Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
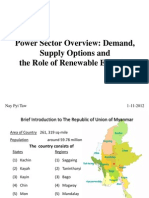
87 viewsPLN Seminar Hotel Borobudur 20052014
PLN Seminar Hotel Borobudur 20052014
Uploaded by
Tri Supir DamriPLN expects to benefit from Indonesia's growing electricity demand driven by economic transformation and population growth. Electricity demand is projected to grow 8.29% annually on average through 2022. However, Indonesia's electrification ratio of 80.4% and per capita electricity consumption are among the lowest in Asia, indicating substantial room for growth. As the dominant player in Indonesia's electricity market and sole provider of transmission and distribution, PLN is well-positioned to meet rising demand.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Electricity Sector in India 1Document55 pagesElectricity Sector in India 1Gautham SidharthNo ratings yet
- Indian Power SectorDocument7 pagesIndian Power SectorAnkush BhandariNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Power SectorDocument38 pagesAnalysis of Power SectorAakankshaNo ratings yet
- Assignment PSADocument8 pagesAssignment PSARitwik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Power Sector in India ProjectDocument23 pagesPower Sector in India ProjectRajesh ParidaNo ratings yet
- Energy Comsats 12oct13 2Document23 pagesEnergy Comsats 12oct13 2Muhammad Arslan UsmanNo ratings yet
- MC Myanmar Power Industry Jun2014Document6 pagesMC Myanmar Power Industry Jun2014Anu ParthaNo ratings yet
- Ippppas@20110621 Faq On Ipps Ppas Lampiran A v3 4Document10 pagesIppppas@20110621 Faq On Ipps Ppas Lampiran A v3 4Hass MohdNo ratings yet
- 35,000 MW: A Light For The Nation: Infrastructure and Capital Projects PT Deloitte Konsultan Indonesia 2016Document50 pages35,000 MW: A Light For The Nation: Infrastructure and Capital Projects PT Deloitte Konsultan Indonesia 2016Andri JordanNo ratings yet
- Power Sector UpdateDocument16 pagesPower Sector UpdatelightsonsNo ratings yet
- Energy The Report Myanmar 2017Document24 pagesEnergy The Report Myanmar 2017chaw htet myat100% (1)
- Myanmar Power Sector OverviewDocument34 pagesMyanmar Power Sector OverviewMichael HengNo ratings yet
- Indian Power SectorDocument38 pagesIndian Power SectorAbhay Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Power Point PerencanaanDocument28 pagesPower Point PerencanaanabdulanasnasutionNo ratings yet
- I-REC Country Assessment Indonesia - v1Document10 pagesI-REC Country Assessment Indonesia - v1Angela NatashaNo ratings yet
- Electricity in PakistanDocument22 pagesElectricity in Pakistanglamoure100% (1)
- Improving Electric Power Supply Using Distributed Generation For Sustainable Entrepreneurship Development in NigeriaDocument9 pagesImproving Electric Power Supply Using Distributed Generation For Sustainable Entrepreneurship Development in NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Matching Electricity Supply With Demand in NigeriaDocument5 pagesMatching Electricity Supply With Demand in NigeriaaishatuNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Applying Distributed Generation-SHANGHAIDocument23 pagesIndonesia Applying Distributed Generation-SHANGHAINyx RubyNo ratings yet
- The Economic Cost Af SubmissionDocument21 pagesThe Economic Cost Af SubmissionvictorNo ratings yet
- 001 SoDocument5 pages001 SoLevanhuongNo ratings yet
- Electricity Supply Industry in Malaysia 2010Document103 pagesElectricity Supply Industry in Malaysia 2010Harzamir BamoreNo ratings yet
- Energy IybDocument9 pagesEnergy IybPrabhu SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Energy Situation - EnergypediaDocument9 pagesIndonesia Energy Situation - EnergypediaZoebairNo ratings yet
- Rural ElectrificationDocument12 pagesRural ElectrificationRavikanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Energy Sector Assignment - FinalDocument18 pagesEnergy Sector Assignment - FinalWalid HasanNo ratings yet
- Energy Sector AssessmentDocument6 pagesEnergy Sector Assessmentmeendhami62No ratings yet
- Adani Power Limited: Supan ShahDocument26 pagesAdani Power Limited: Supan ShahAnonymous V4jDKjUR6No ratings yet
- Victor Jona - Cambodia's Rural Electrification Minigrid Systems, Standard and RegulationDocument28 pagesVictor Jona - Cambodia's Rural Electrification Minigrid Systems, Standard and RegulationAsia Clean Energy ForumNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Electricity Industry in MyanmarDocument20 pagesAn Overview of The Electricity Industry in MyanmarMaria MidiriNo ratings yet
- Power Sector Indian ScenarioDocument98 pagesPower Sector Indian ScenarioJaganathan ChokkalingamNo ratings yet
- 1power ScenarioDocument46 pages1power Scenariosexyakshay2623No ratings yet
- Power Sector OverviewDocument9 pagesPower Sector OverviewMuneer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Upfront Solar Determination 21-01-2014 777-79Document46 pagesUpfront Solar Determination 21-01-2014 777-79Muhammad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Electricity Rates in Pakistan by MIRZA MAJID ALIDocument25 pagesElectricity Rates in Pakistan by MIRZA MAJID ALIEngr Majid Ali BaigNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: Industry ProfileDocument53 pagesExecutive Summary: Industry ProfileBhumi JaanviNo ratings yet
- Peninsular Malaysia Electricity Supply Industry Outlook 2013Document78 pagesPeninsular Malaysia Electricity Supply Industry Outlook 2013cayunk7145No ratings yet
- US Report Energy VietnamDocument7 pagesUS Report Energy VietnamErica KimNo ratings yet
- Performance & Statistical Information 2010 PDFDocument103 pagesPerformance & Statistical Information 2010 PDFMuhammad Herul'sNo ratings yet
- Tata Power Company Limited: - Mr. Prasad R. Menon, Managing Director, Tata PowerDocument22 pagesTata Power Company Limited: - Mr. Prasad R. Menon, Managing Director, Tata PowerncbaraiNo ratings yet
- Power Scenario of IndiaDocument39 pagesPower Scenario of IndiaHoney AbdullahNo ratings yet
- EGHPP Project Introduction For Business SummitDocument3 pagesEGHPP Project Introduction For Business SummitUrtaBaasanjargalNo ratings yet
- Term Paper For Macroeconomics PDFDocument14 pagesTerm Paper For Macroeconomics PDFmanojpuruNo ratings yet
- DescoDocument80 pagesDescosibivarmanNo ratings yet
- Solar 7Document109 pagesSolar 7Probodh MallickNo ratings yet
- Solar Project Full 2-1Document54 pagesSolar Project Full 2-1nwachukwu.nzekwe zekweNo ratings yet
- Combine Scope of Work For TA To NEA 24 Jan 2021Document16 pagesCombine Scope of Work For TA To NEA 24 Jan 2021elkhalfiNo ratings yet
- Guide To Electric Power in GhanaDocument63 pagesGuide To Electric Power in GhanaGiho KimNo ratings yet
- Application of LEAP Model On Long-Term Electricity Demand Forecasting in Indonesia, Period 2010-2025Document9 pagesApplication of LEAP Model On Long-Term Electricity Demand Forecasting in Indonesia, Period 2010-2025Senhao HuangNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Perceptions Towards The Rooftop PV Solar System Policy in IndonesiaDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Perceptions Towards The Rooftop PV Solar System Policy in Indonesiaibtor007No ratings yet
- Energy Vietn IndoDocument11 pagesEnergy Vietn IndoVidhi GhadiNo ratings yet
- Power Sector Market Report EthiopiaDocument11 pagesPower Sector Market Report EthiopiaephremNo ratings yet
- The Power and Energy Sector of BangladeshDocument35 pagesThe Power and Energy Sector of BangladeshAnonymous Cd2KBYjJ100% (1)
- Chapter - 6: Load ForecastDocument46 pagesChapter - 6: Load ForecastGheewala AnkurNo ratings yet
- Nepal Energy Sector Assessment, Strategy, and Road MapFrom EverandNepal Energy Sector Assessment, Strategy, and Road MapNo ratings yet
- On the Road to Achieving Full Electrification in Sri LankaFrom EverandOn the Road to Achieving Full Electrification in Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- EU China Energy Magazine 2023 September Issue: 2023, #8From EverandEU China Energy Magazine 2023 September Issue: 2023, #8No ratings yet
- RE-organising Power Systems for the TransitionFrom EverandRE-organising Power Systems for the TransitionNo ratings yet
- Improving Skills for the Electricity Sector in IndonesiaFrom EverandImproving Skills for the Electricity Sector in IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Emerson Lc195em82 Lc195em87Document59 pagesEmerson Lc195em82 Lc195em87slayer866No ratings yet
- MC4 Vs MC4-EVO2 Application NoteDocument4 pagesMC4 Vs MC4-EVO2 Application NoteJoseph Mahlomola MasenkaneNo ratings yet
- Mutah Univercity Solar Field-2023 1Document16 pagesMutah Univercity Solar Field-2023 1GOD of UniverseNo ratings yet
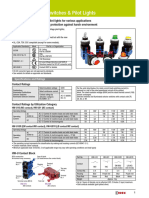
- Product Guide: Protection and ControlDocument16 pagesProduct Guide: Protection and Controljorge664No ratings yet
- Ø25 Illuminated Push Buttons IDEC TWS Series CATALOG 3961Document35 pagesØ25 Illuminated Push Buttons IDEC TWS Series CATALOG 3961Đào MạnhNo ratings yet
- Instruction Book: 2 Phase Digital Stepper DriverDocument9 pagesInstruction Book: 2 Phase Digital Stepper DriverВячеслав ПоповNo ratings yet
- Uh311 Wheeled Unit Pioneering Solutions For You: Technical SpecificationDocument2 pagesUh311 Wheeled Unit Pioneering Solutions For You: Technical SpecificationJulie Ann VeyraNo ratings yet
- L31187 PLC Select ABS Upgrade Kit 10-10Document8 pagesL31187 PLC Select ABS Upgrade Kit 10-10Francisco Santiago GallardoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Part 1Document39 pagesTransformer Part 1Franchesca Therese Caño EncisoNo ratings yet
- 33 KV Sub Station DPDCDocument109 pages33 KV Sub Station DPDCRashed Islam0% (1)
- Harmonics, What You Should Know: What Types of Loads Cause The Problem?Document5 pagesHarmonics, What You Should Know: What Types of Loads Cause The Problem?Richard GumanitNo ratings yet
- Lab Viva QuestionDocument13 pagesLab Viva QuestionNarasimman Don100% (1)
- Milli Ohm AdapterDocument6 pagesMilli Ohm AdapterPeter JordanNo ratings yet
- Makelsan Ups Boxer Series 10 20 Kva User Manual enDocument60 pagesMakelsan Ups Boxer Series 10 20 Kva User Manual enRECEP ÖZTÜRKNo ratings yet
- Generator ProtectionDocument10 pagesGenerator ProtectionVirendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Www.wineYardProjects.comDocument4 pagesWww.wineYardProjects.comrajani02No ratings yet
- Loop Impedance - GFDocument5 pagesLoop Impedance - GFmadhavanNo ratings yet
- L&T Type 2 Co-Ordination Selection ChartsDocument48 pagesL&T Type 2 Co-Ordination Selection Chartsrdeepak99100% (7)
- TC7662A Charge Pump Dc-To-Dc Converter: General Description FeaturesDocument5 pagesTC7662A Charge Pump Dc-To-Dc Converter: General Description FeaturesHAITHAMNo ratings yet
- ETAP User GuideDocument4,762 pagesETAP User Guidebaskaranjay5502100% (11)
- Electrical - Diagramm Bell Piston ProverDocument42 pagesElectrical - Diagramm Bell Piston ProverBragutaAlexandruNo ratings yet
- GD20-EU Manual 66007-00660-SSP - V1.0Document173 pagesGD20-EU Manual 66007-00660-SSP - V1.0renato vitaliNo ratings yet
- Module For PECDocument27 pagesModule For PECFrancis Al Maghanoy GabisonNo ratings yet
- xczl2011005 - ZXDU68 T601 Power System-V3 - 325632Document2 pagesxczl2011005 - ZXDU68 T601 Power System-V3 - 325632Sloan Ian AriffNo ratings yet
- Ece 9403/9043A - High Frequency Power Electronic Converters Assignment #1Document2 pagesEce 9403/9043A - High Frequency Power Electronic Converters Assignment #1anishthNo ratings yet
- An Improved iUPQC Controller To Provide Additional Grid-Voltage Regulation As A StatcomDocument4 pagesAn Improved iUPQC Controller To Provide Additional Grid-Voltage Regulation As A StatcomMaruthi JacsNo ratings yet
- 521G, 621G, 721G, 821G, 921G, 1021G, 1121G Wheel Loader ElectricalDocument6 pages521G, 621G, 721G, 821G, 921G, 1021G, 1121G Wheel Loader ElectricalEl Perro100% (1)
- 00 - Course InfoDocument14 pages00 - Course Infoeve lai100% (1)
- Design: Brushed Axial Flux DC MotorDocument2 pagesDesign: Brushed Axial Flux DC MotorAkshay DeolasiNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument27 pagesSeries and Parallel CircuitsClarence Virata100% (1)
PLN Seminar Hotel Borobudur 20052014
PLN Seminar Hotel Borobudur 20052014
Uploaded by
Tri Supir Damri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views19 pagesPLN expects to benefit from Indonesia's growing electricity demand driven by economic transformation and population growth. Electricity demand is projected to grow 8.29% annually on average through 2022. However, Indonesia's electrification ratio of 80.4% and per capita electricity consumption are among the lowest in Asia, indicating substantial room for growth. As the dominant player in Indonesia's electricity market and sole provider of transmission and distribution, PLN is well-positioned to meet rising demand.
Original Description:
PLN
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPLN expects to benefit from Indonesia's growing electricity demand driven by economic transformation and population growth. Electricity demand is projected to grow 8.29% annually on average through 2022. However, Indonesia's electrification ratio of 80.4% and per capita electricity consumption are among the lowest in Asia, indicating substantial room for growth. As the dominant player in Indonesia's electricity market and sole provider of transmission and distribution, PLN is well-positioned to meet rising demand.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views19 pagesPLN Seminar Hotel Borobudur 20052014
PLN Seminar Hotel Borobudur 20052014
Uploaded by
Tri Supir DamriPLN expects to benefit from Indonesia's growing electricity demand driven by economic transformation and population growth. Electricity demand is projected to grow 8.29% annually on average through 2022. However, Indonesia's electrification ratio of 80.4% and per capita electricity consumption are among the lowest in Asia, indicating substantial room for growth. As the dominant player in Indonesia's electricity market and sole provider of transmission and distribution, PLN is well-positioned to meet rising demand.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 19
PT Perusahaan Listrik Negara (Persero) PT Perusahaan Listrik Negara (Persero)
in Enhancing Growth and Competitiveness on Energy Sector
Syofvi F Roekman
Head of Strategic Planning Division Head of Strategic Planning Division
Borobudur Hotel, Jakarta
May 20
th
, 2014
Electricity Industry Overview
Still Favorable Macroeconomic Outlook
The ongoing transformation of Indonesia from an agricultural to a service-oriented economy is expected to drive GDP
growth and underpin further demand for electricity consumption.
(in TWh)
g p y p
271
306
329
355
384
340
390, 280,0
Growing Electricity Demand
GDP Growth
1
142
155
168
181
194
207
221
236
252
103
113
188
206
225
245
328
284
306
140,
190,
240,
290,
340,
140,0
210,0
2%
4%
6%
46
51
57
64
70
77
85
94
103
-10,0
40,0
90,0
0,0
70,0
2013 2014E 2015E 2016E 2017E 2018E 2019E 2020E 2021E 2022E
J ava-Bali OutsideJ ava-Bali
0%
2%
2011 2012 2013 2014E 2015E 2016E 2017E 2018E
Indonesia Global
PLN expects to benefit from the growth in electricity demand given its
dominant presence in the Indonesian electricity market
Projected electricity demand growth of 8.29% per annum on average
J ava Bali Outside J ava Bali
Indonesia is the largest economy in Southeast Asia
5.9% average real GDP growth over the period of 2008 2012
Indonesia is projected to be the 7
th
largest economy in the world by
between 2013 and 2022E
J ava-Bali represents ~75 80% of energy demand requirements in
Indonesia and more than 70% of total generating capacity
Expansion of the commercial sector has significantly contributed to the
th f l t i it d d
p j g y y
2030 (McKinsey)
Large consumer base with fast growing spending power
Consumer expenditure has grown at a CAGR of 13.8% from 2000
2012
66 6%of the population is of working age (15 64 years old) and
growth of electricity demand
66.6% of the population is of working age (15 64 years old) and
68.5% were 39 years and younger as of 2012
Source: Economist Intelligence Unit, IMF, McKinsey, PLN.
1. Percent change, constant prices.
Electrification Ratio Demonstrates Room for Growth
Ample room for growth in electricity sector based on current Electrification Ratio in Indonesia.
Low electrification ratio of 80.4% compared to other Asian Developing Countries underscores undersupply
PLN is mandated to implement Fast Track Programs for capacity expansion to meet Indonesias growing demand
Aimto achieve >90%electrificationrate by 2019
Electrification Ratio for Asian Developing Countries
1
Aim to achieve >90% electrification rate by 2019
The role of IPPs in providing domestic power will also become increasingly important as the domestic electricity consumption increases
Growing of Indonesias Electrification Ratio
100.0% 99.7% 99.4% 97.6%
87.7%
83.3%
80.4%
75.0%
67.4%
2019 target: >90%
62.4%
63.8%
66.5%
74.3%
76.2%
80.4%
(2)
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Electrification Ratio
Source: PLN, IEA World Energy Outlook 2012
1. Percentage of population with electricity access
2. Indonesias figure as of December 31, 2013
Growing Indonesia Electricity Market Benefits PLN
Backed by strong macroeconomic indicators, energy demand in Indonesia is expected to grow significantly in the next
fewyears.
10,2
Growing of Peak Load Relatively Low Per Capita Electricity Consumption
1
(in MW) (in MWh per Capita)
y
55 2
59,5
64,3
8,4
7,8
5,9
4,2
3,3
2,3
31,9
35,0
38,1
41,3
44,5
47,9
51,3
55,2
1,1
0,7 0,7 0,6
0,4
u
t
h
K
o
r
e
a
S
i
n
g
a
p
o
r
e
J
a
p
a
n
H
o
n
g
k
o
n
g
M
a
l
a
y
s
i
a
C
h
i
n
a
T
h
a
i
l
a
n
d
V
i
e
t
n
a
m
n
d
o
n
e
s
i
a
I
n
d
i
a
h
i
l
i
p
p
i
n
e
s
P
a
k
i
s
t
a
n
2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
Peak Load (MW)
2
S
o
u
SH
I
P
h
With higher income levels, increasing urbanization and improving
standard of living, electricity demand is expected to continue to increase
Ongoing transformation from an agricultural to a manufacturing-oriented
h l l d ti l l i t t l i th th f
Indonesias per capita consumption of electricity, electrification levels
and the installed capacity levels are among the lowest in Asia
Need for substantial increase in generatingcapacity is evident by
Source: 1. World Bank.
2. Indonesias figure as 2013
Source: PLN, MEMR
economy has also played a particularly important role in the growth of
demand for electricity
Need for substantial increase in generating capacity is evident by
increasing number of power outages in recent years
As the major provider of electricity in Indonesia, As the major provider of electricity in Indonesia,
PLN expects to benefit from Indonesias growth in demand for electricity.
Company Overview Company Overview
Corporate Structure
Ministry of State Owned
Enterprises (MSOE)
Ministry of Energy and Mineral
Resources (MEMR)
G I ill ti t h ld
Resources (MEMR)
Ministry of Finance (MoF)
Ministry of the Environment
National Development Planning
A th it (BAPPENAS)
GoI will continue to hold
100% of PLN
PT PLN (Persero)
Oversight
Authority (BAPPENAS)
PT PLN Tarakan
PT PLN Batam PT Indonesia Power
g
PT Pembangkitan
Jawa Bali
Regional Fully Integrated
Electric Utility
Regional Fully Integrated
Electric Utility Electricity Generation
Electricity Generation
PT Indonesia
Comnets Plus
Telecommunications for
the Electricity Sector
PT PLN Batubara
Coal Supplier for PLN
PT Prima Layanan
Nasional Enjiniring
Engineering and
Construction Services
Majapahit Holding
B.V.
Financial Institution
PT PLN Geothermal
Geothermal Energy
Generation
PT Pelayaran
Bahtera Adhiguna
Shipping Activities
PT Haleyora Power
Electricity Supplier
Note: Excludes J oint Ventures.
PLN Presence in the Indonesian Electricity Market
PLN is the only integrated electric utility company in Indonesia, controls the majority of generation capacity and is the sole
transmission and distribution provider. p
38 502MWof installed capacityout which 39 581kmc of transmission lines 809 980kmc of distribution lines
Transmission Distribution Generation
38,502 MW of installed capacity out which
represents 83% of capacity in Indonesia
39,581 kmc of transmission lines
81,343 MVA of transmission transformer capacity
809,980 kmc of distribution lines
42,079 MVA of transformer capacity
IPP
17%
PLN remains the countrys largest electricity producer and the only business entity in charge of transmittingand distributing electric power in Indonesia
PLN
100%
PLN
100%
PLN
83%
PLN remains the countrys largest electricity producer and the only business entity in charge of transmitting and distributing electric power in Indonesia
Under the New Electricity Law (No. 30/2009), PLN has the first priority to supply electricity in a specific area before such right can be awarded to anyone
else
If PLN declines to undertake a public electricity supply business for a certain area, the Government or regional governments may offer this right to
regional-owned companies, private enterprises or cooperatives
f G If there are no regional-owned companies, private enterprises or cooperatives that elect to supply electricity in that area, the Government is
obligated to instruct SOEs (which includes PLN) to supply electricity to the area
Extensive Generation Network
PLN controls 83% of Indonesias total installed generation portfolio of 46,245 MW
Total
Hydro 3,519 MW
Geothermal 568 MW
Steam-turbine 15,710 MW
Maluku
Diesel 295 MW
Others 1 MW
Total 296 MW
Kalimantan
Hydro 32 MW
Steam-turbine 266 MW
Combined Cycle 60 MW
Sumatera
Hydro 864 MW
Geothermal 110 MW
Steam-turbine 1,332 MW
Sulawesi
Hydro 223 MW
Geothermal 80 MW
Steam-turbine 112 MW
Combined
Cycle
8,814 MW
Gas-turbine 3,690 MW
Diesel 6,193 MW
Others 8 MW
IPP 7,743MW
Total 46 245MW
Gas-turbine 179 MW
Diesel 1,382 MW
Others 0 MW
IPP 56 MW
Total 1,975 MW
Combined Cycle 858 MW
Gas-turbine 1,294 MW
Diesel 2,284 MW
Others 0 MW
IPP 1,202 MW
Total 7,944 MW
Gas-turbine 183 MW
Diesel 948 MW
Others 3 MW
IPP 695 MW
Total 2,244 MW
Total 46,245MW
Sumatera
Kalimantan
S l i
Maluku
Papua
Java-Bali
Hydro 2,392 MW
Geothermal 375 MW
Sulawesi
NTT
NTB
Java-Bali
Papua
Diesel 266 MW
Hydro 6 MW
Total 272 MW
NTT
Diesel 237 MW
Geothermal 3 MW
NTB
Steam-turbine 30 MW
Geothermal 375 MW
Steam-turbine 13,970 MW
Combined Cycle 7,896 MW
Gas turbine 2,034 MW
Diesel 457 MW
Others 1 MW
IPP 5 791 MW
Hydro 1 MW
Others 2 MW
Total 243 MW
Diesel 324 MW
Hydro 1 MW
Others 1 MW
Total 356 MW
IPP 5,791 MW
Total 32,916MW
As of December 31, 2013
Companys Performance
PLN is the only state-owned power utility company and the only fully-integrated power utility company in Indonesia.
PLN is Indonesias state-owned electric utility company, wholly-owned by the Republic of Indonesia and is represented by the Ministry of State-Owned
Enterprises
PLN is the major provider of all public electricity and electricity infrastructure in Indonesia, including power generation, transmission, distribution, construction of power
plans and retail sales of electricity
Charges for electricity are based on electricity tariff rates that are set by the Government
Law No. 19/2003 on State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): the Government is obligated to provide subsidy to PLN for the difference between the price charged for
electricity and the cost to produce electricity
Key Business Segments
1
Generation
Controls 83% of installed generating capacity
approximately 38,502 MW including rentals by an
increase 5.2% (vs 36,612MW as at 2012)
Owns and operates 5,593 generation
Transmission
Sole provider of power transmission in Indonesia
Approximately 39,581 kmc of transmission lines by
an increase 3.9% (vs. 38,096 kmc as at 2012)
81,343 MVA of transmission transformer capacity
Distribution
Sole distributor of electricity to end customers in
Indonesia
Approximately 809,980 kmc of distribution lines
and 42,079 MVA of distribution transformer
capacity by an increase 9 2%and 3 5%
Main purchaser of electricity from Independent
Power Producers (IPPs)
by an increase 5.6% (vs. 77,037 MVA as at 2012)
capacity by an increase 9.2% and 3.5%
(vs 741,957 kmc and 40,654 MVA as at 2012)
Serving approximately 54 million customers
Electricity Sales Customer Base
(in TWh) (in millions)
1580
174,0
187,5
540
129,0
134,6
147,3
158,0
,
38,6
40,1
42,4
45,9
49,8
54,0
Note: PLN is also the provider of electricity of last resort, in that if PLN is not supplying a particular area and there are no regional-owned companies, private enterprises or cooperatives that elect to supply electricity in that
area, the Government is obligated to instruct SOEs (which includes PLN) to supply electricity to the area.
1. As of December 31, 2013
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Business Snapshot as of December 31, 2013
PLN distributes and sells electricity to several customer types. The electricity sold is either generated by PLN or
purchased from IPPs. p
Generation Composition PLNs Generating Capacity
Hydro
Diesel
Others
0,02%
Transmission Network Detail Distribution Network Detail
500 kV interconnected transmission
system with 5,052 kmc
275kV t i i t ith
Medium-voltage line distribution
network of 339,137 kmc
L lt li di t ib ti
31%
2%
28%
12%
27%
22%
2%
12%
76%
24%
Own
Production
76%
Purchased
24%
Hydro
9%
Steam-
Turbine
41%
Gas-
Turbine
Combined
Cycle
23%
Geothermal
1%
Diesel
16%
275 kV transmission system with
1,028 kmc
150 kV transmission system with
29,228 kmc
4,272 kmc of transmissions
Low-voltage line distribution
network of 470,843 kmc
371,662 units of distribution
transformers with total capacity of
approximately 42,079 MVA
12%
26%
76%
Total: 216,189 GWh
Turbine
10%
Total: 38,502 MW
systems up to 70 kV
Electricity Transmitted and Distributed by Customer Type Number of Customers by Type
(in millions) (in TWh)
651
72,1
77,2
129,0
134,6
147,3
158,0
174,0
187,5
38,6
40,1
42,4
45,9
49,8
54,0
7,9 8,6 9,3 9,8 10,7
11,5
22,9
24,8 27,2 28,3
31,0
34,5
48,0
46,2 51,0
54,7 60,2
64,4
50,2 54,9
59,8
65,1
,
1,0 1,1 1,2
1,2 1,3 1,4
1,7 1,9 1,9 2,0 2,2 2,4
0,05 0,05
0,05 0,05 0,05
0,06
35,8
37,1
39,3
42,6
46,2
50,1
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Public Business Industrial Residential
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Public Business Industrial Residential
Efficient Operations with Continuing Improvements
PLN has continued to successfully improve its operating efficiency.
Improving and Controlling T&D and Overheads Costs 2
Improving Fuel Mix Reducing Oil Consumption 2012 from 15% (29.6TWh) to
12% (26.6TWh) in 2013
1
Implementation of Efficiency Program
21%
7%
9%
6%
5%
6%
25%
22%
20%
23%
15%
12%
Fuel Mix (IPP +PLN Production)
3
Maintaining Collection Period
4
Implementing Centralized Online Payment System, Centralized Administration
System & Cash Pooling, Centralized Non Cash Loan Facility, On Line Trade Finance
5
Expanding Prepaid System Intensively Increasing Customers in 2013 (13.15M)
vs 2012 (7.83M) up to 68%and has been No.1 in the world for serving largest
28%
28% 27%
30%
33% 35%
2%
2%
2%
2%
2% 2%
13%
18% 19%
18%
20%
21% 7%
7% 6%
5
vs 2012 (7.83M) up to 68% and has been No.1 in the world for serving largest
prepaid customers
6 J oint Procurement for Maintenance and Material Distribution
7
Manufacturers are the only parties eligible to bid in generation, transmission and
distribution tender processes, open book procurement
24% 23% 22% 22%
25% 24%
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
IPP Coal Geothermal Natural Gas Hydro Fuel Oil
13 3
16,7
System Average Interruption Duration Index (SAIDI)
(Hour/customer)
10,5%
9,9%
9,7%
9,4%
9,2%
9,4%
12,0%
Transmission and Distribution Losses
13,3
7,0
4,7
3,9
5,8
2,2% 2,2% 2,3% 2,3%
2,4%
2,3%
8,5%
7,9%
7,6%
7,3%
7,0%
7,8%
0 0%
4,0%
8,0%
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
0,0%
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Transmission Losses Distribution Losses System Losses
Opportunity for 2013 -2022
Demand Growth 2013-2022
26
TWh
66
TWh
TWh
TWh
188
385
Sumatera: 10,6%
TWh
Kalimantan: 10,7%
Maluku: 10,9%
2013 2022
Indonesia: 8,4%
18
44
Sulawesi: 10,8%
Papua: 10%
144 275
IT : 10,8%
18
TWh
TWh
13
JB : 7,6%
TWh TWh Nusa Tenggara: 11,1%
Additional Capacity for Power Plants
Total additional capacity until 2022
=> 60 GW.
MW
> 60 GW.
CFPP : 37,7 GW
Geothermal : 6,2 GW
CCPP : 4,8 GW
Gas : 3,6 GW
Diesel : 1,1 GW
H d 6 9 GW Hydro : 6,9 GW
Others : 0,2 GW
Type of Power Plants
Source : RUPTL 2013-2022
Investment Needed for Electricity Sector 2013 -2022
PLN P Pl t 38 billi US$ PLN Power Plants : 38 billion US$
PLN+IPP Power Plants : 90 billion US$
Transmission : 17 billion US$
Distribution : 15 billion US$
Billion US$
Total PLN : 68 billion US$
Total PLN+IPP : 122 billion US$
Source: RUPTL 2013-2022
What is Needed by PLN?
1 Strengthening the company's capital: 1. Strengthening the companys capital:
PLN internal revenue generation, through rate increase and or subsidies, which can improve
the ability of the investment.
Government support in the provision of investment funds in the State Capital (PMN) to reduce
the loan burden.
PLN loan restructuring, among others, by swapping the Sub-Loan Agreement (SLA) to PMN,
as well as the restructuring of the company's direct loan
2. Controlling power consumption:
Energy Conservation Program, among others, through demand side management, pricing
patterns by time of use the campaign uses energy saving appliances and others patterns by time of use, the campaign uses energy saving appliances and others.
Load growth control among others by controlling the power connection.
3 NewBusiness Model Scheme: 3. New Business Model Scheme:
Power Wheeling
BOT Generation and Transmission
others others
Opportunities in Electricity Sector
D d G th ll f f th i t t Demand Growth call for further investment
Form of Partnership:
Funding Funding
IPP with PPA
Power Wheeling
Excess Power
EPC Contractors
BOT of Generation and Transmission BOT of Generation and Transmission
Others
New Paradigm: Can the market mechanism drive the investors to involve in Electricity Sector without
Sovereign Guarantee and PPA? (which has not been applied in Indonesia yet)
Thank You
You might also like
- Electricity Sector in India 1Document55 pagesElectricity Sector in India 1Gautham SidharthNo ratings yet
- Indian Power SectorDocument7 pagesIndian Power SectorAnkush BhandariNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Power SectorDocument38 pagesAnalysis of Power SectorAakankshaNo ratings yet
- Assignment PSADocument8 pagesAssignment PSARitwik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Power Sector in India ProjectDocument23 pagesPower Sector in India ProjectRajesh ParidaNo ratings yet
- Energy Comsats 12oct13 2Document23 pagesEnergy Comsats 12oct13 2Muhammad Arslan UsmanNo ratings yet
- MC Myanmar Power Industry Jun2014Document6 pagesMC Myanmar Power Industry Jun2014Anu ParthaNo ratings yet
- Ippppas@20110621 Faq On Ipps Ppas Lampiran A v3 4Document10 pagesIppppas@20110621 Faq On Ipps Ppas Lampiran A v3 4Hass MohdNo ratings yet
- 35,000 MW: A Light For The Nation: Infrastructure and Capital Projects PT Deloitte Konsultan Indonesia 2016Document50 pages35,000 MW: A Light For The Nation: Infrastructure and Capital Projects PT Deloitte Konsultan Indonesia 2016Andri JordanNo ratings yet
- Power Sector UpdateDocument16 pagesPower Sector UpdatelightsonsNo ratings yet
- Energy The Report Myanmar 2017Document24 pagesEnergy The Report Myanmar 2017chaw htet myat100% (1)
- Myanmar Power Sector OverviewDocument34 pagesMyanmar Power Sector OverviewMichael HengNo ratings yet
- Indian Power SectorDocument38 pagesIndian Power SectorAbhay Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Power Point PerencanaanDocument28 pagesPower Point PerencanaanabdulanasnasutionNo ratings yet
- I-REC Country Assessment Indonesia - v1Document10 pagesI-REC Country Assessment Indonesia - v1Angela NatashaNo ratings yet
- Electricity in PakistanDocument22 pagesElectricity in Pakistanglamoure100% (1)
- Improving Electric Power Supply Using Distributed Generation For Sustainable Entrepreneurship Development in NigeriaDocument9 pagesImproving Electric Power Supply Using Distributed Generation For Sustainable Entrepreneurship Development in NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Matching Electricity Supply With Demand in NigeriaDocument5 pagesMatching Electricity Supply With Demand in NigeriaaishatuNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Applying Distributed Generation-SHANGHAIDocument23 pagesIndonesia Applying Distributed Generation-SHANGHAINyx RubyNo ratings yet
- The Economic Cost Af SubmissionDocument21 pagesThe Economic Cost Af SubmissionvictorNo ratings yet
- 001 SoDocument5 pages001 SoLevanhuongNo ratings yet
- Electricity Supply Industry in Malaysia 2010Document103 pagesElectricity Supply Industry in Malaysia 2010Harzamir BamoreNo ratings yet
- Energy IybDocument9 pagesEnergy IybPrabhu SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Energy Situation - EnergypediaDocument9 pagesIndonesia Energy Situation - EnergypediaZoebairNo ratings yet
- Rural ElectrificationDocument12 pagesRural ElectrificationRavikanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Energy Sector Assignment - FinalDocument18 pagesEnergy Sector Assignment - FinalWalid HasanNo ratings yet
- Energy Sector AssessmentDocument6 pagesEnergy Sector Assessmentmeendhami62No ratings yet
- Adani Power Limited: Supan ShahDocument26 pagesAdani Power Limited: Supan ShahAnonymous V4jDKjUR6No ratings yet
- Victor Jona - Cambodia's Rural Electrification Minigrid Systems, Standard and RegulationDocument28 pagesVictor Jona - Cambodia's Rural Electrification Minigrid Systems, Standard and RegulationAsia Clean Energy ForumNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Electricity Industry in MyanmarDocument20 pagesAn Overview of The Electricity Industry in MyanmarMaria MidiriNo ratings yet
- Power Sector Indian ScenarioDocument98 pagesPower Sector Indian ScenarioJaganathan ChokkalingamNo ratings yet
- 1power ScenarioDocument46 pages1power Scenariosexyakshay2623No ratings yet
- Power Sector OverviewDocument9 pagesPower Sector OverviewMuneer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Upfront Solar Determination 21-01-2014 777-79Document46 pagesUpfront Solar Determination 21-01-2014 777-79Muhammad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Electricity Rates in Pakistan by MIRZA MAJID ALIDocument25 pagesElectricity Rates in Pakistan by MIRZA MAJID ALIEngr Majid Ali BaigNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: Industry ProfileDocument53 pagesExecutive Summary: Industry ProfileBhumi JaanviNo ratings yet
- Peninsular Malaysia Electricity Supply Industry Outlook 2013Document78 pagesPeninsular Malaysia Electricity Supply Industry Outlook 2013cayunk7145No ratings yet
- US Report Energy VietnamDocument7 pagesUS Report Energy VietnamErica KimNo ratings yet
- Performance & Statistical Information 2010 PDFDocument103 pagesPerformance & Statistical Information 2010 PDFMuhammad Herul'sNo ratings yet
- Tata Power Company Limited: - Mr. Prasad R. Menon, Managing Director, Tata PowerDocument22 pagesTata Power Company Limited: - Mr. Prasad R. Menon, Managing Director, Tata PowerncbaraiNo ratings yet
- Power Scenario of IndiaDocument39 pagesPower Scenario of IndiaHoney AbdullahNo ratings yet
- EGHPP Project Introduction For Business SummitDocument3 pagesEGHPP Project Introduction For Business SummitUrtaBaasanjargalNo ratings yet
- Term Paper For Macroeconomics PDFDocument14 pagesTerm Paper For Macroeconomics PDFmanojpuruNo ratings yet
- DescoDocument80 pagesDescosibivarmanNo ratings yet
- Solar 7Document109 pagesSolar 7Probodh MallickNo ratings yet
- Solar Project Full 2-1Document54 pagesSolar Project Full 2-1nwachukwu.nzekwe zekweNo ratings yet
- Combine Scope of Work For TA To NEA 24 Jan 2021Document16 pagesCombine Scope of Work For TA To NEA 24 Jan 2021elkhalfiNo ratings yet
- Guide To Electric Power in GhanaDocument63 pagesGuide To Electric Power in GhanaGiho KimNo ratings yet
- Application of LEAP Model On Long-Term Electricity Demand Forecasting in Indonesia, Period 2010-2025Document9 pagesApplication of LEAP Model On Long-Term Electricity Demand Forecasting in Indonesia, Period 2010-2025Senhao HuangNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Perceptions Towards The Rooftop PV Solar System Policy in IndonesiaDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Perceptions Towards The Rooftop PV Solar System Policy in Indonesiaibtor007No ratings yet
- Energy Vietn IndoDocument11 pagesEnergy Vietn IndoVidhi GhadiNo ratings yet
- Power Sector Market Report EthiopiaDocument11 pagesPower Sector Market Report EthiopiaephremNo ratings yet
- The Power and Energy Sector of BangladeshDocument35 pagesThe Power and Energy Sector of BangladeshAnonymous Cd2KBYjJ100% (1)
- Chapter - 6: Load ForecastDocument46 pagesChapter - 6: Load ForecastGheewala AnkurNo ratings yet
- Nepal Energy Sector Assessment, Strategy, and Road MapFrom EverandNepal Energy Sector Assessment, Strategy, and Road MapNo ratings yet
- On the Road to Achieving Full Electrification in Sri LankaFrom EverandOn the Road to Achieving Full Electrification in Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- EU China Energy Magazine 2023 September Issue: 2023, #8From EverandEU China Energy Magazine 2023 September Issue: 2023, #8No ratings yet
- RE-organising Power Systems for the TransitionFrom EverandRE-organising Power Systems for the TransitionNo ratings yet
- Improving Skills for the Electricity Sector in IndonesiaFrom EverandImproving Skills for the Electricity Sector in IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Emerson Lc195em82 Lc195em87Document59 pagesEmerson Lc195em82 Lc195em87slayer866No ratings yet
- MC4 Vs MC4-EVO2 Application NoteDocument4 pagesMC4 Vs MC4-EVO2 Application NoteJoseph Mahlomola MasenkaneNo ratings yet
- Mutah Univercity Solar Field-2023 1Document16 pagesMutah Univercity Solar Field-2023 1GOD of UniverseNo ratings yet
- Product Guide: Protection and ControlDocument16 pagesProduct Guide: Protection and Controljorge664No ratings yet
- Ø25 Illuminated Push Buttons IDEC TWS Series CATALOG 3961Document35 pagesØ25 Illuminated Push Buttons IDEC TWS Series CATALOG 3961Đào MạnhNo ratings yet
- Instruction Book: 2 Phase Digital Stepper DriverDocument9 pagesInstruction Book: 2 Phase Digital Stepper DriverВячеслав ПоповNo ratings yet
- Uh311 Wheeled Unit Pioneering Solutions For You: Technical SpecificationDocument2 pagesUh311 Wheeled Unit Pioneering Solutions For You: Technical SpecificationJulie Ann VeyraNo ratings yet
- L31187 PLC Select ABS Upgrade Kit 10-10Document8 pagesL31187 PLC Select ABS Upgrade Kit 10-10Francisco Santiago GallardoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Part 1Document39 pagesTransformer Part 1Franchesca Therese Caño EncisoNo ratings yet
- 33 KV Sub Station DPDCDocument109 pages33 KV Sub Station DPDCRashed Islam0% (1)
- Harmonics, What You Should Know: What Types of Loads Cause The Problem?Document5 pagesHarmonics, What You Should Know: What Types of Loads Cause The Problem?Richard GumanitNo ratings yet
- Lab Viva QuestionDocument13 pagesLab Viva QuestionNarasimman Don100% (1)
- Milli Ohm AdapterDocument6 pagesMilli Ohm AdapterPeter JordanNo ratings yet
- Makelsan Ups Boxer Series 10 20 Kva User Manual enDocument60 pagesMakelsan Ups Boxer Series 10 20 Kva User Manual enRECEP ÖZTÜRKNo ratings yet
- Generator ProtectionDocument10 pagesGenerator ProtectionVirendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Www.wineYardProjects.comDocument4 pagesWww.wineYardProjects.comrajani02No ratings yet
- Loop Impedance - GFDocument5 pagesLoop Impedance - GFmadhavanNo ratings yet
- L&T Type 2 Co-Ordination Selection ChartsDocument48 pagesL&T Type 2 Co-Ordination Selection Chartsrdeepak99100% (7)
- TC7662A Charge Pump Dc-To-Dc Converter: General Description FeaturesDocument5 pagesTC7662A Charge Pump Dc-To-Dc Converter: General Description FeaturesHAITHAMNo ratings yet
- ETAP User GuideDocument4,762 pagesETAP User Guidebaskaranjay5502100% (11)
- Electrical - Diagramm Bell Piston ProverDocument42 pagesElectrical - Diagramm Bell Piston ProverBragutaAlexandruNo ratings yet
- GD20-EU Manual 66007-00660-SSP - V1.0Document173 pagesGD20-EU Manual 66007-00660-SSP - V1.0renato vitaliNo ratings yet
- Module For PECDocument27 pagesModule For PECFrancis Al Maghanoy GabisonNo ratings yet
- xczl2011005 - ZXDU68 T601 Power System-V3 - 325632Document2 pagesxczl2011005 - ZXDU68 T601 Power System-V3 - 325632Sloan Ian AriffNo ratings yet
- Ece 9403/9043A - High Frequency Power Electronic Converters Assignment #1Document2 pagesEce 9403/9043A - High Frequency Power Electronic Converters Assignment #1anishthNo ratings yet
- An Improved iUPQC Controller To Provide Additional Grid-Voltage Regulation As A StatcomDocument4 pagesAn Improved iUPQC Controller To Provide Additional Grid-Voltage Regulation As A StatcomMaruthi JacsNo ratings yet
- 521G, 621G, 721G, 821G, 921G, 1021G, 1121G Wheel Loader ElectricalDocument6 pages521G, 621G, 721G, 821G, 921G, 1021G, 1121G Wheel Loader ElectricalEl Perro100% (1)
- 00 - Course InfoDocument14 pages00 - Course Infoeve lai100% (1)
- Design: Brushed Axial Flux DC MotorDocument2 pagesDesign: Brushed Axial Flux DC MotorAkshay DeolasiNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument27 pagesSeries and Parallel CircuitsClarence Virata100% (1)