Professional Documents
Culture Documents
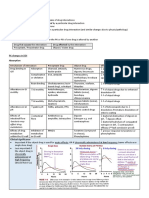
Pharmacology Drug Chart
Pharmacology Drug Chart
Uploaded by
EssentialForLivingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology Drug Chart
Pharmacology Drug Chart
Uploaded by
EssentialForLivingCopyright:
Available Formats
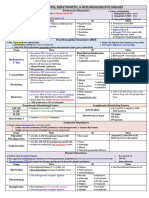
Generic Receptor Class Action Effects
Acetylcholine
NN, NM, M1-
5
Quat
amine
Methacholine M1-5
Quat
amine
Carbachol
NN, NM, M1-
5
Quat
amine
Pilocarpine M1-5
Tert
amine
Bethanechol M1-5
Quat
amine
GI & GU motility; contract
urinary bladder
Cevimeline M1&3 salivation
Nicotine NN, NM
Natural
alkaloid
Physostigmine
Tert
amine
flow of aqueous humor;
crosses BBB
Neostigmine
Pyridostigmine
Quat
amine
GI & GU motility; contract
urinary bladder improve NM
jnc transmission
Edrophonium
Quat
amine
Donepezil Improve cognitive fnc
Echothiophate
flow of aqueous humor
Sarin
Malathion
Pralidoxime
Quat
amine
AChE
reactivator
Hemicholinium
Blocks Ch
transport
Botulinum toxin
Blocks ACh
release
-latrotoxin
Excess ACh
release
Indirect
Irreversible
AChE
inihibitors
Cholinergic Agonists
Direct
intraocular pressure
miosis, and outflow
NN, NM, M1-
5
Indirect
reversible
AChE
inhibitors
Use to treat Complications Admin Duration
Not used to treat
Brief
Test response of bronchial
hyper-reactivity for asthma
Longer
Chronic glaucoma
Topically in eye 2-3 hours (long)
Acute glaucoma Topically in eye
ONLY
2-3 hours
Urine or fecal retention
2-3 hours (long)
Sjogren's Syndrome
Smoking hyperventilation, HTN, persistent
depol., GI/GU motility
Acute glaucoma
atropine poisoning
Alzheimer's
2-4hrs
Treat myasthenia gravis
GI/urinary disorders
Diarrhea
sweating & salivation
bronchial secretions
Diagnosis of myasthenia
gravis
2-10 minutes
Alzheimer's
Open-angle glaucoma
Topically in eye,
doesnt pass skin
100 hours
Not used to treat
Military nerve gas
Not used to treat
Insecticide
Cholinergic OD in PNS Doesnt work in CNS
CNS: respiratory paralysis, ataxia,
confusion, convulsions
PNS: twitches, bronchial
secretions, sweating, miosis,
salivation, hypotension, emesis
Cholinergic Agonists
Salivation
Lacrimation
Urination
Defecation
Sweating
treat OD with atropine
Comments
Not-selective
hydrolyzed by AChE slowly
hydrolyzed even slower
IV or IM administration negates
specificity
Varenicline - NN, selective, smoking
cessation
For CNS
For muscle, doesnt enter CNS
For CNS
supplement w/ atropine
From black widow spider
Easily enter CNS via anywhere,
including skin
"Organophosphate Ch inhibitors"
Poisonous at high doses
Treat OD w/in 1hour aging window:
atropine + pralidoxime
Cholinergic Agonists
Generic Receptor Class Action Effects
Atropine M1-5 Tert amine
Mydriasis (dilation)
blocking cholinergics
GI secretions/motility
sweating -> fever,
bronchial relaxation
bronchial secretions
Scopolamine M1-5 Tert amine
Decrease GI motility, induce
amnesia
Ipratropium
Tiotropium
Propantheline
Meth-scopalamine
M1-5
Pirenzipine M1
Tolterodine M2-3 inhibit bladder contractions
Trimethaphan NN
Ganglion
blocker
BP
d-Tubocurarine NM
2 quat
amines
Atracurium NM
3 quat
amines
Succinylcholine NM
2 choline +
succinic acid
Competitive
agonist
(in plasma)
Phase I: cause persistent depol.
w/ slight initial contraction ->
sensitizes
Phase II: Rapid recovery after
withdrawal, desensitizes over
time. recovery is longer
muscle relaxation
Cholinergic Antagonists
Competitive
antagonist
M1-5 Quat amine
Bronchial relaxation
Quat amine
(synthetic)
Decrease gastric
secretion/motility
Competitive
antagonists
(@ NM jnc)
prevent depol. at NM jnc. ->
muscle relaxation
Use to treat Complications Admin Duration
Eye exam dilation
acute iritis
AChE inhibitor poisoning
Parkinson's (+ L-DOPA)
Induce anesthesia
Parasympathetic block:
normal effects + tachycardia, dry
mouth/skin, atropine flush, delirium
Treat OD: physostigmine
Opthalmic
drops, PO,
subQ
2-4 hours
(longer in
eye)
Motion sickness
Induce anesthesia
Same as atropine + more Drowsiness,
amnesia
Transdermal
patch
Longer
Same as atropine
Very few side effects
Urinary incontinence
HTN crisis; Bloodless view
in short surgery
Constipation, cyclopegia, tachycardia,
decreased sweating, urinary retention
IV
Anesthesia for quick
surgeries, intubation
AChE inhibitors enhance effects
If have malignant hyperthermia (genetic
condition), causes rigidity and rapid rise in
temp
Contraindication: tetracycline, burn pts,
electrolyte imbalance (K+ Loss)
IV drip
2-3
minutes
Cholinergic Antagonists
COPD/asthma
common cold
Not as effective as -agonist
Inhalation
Peptic ulcer disease
PO
20-40
minutes
Paralysis, bronchospasm,
salivary/respiratory secretions, BP
-AChE inhibitors diminish effects
-Ether/halothane intensifies effects
IV only
Comments
Penetrades CNS
Treat Serum Gas/Chem
Less complications than
atropine
Not used much
Neostigmine used to reverse block
Cholinergic Antagonists
Doesn't penetrate CNS
Myasthenia gravis pts,
and those w/ reducd
plasma AChE very
sensitive to these
Generic Class Action Use to Treat:
Mannitol
Glycerin
Physostigmine
Cholinergic
AChE inhibitor
Trabecular outflow
Acute glaucoma
Pilocarpine
Cholinergic muscarinic
agonist
Trabecular outflow
miosis
Acute glaucoma
Epinephrine adrenoreceptor agonist
Secretion
Trabecular outflow
Dorzolamide
Carbonic anhydrase
inhibitor
Secretion
Bimatoprost Prostaglandin
Trabecular outflow
Uveoscleral outflow
Latanoprost Prostanoid agonist Uveoscleral outflow
Timolol -blocker
Secretion
Brimonidine 2-agonist
Secretion
Uveoscleral outflow
Carbachol NN, NM, M1-5 agonist
Trabecular outflow
miosis
Echothiophate Irreversible AChEI Trabecular outflow
Closed angle = Acute
Open angle = chronic
Chronic glaucoma
Drugs of Glaucoma (Inc Intraocular Pressure)
Diuretic
Reduce aqueous humor
volume by osmotic pressure
Acute glaucoma (adjunct)
Administration Complications
IV
PO
Topically in eye
Potential for poisoning, crosses
BBB
Topically in eye
Not used bc of severe toxicities
Bitter taste, blurred vision
Increased skin/iris pigmentation Lengthens eyelashes
Bradycardia, arrhythmia,
bronchospasm, fatigue,
depression
Contra: Pacemaker & Asthmatics
Dermatitis, conjunctivitis,
mydriasis
Hypotension, bradycardia,
bronchial constriction, SLUDS
Topically in eye
Drugs of Glaucoma (Inc Intraocular Pressure)
Generic Receptor Class Effects
Epinephrine ,
contractility, HR, & sBP
TPR, dBP
bronchial relaxation/dilation
prevent mast cell degranulation
Norepinephrine ,1
contractility, BP & TPR
HR (vagal compensation)
Isoproterenol
contractility, sBP & HR (inhibit vagal comp.)
TPR, dBP
+bronchial relaxation/dilation
Dopamine
D1 > 1 >
1
Dose...
Low: renal perfusion (D1)
Med: contractility/HR (1)
High: vasoconstriction -> BP (1)
Dobutamine 1
cardiac output, small increase in HR
Tyramine indirect
Displaces NE out of nerve. Takes up MAOA
active sites
Ephedrine
indirect &
direct
Decongestion (Nasal vasoconstriction)
Bronchial relaxation
BP
Bladder sphincter contraction
Pseudoephedrine
indirect &
direct
Decongestion
Sphincter contraction (for continence)
Amphetamine
Ritalin
indirect &
direct
CNS stimulant, BP, HR
Phenylephrine
(selective)
1
Non-
catecholamine
Vasoconstriction causing:
Decongestion
BP , HR
Mydriasis (Glaucoma) (w/o accom. loss)
Clonidine
(selective)
2
inhibit NE release in CNS medulla -> CO
and TPR -> BP
Salmeterol
Formoterol
Albuterol
Metaproterenol
Terbutaline
Bronchial relaxation (short acting)
Relax uterine muscle
Ritodrine Relax uterine muscle
Clorgyline MOA-A inhibitor
Anti-depressant
Selegiline MOA-B inhibitor
Increased L-DOPA
Anti-depressant
Entacapone &
Tolcapone
COMT
inhibitor
Increased L-DOPA
-Methyltyrosine
tyrosine
hydroxylase
inhibitor
BP (rarely used)
Lorcaserin stimulates satiety
Qsymia
Modafinol
Adrenergic Agonists
Catecholamine
(rapid on/off, no
BBB, no PO)
Non-
catecholamine
(can cross BBB,
can give PO)
2
Bronchial relaxation (long-acting)
Bronchial relaxation (short-acting)
5HT2C serotonin agonist
phenteramine + topiramate
Epenephrine predominates B2 over a1
Asthma - B-agonists hide effects doesnt treat inflammation
a1 = constriction (veins) except relaxation of intestine
Use to Treat Complications
Local anesthesia & hemorrhage control
Acute hypersensitivity rxns (allergy, bees, venom)
Cardiac arrest
Arrhythmias, anxiety, headache, HTN,
palpitations
Local anesthesia & hemorrhage control
(rarely used as drug)
Arrhythmias, HTN, anxiety, palpitations,
headache, renal perfusion
Heart block, asthma rescue therapy, cardiac arrest Tachycardia, arrhythmias, angina
Palpitations, hypotension
Hypotensive shock Nausea, HTN, arrhythmia (short-lived)
cardiogenic shock Increased myocardial work
Arrthymias
Interacts with MAO inhibitors
Congestion
Asthma
Hypotension
Stress incontinence
Nausea, vomiting, HTN, arrhythmia, CNS
stimulation; FDA withdrew
Congestion
Stress incontinence
ADHD
narcolepsy
Fetal toxicity, HTN
Congestion
Hypotension
Atrial tachycardia ( HR by vagal reflex)
HTN
bradycardia
slow nasal mucosa healing
HTN
opioid withdrawal
anxiety/Tics
hypotension
dry mouth
sedation
Rebound HTN (on abrupt stop)
Asthma
Premature contractions
Premature contractions
Mood disorders
Parkinsons
Depression
Parkinson
HTN
Narcolepsy
Adrenergic Agonists
Prophylactic for asthma &
nocturnal asthma
Arrhythmia, tachycardia, tremor
Masks underlying inflammation
Do not use long-term
Asthma/COPD
Arrhythmia, tachycardia, tremor
obesity
B1 = heart, lipolysis
a1 = constriction (veins) except relaxation of intestine
Admin Comments
IV
Inhalation
topically in eye
In allergy rxn:
1 -> elevate BP, prevent suffocate
2 -> inhibit mast
IV
Toxicity = Rarely used
Inhalation
IV
D1 > 1 > 1
IV
in cheese and wine
PO
IV
Triggers release of NE & E
blocks NET (NE re-uptake)
IV
Topically in eye
act on post synapse
(much longer duration than
catecholamines)
PO
act on pre synapse
Strong partial agonist -> will displace
Epi, use care
inhibits serotonin metabolism
inhibits dopamine metabolism
inhibits dopamine metabolism
inhibits NE/E/dopamine syn.
Adrenergic Agonists
Inhalation
Always supplment with
corticosteroids
Inhalation Not used much since A & S are better
B2 = relaxation
a1 = constriction (veins) except relaxation of intestine a2 = decreased insulition
Generic Receptor Class Effects
Prazosin
BP (vasodilation via 1-block)
Doxazosin &
Terazosin
relaxes smooth muscle in bladder neck ->
relieves obstruction
Yohimbine
2
(selective)
(blocks presynaptic negative feedback ->
increased NE release)
Labetalol
S,R: 1
(selective)
R,R:
(non-selective)
BP
Phentolamine
Phenoxybenzamine
Irreversible
(aka covalent)
Propranolol
CO (blocks NE/E)
HR & BP (blocks 1 renin receptors)
reduces tremors
Timolol &
Betaxolol
aqueous humor secretion
BP
Pindolol BP (with only small HR)
Carvedilol 1,
: HR,CO,BP
1: vasodilation, BP
Metoprolol &
Atenolol
1
(kinda selective)
CO & BP (blocks 1 renin receptors)
Reserpine NE depleting VMAT inhibitor BP (blocks VMAT -> vasodilation)
Guanethidine NE depleting NET competitor
BP (taken up by NET -> replaces NE)
Tricyclic
antidepressent
Blocks serotonin and NE reuptake
Cocaine Blocks dopamine reuptake
NET inhibitor
Adrenergic Antagonists
1
(selective)
Reversible
(non-selective)
BP (vasodilation via 1-block)
HR
Competitive
Use to Treat Complications Admin Duration
HTN
Benign prostatic hypertophy
Heart failure
PTSD
Orthostatic hypotension
inhibits ejaculation
some tachycardia
PO
IV
3hr HL
benign prostatic hypertrophy
HTN
Diabetic Impotence
Painful Diabetic neuropathies
Depression
HTN
PO
IV
6hr HL
4 hours
24+ hours
HTN
arrhythmia
angina
Migrane/anxiety
Exacerbates asthma, COPD,
emphysema, HF, hypoglycemia
Abrupt cessation causes angina
and death
PO 3-4 hours
HTN
arrhythmia
Chronic glaucoma
does not cause miosis
Topically
HTN (w/ bradycardia or CO) diminished effects & toxicities
CHF
PO
HTN
CHF
Less bronchial constriction than -
blockers, but still exacerbates
asthma, COPD, HF
HTN
HTN
Mood disorders
Adrenergic Antagonists
Pheochromocytoma (adrenal
tumor secreting E and NE)
ED
Inhibits serotonin
Agonist @ muscarinic &
histamine receptors
IV
IM
Comments
competitive
Relaxation of prostatic smooth muscle -> improved urine flow
Used by body-builders
Causes less tachycardia than
non-selectives
oraverse is phentolamine densists use to treat EPI overdose
Crosses BBB
Significant first-pass metabolsim -
> very low bioavailability
Used in MI
Partial agonist too!
Supplement with diuretics and
ACE inhibitors
no longer used
Being replaced by SSRIs and
SNRIs
Adrenergic Antagonists
Non-selectively blocking
receptors causes tachycardia,
limiting use of these drugs
Generic Class Action
Cholestyramine
Colestipol
Colesevelam
Bile resin
LDL (Prevents bile acid reabsorption -> use cholesterol in liver to
make more bile acids -> liver pulls cholesterol from blood via LDL-
receptors)
*-statin Statins
LDL (Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, blocks production of
mevalonate, LDL-receptors everywhere)
Regression of Plaques
Ezetimibe
Cholesterol
uptake
inhibitor
Blocks cholesterol absorption in gut
Niacin
Nicotinic Acid
Vitamin B3
FFA's (Inhibits lipolysis in adipose -> decreased FAs available to
liver)
Also VLDL, LDL, and HDL
*-cetrapib
CETP
inhibitors
HDL
Clofibrate
Fenofibrate
HDL, VLDL, LDL, TGs (Binds nuclear steroid receptor PPARs,
lipoprotein lipase activity -> catabolism of TGs in VLDL & CMs)
Gemfibrozil
Fish oils
Omega-3
Fatty Acids
TG (Inhibit liver TG synthsis)
Anti-inflammatory, anti-clotting, HTN (binds to COX and
lipoxygenase to make less-potent thromboxanes & leukotrienes
Drugs of Hyperlipidemia
Fibrates
Use to Treat: Complications
Primary Hypercholesterolemia
NOT for homozygous fam hyperhcol. (can't male LDLR)
Digoxin toxicity (stops absorption)
Pruritis of biliary obstruction
VLDL
Interferes w/ digitalis, phenobarbital,
warfarin, & vitamin ADEK absorption
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial Ligand-Defective Apo B
Familial Combined hyperlipoproteinemia (VLDL+LDL)
Hepatotoxicity 1-2%
Myopathy 0.2% - Muscle Soar See Doc
teratogenic -avoid in pregnancy
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial Ligand-Defective Apo B
Hypersensitivity rxns (ex: rash)
All hyperlipidemias
THIS IS THE ONLY ONE THAT WORKS FOR LP(a)
hyperlipoproteinemia
Flushing & pruritus
Peptic ulcer, jaundice,
uric acid
contraindicated in arrhythmias
New, not used yet
Cholelithiasis/cystitis
Arrhythmias in CAD
Interferes w/ warfarin & platelets
Rash
Increased LDL receptors
Type IV
Drugs of Hyperlipidemia
Primary chylomicronemia
Familial Hypertriglyceridemia
Familial Combined Hyperlipoproteinemia
Dysbetalipoproteinemia (VLDLs+CM remnants)
Comments
Combine w/ statin to prevent liver from
just making its own cholesterol
Combine w/ niacin to prevent liver VLDL
synthesis / release
Compliance (Tastes like sand)
Many good side effects like anti-
inflammatory
Often combine with statin
Often combine with resin
Side effects prevent use in USA
Often combine with resin for HLD
Drugs of Hyperlipidemia
Generic Class Vasodilates how:
*-dipine
Ca2+ blockers
(dihydropyridine)
(alpha-1 selective)
Verapamil
& Diltiazem
Ca2+ blockers
(non-dihydropyridine)
Isosorbide Dinitrate
Nitroglycerin
Nitroprusside
Amyl nitrate
Prazosin
Doxazosin
*-pril ACE inhibitors
*-sartan Angiotensin II blockers
Aliskiren Renin antagonist
Diazoxide
Hydralazine
Minoxidil
*-afil Phosphodiesterase (PDE) 5 inhibitors
cGMP in genitalia, lungs, &
esophagus
Fenoldopam Dopaminergic Agonist
*-sentan Endothelin blockers
*-prost-* Pulmonary vasodilators
Vasodilators
Prevents Ca+ influx
(arterial > venous)
Organic Nitrates
Produces NO, cGMP:
MLK dephosphorylation
K efflux
Ca++ activity
(venous > arterial)
preload & afterload
1 blockers
Block vasoconstriction
(arterial > venous)
Blocks angiotensin II effects
(arterial > venous)
K+ channel activators
K+ efflux -> hyperpol.
(arterial > venous)
Use to Treat Admin Duration Complications
PO 2-4hrs
Various
Acute HF
Malignant HTN IV
Hypotensive crisis
Cyanide accumulation (treat
w/ B12)
Dx angina Inhalation
3 hours
20 hours
HTN, CHF, angina
PO
Cough, orthostatic
hypotension, K+; not in
pregnancy!
HTN
PO
Orthostatic hypotension; not
in pregnancy!
HTN Same efficacy as
ACEs/ARBs, may have
greater renin rebound
PO, IV
PO = hyperglycemia
IV = hypotension
PO
Flushing
Drug-induced lupus
PO, topical
Flushing
Hypertrichosis
ED
Pulmonary HTN PO 3-4hrs
Hypotension
Arrhythmias
Flushing
Vasodilators
HTN
Angina from coronary
artery spasm
PO Long acting
HA, flushing, constipation
Angina
CHF
Short acting
PO
HTN, BPH Syncope
HTN
Comments
Nifedipine (short acting) is cardio
sparing (very little effect on heart)
Has IV form
Most potent. Both arteries & veins
Kidney-sparing
"Don't take viagra If you take nitrates for
chest pain.."
Vasodilators
Can develop tolerance
Supplement with a diuretic and/or -
blocker because:
--compensatory baroreceptor reflex
produces renin -> water retention
A-fib&flutter AVNRT
Procainamide
(Class A)
moderate Na+ block (slows conduction)
prolongs AP duration
Cardioversion (slows RHYTHM): (inhibits K+
channels (prolongs refrac))
Short term
X
(+ WPW)
Lidocaine
(Class B)
mild Na+ block (slows conduction)
shorten AP duration - -
Flecainide
(Class C)
large Na+ block (slows conduction)
no change in AP duration
Slows RHYTHM (inhibits K+ channels to
prolong refractory period)
Short term
X
(+ WPW)
Propranolol Short-term
Metoprolol Long-term
dl-Sotalol Class II & III
L: pan -blocker -Slows RATE
D: K+ channel blocker -Slows RHYTHM Long-term
X
(not WPW)
Amiodarone
Cardioversion (slows RHYTHM)
prolong AP / refractory period (K+-block)
vasodilates (-antag), HR (-antag),
Short term
(long term is
toxic)
-
Dofetilide X -
Ibutilde X #NAME?
Verapamil
(direct)
Short-term
Diltiazem Long-term
Adenosine
(indirect)
suppresses AV node conduction (binds to
purinurgic AV node receptors only)
-
Digoxin
Digitalis
cardiac glycoside
Slows RATE & RHYTHM ( vagal tone aka
ACh release on muscar. -> slows AV node) (FLUTTER)
Long-term
(rate&rhythm)
X
(not WPW)
Magnesium Ion
Supresses EADs
- -
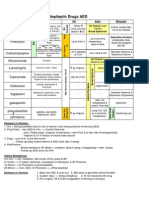
Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs
Generic Class Action
Use to Treat
Class I
Na+ Channel Blocker
(lowers I f ,
raise AP threshold,
inhibits conduction,
slows HR)
Class II:
-Blocker
Slows RATE (block catecholamines: prolong
AV node refractory period)
X
(not WPW)
Class III
K+ Channel Blocker
(inhibits refractory,
slows repol.,
prolongs AP) Cardioversion (slows RHYTHM)
prolong refractory period
Class IV
Ca2+ L Channel
Blocker
Slows RATE (delay Ca++ reactivation,
prolong AV node refractory period)
X
(not WPW)
PSVT/PAT Vtach Also:
Short-term
(if stabile)
Short-term
MAT EADs -> Torsades (if prolonged use)
"Lupus" Syndrome (+ANA)
IV
PO
- Short-term
Digitalis-induced
arrhythmias
CNS: sedation, hallucination, seizures,
Pretty mild. IV
Short term -
MAT Increases mortality in pts w/ CAD
PO
- - IV
- Long-term PO
Long-term
Low dose: -blocker side effects
High dose: K+ inhibition -> Torsades PO
X
Short-term
& Long-term
Sequesters in organs -> thyroid probs,
pulmonary fibrosis, corneal deposits
EADs from prolonged K+ inhibition->
Torsades
Poor Bioabailability
X - EADs -> Torsades (if prolonged use)
X -
EADs (K+ inhibition) -> Torsades
- -
MAT Headache, flushing, constipation,
premature labor, peripheral edema; NOT
in CHF, heart block
IV
- - PO
- -
life-threatening
tachycardia
minimal
25% of the time may come back
IV bolus
- -
cardiac O2 demand
bradycardia
hyperkalemia
IV (acute)
PO (chronic)
-
Torsades-de-
Pointes
IV
Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs
Use to Treat
Complications Admin
PVCs
MAT
Bradycardia (suppress SA node)
Heart block (suppress AV node)
Worsen CHF (contractility & CO)
Bronchospasms (2)
IV: acute
PO: long-term
3-4hrs
Widened QRS
Prolong QT-interval
Its metabolite, NAPA, is also anti-
arrhythmic
(supplement w/ a Rate control for
Afib/flutter)
60 min
Shorten action potential
Very specific to target ischemic
Na+ channels
HL: 20hrs
Widened QRS
(supplement w/ a Rate control for
Afib/flutter)
Rapid, but
longer than
adenosine
Prolong PR-interval
Longer than
Propranolol
Prolong PR-interval
HL: 20hrs
Supplemented w/ defib Implant
HL: 30days
Also blocks , , and ACh (a bit)
Supplemented w/ defib implant
Supress nodal firing (long PQ),
automaticity (long QRS), & reentry
(long QT)
(supplement w/ a Rate control for
Afib/flutter)
Longer than
adenosine
Only blocks AV node, not
accessory fibers. Thus not for
WPW
10sec
does not affect myocytes
Slow
clearance
Prolong PR-interval (from HR)
--ST-depression too First
signs of tox = 'flu like sx' (loss of
appetite and fatigue)
Not long term!
Increase mortality
long term
Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs
Duration Comments
CHF Acute HF
Spironolactone
Eplerenone
Aldosterone antagonist
(K+ sparing)
BP
1st
Hydralazine Antihypertensive vasodilator (increases cGMP levels) 1st
Losartan
Angiotensin receptor
blocker (ARB)
BP
1st
Enalapril ACE Inhibitor
BP
1st X
Nesiritide Natriuretic Peptide Vasodilator (activates cGMP -> NO) 1st X
Furosemide Loop diuretic
BP (promote Na+ excretion (naturesis) ->
decrease volume)
1st X
Nitroglycerin
Nitroprusside
Isosorbide dinitrate
Nitrates
vasodilator
Moves blood to ischemia areas of heart
reduce pre and afterload
1st
Carvedilol 1, 1, 2 antagonist
1: TPR & BP (vasodilator)
1: HR
2: bronchoconstriction/spasm
2nd
Metoprolol 2nd
Atenolol 2nd
Propranolol -blocker 2nd
Digoxin
Digitalis
Cardiac glycoside
(inhibits Na+/K+ ATPase)
vagal activity (HR)
-----blockers will intensify this
contractility (Ca++ efflux)
3rd X
Milrinone
Phosphodiesterase
inhibitor
( cAMP)
vasodilation
contractility
X
Dobutamine 1 agonist
HR & contractility (binds -> activate cAMP -
> phosphorylate Ca++ channels ->
increased Ca++ influx)
X
Dopamine D1>1>1
D1: renal vasodilation, prevents ATN
1: same as above
1: vasoconstrict -> BPnull
X
Diltiazem
Nifedipine
Ca2+ channel blocker
contractility (block Ca++ influx)
HR (acts on SA & AV nodes)
Note:
inotropic = increases contractile force
chronotropic = increases HR/conduction
CHF
Drugs of Heart Failure
Generic Class Action
Use to treat
1-antagonist
(selective)
HR & contractility
Angina Also
HTN, edema Hyperkalemia, endocrine abnormalities,
GI discomfort
PO HL: 24hrs
HTN in pregnancy Can HR/CO HL: 4hrs
HTN Dry cough, stomach pain, muscle
cramps, HA, dizziness, trouble
concentrating, palpitations
HL: 90min
HTN Hypotension, dizziness, Dry cough,
angioedema, jaundice + icterus (liver
failure), arrythmia
HL: 11hrs
Hypotension, renal failure, hemoptysis
IV HL: 18min
Ototoxicity, hypokalemia, gout,
hypovolemia, hypomagnesemia
IV
X
headache, nausea, flushing, syncope
IV
very short HL, multiple
admin routes
X
HTN, post MI Hypotension
1st degree heart block -> bradycardia
X
X longer than metoprolol
X
HL too short to treat
angina
short HL
A-fib / arrhythmias
Note: improves CHF
symptoms, but
doesn't prolong life
Arrhythmias / heart block
GI disturbances
Halos around bright lights
Causes hyperkalemia if over-inhibit
Treat OD: Digitoxin Abs
PO, IV
Long HL (36hrs)
does not desensitize
arrhythmias
hypotension
angina
bronchospasm
IV, PO HL: 3hrs
Acute HF with:
pulmonary edema
Acute HF with:
hypotension
X
Hypotension
constipation
peripheral edema
Drugs of Heart Failure
Use to treat
Complications Admin Duration
Bronchospasm
Hypoglycemia
Sleeping disorders
PO, IV
stress on heart -> ischemia
IV only
short term
desensitizes <72hrs
Increases potency of ACE
inhibitors, lithium, or digoxin
severe hypotension with other
vasodilators
Competes w/ K+ to bind to
extracellular Na+/K+ ATPase ->
hypokalemia from diuretics will
intensify effects
actually worsens HF, use in
palliative end-stage HF only
Don't use in pts w/ WPW, CHF,
or conduction probs
Drugs of Heart Failure
Comments
afterload
Don't use in pts w/ arrhythmias,
WPW, heart block, insulin
dependent, asthma/COPD
Do not abruptly stop use
Generic Class Action Use to treat:
Abciximab Monoclonal Ab
Eptifibatide Peptide
Acetylsalicylic acid
(aspirin)
COX inhibitor
Long-term platelet inhibition (Irreversible
COX inhibitor; blocks platelet production
of TxA2)
Prophylactic for stroke
Given to pts with CAD,
atherosclerosis, and abnormal
valves
Clopidogrel
('Plavix')
ADP-receptor
inhibitor
Long-term platelet inhibition (inhibits
ADP receptor on platelets)
Prophylaxis for PCI & stroke
Unstabile angina, MI, CAD
Tissue Plasminogen
Activator (TPA)
Streptokinase
Urokinase
Heparin
Sulfated
proteoglycan
Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Fondaparinux
Rivaroxaban
Factor Xa
Antagonist
Prophylactic for DVT &
thrombophlebitis
Warfarin
(coumadin)
Vitamin K
inhibitor
Long-term (aka PARTIAL) anti-
coagulation (competitively inhibits
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase -> factors
7, 9, 10, & 2(thrombin) not activated)
Prophylactic for DVT &
thrombophlebitis (including
patients with Afib or abnormal
valves)
Drugs of Hemostasis
Short-term glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor PCI
Unstabile angina, MI
Fibrinolytic
Acute MI / stroke
Acute clot lysis (binds to fibrin, activates
bound plasminogen)
Low molecular
weight heparin Long-term anti-coagulation (Inhibit
Factor Xa)
Short-term anti-coagulation (binds to anti-
thrombin, inhibits clotting factors 9-12,
thrombin, & kallikrein
Prophylactic for stroke; safe in
pregnancy
Admin Duration Complications Comments
Onset immediate
Lasts 24-48hrs
Onset immediate
rapid clearance
competitive inhibitor
HL= 3-6hrs
Lasts 1-2weeks
Rare
Bleeding Ticlopidine: used for TIAs and
strokes
Rapid onset
HL= 5-10min
HL= 40-80min
Increase PTT by 1.5-2.5x
PO
PO Onset in 7-10days
Hemorrhage
Teratogenic
Increase PT by 2-3x
Intensify effects with:
Antibiotics, sulfinpyrazone,
cimetitidine, & allopurinol
Diminish effects with:
Barbiturates, phenytoin & Vit K
Drugs of Hemostasis
IV
Bleeding
PO
IV
Bleeding
Hemorrhage
Normal PTT
Hemorrhage
No immune thrombocytopenia
Block fibrinolysis:
Aminocaproic acid (inhibits
plasminogen binding to fibrin)
IV
(also
SUBQ if
LMWH)
Onset immediate
cleared rapidly by
macrophages
Hemorrhage
immune thrombocytopenia
You might also like
- MandalaDocument80 pagesMandalavanag99152100% (1)
- Saving My Knee Guide by The Stone Clinic Copy (New)Document11 pagesSaving My Knee Guide by The Stone Clinic Copy (New)Aleksandra LSNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNo ratings yet
- SNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Document5 pagesSNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Whitney Krabbenhoft100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Document2 pagesAntiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Linlin100% (1)
- Lange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e Pharmacologic SuffixesDocument2 pagesLange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e Pharmacologic SuffixesSolNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiDocument146 pagesMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 pagesPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.DDocument28 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.Dmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Prefix Suffix MnemonicsDocument5 pagesPrefix Suffix MnemonicsPj MontecilloNo ratings yet
- Drug-Drug InteractionDocument9 pagesDrug-Drug InteractionHo Shi XianNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology A - NSAIDSDocument14 pagesPharmacology A - NSAIDSselflessdoctorNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Pharm GuideDocument41 pagesUltimate Pharm GuideeanguyenNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument25 pagesAntiemeticsPridho GaziansyahNo ratings yet
- KDT Only ClassificationsDocument72 pagesKDT Only ClassificationsDebashis ParidaNo ratings yet
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocument28 pagesA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 pageAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88No ratings yet
- Drug Recommendation GuideDocument6 pagesDrug Recommendation GuideGenNo ratings yet
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDocument2 pagesPharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaNo ratings yet
- PCOL Maps PDFDocument11 pagesPCOL Maps PDFZinc YuloNo ratings yet
- Chart Antibacterial Drugs PDFDocument1 pageChart Antibacterial Drugs PDFMunaf AlsumaryNo ratings yet
- Gout DrugsDocument1 pageGout DrugsMichael BrownNo ratings yet
- Agents For Anemia, Hematopoietic, & Myeloproliferative DiseasesDocument2 pagesAgents For Anemia, Hematopoietic, & Myeloproliferative Diseaseskaylakmills_10135868No ratings yet
- Pharmacology TableDocument9 pagesPharmacology TableMaryam KhushbakhatNo ratings yet
- Drug of Choice in Various Diseases - Candidiasis - PharmacologyDocument1 pageDrug of Choice in Various Diseases - Candidiasis - PharmacologyPragnesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- (CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsDocument6 pages(CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsHanifa Shereen B. AliNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument155 pagesDrugsAkankshaNo ratings yet
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 pagesCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDocument6 pagesMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- Anti HypertensivesDocument15 pagesAnti HypertensivesFaye MillanesNo ratings yet
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 pagesRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezNo ratings yet
- Beta BlockersDocument1 pageBeta BlockersShrikant ThakurNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument30 pagesIschaemic Heart DiseaseEB100% (1)
- Cancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationDocument5 pagesCancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationOndari gisemba OSINDENo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Document4 pagesDrug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Leyla MajundaNo ratings yet
- A New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMDocument26 pagesA New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMKartik Mendiratta100% (1)
- Antihistamines - AMBOSS PDFDocument5 pagesAntihistamines - AMBOSS PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- DRUG of CHOICE - InfectiousDocument1 pageDRUG of CHOICE - InfectiousJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Drugs PDFDocument15 pagesClassification of Drugs PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanNo ratings yet
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocument6 pagesHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, Interactionswaste78No ratings yet
- Anticoagulants Drug TableDocument1 pageAnticoagulants Drug TableNicole HoNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS MnemonicsDocument4 pagesNERVOUS MnemonicsHimNo ratings yet
- Drug TerminologyDocument5 pagesDrug Terminologyimdaking123No ratings yet
- OTC Pain Relievers Dosage Chart For Adults and Children 12 Years and OlderDocument2 pagesOTC Pain Relievers Dosage Chart For Adults and Children 12 Years and OlderAdocueNo ratings yet
- Drug ListsDocument10 pagesDrug ListsAmber Merritt100% (1)
- List of Look-Alike MedicationsDocument5 pagesList of Look-Alike MedicationsAhmad TaramsyNo ratings yet
- Whole Pharmacology Classification: Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha 1 AntagonistsDocument17 pagesWhole Pharmacology Classification: Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha 1 AntagonistsFlorina TrutescuNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrDocument1 pagePharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezNo ratings yet
- Mu 002Document10 pagesMu 002chandanNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disorder - Classification and MechanismDocument1 pageParkinson's Disorder - Classification and MechanismVương TúNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Blood DisordersDocument1 pageDrugs in Blood DisordersSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- C. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Document10 pagesC. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Nabeel AsifNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug InteractionsDocument3 pagesDrug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug Interactionsazhar hussinNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDeboyjackNo ratings yet
- Clinical Use of Monoclonal Antibodies: Abciximab Infliximab TrastuzumabDocument15 pagesClinical Use of Monoclonal Antibodies: Abciximab Infliximab TrastuzumabAndleeb ImranNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNo ratings yet
- DRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesDocument3 pagesDRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesManuel BetancurNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet Drug Comparison Chart (Asa-Clopi-Prasu-Tica)Document1 pageAntiplatelet Drug Comparison Chart (Asa-Clopi-Prasu-Tica)Ponpimol Odee BongkeawNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument23 pagesPharmacologyAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic System: e CarbamatesDocument26 pagesCholinergic System: e CarbamatesAcai BoncaiNo ratings yet
- SettingsDocument2 pagesSettingsbjpalmer100% (3)
- The Profession of Physical Therapy - Definition and DevelopmentDocument50 pagesThe Profession of Physical Therapy - Definition and DevelopmentJiggs LimNo ratings yet
- Addiction ScienceDocument72 pagesAddiction ScienceAnizan SalimNo ratings yet
- Classification of Electrical Installations in Healthcare Jul10 enDocument20 pagesClassification of Electrical Installations in Healthcare Jul10 enAndres ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Gladys Bautista Jaime 2010Document10 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Gladys Bautista Jaime 2010Clarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Nutraceuticals Leaflet ENGDocument2 pagesNutraceuticals Leaflet ENGDr. Dragos CobzariuNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Therapy of Anxiety DisordersDocument50 pagesCognitive Therapy of Anxiety DisordersJacquiNo ratings yet
- Enteral Feeding: Gastric Versus Post-Pyloric: Table 1Document22 pagesEnteral Feeding: Gastric Versus Post-Pyloric: Table 1tasmeow23No ratings yet
- Ilaç Listesi ESKIDocument11 pagesIlaç Listesi ESKIDursun KorkmazNo ratings yet
- Chronic Total OcclusionsDocument37 pagesChronic Total OcclusionsValentin CHIONCELNo ratings yet
- TB DrugsDocument14 pagesTB DrugsLexy CadigalNo ratings yet
- Community Pharmacy Case Studies: Case Study - Patient SafetyDocument2 pagesCommunity Pharmacy Case Studies: Case Study - Patient SafetyNuwaira BalochNo ratings yet
- Oxy CadDocument21 pagesOxy CadrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Biology 4411Document13 pagesMark Scheme: Biology 4411monjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy and Postpartum - ATADocument61 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy and Postpartum - ATAtabhsinghiNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument25 pagesHepatitis BJevon AndraNo ratings yet
- Countertransference As Active ImaginationDocument19 pagesCountertransference As Active ImaginationGubs SabanNo ratings yet
- BJD Methotrxate PDFDocument22 pagesBJD Methotrxate PDFSoumya MarangadNo ratings yet
- Vitamin b12 and Pregnancy - With ReferencesDocument2 pagesVitamin b12 and Pregnancy - With Referencesapi-271190857No ratings yet
- Portugal April 2014Document54 pagesPortugal April 2014Olga MihaelaNo ratings yet
- GK QA ProceduresDocument64 pagesGK QA ProceduresJared MehargNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical Psychology 8th Edition Kramer Test BankDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Clinical Psychology 8th Edition Kramer Test Bankkayleelopezotwgncixjb100% (36)
- Renal Ultrasound in CKD OmicsDocument24 pagesRenal Ultrasound in CKD Omicskrishnadoctor1No ratings yet
- Assignement Blood Sugar LevelDocument4 pagesAssignement Blood Sugar LevelDeo NzigilwaNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients Assignment-14th EdDocument3 pagesMicronutrients Assignment-14th EdMan Tue ThaiNo ratings yet
- Red BiotechnologyDocument17 pagesRed BiotechnologyJonas SaintNo ratings yet
- Systematic Review On Sucess of Narrow-Diameter Dental ImplantsDocument37 pagesSystematic Review On Sucess of Narrow-Diameter Dental ImplantsMaryGonzalesʚïɞNo ratings yet
- Mr. Shoaib Hakeem How To Manage Recalls and Withdrawls of PharmaceuticalsDocument25 pagesMr. Shoaib Hakeem How To Manage Recalls and Withdrawls of PharmaceuticalsSally PujaNo ratings yet