Sarie100% (3)
- Diabetic NeuropathyDocument4 pagesDiabetic NeuropathyAsish GeiorgeNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument8 pagesJuvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisDhanNie CenitaNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument2 pagesParkinsongoyaNo ratings yet
- Substance Use DisorderDocument7 pagesSubstance Use DisorderSora HeartsNo ratings yet
- Irogue Seminar Presentation October 2010Document186 pagesIrogue Seminar Presentation October 2010Kennedy Eghosa Irogue100% (2)
- Treatment and Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument32 pagesTreatment and Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisamirthaNo ratings yet
- Artery Bypass GraftDocument3 pagesArtery Bypass GraftJasmine ChuaNo ratings yet
- Arthritis PowerpointDocument25 pagesArthritis PowerpointDanette PriceNo ratings yet
- Acute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDDocument49 pagesAcute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDHendraDarmawanNo ratings yet
- Buerger'S Disease: By: Ns. Yulia Prodi S1 Keperawatan Stikes Kepanjen 2014Document18 pagesBuerger'S Disease: By: Ns. Yulia Prodi S1 Keperawatan Stikes Kepanjen 2014atik mayasariNo ratings yet
- Arthritis PDFDocument3 pagesArthritis PDFMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument5 pagesOsteoarthritisRobby Dwitria MaulanaNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument25 pagesArthritisJan Jamison ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- EndocarditisDocument24 pagesEndocarditisamyNo ratings yet
- Parkinson - S DiseaseDocument3 pagesParkinson - S Diseaseapi-3822433No ratings yet
- Psoriatic ArthritisDocument33 pagesPsoriatic Arthritisini_etuk100% (1)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Hozan Jaza MSC Clinical Pharmacy College of Pharmacy 2/ 11/ 2020Document54 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: Hozan Jaza MSC Clinical Pharmacy College of Pharmacy 2/ 11/ 2020Alan K Mhamad100% (1)
- StrokeDocument19 pagesStrokesridhar100% (4)
- EmphysemaDocument21 pagesEmphysemaEdmund RufinoNo ratings yet
- Motor Neuron DiseaseDocument8 pagesMotor Neuron DiseaseyigoNo ratings yet
- Bells PalsyDocument18 pagesBells PalsyDr AnandNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Cad2Document182 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Cad2Mamot Mot0% (1)
- Multiple Sclerosis: Case Study by Trcoski ElenaDocument43 pagesMultiple Sclerosis: Case Study by Trcoski ElenaElena TrcoskiNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar InfarctionDocument23 pagesCerebellar InfarctionShane LuyNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Arterial Occlusive DiseaseDocument4 pagesPeripheral Arterial Occlusive Diseasekrisfred14100% (1)
- The Lower Respiratory Tract Infection: Pneumonia: Ida Bagus Ngurah RaiDocument32 pagesThe Lower Respiratory Tract Infection: Pneumonia: Ida Bagus Ngurah RaiFelicia adeline ChristianNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument23 pagesColorectal Cancerralph_gail100% (1)
- Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument39 pagesAlzheimer's DiseaseLex CramerNo ratings yet
- A. I. II. Iii. IV. V. B. I. II. B. I. II. Iii. IV. V. VI. Vii. B. I. II. Iii. IV. ADocument39 pagesA. I. II. Iii. IV. V. B. I. II. B. I. II. Iii. IV. V. VI. Vii. B. I. II. Iii. IV. AmarkkkkkkkheeessNo ratings yet
- Parkinson - S Disease Case PresentationDocument39 pagesParkinson - S Disease Case PresentationAnonymous dpxYTE0% (1)
- Case Study On Seizure Disorder On InfantsDocument6 pagesCase Study On Seizure Disorder On InfantsarturogarcesjrNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument36 pagesPeripheral Vascular DiseaseKeishla M Rios CardonaNo ratings yet
- Normal Laboratory ValuesDocument5 pagesNormal Laboratory ValuesensooooooooooNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular Disease - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesPeripheral Vascular Disease - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDr. Mohammed AbdulWahab AlKhateebNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument7 pagesOsteoporosisLorebell100% (2)
- Hyponatremia: Presenter: DR Arun Karmakar Moderator: Prof. N. SharatkumarDocument50 pagesHyponatremia: Presenter: DR Arun Karmakar Moderator: Prof. N. SharatkumarLyra FebriandaNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Chinwon Rim Department of Chemistry Southern Methodist UniversityDocument18 pagesIrritable Bowel Syndrome: Chinwon Rim Department of Chemistry Southern Methodist UniversityAviation MedicineNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy in Skin Conditions: A.Thangamani RamalingamDocument17 pagesPhysiotherapy in Skin Conditions: A.Thangamani Ramalingamakheel ahammedNo ratings yet
- Cad ....Document94 pagesCad ....AnanthibalaNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandNephrotic Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Synovial Chondromatosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSynovial Chondromatosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Transient Ischemic Attack, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandTransient Ischemic Attack, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ebstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandEbstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument6 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisSumaya M. DagalangitNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic ArtheritiesDocument10 pagesRheumatic Artheritiessen_subhasis_58No ratings yet
- 1st August (Porifera)Document7 pages1st August (Porifera)tayyabuetlhrNo ratings yet
- Instructional Module and Its Components (Guide) : Course Ccs 3 Developer and Their BackgroundDocument7 pagesInstructional Module and Its Components (Guide) : Course Ccs 3 Developer and Their BackgroundAhljairo TerradoNo ratings yet
- Wearable 2D Ring Scanner: FeaturesDocument2 pagesWearable 2D Ring Scanner: FeaturesYesica SantamariaNo ratings yet
- Habib Ur Rehman (049) & Shahab MughalDocument7 pagesHabib Ur Rehman (049) & Shahab MughalHabib ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- PTR 38Document23 pagesPTR 38CyNo ratings yet
- BELBIN Team Role Summary DescriptionsDocument1 pageBELBIN Team Role Summary DescriptionsashairwaysNo ratings yet
- Product Design Development - Electronic Engineering (MCQ) Questions & AnswersDocument4 pagesProduct Design Development - Electronic Engineering (MCQ) Questions & AnswersAnkit SinghNo ratings yet
- Desk Guide - Ag and Food Careers in Pennsylvania - FINALDocument121 pagesDesk Guide - Ag and Food Careers in Pennsylvania - FINALKuhnNo ratings yet
- Browning 2020 EN PDFDocument142 pagesBrowning 2020 EN PDFPedroNo ratings yet
- Cases 4-6Document13 pagesCases 4-6CHAN SIN JIANNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2. Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesChapter - 2. Literature ReviewKUNAL SHAHNo ratings yet
- Tu Vung Ngu Phap Bai Tap Global Success 8Document8 pagesTu Vung Ngu Phap Bai Tap Global Success 8Han LangNo ratings yet
- Akanksha Ranjan Christ (Deemed To Be University) RESUMEDocument2 pagesAkanksha Ranjan Christ (Deemed To Be University) RESUMEAkanksha Ranjan 2028039No ratings yet
- Moving-Up Ceremony Closing Prayer: by Raizel Arabella MisluhaniDocument1 pageMoving-Up Ceremony Closing Prayer: by Raizel Arabella MisluhaniAngel CrisolNo ratings yet
- Freight Chargers CalclationDocument2 pagesFreight Chargers CalclationAkama KulasekaraNo ratings yet
- Merit List MBA Scholarship 2020 March 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMerit List MBA Scholarship 2020 March 1 PDFPrakash SitaulaNo ratings yet
- AGR3502 Rice Production: Food CropsDocument36 pagesAGR3502 Rice Production: Food CropsSleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Electric Flight 1DB18ME040Document10 pagesElectric Flight 1DB18ME040Karthik NNo ratings yet
- Public Revenue Management 6Document43 pagesPublic Revenue Management 6mohamedNo ratings yet
- Offshore BrochureDocument5 pagesOffshore BrochureAhmed Ben Hmida0% (1)
- Shark Finning Final DraftDocument11 pagesShark Finning Final Draftilana lutzNo ratings yet
- Effects of Anacetrapib in Patients With Atherosclerotic Vascular DiseaseDocument11 pagesEffects of Anacetrapib in Patients With Atherosclerotic Vascular DiseaseCirca NewsNo ratings yet
- Installation Qualification For Informatic System ExampleDocument7 pagesInstallation Qualification For Informatic System ExampleCarlos SanchezNo ratings yet
- Estimate Electrical Guwahati UniversityDocument19 pagesEstimate Electrical Guwahati UniversityTandon Abhilash BorthakurNo ratings yet
- The History of MoneyDocument30 pagesThe History of MoneyBea Nicole AugustoNo ratings yet
- Red Tact OnDocument12 pagesRed Tact Onnavita466No ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/41Document7 pagesCambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/41MUHAMMAD SHAZIL AYUBNo ratings yet
- Milan AssignmentDocument5 pagesMilan AssignmentMilan DeepNo ratings yet
- NP181Document5 pagesNP181Psycho ScorpionNo ratings yet