Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Central Bank Is Bank For Banks.: Mandric+I+G+ (X-Im) Yandp
Central Bank Is Bank For Banks.: Mandric+I+G+ (X-Im) Yandp
Uploaded by
sheeplordOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Central Bank Is Bank For Banks.: Mandric+I+G+ (X-Im) Yandp
Central Bank Is Bank For Banks.: Mandric+I+G+ (X-Im) Yandp
Uploaded by
sheeplordCopyright:
Available Formats
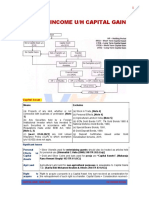
Federal Reserve
Policy
M and r I C + I + G + (X IM)
1 2 3 4
Y and P
1. central bank is bank for banks.
2. The Federal Reserve System is Americas central bank.
There are 12 Federal Reserve banks, but most of the
power is held by the Board of Governors in Washington
and by the Federal Open Market Committee.
3. The Federal Reserve acts independently of the rest of the
government. Over the past 20 to 25 years, many countries
have decided that central bank independence is a
good idea and have moved in this direction.
4. The Fed has three major monetary policy weapons:
open-market operations, reserve requirements, and its
lending policy to banks. But only open-market operations
are used frequently.
5. The Fed increases the supply of bank reserves by purchasing government securities in the open
market.
When it pays banks for such purchases by creating new
reserves, the Fed lowers interest rates and induces a
multiple expansion of the money supply. Conversely,
open-market sales of securities take reserves from banks,
raise interest rates, and lead to a contraction of the
money supply.
6. When the Fed buys bonds, bond prices rise and interest
rates fall. When the Fed sells bonds, bond prices fall and
interest rates rise.
7. The Fed can also pursue a more expansionary monetary
policy by allowing banks to borrow more reserves, perhaps
by reducing the interest rate it charges on such loans
(the discount rate) or by reducing reserve requirements.
8. None of these weapons, however, gives the Fed perfect
control over the money supply in the short run, because it
cannot predict perfectly how far the process of deposit creation
or destruction will go. The Fed can, however, control
the interest rate paid to borrow bank reserves, which is
called the federal funds rate, much more tightly.
9. Investment spending (I), including business investment
and investment in new homes, is sensitive to interest
rates (r). Specifically, I is lower when r is higher.
10. Monetary policy works in the following way in the Keynesian
model: Raising the supply of bank reserves leads
to lower interest rates; the lower interest rates stimulate
investment spending; and this investment stimulus, via
the multiplier, then raises aggregate demand.
11. Prices are likely to rise as output rises. The amount of inflation
caused by expansionary monetary policy depends
on the slope of the aggregate supply curve. Much
inflation will occur if the supply curve is steep, but little
inflation if it is flat.
12. The main reason why the aggregate demand curve
slopes downward is that higher prices increase the demand
for bank deposits, and hence for bank reserves.
Given a fixed supply of reserves, this higher demand
pushes interest rates up, which, in turn, discourages
investment.
You might also like
- Mariia Deremenda 457group: Vocabulary Stormgard Shines When Others StumbleDocument2 pagesMariia Deremenda 457group: Vocabulary Stormgard Shines When Others StumbleМарiя Деременда100% (1)
- PH Protocol For RainsDocument30 pagesPH Protocol For RainsprachiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Anthony Crescenzi's The Strategic Bond Investor, Third EditionFrom EverandSummary of Anthony Crescenzi's The Strategic Bond Investor, Third EditionNo ratings yet
- Chapter07 - Managing Interest Risk Using Off Balance-Sheet InstrumentsDocument50 pagesChapter07 - Managing Interest Risk Using Off Balance-Sheet InstrumentsDuy ThứcNo ratings yet
- FIN122 Chapter 9. SeminarDocument3 pagesFIN122 Chapter 9. SeminarНурбол АсылбекNo ratings yet
- TCHE 303 - Tutorial 10Document5 pagesTCHE 303 - Tutorial 10Bách Nguyễn XuânNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Monetary Policy Goal and TargetsDocument12 pagesConduct of Monetary Policy Goal and TargetsSumra KhanNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document12 pagesCH 16Deepansh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 15 Lecture NotesMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Chapter Fifteen Monetary PolicyDocument12 pagesChapter Fifteen Monetary PolicyElie MenassaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 NarrativeDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 4 NarrativeJoyce Anne GarduqueNo ratings yet
- The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy: Principles of Economics in Context (Goodwin, Et Al.)Document14 pagesThe Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy: Principles of Economics in Context (Goodwin, Et Al.)RONALD ARTILLERONo ratings yet
- h#24 Fiscal Policy and Monetary PolicyDocument14 pagesh#24 Fiscal Policy and Monetary PolicyMd. Didarul AlamNo ratings yet
- History of Quantitative EasingDocument8 pagesHistory of Quantitative Easingapi-276870368No ratings yet
- History of Quantitative EasingDocument8 pagesHistory of Quantitative Easingapi-276870368No ratings yet
- Tute-9 FMTDocument6 pagesTute-9 FMTHiền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Test Banks Short AnswerDocument10 pagesTest Banks Short AnswerNam Anh VũNo ratings yet
- FIM Tutorial 5 (Week 6)Document4 pagesFIM Tutorial 5 (Week 6)Cindy LewNo ratings yet
- GR Fed Hidden Agenda-Drive Into DepressionDocument8 pagesGR Fed Hidden Agenda-Drive Into Depressionanon_717974No ratings yet
- Economics 8Document3 pagesEconomics 8M IMRANNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document29 pagesChap 12janvi100No ratings yet
- FIN350 - Solutions Slides 9Document4 pagesFIN350 - Solutions Slides 9David NguyenNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy ToolsDocument8 pagesMonetary Policy ToolsFreddie254No ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument6 pagesFinancial MarketsRudella LizardoNo ratings yet
- The Federal Reserve's Balance SheetDocument19 pagesThe Federal Reserve's Balance SheetKapeel KumarNo ratings yet
- The U.S. Federal Reserve Is On The Verge of Raising Short-Term Rates For The Third Time Since The Global Financial Markets Crisis Hit Ten Years AgoDocument2 pagesThe U.S. Federal Reserve Is On The Verge of Raising Short-Term Rates For The Third Time Since The Global Financial Markets Crisis Hit Ten Years AgoEli LiNo ratings yet
- Fed and Financial PolicyDocument2 pagesFed and Financial PolicyjosephjbucciNo ratings yet
- chapter 5 Policy Makers and The Money Supply: True-False QuestionsDocument27 pageschapter 5 Policy Makers and The Money Supply: True-False QuestionsDuyen Pham DieuNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Functions of The Federal Reserve System: Policy, Banking Supervision, Financial ServicesDocument18 pagesThe Structure and Functions of The Federal Reserve System: Policy, Banking Supervision, Financial ServicesJapish MehtaNo ratings yet
- Interest On Reserve and Monetary PolicyDocument8 pagesInterest On Reserve and Monetary Policydungtran0989No ratings yet
- Johnny FinalDocument4 pagesJohnny FinalNikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch09 Monetary PolicyDocument21 pagesCh09 Monetary Policymxdxcr2229No ratings yet
- Chapter 11b: Federal Reserve and Monetary PolicyDocument26 pagesChapter 11b: Federal Reserve and Monetary PolicyAli ZafarNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument27 pagesMonetary PolicyYinying GuoNo ratings yet
- Fed Rate Cut N ImplicationsDocument8 pagesFed Rate Cut N Implicationssplusk100% (1)
- Macroeconomics and Financial CrisisDocument11 pagesMacroeconomics and Financial Crisisslarti007No ratings yet
- Tools of Monetary Policy: Open - Market Operations Discount Rate Reserve RequirementsDocument15 pagesTools of Monetary Policy: Open - Market Operations Discount Rate Reserve RequirementsAngelica BeltranNo ratings yet
- Answers of Money and Banking AssignmentDocument2 pagesAnswers of Money and Banking AssignmentHamda HassanNo ratings yet
- Money and Monetary Policy: Chapter 11Document18 pagesMoney and Monetary Policy: Chapter 11Ji YuNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate Determination TopicsDocument6 pagesInterest Rate Determination TopicsGian ErickaNo ratings yet
- Proiect EnglezaDocument11 pagesProiect EnglezaAmy JonesNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 Tools of Monetary PolicyDocument29 pagesCh. 3 Tools of Monetary PolicycarsongoticosegalesNo ratings yet
- Life After Debt - Debtless by 2012, The U.S and The World Without US Treasury Bonds (FOIA Document)Document43 pagesLife After Debt - Debtless by 2012, The U.S and The World Without US Treasury Bonds (FOIA Document)Ephraim DavisNo ratings yet
- Overview of Central BanksDocument6 pagesOverview of Central BanksMehwish AsimNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Money Supply ProcessDocument22 pagesWeek 1 - Money Supply ProcessIlham AtmajaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Money Supply ProcessDocument22 pagesWeek 1 - Money Supply ProcessIlham AtmajaNo ratings yet
- 4.2.4. Interest Rate DeterminationDocument21 pages4.2.4. Interest Rate DeterminationGuy WilkinsonNo ratings yet
- Clarifying Central Bank Responsibilities For Monetary Policy, Credit Policy, and Financial StabilityDocument10 pagesClarifying Central Bank Responsibilities For Monetary Policy, Credit Policy, and Financial StabilitySidhanshu DhallNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy and Central Banking: Geriel I. Fajardo 3FM3 Assignment 2Document3 pagesMonetary Policy and Central Banking: Geriel I. Fajardo 3FM3 Assignment 2Geriel FajardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 OutlineDocument7 pagesChapter 2 OutlinemacysilveniaNo ratings yet
- Contractionary and Expansionary Monetary PolicyDocument8 pagesContractionary and Expansionary Monetary PolicyNavin SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Central Banking - ESP Int'l Banking and FinanceDocument27 pagesUnit 7 Central Banking - ESP Int'l Banking and FinanceUyên PhươngNo ratings yet
- Central Bank Deposits Federal Reserve BankDocument2 pagesCentral Bank Deposits Federal Reserve Bankarvin cleinNo ratings yet
- Money Market Interest RatesDocument4 pagesMoney Market Interest RatesTeffi Boyer MontoyaNo ratings yet
- FIN350 - Solutions Slides 10Document3 pagesFIN350 - Solutions Slides 10David NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris UTSDocument52 pagesBahasa Inggris UTSFania LutuNo ratings yet
- Government Policy: Monetary & Fiscal PolicyDocument27 pagesGovernment Policy: Monetary & Fiscal PolicyGeorgia HolstNo ratings yet
- Fin 464 Chapter 2Document18 pagesFin 464 Chapter 2Ibteda Bin Sakayet 2013312630No ratings yet
- Ife - UsaDocument13 pagesIfe - Usagiovanni lazzeriNo ratings yet
- Seminar 4 AnswersDocument3 pagesSeminar 4 AnswersQuỳnh TrangNo ratings yet
- Commodity Money 3iat Money Jank MoneyDocument11 pagesCommodity Money 3iat Money Jank MoneyRabia RabiNo ratings yet
- Abm161 Lessons 8 9 2023Document24 pagesAbm161 Lessons 8 9 2023Norhaliza D. SaripNo ratings yet
- ICM Practice Questions - Money Markets - 9-5-23Document9 pagesICM Practice Questions - Money Markets - 9-5-23Haris AliNo ratings yet
- Ratios and Common-Size AnalysisDocument1 pageRatios and Common-Size Analysisarmor.coverNo ratings yet
- Lesson 09 Dividend PolicyDocument35 pagesLesson 09 Dividend PolicyTomy BoscoNo ratings yet
- Mergers and AcquisitionDocument17 pagesMergers and AcquisitionRaghu NarayanNo ratings yet
- TiconderogaDocument5 pagesTiconderogaJCGonzales100% (1)
- GP - Consumer Behaviour For Third Party Products at Private BanksDocument75 pagesGP - Consumer Behaviour For Third Party Products at Private Banksjignay100% (4)
- Management of Funds and AssetsDocument231 pagesManagement of Funds and AssetsSM Friend100% (2)
- Presentation ReportDocument8 pagesPresentation ReportJohn ArjunNo ratings yet
- Moneylife 2 October 2014Document68 pagesMoneylife 2 October 2014krishnakumarsistNo ratings yet
- 3 E-Mai L: Chaotak@ Embarqmai L. Com - . - . % Telephone: (702) 647-7925 - . (4Document111 pages3 E-Mai L: Chaotak@ Embarqmai L. Com - . - . % Telephone: (702) 647-7925 - . (4glimmertwinsNo ratings yet
- SAP Reports For All ModulesDocument52 pagesSAP Reports For All ModulesrajeswariNo ratings yet
- Share Management and Securities Exchange Laws of Bangladesh: Determining Efficacy and FalloutsDocument415 pagesShare Management and Securities Exchange Laws of Bangladesh: Determining Efficacy and Falloutsshakhawat HossainNo ratings yet
- Asca Liability InsuranceDocument2 pagesAsca Liability Insuranceapi-240593576No ratings yet
- Brittania BiscuitDocument78 pagesBrittania BiscuitgoswamiphotostatNo ratings yet
- Au Navy 5417Document31 pagesAu Navy 5417AVRM Magazine StandNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On Working Capital MangementDocument64 pagesSummer Training Report On Working Capital Mangementrakesh kumar baral71% (7)
- Update Sept 07Document44 pagesUpdate Sept 07api-27370939No ratings yet
- Results Press Release For September 30, 2016 (Result)Document3 pagesResults Press Release For September 30, 2016 (Result)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- CG Notes PDFDocument49 pagesCG Notes PDFT S NarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Esbm 4Document3 pagesEsbm 4rehman11424No ratings yet
- Nama: Sannia Rahma Masrura NIM: 4112001049: Preemptive RightDocument3 pagesNama: Sannia Rahma Masrura NIM: 4112001049: Preemptive RightSannia Rahma MNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Position and Action Evaluation MatrixDocument5 pagesThe Strategic Position and Action Evaluation MatrixEhab elhashmyNo ratings yet
- ACTL 4001 - 5100 S1 2015 Mid Semester With MarkingDocument4 pagesACTL 4001 - 5100 S1 2015 Mid Semester With MarkingBobNo ratings yet
- SMCH 13Document47 pagesSMCH 13Lara Lewis AchillesNo ratings yet
- Final AnswerDocument15 pagesFinal AnswerHedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Not-for-Profit EntitiesDocument50 pagesChapter 19 - Not-for-Profit EntitiesDewi PertiwiNo ratings yet
- The Global Financial Crisis and The Challenge To Neoliberalism ...Document11 pagesThe Global Financial Crisis and The Challenge To Neoliberalism ...ian laurence pedranoNo ratings yet
- Lehman Fixed Income PresentationDocument29 pagesLehman Fixed Income PresentationAndy Stone100% (1)