Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
444 viewsGNAV Key Facts
GNAV Key Facts
Uploaded by
RapsakThe document provides information on navigation formulas and conversions. It includes formulas for convergency, conversion angle, scale, departure, and finding the vertex. It also provides instructions for plotting bearings from VORs, NDBs, and using radio bearings on different map projections like Lambert and Mercator.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Navigation Questions: Triangle of VelocitiesDocument18 pagesNavigation Questions: Triangle of VelocitiesScipio100% (1)
- C0337-Socialscience03 Cam Term1 TestDocument4 pagesC0337-Socialscience03 Cam Term1 TestMARTA100% (7)
- PPL Exam Secrets Guide: Aviation Law & Operational ProceduresFrom EverandPPL Exam Secrets Guide: Aviation Law & Operational ProceduresRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- GNAV QuestionDocument29 pagesGNAV QuestionMahesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Altimeter Practice Question1Document4 pagesAltimeter Practice Question1Rohit100% (1)
- KW Gen. Nav. QsDocument128 pagesKW Gen. Nav. QsMonica Mohani0% (1)
- Dgca NavDocument50 pagesDgca Navasth100% (4)
- Latitude and Longitude PT 2Document1 pageLatitude and Longitude PT 2api-3294607660% (2)
- Commercial Pilots License - Radio Aids (Typical Questions)Document60 pagesCommercial Pilots License - Radio Aids (Typical Questions)tanmayNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - NavigationDocument62 pagesVolare Questions - NavigationChabou Rafik100% (1)
- GNAV Questions by LessonDocument83 pagesGNAV Questions by LessonLucasNo ratings yet
- Air Navigation in IndiaDocument14 pagesAir Navigation in IndiaRamBabuMeena100% (1)
- 1 in 60 RuleDocument8 pages1 in 60 Rulevivek100% (1)
- 3.efis Jaa QuestionsDocument20 pages3.efis Jaa QuestionschoppingcloudsNo ratings yet
- GSP Vol IV METDocument267 pagesGSP Vol IV METSojin Soman100% (2)
- DEparture GeneralDocument8 pagesDEparture GeneralCHANDAN KUMAR100% (1)
- Fragen - Principles of FlightDocument313 pagesFragen - Principles of FlightTomasz Kurdziel50% (2)
- ATPL Sample Questions - Radio AidsDocument5 pagesATPL Sample Questions - Radio AidsAbhinaya Sekar100% (2)
- Building and Structural Surveying N4 Aug 2018 QP PDFDocument7 pagesBuilding and Structural Surveying N4 Aug 2018 QP PDFZamabomvu100% (2)
- The Importance of SurveyingDocument9 pagesThe Importance of SurveyingJhun Waren83% (6)
- Air Navigation Questionnaire CPL PatternDocument18 pagesAir Navigation Questionnaire CPL Patternnodynaren100% (1)
- Decents 100Document11 pagesDecents 100Soumyadip SheetNo ratings yet
- Explainations of General Navigation QuestionsDocument11 pagesExplainations of General Navigation QuestionsZarrar Khan100% (1)
- Nav VivaDocument6 pagesNav Vivasupandeepsingh9394100% (1)
- Radio Nav Sample Q's (1-2-3) 2008Document45 pagesRadio Nav Sample Q's (1-2-3) 2008momanbh100% (3)
- Systems Atpl PDFDocument111 pagesSystems Atpl PDFMay Be100% (1)
- Nav Test For CPL CandidatesDocument8 pagesNav Test For CPL CandidatesVivek BaskarNo ratings yet
- DgcaDocument50 pagesDgcaasthNo ratings yet
- Air Navigation Full - 2Document10 pagesAir Navigation Full - 2Harshit dubey100% (1)
- Nav VivaDocument6 pagesNav VivaprachatNo ratings yet
- Navigation Test Paper (156 Q.)Document33 pagesNavigation Test Paper (156 Q.)Dipanjan Choudhury60% (5)
- Air Navigation Full-1Document12 pagesAir Navigation Full-1Harshit dubeyNo ratings yet
- DGCA Meteorology QuestionDocument2 pagesDGCA Meteorology QuestionShibin Johney100% (1)
- Principles of FlightDocument58 pagesPrinciples of FlightQuentin Caselli100% (2)
- FLIGHT PLANNING Ref ALLDocument40 pagesFLIGHT PLANNING Ref ALLZahoor Ali100% (2)
- 032 - Performance - AnswersDocument139 pages032 - Performance - AnswersEASA ATPL Question BankNo ratings yet
- Atpl - Meteorology SetDocument5 pagesAtpl - Meteorology SetHamidK.FarhatNo ratings yet
- Q Bank MetDocument94 pagesQ Bank MetsajjadNo ratings yet
- Instruments Keith Willams PDFDocument173 pagesInstruments Keith Willams PDFRyu100% (1)
- Gen Nav Final Test For PilotsDocument62 pagesGen Nav Final Test For PilotsAnandhanNo ratings yet
- NavigationDocument68 pagesNavigationsakshee gojre100% (1)
- Sahil Khurana Answer KeyDocument9 pagesSahil Khurana Answer KeyAmit KhannaNo ratings yet
- Meteorology March 2019Document3 pagesMeteorology March 2019Harshdeep Singh0% (1)
- General NavigationDocument162 pagesGeneral Navigationredbeard_060% (1)
- GNAV SofarDocument23 pagesGNAV SofarNikola100% (1)
- ATPL (A) Meteorology SummaryDocument174 pagesATPL (A) Meteorology Summarywilliambasket990% (1)
- CPL Nav9 Speed&Time.Document2 pagesCPL Nav9 Speed&Time.vivekNo ratings yet
- Meteorology AtplDocument27 pagesMeteorology Atpledward davisNo ratings yet
- CPL InstrumentsDocument160 pagesCPL InstrumentscostypNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 1Document8 pagesSample Paper 1Kunal Thakran100% (1)
- 01 - General Question 1 of 109: Question: Which of The Following Statements Is Correct ?Document118 pages01 - General Question 1 of 109: Question: Which of The Following Statements Is Correct ?Yahya Yıldırım100% (4)
- Albatross - Regs QBDocument47 pagesAlbatross - Regs QBtopgun320100% (1)
- General Nav - KWDocument147 pagesGeneral Nav - KWRohit PunamiyaNo ratings yet
- CPL RNav5 NDB - ADFDocument5 pagesCPL RNav5 NDB - ADFvivekNo ratings yet
- 5 - CPL Questions - AGK4 InstrumentsDocument114 pages5 - CPL Questions - AGK4 InstrumentsMoshiurRahman100% (1)
- Surender Conv of Units (10 Files Merged)Document25 pagesSurender Conv of Units (10 Files Merged)Anmoldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere - AnswersDocument12 pagesAtmosphere - AnswersAvinash Vijaykumar0% (1)
- Explainations of General Navigation QuestionsDocument11 pagesExplainations of General Navigation QuestionsZarrar KhanNo ratings yet
- Radio Bearings QuestionsDocument5 pagesRadio Bearings QuestionsJai Sachdev50% (2)
- Air Regulations 001Document116 pagesAir Regulations 001prachat100% (1)
- Gen Nav BFCDocument12 pagesGen Nav BFCTushar MantriNo ratings yet
- PPL Q. Bank (Nav)Document45 pagesPPL Q. Bank (Nav)Sabik Rahim100% (1)
- 1 - Ce 103Document22 pages1 - Ce 103Ann Nazmun SakibNo ratings yet
- Cartography Unit 3: Basic Geodesy Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesCartography Unit 3: Basic Geodesy Flashcards - QuizletTJ CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Ad 2 Lddu Instrument Approach Chart - Icao - Rnav (GNSS) Rwy12 PDFDocument4 pagesAd 2 Lddu Instrument Approach Chart - Icao - Rnav (GNSS) Rwy12 PDFTesla DrugiNo ratings yet
- Geomatica 2015 ATCORDocument11 pagesGeomatica 2015 ATCORRoyna Sidrotul MNo ratings yet
- Furuno GP30-35 GPS Operators ManualDocument67 pagesFuruno GP30-35 GPS Operators Manualjsdoodnath100% (1)
- History of SurveyingDocument2 pagesHistory of SurveyingBrian WafulaNo ratings yet
- GRIDNAVDocument3 pagesGRIDNAVNikhilesh 'gamble' IngaleNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Moore StationDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Moore StationHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- 01wknm20 Week01 2020Document109 pages01wknm20 Week01 2020muratkelescptNo ratings yet
- Civil III Surveying I (10cv34) NotesDocument109 pagesCivil III Surveying I (10cv34) NotesEmmanuel PeterNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of ShelbyvilleDocument1 pageTopographic Map of ShelbyvilleHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- 6geography PDFDocument81 pages6geography PDFSaket Deshmukh100% (1)
- Geodesy and CartographyDocument65 pagesGeodesy and CartographyGiniux PreezNo ratings yet
- Lat - Long or XY CoordinatesDocument4 pagesLat - Long or XY Coordinateshooty_OWLNo ratings yet
- Iala Dgps EngDocument2 pagesIala Dgps EngtommagneNo ratings yet
- Surveying ReviewerDocument2 pagesSurveying ReviewerRochelle Adajar-Bacalla100% (2)
- 5.2 Tachimetri Dan KonturDocument48 pages5.2 Tachimetri Dan KonturArif RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Global Positioning System (GPS) : Block II/IIA/IIR/IIR-M SatellitesDocument49 pagesGlobal Positioning System (GPS) : Block II/IIA/IIR/IIR-M SatellitesKriti ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal PlymouthDocument8 pagesResearch Proposal PlymouthKetutTomySuhariNo ratings yet
- Elementary Surveying Topic 1Document31 pagesElementary Surveying Topic 1Charles CarpoNo ratings yet
- CVE202 Lecture Notes-7 Angels Azimuths and BearingsDocument16 pagesCVE202 Lecture Notes-7 Angels Azimuths and BearingsAnteneh GeremewNo ratings yet
- RISM Competency Guide (F)Document12 pagesRISM Competency Guide (F)zili yeNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Vat CampDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Vat CampHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Survey II - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSurvey II - Lesson PlanSumethaRajasekarNo ratings yet
- Vacancies For Various Positions in The County Government of Taita Taveta Dated Thursday 2nd November 2023Document24 pagesVacancies For Various Positions in The County Government of Taita Taveta Dated Thursday 2nd November 2023Pastor_EdduNo ratings yet
- 52 Sample ChapterDocument29 pages52 Sample ChapterSaroj GaireNo ratings yet
GNAV Key Facts
GNAV Key Facts
Uploaded by
Rapsak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
444 views2 pagesThe document provides information on navigation formulas and conversions. It includes formulas for convergency, conversion angle, scale, departure, and finding the vertex. It also provides instructions for plotting bearings from VORs, NDBs, and using radio bearings on different map projections like Lambert and Mercator.
Original Description:
GNAV Key Facts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information on navigation formulas and conversions. It includes formulas for convergency, conversion angle, scale, departure, and finding the vertex. It also provides instructions for plotting bearings from VORs, NDBs, and using radio bearings on different map projections like Lambert and Mercator.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
444 views2 pagesGNAV Key Facts
GNAV Key Facts
Uploaded by
RapsakThe document provides information on navigation formulas and conversions. It includes formulas for convergency, conversion angle, scale, departure, and finding the vertex. It also provides instructions for plotting bearings from VORs, NDBs, and using radio bearings on different map projections like Lambert and Mercator.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
GNAV - All ()
1) What is the formula for convergency?
Convergency = ch long. x sin mean lat.
2) What is the formula for conversion angle?
Conversion angle = convergency
3) What is a rhumb line?
A line of constant direction and cuts all meridians and parallels at the same angle
4) What is nearer the pole, a rhumb line or a great circle?
A great circle
5) A great circle constantly changes direction, at what point does it have the same direction as a rhumb line?
At the mid-meridian of the track
6) How many NM is 1
o
of latitude?
60 NM (1 min is 1 NM)
7) What are the fuel conversions?
kg ( x 2.2 ) = lbs
Imp gallons ( x 1.205 ) = US gallons
US gallons ( x 3.784 ) = litres
litres ( x S.G.) = kg
US gallons ( x 6 ) = lbs
Imp gallons ( x 10 x S.G.) = lbs
8) What are the distance conversions?
1 NM ( x 1.15 ) = SM ( x 1.6 ) = KM
1 inch = 2.54 cm
1 NM = 6080 feet
1 SM = 5280 feet
1 KM = 3280 feet
1 NM = 1852 m
1 NM = 72960 inches (6080 x 12")
9) What is the formula for scale?
Scale = 1 / D = Chart length / Earth distance
10) What is the difference between a large and a small scale?
1 : 250 000 UK chart has a larger scale than 1 : 4 000 000 instructional plotting chart
11) What is the departure formula?
Departure = d.long (in min) x cos mean lat.
12) On a Mercator how does chart convergency relate to Earth convergency?
On a standard Mercator, chart convergency = zero everywhere because the meridians are straight. On the Earth, convergency is only
zero at the equator, therefore at higher latitude, chart convergency has got to be less than Earth convergency
13) On a Lambert how does chart convergency relate to Earth convergency?
At the parallel of origin, chart convergency = Earth convergency and remains constant everywhere on the chart.
On the Earth, convergency is greater at higher latitude and is less at lower latitude.
14) On a Polar stereographic how does chart convergency relate to Earth convergency?
At the pole, chart convergency = Earth convergency and remains constant everywhere on the chart.
On the Earth, convergency is maximum at the pole and zero at the equator.
15) How do you calculate the time and distance to start a speed reduction for a delayed arrival?
Eg. You are asked to reduce speed from 360 kts to 300 kt and delay arrival by 5 min when should this happen?
i) If you are not given an original ETA, assume one eg. 1000 h
ii) Draw out problem
ETA 1000 h ---------------------------- P
iii) Work out distance travelled at original GS
360 kts x 5 min / 60 = 30 NM (This distance needs to be 'lost')
iv) Work out speed reduction = 360 - 300 = 60 kt
30 NM x 60 / 60 KT = 30 min
v) Arrival has to be delayed by 5 min ie. 1005 h
The time to make the speed reduction is 30 min back from this ie. 0935 h
vi) The distance before the arrival point is 30 min at reduced GS of 300 kts = 150 NM
16) How do you calculate wind velocity when given values for multiple drift?
Set HDG and TAS on the CRP-5
Draw on each drift line in turn
Read off the WV
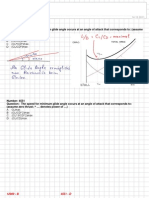
17) How do you find the vertex?
The longitude is way at the midpoint.
The latitude is found using the formula: Vertex (NM) = (tan CA x departure) / 2
or: Vertex (NM) = CA x departure / 230
18) How do you use unidentified ground features to find aircraft GS?
Eg. An A/C on HDG 032oM, var 9oE with two bearings observed 1000 h Rel bearing 030o, range 100 NM 1015 h Rel bearing 075o,
range 60 NM Work out HDG in true 032oM with VAR 9oE gives HDG 041oT Add the relative bearings to the true HDG and
calculate reciprocals to plot 1000 h 041oT + 030o = 071 + 180 = 251 to plot 1015 h 041oT + 075o = 116 + 180 = 296 to plot Draw
out the problem,
19) How do you calculate polar stereographic tracks?
Eg. An A/C on HDG 032oM, var 9oE with two bearings observed 1000 h Rel bearing 030o, range 100 NM 1015 h Rel bearing 075o,
range 60 NM Work out HDG in true 032oM with VAR 9oE gives HDG 041oT Add the relative bearings to the true HDG and
calculate reciprocals to plot 1000 h 041oT + 030o = 071 + 180 = 251 to plot 1015 h 041oT + 075o = 116 + 180 = 296 to plot Draw
out the problem, How do you calculate polar stereographic tracks? If you have time draw it accurately Draw a circle Identify the
hemisphere Add in W and E (with W on the left of the circle) Apply SCREW or UNSCREW for W0E (which means for the Southern
hemisphere draw out W0E in a clockwise fashion and for the Northern hemisphere draw out W0E in an anti-clockwise fashion) Align
Grid North: UP for Greenwich meridian DOWN for Greenwich Anti-meridian Draw a line to the position of longitude Reposition
Grid North over A/C position Draw in the A/C Grid or True HDG Check where True North is
20) How do you plot a bearing from a VOR?
Take reciprocal if necessary to get QDR Apply variation at station to get QTE to plot using true meridian at station
21) How do you plot a relative bearing to a NDB?
Add aircraft true HDG to relative bearing Apply chart convergency if any Apply variation at aircraft Take reciprocal to get QTE to
plot using true meridian at station
22) How do you plot a RMI bearing to a NDB?
Apply chart convergency if any Apply variation at aircraft Take reciprocal to get QTE to plot using true meridian at station
23) How do you plot bearings using AWR?
Add aircraft true HDG to relative bearing Apply chart convergency if any Take reciprocal Plot using true meridian at position bearing
was taken
24) How are radio bearings represented?
As great circles
25) How is a radio bearing plotted on a Lambert?
How is a radio bearing plotted on a Lambert?
26) How is a radio bearing plotted on a Mercator?
It must be converted to a rhumb line which is a straight line
You might also like
- Navigation Questions: Triangle of VelocitiesDocument18 pagesNavigation Questions: Triangle of VelocitiesScipio100% (1)
- C0337-Socialscience03 Cam Term1 TestDocument4 pagesC0337-Socialscience03 Cam Term1 TestMARTA100% (7)
- PPL Exam Secrets Guide: Aviation Law & Operational ProceduresFrom EverandPPL Exam Secrets Guide: Aviation Law & Operational ProceduresRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- GNAV QuestionDocument29 pagesGNAV QuestionMahesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Altimeter Practice Question1Document4 pagesAltimeter Practice Question1Rohit100% (1)
- KW Gen. Nav. QsDocument128 pagesKW Gen. Nav. QsMonica Mohani0% (1)
- Dgca NavDocument50 pagesDgca Navasth100% (4)
- Latitude and Longitude PT 2Document1 pageLatitude and Longitude PT 2api-3294607660% (2)
- Commercial Pilots License - Radio Aids (Typical Questions)Document60 pagesCommercial Pilots License - Radio Aids (Typical Questions)tanmayNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - NavigationDocument62 pagesVolare Questions - NavigationChabou Rafik100% (1)
- GNAV Questions by LessonDocument83 pagesGNAV Questions by LessonLucasNo ratings yet
- Air Navigation in IndiaDocument14 pagesAir Navigation in IndiaRamBabuMeena100% (1)
- 1 in 60 RuleDocument8 pages1 in 60 Rulevivek100% (1)
- 3.efis Jaa QuestionsDocument20 pages3.efis Jaa QuestionschoppingcloudsNo ratings yet
- GSP Vol IV METDocument267 pagesGSP Vol IV METSojin Soman100% (2)
- DEparture GeneralDocument8 pagesDEparture GeneralCHANDAN KUMAR100% (1)
- Fragen - Principles of FlightDocument313 pagesFragen - Principles of FlightTomasz Kurdziel50% (2)
- ATPL Sample Questions - Radio AidsDocument5 pagesATPL Sample Questions - Radio AidsAbhinaya Sekar100% (2)
- Building and Structural Surveying N4 Aug 2018 QP PDFDocument7 pagesBuilding and Structural Surveying N4 Aug 2018 QP PDFZamabomvu100% (2)
- The Importance of SurveyingDocument9 pagesThe Importance of SurveyingJhun Waren83% (6)
- Air Navigation Questionnaire CPL PatternDocument18 pagesAir Navigation Questionnaire CPL Patternnodynaren100% (1)
- Decents 100Document11 pagesDecents 100Soumyadip SheetNo ratings yet
- Explainations of General Navigation QuestionsDocument11 pagesExplainations of General Navigation QuestionsZarrar Khan100% (1)
- Nav VivaDocument6 pagesNav Vivasupandeepsingh9394100% (1)
- Radio Nav Sample Q's (1-2-3) 2008Document45 pagesRadio Nav Sample Q's (1-2-3) 2008momanbh100% (3)
- Systems Atpl PDFDocument111 pagesSystems Atpl PDFMay Be100% (1)
- Nav Test For CPL CandidatesDocument8 pagesNav Test For CPL CandidatesVivek BaskarNo ratings yet
- DgcaDocument50 pagesDgcaasthNo ratings yet
- Air Navigation Full - 2Document10 pagesAir Navigation Full - 2Harshit dubey100% (1)
- Nav VivaDocument6 pagesNav VivaprachatNo ratings yet
- Navigation Test Paper (156 Q.)Document33 pagesNavigation Test Paper (156 Q.)Dipanjan Choudhury60% (5)
- Air Navigation Full-1Document12 pagesAir Navigation Full-1Harshit dubeyNo ratings yet
- DGCA Meteorology QuestionDocument2 pagesDGCA Meteorology QuestionShibin Johney100% (1)
- Principles of FlightDocument58 pagesPrinciples of FlightQuentin Caselli100% (2)
- FLIGHT PLANNING Ref ALLDocument40 pagesFLIGHT PLANNING Ref ALLZahoor Ali100% (2)
- 032 - Performance - AnswersDocument139 pages032 - Performance - AnswersEASA ATPL Question BankNo ratings yet
- Atpl - Meteorology SetDocument5 pagesAtpl - Meteorology SetHamidK.FarhatNo ratings yet
- Q Bank MetDocument94 pagesQ Bank MetsajjadNo ratings yet
- Instruments Keith Willams PDFDocument173 pagesInstruments Keith Willams PDFRyu100% (1)
- Gen Nav Final Test For PilotsDocument62 pagesGen Nav Final Test For PilotsAnandhanNo ratings yet
- NavigationDocument68 pagesNavigationsakshee gojre100% (1)
- Sahil Khurana Answer KeyDocument9 pagesSahil Khurana Answer KeyAmit KhannaNo ratings yet
- Meteorology March 2019Document3 pagesMeteorology March 2019Harshdeep Singh0% (1)
- General NavigationDocument162 pagesGeneral Navigationredbeard_060% (1)
- GNAV SofarDocument23 pagesGNAV SofarNikola100% (1)
- ATPL (A) Meteorology SummaryDocument174 pagesATPL (A) Meteorology Summarywilliambasket990% (1)
- CPL Nav9 Speed&Time.Document2 pagesCPL Nav9 Speed&Time.vivekNo ratings yet
- Meteorology AtplDocument27 pagesMeteorology Atpledward davisNo ratings yet
- CPL InstrumentsDocument160 pagesCPL InstrumentscostypNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 1Document8 pagesSample Paper 1Kunal Thakran100% (1)
- 01 - General Question 1 of 109: Question: Which of The Following Statements Is Correct ?Document118 pages01 - General Question 1 of 109: Question: Which of The Following Statements Is Correct ?Yahya Yıldırım100% (4)
- Albatross - Regs QBDocument47 pagesAlbatross - Regs QBtopgun320100% (1)
- General Nav - KWDocument147 pagesGeneral Nav - KWRohit PunamiyaNo ratings yet
- CPL RNav5 NDB - ADFDocument5 pagesCPL RNav5 NDB - ADFvivekNo ratings yet
- 5 - CPL Questions - AGK4 InstrumentsDocument114 pages5 - CPL Questions - AGK4 InstrumentsMoshiurRahman100% (1)
- Surender Conv of Units (10 Files Merged)Document25 pagesSurender Conv of Units (10 Files Merged)Anmoldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere - AnswersDocument12 pagesAtmosphere - AnswersAvinash Vijaykumar0% (1)
- Explainations of General Navigation QuestionsDocument11 pagesExplainations of General Navigation QuestionsZarrar KhanNo ratings yet
- Radio Bearings QuestionsDocument5 pagesRadio Bearings QuestionsJai Sachdev50% (2)
- Air Regulations 001Document116 pagesAir Regulations 001prachat100% (1)
- Gen Nav BFCDocument12 pagesGen Nav BFCTushar MantriNo ratings yet
- PPL Q. Bank (Nav)Document45 pagesPPL Q. Bank (Nav)Sabik Rahim100% (1)
- 1 - Ce 103Document22 pages1 - Ce 103Ann Nazmun SakibNo ratings yet
- Cartography Unit 3: Basic Geodesy Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesCartography Unit 3: Basic Geodesy Flashcards - QuizletTJ CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Ad 2 Lddu Instrument Approach Chart - Icao - Rnav (GNSS) Rwy12 PDFDocument4 pagesAd 2 Lddu Instrument Approach Chart - Icao - Rnav (GNSS) Rwy12 PDFTesla DrugiNo ratings yet
- Geomatica 2015 ATCORDocument11 pagesGeomatica 2015 ATCORRoyna Sidrotul MNo ratings yet
- Furuno GP30-35 GPS Operators ManualDocument67 pagesFuruno GP30-35 GPS Operators Manualjsdoodnath100% (1)
- History of SurveyingDocument2 pagesHistory of SurveyingBrian WafulaNo ratings yet
- GRIDNAVDocument3 pagesGRIDNAVNikhilesh 'gamble' IngaleNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Moore StationDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Moore StationHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- 01wknm20 Week01 2020Document109 pages01wknm20 Week01 2020muratkelescptNo ratings yet
- Civil III Surveying I (10cv34) NotesDocument109 pagesCivil III Surveying I (10cv34) NotesEmmanuel PeterNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of ShelbyvilleDocument1 pageTopographic Map of ShelbyvilleHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- 6geography PDFDocument81 pages6geography PDFSaket Deshmukh100% (1)
- Geodesy and CartographyDocument65 pagesGeodesy and CartographyGiniux PreezNo ratings yet
- Lat - Long or XY CoordinatesDocument4 pagesLat - Long or XY Coordinateshooty_OWLNo ratings yet
- Iala Dgps EngDocument2 pagesIala Dgps EngtommagneNo ratings yet
- Surveying ReviewerDocument2 pagesSurveying ReviewerRochelle Adajar-Bacalla100% (2)
- 5.2 Tachimetri Dan KonturDocument48 pages5.2 Tachimetri Dan KonturArif RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Global Positioning System (GPS) : Block II/IIA/IIR/IIR-M SatellitesDocument49 pagesGlobal Positioning System (GPS) : Block II/IIA/IIR/IIR-M SatellitesKriti ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal PlymouthDocument8 pagesResearch Proposal PlymouthKetutTomySuhariNo ratings yet
- Elementary Surveying Topic 1Document31 pagesElementary Surveying Topic 1Charles CarpoNo ratings yet
- CVE202 Lecture Notes-7 Angels Azimuths and BearingsDocument16 pagesCVE202 Lecture Notes-7 Angels Azimuths and BearingsAnteneh GeremewNo ratings yet
- RISM Competency Guide (F)Document12 pagesRISM Competency Guide (F)zili yeNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Vat CampDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Vat CampHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Survey II - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSurvey II - Lesson PlanSumethaRajasekarNo ratings yet
- Vacancies For Various Positions in The County Government of Taita Taveta Dated Thursday 2nd November 2023Document24 pagesVacancies For Various Positions in The County Government of Taita Taveta Dated Thursday 2nd November 2023Pastor_EdduNo ratings yet
- 52 Sample ChapterDocument29 pages52 Sample ChapterSaroj GaireNo ratings yet